Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Structure and Function of Neuron
Caricato da
Ahsan IqbalDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Structure and Function of Neuron
Caricato da
Ahsan IqbalCopyright:
Formati disponibili
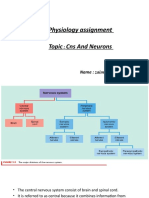
Structure and function of neurons:
Neuron or nerve cell is the structural and functional unit of nervous system. Neurons are
specialized for the transmission and the conduction of nerve impulses.
Structure of neuron: A neuron consists of three parts;
1) A cell body consisting of cytoplasm and a nucleus containing a prominent nucleolus.
The cell body also contains Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum and ribosomes.
2) One or more short processes called dendrons which conduct impulses towards the cell
body.
3) A long un-branched process the axon that carries nerve impulses away from the cell
body. The cytoplasm of the axon contains mitochondria and rough endoplasmic
reticulum. Both the axon and dendron give fine branches at their free ends. These are
called dendrites. The axon and the dendrons are collectively called nerve fiber.
A nerve is essentially a cable containing numerous nerve fibers. Between the nerve fibers
of the nerve cells are bodies called the Nissl’s Granules that provide a nutritive substance
for nerve cells. Axons of most large neurons are covered by an insulating layer of lipid
rich whitish material called myelin that is produced through the action of specialized
Schwann cells. Nodes of Ranveir are spaces along a myelinated neuron that are gaps
between adjacent Schwann cells. Myelinated neurons are better insulated and conduct
impulses faster than non myelinated neurons. The axons may be branched and each
branch may give rise to hundreds of thousands of specialized endings called synaptic
terminals which relay signals to other cells by releasing chemical messengers called
neurotransmitters. The gap at the site of contact between a synaptic terminal and a target
cell (either another neuron or an effector cell such as a muscle cell) is called a synapse.
This gap is traversed by certain chemicals like acetylcholine.
A neuron with one axon and numerous dendrites is called multi-polar, while those with
one axon and one dendron are known as bipolar. A mono-polar neuron possesses only
one process arranged into two branches in a T-shaped manner.
There are generally three types of neuron based on the function they perform;
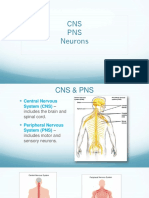
Sensory or afferent neuron: It carries message from a sense organ to the central nervous
system. In sensory neuron the cell body is present at the sides. The axon is short and the
dendron is long.
Motor or efferent neuron: It takes message away from the central nervous system to an
effector. The cell body is in the length of the neuron. A motor neuron has short dendrites
and long axon.
Associative neuron or interneuron: It is always found completely within the central
nervous system with many short dendrites and either a short or a long axon. They link the
sensory and motor neurons. Brain and spinal cord is made of thousands of associative
neurons.
Source: Textbook of Biology Experimental Edition by Waqas Ahmad.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Nervous System: The Dog Stole the Professor's NotesDa EverandNervous System: The Dog Stole the Professor's NotesNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous SystemDocumento12 pagineNervous SystemLeon MarkoNessuna valutazione finora
- Excitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesDa EverandExcitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesNessuna valutazione finora
- NeuroconductivityDocumento16 pagineNeuroconductivitysandrajoshy06Nessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled DocumentDocumento15 pagineUntitled DocumentmaNessuna valutazione finora
- L12 Nerves TissueDocumento8 pagineL12 Nerves Tissueعلي اياد شبيب حناشNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of Nervous TissueDocumento54 pagineAnatomy of Nervous TissueNand PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Samenvatting Hoofdstuk 3 B&CDocumento3 pagineSamenvatting Hoofdstuk 3 B&CMarlijn Ter MorsNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 9 Histology College of Education34351Documento6 pagineLecture 9 Histology College of Education34351Zelal Doski100% (1)
- A2 Level Biology: Coordination-Lecture 1 by Muhammad Ishaq KhanDocumento10 pagineA2 Level Biology: Coordination-Lecture 1 by Muhammad Ishaq KhanAwais BodlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous Tissue-06.11-2wlDocumento57 pagineNervous Tissue-06.11-2wlapi-19641337Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous TissueDocumento15 pagineNervous TissueStar ManavNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment 8Documento3 pagineAssessment 8Dianne LarozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Neurons PDFDocumento2 pagineTypes of Neurons PDFPerry Sin100% (2)
- The Nervous SystemDocumento9 pagineThe Nervous SystemNoar RamadaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 9SUMMARYNERVOUSSYSTEMDocumento24 pagine9SUMMARYNERVOUSSYSTEMArvenBitasNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous SystemDocumento20 pagineNervous SystemxoxogeloNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous System: Communications NetworkDocumento22 pagineNervous System: Communications NetworkAaron TilAhunNessuna valutazione finora
- The NeuronsDocumento3 pagineThe NeuronsAsim ZafarNessuna valutazione finora
- Anfis System NeurologiDocumento51 pagineAnfis System Neurologianon_822636748Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous TissueDocumento25 pagineNervous TissueSumayya KabeerNessuna valutazione finora
