Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Hot Topics 2 Months
Caricato da
Pathways Awareness0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
256 visualizzazioni2 pagineBy studying the comparison of these two children, physicians, nurses and other healthcare professionals will become better able to recognize early motor delays and take appropriate action once a possible delay is identified.
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoBy studying the comparison of these two children, physicians, nurses and other healthcare professionals will become better able to recognize early motor delays and take appropriate action once a possible delay is identified.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
256 visualizzazioni2 pagineHot Topics 2 Months
Caricato da
Pathways AwarenessBy studying the comparison of these two children, physicians, nurses and other healthcare professionals will become better able to recognize early motor delays and take appropriate action once a possible delay is identified.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
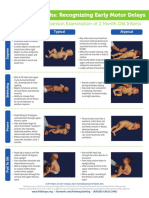
Recognizing Early Motor Delays
A Comparison Examination of 2 Month Old Infants
Typical Atypical
• Maintains head in midline • May show more asymmetrical
for brief periods movement with predominance
of head to one side; or strong
• Locates objects visually and
Supine
asymmetrical tonic neck reflex
tracks from left to right (ATNR)
• Begins to show antigravity • Difficulty visually tracking, may
movements of upper and only track to one side or only
lower extremities to midline
• Not yet able to reach and • Decreased ability to generate
grasp toys upper and lower extremity
antigravity movements
• Longer periods of inactivity
• Able to lift head and upper trunk • May be unable to right head
during facilitated roll, showing
Sidelying
during facilitated rolling
lateral headrighting
• Begins to balance activity of • May look more competent in
trunk flexor and extensor sidelying, therefore important
muscles to observe baby in all eight
• Ability to change from positions
predominant use of flexors to
use of extensors as position
requires
• Head lifting to 45 degrees
and extension through
upper thoracic spine • Posture looks more like a
• Hips and knees begin to newborn; infant does not
move from flexed show hip extension; hips and
Prone
“newborn” posture into knees remain in flexed
extended, abducted abducted posture.
position, which allows head
and trunk lifting • No independent head lifting;
• Elbows typically not directly can move head only with
under the shoulders until assistance
3 months
• Head-lag is typical until • May exhibit head-lag
the infant is about 15 through the entire pull to
sit maneuver.
Pull to Sit
degrees from upright.
• Uses shoulder elevation • Poor head control when in
and elbow flexion to assist upright sitting
• Able to engage neck • Little muscle activity in
muscles to sustain midline the upper extremities or
head control when upright cervical spine
• Good extension through • When upright, rounding
the cervical and upper of the thoracic and lumbar
thoracic spine spine
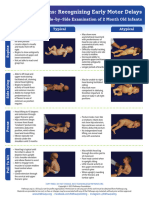
Recognizing Early Motor Delays
A Comparison Examination of 2 Month Old Infants
Typical Atypical
• Head is aligned with ear
directly over the shoulder • Needs more support to
• Holds and sustains sustain sitting posture
Sitting
posture with assistance • Inability to achieve and sustain
• Head turning may or may head lifting in upright position
not be present at • Little to no antigravity arm
2 months, but should be activity
seen by 3 months
Horizontal Suspension
• Able to activate adequate
neck and trunk extension to • Difficulty or inability to
sustain posture activate neck or upper
• Can maintain brief periods of thoracic extensors to lift head
head control, but may not be • May try to use arm and leg
able to hold the head in movements to sustain
midline posture
Protective Extension
• Aware of being tilted
forward; increases head
and neck extension • Unable to generate
