Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
C3 Method of Separation PDF
Caricato da
HarshaWakodkarTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
C3 Method of Separation PDF
Caricato da
HarshaWakodkarCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Dr.
Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series
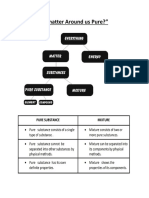
Method Of Separation
(A) Methods of Separation
Threshing
Winnowing
Sifting/Sieving
Solid Solid
Hand Picking
Separation
Sublimation
Magnetic separation
Fractional crystallization
Sedimentation
Decantation
Insoluble solid
from liquid Coagulation or loading
Separation
Filtration
Centrifugation
Soluble solid Evaporation
from liquid
Distillation
Separation
Separation of Separating funnel
liquid from
Fractional Distillation
Liquid
Separation
Strictly for Private Circulation
www.homibhabhacompetition.com
Dr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series
(1) Solid Solid Separation:
Following are the method of separation for Solid-Solid Separation
a. Threshing: Is the method to separate the grain from ears. Act of removing
grain or seeds from hulls or husks
b. Winnowing: Is the method to separate lighter part from heavier part of
mixture
c. Sifting/Sieving: Method of separating mixture based on size of particles.
d. Hand Picking: Method of separating mixture based on size of particles.
Strictly for Private Circulation
www.homibhabhacompetition.com
Dr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series
e. Sublimation: Method of separating sublimative substance.
Sublimation is the process where solid gets converted into gas after heating.
f. Magnetic separation: Method Used to separate particles out based on
magnetic properties
g. Fractional crystallization Separation of two soluble solid. In this both the
solid is dissolved in a particular liquid(Solvent).After cooling, hot saturated
solution ,crystals of less soluble substance is first formed. Using filtration
method they are separated from solution.
e.g. Common salt and potassium nitrate
(2) Insoluble solid from liquid
a. Sedimentation: Method of separation heavy insoluble solid from liquid. We
allow the mixture to settle down for some time. Settling of heavy particles at
bottom is called sedimentation.
Strictly for Private Circulation
www.homibhabhacompetition.com
Dr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series
b.Decantation: The method of removing upper clear liquid without disturbing
settled solid is called decantation.
b. Coagulation or loading : Method of removing heavy suspended particle by
adding alum or coagulating agent. Example: Alum
c. Filtration: Method of separating insoluble solid from liquid by using filter like
filter paper ,cloth ,cotton ,sand Bed
Strictly for Private Circulation
www.homibhabhacompetition.com
Dr. Homi Bhabha
habha Competition Test Series
d. Centrifugation: Remove
Removes fine insoluble suspended
spended particles from solution by
applying centrifugal force.
e.g. Butter from curd ,washing machine squeeze wa
water
(3) Soluble solid from liquid
a.Evaporation: is used to remove liquids from solutes which cannot be done
through filtration due
ue to the small size of the substances.
b. Distillation: 1. The evaporation and subsequent collection of a liquid by
condensation as a means of purification: the distillation of water.
water.2. The extraction of the
volatile components of a mixture by the condensation and collection of the vapors that
are produced as the mixtureture is heated: petroleum distillation also called as fractional
distillation.
Strictly for Private Circulation
www.homibhabhacompetition.com
Dr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series
(4) Solid from Gas
Cyclone separation : the cyclone technology forces air to spin round at very high
speed, creating centrifugal force and causing the dust particles to be pulled out into the
bin.
(5) Separation of liquid –liquid mixture
a. Separating funnel : For Immiscible Liquid
A separating funnel is a glass funnel with a tap at the bottom. A separating funnel
is a separation technique that is used for two liquids that do not dissolve in each
other. Liquids that do not dissolve in each other are called immiscible.
Strictly for Private Circulation
www.homibhabhacompetition.com
Dr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series
b. Fractional Distillation
Liquids that dissolve in each other can be separated by fractional distillation.
Liquid that dissolve each other are called as Miscible liquid
Principle is based on difference in boiling point
The solution is heated until it boils. The liquid with the lowest boiling point boils first and
becomes a vapour (gas). The vapour is cooled in the condenser until the temperature
falls below the boiling point when it condenses back into a liquid which is collected in a
container. The collected liquid is called the distillate. It has been distilled. The condenser
has cold water running through a jacket around the outside to keep the temperature
below the boiling point of the vapour.