- Physiology Handouts (Topic 16-26)Documento35 paginePhysiology Handouts (Topic 16-26)bc200411046Nessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Nervous System: Logo HereDocumento32 pagineAnimal Nervous System: Logo HereAnne Claudette Capin TeofiloNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous System-WPS OfficeDocumento36 pagineNervous System-WPS OfficeShubhendu Chattopadhyay100% (1)
- Presentation 1Documento12 paginePresentation 1Maryam KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- FinalDocumento14 pagineFinalsukhleenNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 14Documento65 pagineModule 14sukhleenNessuna valutazione finora
- The Nervous SystemDocumento5 pagineThe Nervous SystemStephen YorNessuna valutazione finora
- The Nervous SystemDocumento124 pagineThe Nervous SystemKeanan GwapoNessuna valutazione finora
- CNS PNS NeuronsDocumento20 pagineCNS PNS NeuronsTyrese SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurones HWDocumento1 paginaNeurones HWTanvir AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Histology - Nerve Tissue and The Nervous SystemDocumento21 pagineHistology - Nerve Tissue and The Nervous SystemDan UvarovNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous System 1 2023Documento84 pagineNervous System 1 2023odiodi57Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ervous Ystem: Structural ClassificationDocumento95 pagineErvous Ystem: Structural ClassificationJobelle AcenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Neural Control and Coordination Grade 11Documento30 pagineNeural Control and Coordination Grade 11Dr. Remya RanjithNessuna valutazione finora
- Nscelec4-Week 15Documento23 pagineNscelec4-Week 15Jeune Kristine OngNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous System BSC 20161Documento45 pagineNervous System BSC 20161Arohi ParlikarNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous TissuesDocumento13 pagineNervous TissuesSafura IjazNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of A NeuronDocumento8 pagineStructure of A NeuronKrithiga RNessuna valutazione finora
- Histology: Neuron Cells Types and StructureDocumento7 pagineHistology: Neuron Cells Types and StructureAli HayderNessuna valutazione finora
- The Nerve Cell - NeuronDocumento2 pagineThe Nerve Cell - NeuronibrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.physiology of Nervous System DR Hasnain Northwest Univerty PeshawarDocumento27 pagine1.physiology of Nervous System DR Hasnain Northwest Univerty PeshawarHasin's QueenNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 BMCDocumento18 pagine5 BMCRPh FarhatainNessuna valutazione finora
- The Nervous System Is A Complex Network of Nerves and Cells That Carry Messages To and From TheDocumento18 pagineThe Nervous System Is A Complex Network of Nerves and Cells That Carry Messages To and From TheJanineLingayoCasilenNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomi Fisiologi SarafDocumento37 pagineAnatomi Fisiologi SarafUun PrastiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Nerve CellDocumento9 pagineThe Nerve Celljonelllantero032Nessuna valutazione finora
- GenBio2 Lesson 1 Muscular and Nervous TissuesDocumento5 pagineGenBio2 Lesson 1 Muscular and Nervous TissuesAnne BeatrizNessuna valutazione finora
- Psy 413 ProjectDocumento38 paginePsy 413 ProjectDumebi AneneNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento26 pagineNervous System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBD100% (3)
- 5 The Nervous SystemDocumento72 pagine5 The Nervous SystemNardos TesfayeNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation 2Documento23 paginePresentation 2Maria KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bilology XII 2014 Ch-17 Nervous CoordinationDocumento26 pagineBilology XII 2014 Ch-17 Nervous CoordinationMuhammad UsmanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Nervous System RECORDINGSDocumento52 pagineThe Nervous System RECORDINGSKathy Angeli Bel-idaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5Documento51 pagineUnit 5JAYANT CH (RA2111004010265)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous SystemDocumento15 pagineNervous SystemSatrioNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous System I: Basic Structure and FunctionDocumento4 pagineNervous System I: Basic Structure and FunctionrohitNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous Tissue: Prof. Dr. Anas Sarwar QureshiDocumento12 pagineNervous Tissue: Prof. Dr. Anas Sarwar QureshiShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Table of Content: Seria L No Page NoDocumento48 pagineTable of Content: Seria L No Page NoHadia NoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous CoordinationDocumento2 pagineNervous CoordinationParty CularNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous System ResonanceDocumento72 pagineNervous System ResonanceEkta ManglaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 21 NOTESDocumento13 pagineClass 11 Biology Chapter 21 NOTESYashica PradhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet - I: Biology XDocumento5 pagineWorksheet - I: Biology XDharmendra SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Ebook PDF Vanders Human Physiology The Mechanisms of Body Function 13th Edition PDFDocumento40 pagineEbook PDF Vanders Human Physiology The Mechanisms of Body Function 13th Edition PDFmarie.simons156100% (30)
- The Neuronal Environment Brain Homeostasis in Health and Disease by Wolfgang WalzDocumento428 pagineThe Neuronal Environment Brain Homeostasis in Health and Disease by Wolfgang WalzMateja PantićNessuna valutazione finora
- PYC1501Documento43 paginePYC1501Anonymous fFqAiF8qYg100% (2)
