Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Market Integration
Caricato da
Paul Avila SorianoTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Market Integration
Caricato da
Paul Avila SorianoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Controlling – management function, organizational activities
Role of manager:
Manager develop appropriate standards
Compare performance against those standards
Corrective actions are taken necessary
Depends on human behaviour – largely geared
Highlights needed behaviours & discourage behaviours
Roles of Controls (CHIDD)
Coping with uncertainty – uncertainty arises set for future events (changes in customer demands)
Handling complex situations – controls enhance coordination (erroneous results)
Identify opportunities – control highlight situations (monthly statistics census)
Detecting irregularities - poor quality, overruns, early detection save time (erroneous results)
Decentralizing authority – managers foster decision (decision Medtech to repeat test or not)
Roles of Controls (STO)
-parallel control responsibilities exist each level
Strategic Control – Top management. Environmental factors for strategic plans
Reporting is done annually, semi-annually, quarterly
Tactical Control- Middle management, tactical plans periodic results
Reporting is done weekly or monthly
Operational control- low management, implementation of operating plans
Daily plotting of QC graphs
Steps in the Control process (DEMCRAT)
1. Determine the areas to control – decide major areas to control (main control goals & objectives)
2. Establish Standards – purposes:
Timely identification of deficiencies take correlative action before become serious
Reduce the potential negative effects of global incongruence (major in incompatabilities)
Enables employers understand what is expected
Provide basis for detecting job difficulties to person limitations
3. Measure Performance – measuring will depend on standards set (measure actual performance)
4. Compare performance against the standard based on the reports that summarize planned
- Presentation orally, generated by computer
Management by Exception – control principle (managers informed in situation)
Management by Wandering Around – walk around
360-degree feedback mechanism – evaluation approach (individual ratings)
5. Recognize Positive Performance – performance meets or exceeds standards
- Spoken (welldone) , bonuses, pay raises
6. Adjust Standards & measures necessary – tended check standards periodically
Exceeding standards signal unforeseen opportunities
Standards are met changing condition may raise standards for future
7. Take corrective action as necessary –assessment of action (standards are inappropriate)
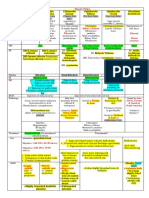
Types of control
Major control by timing - basis on their timing/stage cycle
Pre- analytical Analytical Post analytical
Feed forward Concurrent Feedback
Preliminary Screening Post-Action
Other names Pre-control Yes or No Control Output Control
Preventive
Steering Control
Regulation of inputs Regulation of ongoing process Regulation after product
Focus service completed
Emphasis Prevention to preclude Identifying the difficulties in *Serve for final means
serious difficulties productive process *Provide information
facilitate planning process
*Provides output
information rewarding
employee
Multiple Control System – 2 or more feed forward (includes inputs & outputs)
Cybernetic Control - Self regulating control system (corrective action)
Non-cybernetic Control – relies human discretion
Managerial Approaches (CIMB)
Clan Control – value, beliefs, traditions, Shared norms
Instrumentalist approach – heavily clan & phased set of plans bureaucratic
- Managers strike appropriate balance encourage innovations
Market Control – market mechanism
Bureaucratic Control – rules, policies, budgets, schedules, supervision
Potential dysfunction (BONG)
Behavioral displacement
Operating delays
Negative altitudes
Game playing
Types of control
Multidimensional
Monitorable
Accurate
Realistic
Cost-effective
Timely
Flexible
Future oriented
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Reaction rate determination and simulation of hydrogenation processDocumento3 pagineReaction rate determination and simulation of hydrogenation processToMemNessuna valutazione finora
- Small Coccobacilli: Pinpoint ColoniesDocumento33 pagineSmall Coccobacilli: Pinpoint ColoniesPaul Avila SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Diagnostic CytologyDocumento36 pagineBasic Diagnostic CytologyPaul Avila SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- MICROBIOLOGYDocumento33 pagineMICROBIOLOGYPaul Avila SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- CestodesDocumento82 pagineCestodesPaul Avila Soriano100% (1)