• Will not be fully able to antigravity head and trunk
bring arms forward for full activity
protective response
protection until 6 months
• Able to sustain weight on
lower extremities with
Standing
support at the trunk • May support little if any
• Typically shows weight on feet
intermittent bouts of • Little or no intermittent
extension and flexion muscle activity to attain or
• Good vertical alignment maintain standing
from head through trunk
and feet
For more information please contact
Pathways Awareness
Toll-free (800) 955-2445 · Fax (888) 795-5884 · TTY (800) 326-8154
http://www.pathwaysawareness.org · friends@pathwaysawareness.org
Copy freely, do not change. Must acknowledge Pathways Awareness.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Pencegahan & Pengendalian Infeksi Covid 19: Komite Ppi Rsud Al Ihsan 2020Documento37 paginePencegahan & Pengendalian Infeksi Covid 19: Komite Ppi Rsud Al Ihsan 2020sate ususpedasNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Months: Recognizing Early Motor Delays: A Comparison Examination of 2 Month Old InfantsDocumento2 pagine2 Months: Recognizing Early Motor Delays: A Comparison Examination of 2 Month Old InfantsMarinVaderŠamijaNessuna valutazione finora
- Motordelays EnglishDocumento23 pagineMotordelays Englishicevie00Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2MonthMotorDelays 2023copyright-1Documento2 pagine2MonthMotorDelays 2023copyright-1Aleh LucianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Recognizing Early Motor Delays: A Comparison Examination of Six-Month-Old Infants Typical AtypicalDocumento2 pagineRecognizing Early Motor Delays: A Comparison Examination of Six-Month-Old Infants Typical AtypicalMarinVaderŠamijaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hot Topics 4 MonthsDocumento2 pagineHot Topics 4 MonthsPathways AwarenessNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Months: Recognizing Early Motor Delays: A Comparison Examination of 4 Month Old InfantsDocumento2 pagine4 Months: Recognizing Early Motor Delays: A Comparison Examination of 4 Month Old InfantsMarinVaderŠamijaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care of A Family With An InfantDocumento42 pagineNursing Care of A Family With An InfantShenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care of A Family With An InfantDocumento41 pagineNursing Care of A Family With An InfantDaniela Claire FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Position Glossary: Key RPM Riding Positions RacingDocumento2 paginePosition Glossary: Key RPM Riding Positions RacingJozef SetyawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Typical Development Global PatternsDocumento4 pagineTypical Development Global PatternsRiani DwiastutiNessuna valutazione finora
- Typical Movements at 1 Month - Final 1Documento1 paginaTypical Movements at 1 Month - Final 1Aleh LucianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hot Topics 6 MonthsDocumento2 pagineHot Topics 6 MonthsclarafranNessuna valutazione finora
- PathFit ReviewerDocumento3 paginePathFit ReviewerChristina ErminoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hinge NotesDocumento1 paginaHinge Notesabyiee fonaNessuna valutazione finora
- Global Delay DevelopmentDocumento2 pagineGlobal Delay DevelopmentRiani DwiastutiNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 Key Labor Positions Proven To Help Labor Progress: Walking/StandingDocumento2 pagine8 Key Labor Positions Proven To Help Labor Progress: Walking/StandingNorhane HeshamNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 Key Labor Positions Proven To Help Labor Progress: Walking/Standing SquattingDocumento2 pagine8 Key Labor Positions Proven To Help Labor Progress: Walking/Standing SquattingIonela StoicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Final FW ProjectDocumento11 pagineFinal FW Projectapi-412489828Nessuna valutazione finora
- Normaldevelopmentnew 140904124938 Phpapp02Documento104 pagineNormaldevelopmentnew 140904124938 Phpapp02Hello VintunnaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Neck ExercisesDocumento8 pagineNeck ExercisesAnthony Dinicolantonio100% (1)