After the liquid with the lowest boiling point has been collected, the temperature of the
remaining mixture will rise to a new temperature when the liquid with the next lowest
boiling point will boil and be collected. The process can be continued to separate all the
liquids in the mixture.
Fractional distillation is used to separate the components of crude oil and to separate
nitrogen and oxygen from liquid air.
(6) Chromatography:
Separation of different dissolved constituent of a mixture present in a very minute
quantity.
Strictly for Private Circulation
www.homibhabhacompetition.com
Dr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series
Important Definition:
Settling: Settling is the process by which particulates settle to the bottom of a
liquid and form a sediment. It happens due to force which could be due to
Gravitational force or centrifugal force.
E.g. Removal of solids from liquid sewage waste, settling of solid food particles
from a liquid food
Filtrate: The liquid or solution that has passed through a filter.
Residue: The substance that remains after evaporation, distillation, filtration or
any similar process.
Sublimating substance: Ammonium chloride , Sal ammoniac, Camphor,
Naphthalene, Iodine
Identify chemical instrument
1. Iron gauze: Wire gauze can be used to support a container (such as a beaker or
flask) during heating. When the bunsen burner flame is beneath it, with a tripod, the
wire gauze helps to spread the flame (and heat) out evenly over the container.
Strictly for Private Circulation
www.homibhabhacompetition.com
Dr. Homi Bhabha
habha Competition Test Series
2. Tripod: Used to support and hold various flasks, beakers and other glass ware.
ware
3. Round bottom flask:
4. Condenser: One that condenses, especially an apparatus used to condense vapor to
liquid
Write notes on following topics
Define
Vaporization
Freezing
Condensation
Melting Point
Boiling point
Evaporation
Fractional Distillation Principle is difference in boiling point
Crude Oil Low Boiling Point Petrol
Higher Boiling Point Diesel
Strictly for Private Circulation
www.homibhabhacompetition.com
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Dr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series MethodsDocumento8 pagineDr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series MethodsSanjeev Sadanand PatkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Separating Components of MixturesDocumento2 pagineSeparating Components of MixturesAnna Dominic De RomaNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes of "Is Matter Around Us Pure?"Documento20 pagineNotes of "Is Matter Around Us Pure?"SKULL XT GAMINGNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry 2 - Separating MixturesDocumento7 pagineChemistry 2 - Separating MixturesNaseeb AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento10 pagineChapter 2skywalkerNessuna valutazione finora
- Separation of Substances (G6) : Handout I. Short Answer QuestionsDocumento3 pagineSeparation of Substances (G6) : Handout I. Short Answer Questionsdon shiphrahNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 Chemistry - Is Matter Around Us Pure - Notes & Video LinkDocumento8 pagine9 Chemistry - Is Matter Around Us Pure - Notes & Video LinkYash TripathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Purification TechniquesDocumento1 paginaPurification TechniqueschinnagandiNessuna valutazione finora
- HARAM SIDDIQUI - Exercise No. 1 - Demonstration Sessions For Various Purification Techniques Such As Filtration, Decantation, Crystallization, Distillation and Chromatography.Documento7 pagineHARAM SIDDIQUI - Exercise No. 1 - Demonstration Sessions For Various Purification Techniques Such As Filtration, Decantation, Crystallization, Distillation and Chromatography.Arya SayedNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Ch.3Documento14 pagineChemistry Ch.3OmlNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry - Part 4Documento10 pagineChemistry - Part 4BALA GANESHNessuna valutazione finora
- SEPARATION METHODS-I BY K.N.S.SWAMI - pdf476Documento44 pagineSEPARATION METHODS-I BY K.N.S.SWAMI - pdf476Usman KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter No.1 (Notes)Documento5 pagineChapter No.1 (Notes)IlafNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic ChemistryDocumento39 pagineOrganic Chemistryh2312416Nessuna valutazione finora
- Science 6 (Week 4)Documento16 pagineScience 6 (Week 4)leana marie ballesterosNessuna valutazione finora
- Powerpoint Slides - Separation TechniquesDocumento66 paginePowerpoint Slides - Separation Techniquesapi-30590932560% (5)
- General Chemistry 1 First Quarter - Module 1 Properties of MatterDocumento28 pagineGeneral Chemistry 1 First Quarter - Module 1 Properties of MatterJRAVPNessuna valutazione finora
