Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Hypertension CHF
Caricato da
Edgel QuidolesTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Hypertension CHF
Caricato da
Edgel QuidolesCopyright:
Formati disponibili
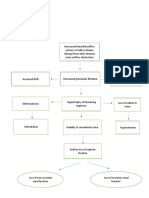
Risk Factors:
Old age
Familial History of Genetics
Hypertension
High salt diet
Dysfunction of SNS & RAA, adducin and
natriuretic hormones
Vasoconstriction Renal salt and water retention
Increased peripheral Increased blood volume
resistance
Chronic
hypertension
Vasoconstriction of blood
vessels
Vasoconstriction of
↑ afterload
coronary arteries
Increase pressure of ↑ workload
blood flow
of the LV
Injury of the
↑ force of LV contraction
endothelial vessel layer
(Coronary artery)
↑ stress on the left
Vessel damage ventricular wall
Left ventricular
Monocytes, platelets, ↑ cardiac output Hypertrophy and
cholesterol and other blood dilation
components come in contact
LV Hypoxia Ventricular
remodeling
Scarring
↓ left ventricular
↓ Brain perfusion: dizziness, light
Atherosclerosis headedness, confusion, anxiety, contractility
restlessness. ↓Response to
energy demands causing easily
CAD fatigued, ↑ residual blood of
the LV at the time of
↓activity tolerance
diastole
↓ Skin perfusion:
↓ cardiac tissue
blood flow Skin feels cool and clammy. ↑ LV pressure
↓ cardiac muscle blood backflows from
contraction ↓ Cardiac Output LV to LA
↑ residual blood of the
Activation of ↓ Systemic blood LA during diastole
baroreceptors in the LV,
aortic arch, carotid sinus pressure
↑ LA pressure
Stimulation of vasomotor ↓ Perfusion of tissues of
regulatory centers in the body blood returns to
medulla pulmonary circulation
Activation of sympathetic ↓GFR ↓ Renal
nervous system Perfusion Accumulation of blood in
the pulmonary capillary
Activation of sympathetic ↓GFR Accumulation of blood in
↓ Renal
nervous system the pulmonary capillary
Perfusion
↑ catecholamines Renin
↑ urea
(epinephrine/
norepinephrine) ↑ crea formation of Pulmonary edema
Angiotensin I
Angiotensin II ↑ pulmonary
vascular
resistance
Sodium and
Water retention
↑ RV contraction
↑osmotic pressure ↓ urine
output ↑ force of RV
contraction
↑ residual blood of
the RV at the time
of diastole
Peripheral edema, liver ↑ RV preload
congestion, ascites,
weakness, weight gain due to
retention of fluid blood backflows
from RV to RA
↑ RA pressure
↑ fluid moves into the
interstitial space
↑ RA preload
↑ venous pressure blood backflows
from RA to
JVD
systemic circulation
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Course in The WardDocumento2 pagineCourse in The WardEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- Host DefenseDocumento76 pagineHost DefenseEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- Glaucoma Case StudyDocumento5 pagineGlaucoma Case StudyEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocumento4 pagineCues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- DengueDocumento13 pagineDengueEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- PowerlessnessDocumento2 paginePowerlessnessEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- Seizure Dsiorder: University of Nueva Caceres College of Nursing City of NagaDocumento4 pagineSeizure Dsiorder: University of Nueva Caceres College of Nursing City of NagaEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan for Disturbed Thought Processes and Impaired MobilityDocumento6 pagineNursing Care Plan for Disturbed Thought Processes and Impaired MobilityEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- Alternative Mode of Teaching-Learning in Competency Appraisal 2 Case 1Documento1 paginaAlternative Mode of Teaching-Learning in Competency Appraisal 2 Case 1Edgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- Schizophrenia NCPDocumento4 pagineSchizophrenia NCPGladys Barcelona91% (55)
- Glaucoma Case StudyDocumento5 pagineGlaucoma Case StudyEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- PathoDocumento2 paginePathoEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- AMELIADocumento2 pagineAMELIAEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- QUIDOLES PsychCADocumento4 pagineQUIDOLES PsychCAEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Homework May 14, 2017Documento3 paginePhysics Homework May 14, 2017Edgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- Anticancer & BRM HandoutsDocumento19 pagineAnticancer & BRM HandoutsEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- Glaucoma Case StudyDocumento5 pagineGlaucoma Case StudyEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- Family Nursing Care Plan AsthmaDocumento2 pagineFamily Nursing Care Plan AsthmaEdgel Quidoles100% (2)