- Body Mechanics For The Caregiver: General Rules 2Documento2 pagineBody Mechanics For The Caregiver: General Rules 2Joanne Cristie TolopiaNessuna valutazione finora
- G& D Infant and NeonateDocumento142 pagineG& D Infant and NeonateJoy JoycNessuna valutazione finora
- Motor Development (1year) - 1Documento31 pagineMotor Development (1year) - 1Ashwini BajajNessuna valutazione finora
- Body Condition ScoringDocumento49 pagineBody Condition ScoringTaqi MehdiNessuna valutazione finora
- Body Condition Scoring and OtherDocumento51 pagineBody Condition Scoring and OtherTaqi MehdiNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Good Body MechanicsDocumento16 paginePrinciples of Good Body MechanicsGiralph NikkoNessuna valutazione finora
- PortfoliorubricsDocumento4 paginePortfoliorubricsapi-356277132Nessuna valutazione finora
- Thera Neuromotor Approaches NirDocumento10 pagineThera Neuromotor Approaches NirCeline Kyla MalloNessuna valutazione finora
- Reflexes and Stereotypies WebDocumento36 pagineReflexes and Stereotypies WebBillal HossenNessuna valutazione finora
- Active Rom Exercise - ViosDocumento6 pagineActive Rom Exercise - ViosIra Velle ViosNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Module 4 - ReflexesDocumento3 pagineLab Module 4 - Reflexeskxb22bNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoulder ExercisesDocumento2 pagineShoulder Exercisesstates02Nessuna valutazione finora
- Handling and Assisting DeliveryDocumento4 pagineHandling and Assisting DeliveryMc Ramil B. PraderoNessuna valutazione finora
- BOSU® Core Flow OverviewDocumento4 pagineBOSU® Core Flow OverviewabhijitgreatNessuna valutazione finora
- NCM 107.1 NotesDocumento7 pagineNCM 107.1 NoteskrischaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Barbell Squat: Comments and TipsDocumento10 pagineBarbell Squat: Comments and TipsDavid RomeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Acc5053 Stretches Office A2Documento1 paginaAcc5053 Stretches Office A2Sabina GartaulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Assessment Powerpoint (Assessing Newborn and Infant)Documento33 pagineHealth Assessment Powerpoint (Assessing Newborn and Infant)rick_wb0% (1)
- Posture Group 3Documento13 paginePosture Group 3Jim Roger Malabo LorenzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Positioning and Handling To Foster Motor FunctionDocumento60 paginePositioning and Handling To Foster Motor FunctionBambang Ulan AeiyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Theraband Exercises Back and NeckDocumento4 pagineTheraband Exercises Back and NeckRaina SmartNessuna valutazione finora
- The HipDocumento1 paginaThe HipRia Manku100% (1)
- Pilates Stretch Class FormatDocumento3 paginePilates Stretch Class FormatDieu Thu NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Assesment FisioterapiDocumento42 pagineAssesment FisioterapiodyNessuna valutazione finora
- Suspension Training For BeginnersDocumento22 pagineSuspension Training For BeginnersSarah ChalhoubNessuna valutazione finora
- Cquili Brium: Total BalanceDocumento22 pagineCquili Brium: Total BalanceSarah ChalhoubNessuna valutazione finora
- 151426835-Pullup-Basic-Poster-web Copy-2Documento1 pagina151426835-Pullup-Basic-Poster-web Copy-2Alberto CanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Impact of Covid Patient RecoveryDocumento14 pagineImpact of Covid Patient RecoveryMazhar IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- 2-Sitting PositionDocumento49 pagine2-Sitting PositionSaira SolNessuna valutazione finora
- Jump NotesDocumento3 pagineJump NotesApril Jane ZambranoNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer BODY MECHANICSDocumento3 pagineReviewer BODY MECHANICSKERL RAMANessuna valutazione finora
- Homeworkout (1.0)Documento7 pagineHomeworkout (1.0)Marcus VoNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Science LabsDocumento8 pagineHealth Science LabsHamza ElmoubarikNessuna valutazione finora
- FPQC Positions For LaborDocumento3 pagineFPQC Positions For LaborAukia HyuugaNessuna valutazione finora