- Centrifugation, Desiccation and LevigationDocumento16 pagineCentrifugation, Desiccation and Levigationengr587Nessuna valutazione finora
- Various Separation Techniques ExplainedDocumento6 pagineVarious Separation Techniques Explainedmay ann dimaanoNessuna valutazione finora
- CHE 414 Separation TechniquesDocumento12 pagineCHE 414 Separation Techniquesbenjamin bosireNessuna valutazione finora
- 06 Science Ch5 Seperation of SubstancesDocumento2 pagine06 Science Ch5 Seperation of SubstancesGSSS udhopur barsalNessuna valutazione finora
- Different Processes in Separating and Purifying Substances and MixturesDocumento3 pagineDifferent Processes in Separating and Purifying Substances and MixturesLarry MarNessuna valutazione finora
- General Chemistry Group 2 Report FinalDocumento34 pagineGeneral Chemistry Group 2 Report FinalMara ClaireNessuna valutazione finora
- Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds (Theory) Module-6-3Documento12 paginePurification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds (Theory) Module-6-3Raju SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods of Separating Components of MixturesDocumento27 pagineMethods of Separating Components of MixturesSrynnENessuna valutazione finora
- Separation TechniquesDocumento7 pagineSeparation TechniquesPriyanka WadhwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- chapter 1Documento9 paginechapter 1アNessuna valutazione finora
- Purification Techniques for Organic CompoundsDocumento57 paginePurification Techniques for Organic CompoundsNor Azila100% (1)
- SP Typed NotesDocumento20 pagineSP Typed NotesNur Zaimah WafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Material - Separation MethodsDocumento7 pagineStudy Material - Separation MethodsSahil NarkhedeNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022 - 3NA - Separation Technique - NotesDocumento19 pagine2022 - 3NA - Separation Technique - NotesNitin Yadav Praduman (Qss)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pengantar Metode PemisahanDocumento43 paginePengantar Metode PemisahanMili APRILIANessuna valutazione finora
- EXPE4Documento6 pagineEXPE4K-yanVehraaYomomaNessuna valutazione finora
- Separation of Mixtures (Continuation of Notes)Documento6 pagineSeparation of Mixtures (Continuation of Notes)mohammed mahdyNessuna valutazione finora
- Separating MixturesDocumento13 pagineSeparating Mixturesver_at_workNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods of Separating Components of MixturesDocumento27 pagineMethods of Separating Components of MixturesJhayce Christian S. CapanayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Separation Tec-Wps OfficeDocumento14 pagineSeparation Tec-Wps OfficeJoel TitusNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE 6th Methods of Separation of SubstancesDocumento2 pagineCBSE 6th Methods of Separation of SubstancesSwapnil ChaudhariNessuna valutazione finora
- Pption 2Documento17 paginePption 2areeshwaseem313Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2, 3 & 4Documento59 pagineChapter 2, 3 & 4Dawit Mulugeta100% (1)
- Separation Techniques Part 2Documento45 pagineSeparation Techniques Part 2Maan Joy Revelo GallosNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaporation Can Be Used As A Separation Method To Separate Components of ADocumento3 pagineEvaporation Can Be Used As A Separation Method To Separate Components of APearl PearlNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - 5 Separation of Substances: Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksDocumento2 pagineChapter - 5 Separation of Substances: Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksAahana CharanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6Documento15 pagineChapter 6bahru demekeNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 1 Experimental DesignDocumento31 pagineTopic 1 Experimental DesignKaixin HuangNessuna valutazione finora
- MixturesDocumento25 pagineMixturesJoma Guerra ina moNessuna valutazione finora
- Separation Techniques: Composed With Epsilon Notes in AndroidDocumento7 pagineSeparation Techniques: Composed With Epsilon Notes in AndroidBrãñdøn DzîñgáíNessuna valutazione finora
- The ABC's of Filtration MethodsDocumento3 pagineThe ABC's of Filtration MethodsHanna CarpioNessuna valutazione finora
- Seperation TechniqueDocumento6 pagineSeperation TechniquelindaoeghagharaNessuna valutazione finora
- Method of PurificationDocumento18 pagineMethod of PurificationPratyush KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Colloids Are Mixtures Whose Particles Are Larger Than The Size of ADocumento2 pagineColloids Are Mixtures Whose Particles Are Larger Than The Size of AKyla Angela GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Separate the Ice from WaterDocumento13 pagineSeparate the Ice from WaterFauzan AkbarNessuna valutazione finora