- CaseAnalysis QuidolesDocumento4 pagineCaseAnalysis QuidolesEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- Health HazardsDocumento4 pagineHealth HazardsEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- POTTs Disease PathoDocumento3 paginePOTTs Disease PathoEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- ESRD Secondary To DM Type 2 PathophyDocumento3 pagineESRD Secondary To DM Type 2 PathophyEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- La Lan NCPDocumento4 pagineLa Lan NCPEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- Seizure NCPDocumento6 pagineSeizure NCPEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- Congenital Amelia: Birth Defect of Lacking LimbsDocumento3 pagineCongenital Amelia: Birth Defect of Lacking LimbsEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- An Introduction to EFTDocumento25 pagineAn Introduction to EFTdiplomat0Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Mock GA MayDocumento124 paginePractice Mock GA MaydatwbfaqsjvmsNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal 2Documento9 pagineJurnal 2Rio ArdiantoruNessuna valutazione finora
- Pesticide Poisoning from Contaminated WatermelonsDocumento5 paginePesticide Poisoning from Contaminated Watermelonsnathan brionesNessuna valutazione finora
- Oet ReadingDocumento7 pagineOet ReadingAditi ParmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento10 pagineChapter 1Jean Salaveria CenasNessuna valutazione finora
- Mental Health Studyguide Part 1Documento39 pagineMental Health Studyguide Part 1Ngoc TB VoNessuna valutazione finora
- Corporate Ergonomics ProgramsDocumento16 pagineCorporate Ergonomics ProgramsJharef Rupire DelgadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Case ConferenceDocumento22 pagineClinical Case ConferenceTallal BurwagNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal AutismDocumento7 pagineJurnal AutismArianiNessuna valutazione finora
- Fenugreek Benefits PDFDocumento10 pagineFenugreek Benefits PDFrecianzubyNessuna valutazione finora
- Histrionic Personality DisorderDocumento24 pagineHistrionic Personality DisorderGERSON RYANTONessuna valutazione finora
- Long Cases ABM ABDULLAH 1st Edition PDFDocumento844 pagineLong Cases ABM ABDULLAH 1st Edition PDFProthoma Dey64% (11)
- Activation On Application.: 3M's Tri-Calcium Phosphate (SS-TCP) - Smart Technology For Your SmileDocumento1 paginaActivation On Application.: 3M's Tri-Calcium Phosphate (SS-TCP) - Smart Technology For Your Smiledrg. Rifqie Al HarisNessuna valutazione finora
- DreamlandDocumento3 pagineDreamlandmoiravictoria.genovaNessuna valutazione finora
- X-Ray: X-Radiation (Composed of X-Rays) Is A FormDocumento18 pagineX-Ray: X-Radiation (Composed of X-Rays) Is A FormFDELNessuna valutazione finora
- Visible Safety and Induction: Hse Management Visit ChecklistDocumento6 pagineVisible Safety and Induction: Hse Management Visit ChecklistHARSHALNessuna valutazione finora
- Program of Exam - Criminologists Feb 2024Documento4 pagineProgram of Exam - Criminologists Feb 2024PRC BaguioNessuna valutazione finora
- Retention and Stability of Complete DentureDocumento7 pagineRetention and Stability of Complete Denturemanishpankaj123Nessuna valutazione finora
- 7 in 1 Hydrafacial With Led MaskDocumento3 pagine7 in 1 Hydrafacial With Led MaskRameez HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Emergency Response Plan TemplateDocumento4 pagineEmergency Response Plan TemplateDilkhaz HSENessuna valutazione finora
- English Grammar PDFDocumento106 pagineEnglish Grammar PDFasima rath0% (1)
- Accomplishment ReportDocumento3 pagineAccomplishment ReportLorelyn CamarigNessuna valutazione finora
- Building J Renovation-PlansDocumento83 pagineBuilding J Renovation-PlansBala Hemanth KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Ethics Article Highlights Need for Nurses to Engage in Public Policy DevelopmentDocumento11 pagineNursing Ethics Article Highlights Need for Nurses to Engage in Public Policy Developmentlorelyn cabreraNessuna valutazione finora
- Stock report for drug store sectionDocumento113 pagineStock report for drug store sectionsriramNessuna valutazione finora
- Palliative Care: Improving Quality of Life When Seriously IllDocumento16 paginePalliative Care: Improving Quality of Life When Seriously IllHashim Ahmad100% (1)
- Vata RaktaDocumento27 pagineVata RaktaKristina Babic100% (2)
- AE PostGrad SyllabusDocumento265 pagineAE PostGrad Syllabusaquib yousufNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Stoma, Cut and WoundsDocumento40 pagineManagement of Stoma, Cut and WoundsLalita KumariNessuna valutazione finora