- Vaginal SecretionsDocumento4 pagineVaginal SecretionsPaul Avila SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hepatic FlukesDocumento3 pagineHepatic FlukesPaul Avila SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Amniotic FluidDocumento14 pagineAmniotic FluidPaul Avila SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- AscarisDocumento6 pagineAscarisPaul Avila SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hepatic FlukesDocumento3 pagineHepatic FlukesPaul Avila SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Appreciation LessonDocumento2 pagineAppreciation LessonPaul Avila Soriano100% (1)
- Anima STructureDocumento32 pagineAnima STructurePaul Avila SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Capillaria PhilippinensisDocumento19 pagineCapillaria PhilippinensisPaul Avila SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Angiostrongylus CantonensisDocumento9 pagineAngiostrongylus CantonensisPaul Avila SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hymenolepis DiminutaDocumento6 pagineHymenolepis DiminutaPaul Avila SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Trichuris TrichiuraDocumento16 pagineTrichuris TrichiuraPaul Avila SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Samsung 55 Inch LCD LED 8000 User ManualDocumento290 pagineSamsung 55 Inch LCD LED 8000 User ManuallakedipperNessuna valutazione finora
- CV Abdalla Ali Hashish-Nursing Specialist.Documento3 pagineCV Abdalla Ali Hashish-Nursing Specialist.Abdalla Ali HashishNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessing Eyes NCM 103 ChecklistDocumento7 pagineAssessing Eyes NCM 103 ChecklistNicole NipasNessuna valutazione finora
- OLA CAB MARKET ANALYSIS AND TRENDSDocumento55 pagineOLA CAB MARKET ANALYSIS AND TRENDSnitin gadkariNessuna valutazione finora
- Main Hoon Na - WikipediaDocumento8 pagineMain Hoon Na - WikipediaHusain ChandNessuna valutazione finora
- JR Hydraulic Eng. Waterways Bed Protection Incomat BelfastDocumento2 pagineJR Hydraulic Eng. Waterways Bed Protection Incomat Belfastpablopadawan1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Caribbean Examinations Council Caribbean Secondary Certificate of Education Guidelines For On-Site Moderation SciencesDocumento9 pagineCaribbean Examinations Council Caribbean Secondary Certificate of Education Guidelines For On-Site Moderation SciencesjokerNessuna valutazione finora
- FINAL - Plastic Small Grants NOFO DocumentDocumento23 pagineFINAL - Plastic Small Grants NOFO DocumentCarlos Del CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Management NotesDocumento61 paginePrinciples of Management Notestulasinad123Nessuna valutazione finora
- PGP TutorialDocumento21 paginePGP TutorialSabri AllaniNessuna valutazione finora
- CH - 3Documento3 pagineCH - 3Phantom GamingNessuna valutazione finora
- DAT MAPEH 6 Final PDFDocumento4 pagineDAT MAPEH 6 Final PDFMARLYN GAY EPANNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Air Centrifugal Compressors: Turbo-Air Series Featuring Oil-Free AirDocumento20 paginePlant Air Centrifugal Compressors: Turbo-Air Series Featuring Oil-Free AirSharad KokateNessuna valutazione finora
- Compare and Contrast High School and College EssayDocumento6 pagineCompare and Contrast High School and College Essayafibkyielxfbab100% (1)
- Genre Worksheet 03 PDFDocumento2 pagineGenre Worksheet 03 PDFmelissaNessuna valutazione finora
- Brooks Cole Empowerment Series Becoming An Effective Policy Advocate 7Th Edition Jansson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocumento36 pagineBrooks Cole Empowerment Series Becoming An Effective Policy Advocate 7Th Edition Jansson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFlois.guzman538100% (12)
- ArtigoPublicado ABR 14360Documento14 pagineArtigoPublicado ABR 14360Sultonmurod ZokhidovNessuna valutazione finora
- Raychem Price ListDocumento48 pagineRaychem Price ListramshivvermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mark Dean GR6211 Fall 2018 Columbia University: - Choice Theory'Documento5 pagineMark Dean GR6211 Fall 2018 Columbia University: - Choice Theory'bhaskkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Using Snapchat For OSINT - Save Videos Without OverlaysDocumento12 pagineUsing Snapchat For OSINT - Save Videos Without OverlaysVo TinhNessuna valutazione finora
- A.2.3. Passive Transport Systems MCQsDocumento3 pagineA.2.3. Passive Transport Systems MCQsPalanisamy SelvamaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Critique On A Film Director's Approach To Managing CreativityDocumento2 pagineCritique On A Film Director's Approach To Managing CreativityDax GaffudNessuna valutazione finora
- Agricultural Sciences P1 Nov 2015 Memo EngDocumento9 pagineAgricultural Sciences P1 Nov 2015 Memo EngAbubakr IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- 9AKK101130D1664 OISxx Evolution PresentationDocumento16 pagine9AKK101130D1664 OISxx Evolution PresentationfxvNessuna valutazione finora
- Center of Gravity and Shear Center of Thin-Walled Open-Section Composite BeamsDocumento6 pagineCenter of Gravity and Shear Center of Thin-Walled Open-Section Composite Beamsredz00100% (1)
- Lab ReportDocumento5 pagineLab ReportHugsNessuna valutazione finora
- Obsolescence 2. Book Value 3. Depreciation 4. Depletion EtcDocumento9 pagineObsolescence 2. Book Value 3. Depreciation 4. Depletion EtcKHAN AQSANessuna valutazione finora