- Physicochemical Processes: Dr. Sana Hanif Assistant ProfessorDocumento12 paginePhysicochemical Processes: Dr. Sana Hanif Assistant ProfessorMohammad ZohaibNessuna valutazione finora
- Sfo NotesDocumento56 pagineSfo NotesJdNessuna valutazione finora
- Separating MixturesDocumento9 pagineSeparating Mixturesm_frajman75% (4)
- Separation TechniquesDocumento48 pagineSeparation TechniquesNaeem ShayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp 3Documento9 pagineExp 3tamanranya234Nessuna valutazione finora
- 9april2020 Filtration.8554.1584691329.6752Documento72 pagine9april2020 Filtration.8554.1584691329.6752Pun AditepNessuna valutazione finora
- Purification and Charaterisasation of Organic Compounds (CP)Documento11 paginePurification and Charaterisasation of Organic Compounds (CP)Something AwesomeNessuna valutazione finora
- Anemia Mukt Bharat-Converted (1) - 5Documento1 paginaAnemia Mukt Bharat-Converted (1) - 5HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- S Form For Health Workers in Mobile App (1) - 8Documento1 paginaS Form For Health Workers in Mobile App (1) - 8HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- S Form For Health Workers in Mobile App (1) - 7Documento1 paginaS Form For Health Workers in Mobile App (1) - 7HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Providing optimal nutrition for infant growth and developmentDocumento21 pagineProviding optimal nutrition for infant growth and developmentHarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- S Form For Health Workers in Mobile App (1) - 6Documento1 paginaS Form For Health Workers in Mobile App (1) - 6HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Anemia Mukt Bharat-Converted (1) - 1Documento1 paginaAnemia Mukt Bharat-Converted (1) - 1HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Anemia Mukt Bharat-Converted (1) - 4Documento1 paginaAnemia Mukt Bharat-Converted (1) - 4HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- S Form For Health Workers in Mobile App (1) - 4Documento1 paginaS Form For Health Workers in Mobile App (1) - 4HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- S Form For Health Workers in Mobile App (1) - 1Documento1 paginaS Form For Health Workers in Mobile App (1) - 1HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 13Documento1 pagina2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 13HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Anemia Mukt Bharat-Converted (1) - 3Documento1 paginaAnemia Mukt Bharat-Converted (1) - 3HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Anemia Mukt Bharat-Converted (1) - 2Documento1 paginaAnemia Mukt Bharat-Converted (1) - 2HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 15Documento1 pagina2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 15HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 18Documento1 pagina2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 18HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Definitions - Suspect/Probable Infected PersonDocumento1 paginaDefinitions - Suspect/Probable Infected PersonHarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study Answers: Question 1: If You Were There As A Customer What Would You Have Done?Documento1 paginaCase Study Answers: Question 1: If You Were There As A Customer What Would You Have Done?HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 11Documento1 pagina2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 11HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 2Documento1 pagina2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 2HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 12Documento1 pagina2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 12HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 9Documento1 pagina2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 9HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2COVID19PPT 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 1Documento1 pagina2COVID19PPT 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 1HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 7Documento1 pagina2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 7HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 4Documento1 pagina2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 4HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2COVID19PPT 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 5Documento1 pagina2COVID19PPT 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 5HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 6Documento1 