- Mechanism of Smell - Electrochemistry, Receptors and Cell SignalingDocumento6 pagineMechanism of Smell - Electrochemistry, Receptors and Cell SignalingChristan Chaputtra MaharibeNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Adaptation To Physical Stress: A Proposed "Physical Stress Theory" To Guide Physical Therapist Practice, Education, and ResearchDocumento21 pagineTissue Adaptation To Physical Stress: A Proposed "Physical Stress Theory" To Guide Physical Therapist Practice, Education, and ResearchGavin Cao100% (1)
- Case Study - Multiple SclerosisDocumento3 pagineCase Study - Multiple SclerosisRachel KoenigsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Origin of Bioelectric Signal1Documento65 pagineOrigin of Bioelectric Signal1SanathNessuna valutazione finora
- Encoding ArchitectureDocumento280 pagineEncoding ArchitectureMohammed Younus AL-Bjari100% (2)
- Rules and Regulations For BPTDocumento54 pagineRules and Regulations For BPTSherin KNessuna valutazione finora
- IB SL Psychology Brief Revision NotesDocumento30 pagineIB SL Psychology Brief Revision NotesSeoyoung KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Schizophrenia: The Fundamental Questions: Nancy C. AndreasenDocumento7 pagineSchizophrenia: The Fundamental Questions: Nancy C. AndreasenJuan InsignaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Kami Export - Hhmi Electrical Activity of NeuronsDocumento2 pagineKami Export - Hhmi Electrical Activity of NeuronsKylie Wimbish0% (1)
- Muscular System ReviewerDocumento4 pagineMuscular System ReviewerMadelle Capending DebutonNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Physiology An Integrated Approach 6th Edition Silverthorn Test BankDocumento38 pagineHuman Physiology An Integrated Approach 6th Edition Silverthorn Test Bankbufochauswu2w100% (14)
- 0610 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocumento12 pagine0610 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersIf HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Toppers Study Hacks by Avinash Agarwal Z LibDocumento245 pagineToppers Study Hacks by Avinash Agarwal Z LibPranav GaikwadNessuna valutazione finora
- Philosophical Perspective of The Self Understanding The SelfDocumento16 paginePhilosophical Perspective of The Self Understanding The Selfmarie parfanNessuna valutazione finora
- Quarter 2 Summative Test in ScienceDocumento4 pagineQuarter 2 Summative Test in ScienceSharmaine RamirezNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12 Coordination and Response (Repaired)Documento18 pagineChapter 12 Coordination and Response (Repaired)yokekeannNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To HistologyDocumento14 pagineIntroduction To HistologyFatima SyedNessuna valutazione finora
- Kohonen 82Documento11 pagineKohonen 82Thoi Ke No DiNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 Biology Notes ch21 Neural Control and Coordination PDFDocumento3 pagine11 Biology Notes ch21 Neural Control and Coordination PDFRamachandranPerumal100% (1)
- Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary LevelDocumento20 pagineCambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary LevelTimNessuna valutazione finora
- Smith, LS - Neuromorphic Systems-Past, Present and FutureDocumento16 pagineSmith, LS - Neuromorphic Systems-Past, Present and FutureAngel MartorellNessuna valutazione finora
- TNCT 4TH QuarterDocumento4 pagineTNCT 4TH QuarterJhonel Mogueis Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Dancing Molecules' Successfully Repair Severe Spinal Cord InjuriesDocumento6 pagineDancing Molecules' Successfully Repair Severe Spinal Cord InjuriesPili RemersaroNessuna valutazione finora
- Functions of The Nervous SystemDocumento5 pagineFunctions of The Nervous SystemJungkookie BaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Apollo Root Cause AnalysisDocumento20 pagineApollo Root Cause AnalysisMohd Fakhruddin Basar100% (2)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDa EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (81)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDa EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (6)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDDa EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeDa EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeValutazione: 2 su 5 stelle2/5 (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityDa EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (27)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionDa EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (404)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (42)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsDa EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaDa EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsDa EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNessuna valutazione finora
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDa EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (3)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryDa EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (44)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Da EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (110)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerDa EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (392)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsDa EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (3)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlDa EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (58)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingDa EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1138)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningDa EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsDa EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (170)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessDa EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (328)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsDa EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (6)