- Towards Health And: Fitness IiDocumento38 pagineTowards Health And: Fitness IiApril JacintoNessuna valutazione finora
- Forward Backward Rolls GymnasticsDocumento2 pagineForward Backward Rolls Gymnasticsapi-443450374Nessuna valutazione finora
- X-Ray Views HipDocumento1 paginaX-Ray Views Hipjuly mirandillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rings - Workout Guide ENDocumento21 pagineRings - Workout Guide ENcuvaj.martinNessuna valutazione finora
- Temporal Bone AnatomyDocumento27 pagineTemporal Bone AnatomyChangho Lee100% (5)
- 16 Text-Book of OsteopathyDocumento104 pagine16 Text-Book of OsteopathyHatfulloftricks70075% (4)
- Muscle Energy Technique Powerpoint PDFDocumento21 pagineMuscle Energy Technique Powerpoint PDFMjidKarim0% (1)
- Duke Anatomy - Lab 20 - Eye & EarDocumento19 pagineDuke Anatomy - Lab 20 - Eye & EarabidalibpNessuna valutazione finora
- Parts of The BodyDocumento2 pagineParts of The BodyKru EkachaiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Sacred Silence MeditationsDocumento8 pagineThe Sacred Silence MeditationsParanormalNetworks100% (2)
- Root of The Neck (Gross)Documento21 pagineRoot of The Neck (Gross)Kimsha ConcepcionNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoulder InjuryDocumento79 pagineShoulder InjurySudipta BhowmickNessuna valutazione finora
- Mass Training 12 WeeksDocumento3 pagineMass Training 12 WeeksharaNessuna valutazione finora
- Free Printable at Home Brain Breaks and Active CalmingDocumento12 pagineFree Printable at Home Brain Breaks and Active Calmingapi-505036826Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Anatomy & Physiology of Eye For Ophthalmic NursesDocumento124 pagine1 Anatomy & Physiology of Eye For Ophthalmic NursesSMEY204100% (1)
- Essentials of Caprine Anatomy: A Complete Text On General and Systemic AnatomyDocumento5 pagineEssentials of Caprine Anatomy: A Complete Text On General and Systemic AnatomyBharat KafleNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurologic Examination of Newborn and InfantsDocumento6 pagineNeurologic Examination of Newborn and InfantsRem AlfelorNessuna valutazione finora
- Head InjuriesDocumento9 pagineHead InjuriesQasim HaleimiNessuna valutazione finora
- Otal Aryngectomy: Alexander C VlantisDocumento12 pagineOtal Aryngectomy: Alexander C VlantisKumaran Bagavathi RagavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mnemonics Unit 2Documento6 pagineMnemonics Unit 2Anuraj PillaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 002Documento8 pagineChapter 002api-281340024Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lumbar Disc HerniationDocumento19 pagineLumbar Disc HerniationPutri WulandariNessuna valutazione finora
- BSDocumento6 pagineBSBeda MalecdanNessuna valutazione finora
- Facial Trauma: Joni Skipper, MS-IV USC School of MedicineDocumento22 pagineFacial Trauma: Joni Skipper, MS-IV USC School of MedicineReggy Amalia NurgammaNessuna valutazione finora
- Role of Imaging in RhinologyDocumento223 pagineRole of Imaging in RhinologyDr. T. Balasubramanian100% (2)
- 16-Clinical Anatomy of The Upper LimbDocumento27 pagine16-Clinical Anatomy of The Upper LimbAlapati Vinod KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepare and RepairDocumento38 paginePrepare and RepairPete PuzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Extrapyramidal System PDFDocumento4 pagineExtrapyramidal System PDFAbdulla AlsalhiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Elbow ComplexDocumento12 pagineThe Elbow ComplextafelaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Nasal Septum PDFDocumento18 pagineThe Nasal Septum PDFalit100% (1)
- Pop Quiz Nervous SystemDocumento5 paginePop Quiz Nervous Systemapi-242868690100% (1)
- Labelling Medical IllustrationDocumento7 pagineLabelling Medical IllustrationunddeadNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise Chart: Work The Upper BodyDocumento3 pagineExercise Chart: Work The Upper BodyseregearNessuna valutazione finora
- Your First Muscle UpDocumento37 pagineYour First Muscle Upjonh Alexander100% (2)