pagina2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 6HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Session 1: Communication for ResponseDocumento1 paginaSession 1: Communication for ResponseHarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 8Documento1 pagina2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 8HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 12Documento1 pagina2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 12HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 4Documento1 pagina2COVID19PPT - 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 4HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2COVID19PPT 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 1Documento1 pagina2COVID19PPT 25MarchPPTWithAnimation (1) - 1HarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- PPT, Indicator and Acid StrengthDocumento20 paginePPT, Indicator and Acid StrengthZUNINessuna valutazione finora
- MCB 410 Petroleum Microbiology Lecture 1 and 2 Amd & BioleahingDocumento10 pagineMCB 410 Petroleum Microbiology Lecture 1 and 2 Amd & BioleahingBarnabasNessuna valutazione finora
- Precast Meadow Burke Manual Inserts in PrecastDocumento184 paginePrecast Meadow Burke Manual Inserts in Precastgemotorres0% (1)
- 2010-F3-CHEM Final Exam Paper ReviewDocumento39 pagine2010-F3-CHEM Final Exam Paper Review2E (04) Ho Hong Tat AdamNessuna valutazione finora
- TUTTENHAUERDocumento148 pagineTUTTENHAUERViktoras ŽvirzdinasNessuna valutazione finora
- Mastertile 30: Highly Polymer Modified Grey Coloured Cementitious Tile AdhesiveDocumento3 pagineMastertile 30: Highly Polymer Modified Grey Coloured Cementitious Tile AdhesiveChaitanya IdateNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3.2 - FlocculationDocumento20 pagineChapter 3.2 - FlocculationHanif NifNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.2 Identification of Common Gases QPDocumento27 pagine8.2 Identification of Common Gases QPRNessuna valutazione finora
- Csec Chemistry - A5Documento17 pagineCsec Chemistry - A5Mencarty DocentNessuna valutazione finora
- General ClO2 Generation of ClO2 PDFDocumento37 pagineGeneral ClO2 Generation of ClO2 PDF1105195794Nessuna valutazione finora
- Iridium Platinum AlloysDocumento9 pagineIridium Platinum Alloysnguyen9si9nguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Prospects For Alkaline Zero Gap Water Electrolysers For Hydrogen ProductionDocumento16 pagineProspects For Alkaline Zero Gap Water Electrolysers For Hydrogen Productionkhan47pkNessuna valutazione finora
- SNI - 06 2385 2006 Minyak - NilamDocumento8 pagineSNI - 06 2385 2006 Minyak - NilamEuis Wulan AnggraeniNessuna valutazione finora
- Clin Chem Labbbbbb Long QuizDocumento7 pagineClin Chem Labbbbbb Long QuizAngela ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- AA - MINDRAY BS-120 BS-200 BS200E-ASSLmono-1Documento1 paginaAA - MINDRAY BS-120 BS-200 BS200E-ASSLmono-1Patricia MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- HW 01 SolutionDocumento12 pagineHW 01 SolutionJuan Sebastian Suarez Ospina63% (8)
- Exp 8 CHM420Documento15 pagineExp 8 CHM420Nur Faizatul Atiqah100% (1)
- Laporan Rahma (2) - CompressedDocumento36 pagineLaporan Rahma (2) - CompressedFransisca Rosari SitinjakNessuna valutazione finora
- DSDA Sulphuric Acid PlantDocumento4 pagineDSDA Sulphuric Acid PlantAbijithNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm B 570Documento4 pagineAstm B 570Telmo VianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Identification of Plant Pigments Using Paper ChromatographyDocumento7 pagineIdentification of Plant Pigments Using Paper ChromatographyPaolo TenorioNessuna valutazione finora
- 13 Cellular Respiration KEYDocumento6 pagine13 Cellular Respiration KEYLilOgLemon 101Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1280a4-8310-43c1 Rev F1Documento31 pagine1280a4-8310-43c1 Rev F1Stephen LowNessuna valutazione finora
- Boiling Point ElevationDocumento6 pagineBoiling Point ElevationJohn Gil Peñas OdsinadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecolab Liquid Laundry Program - S53035Documento4 pagineEcolab Liquid Laundry Program - S53035Nikesh ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- SteelContainerBrochure05 2012v5Documento24 pagineSteelContainerBrochure05 2012v5yasirfayyaz1992Nessuna valutazione finora
- European Steel and Alloy GradesDocumento2 pagineEuropean Steel and Alloy Gradesfarshid KarpasandNessuna valutazione finora
- 2019-PTQC-Catalog (Web)Documento48 pagine2019-PTQC-Catalog (Web)LuisNessuna valutazione finora
- Iec - 60296-2020Documento42 pagineIec - 60296-2020enriqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochem CH 24 Amino Acid BiosynthesisDocumento6 pagineBiochem CH 24 Amino Acid BiosynthesisSchat ZiNessuna valutazione finora