Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Abstrak SPPBM BI Final
Caricato da
Norhapidah Mohd SaadDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Abstrak SPPBM BI Final
Caricato da
Norhapidah Mohd SaadCopyright:
Formati disponibili
METACOGNITIVE-FOCUSED LEARNING STRATEGIES ON DIFFERENTIATION
TO ELEVATE MATEMATICAL REASONING SKILLS
Abstract
Mathematical reasoning (PM) is one of many important skills required by students to succeed
in learning analytical mathematics topics such as Differentiation. Nevertheless, many studies
have reported that the overall levels of PM among students were still below par. Several studies
and scientific debates have suggested that there exists a connection between mastering PM and
the metacognitive processes practiced by individual when learning mathematics. This study was
conducted to address two main objectives, namely (i) to design and develop a metacognitive-
focused learning strategy (called SPPBM) that assists students in elevating PM in the learning
of Differentiation (ii) to study the effects of SPPBM on students’ levels of PM in the learning
of Differentiation. The first objective was addressed using Marzano’s model of Dimension of
Expanding and Enhancing Knowledge on four essential components of PM (i.e. comparing and
contrasting, classifying, inductive reasoning and deductive reasoning) to provide a theoretical
framework of study. In addition, the design, development and integration of metacognitive-
focused learning activities were made in accordance with Wilson’s model of metacognition.
The second research objective was investigated using a pre-test versus post-test of a single group
repeated time series approach. This design and development type of study was conducted in two
stages according to ADDIE model. The first stage involved five phases beginning with analyzing
of fundamental information of PM skills, metacognitive-focused learning strategies to assist
students in elevating PM, selection of relevant mathematical contents and the compatibility
between the adopted models. The results of analyses were then used to provide a foundation for
designing and developing SPPBM. The design phase involved the structuring and arrangement
of learning activities with detailed attention given on the integration of metacognitive-focused
activities onto each PM activity prescribed by Marzano’s model. The development phase
involved constructing and integrating suitable learning activities with respect to the PM and each
of its four components. A small scale pilot study was first conducted to check for obvious flaws
and deficiencies of SPPBM as well as to help researcher to get familiar with the intervention
activities during the real field work. The SPPBM was given to six expert mathematics educators
to validate and evaluate its suitability in terms of the metacognitive-focused learning strategies
as well as its function to assist students in elevating PM. In the second stage, the SPPBM was
tried out to 31 students in a common classroom setting. Before the intervention, these students
(who have learnt the topic of Differentiation using traditional approach earlier) were given a
Differentiation Reasoning Test (UPP) to measure the level of PM (TPM) as well as the level of
each of the four essential PM components of compare and contrast (TPMMB), classify
(TPMMK), inductive reasoning (TPMI) and deductive reasoning (TPMD). Following to that,
the students were directed to re-learn Differention using SPPBM for a period of six weeks.
During this period, a three series of tests were conducted using smaller scale of similar version
of UPP. At the end of intervention period, the TPM and each of the TPMMB, TPMMK, TPMI
and TPMD were measured again using a similar version of UPP post-test. The data were
analyzed using descriptive statistics, paired t-test and one-way ANOVA. The results from the
paired t-test revealed a significant increase of PM mean after the learning of Differentiation
using SPPBM (t=-27.47; p < 0.05). Similar findings were also found in each of levels of
components TKPM where the paired t-test results showed the following: TPMMB [(31)=-
22.097, p<0.05], TPMMK [(31)=-32.416, p<0.05], TPMI [(31)=-38.325, p<0.05] and TPMD
[(31)=-26.843, p<0.05]. The findings from the one-way ANOVA test appeared to have
confirmed the existence of significant mean increases (at level 0.05) of TPM and each of the
levels of PM components after the learning using SPPBM. These findings suggested that the
SPPBM appereared to have positive effects in assisting the students to elevate the PM especially
in the learning of Differentiation.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- REVIEWER FOR INTRO TO PHILO 2nd QuarterDocumento8 pagineREVIEWER FOR INTRO TO PHILO 2nd QuarterLeigh Margarrette CabayaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Sukatan Membulat Kelas14feb 2020Documento34 pagine1 Sukatan Membulat Kelas14feb 2020Norhapidah Mohd SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- An Introduction To The Black Arts MovementDocumento12 pagineAn Introduction To The Black Arts MovementsiesmannNessuna valutazione finora
- Summative Test in UCSPDocumento3 pagineSummative Test in UCSPQuarentai Siete LptNessuna valutazione finora
- Team Learning in Projects: Theory and PracticeDa EverandTeam Learning in Projects: Theory and PracticeNessuna valutazione finora
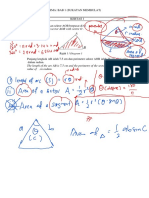
- Diagram 1 Shows A Sector AOB With Centre O A: Modul/Tingkatan Lima: Bab 1 (Sukatan Membulat)Documento19 pagineDiagram 1 Shows A Sector AOB With Centre O A: Modul/Tingkatan Lima: Bab 1 (Sukatan Membulat)Norhapidah Mohd SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Critique Paper On Quantitative ResearchDocumento6 pagineCritique Paper On Quantitative ResearchFidel ManaolNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan in WH QuestionsDocumento10 pagineLesson Plan in WH QuestionsMel Anthony Cerilo50% (2)
- JRME (Jurnal NCTM) ReviewDocumento6 pagineJRME (Jurnal NCTM) ReviewPetty MutiaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Improving Students Reading Comprehension Skills Effects of StrategyDocumento15 pagineImproving Students Reading Comprehension Skills Effects of StrategyNora SánchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal MatematikDocumento20 pagineJurnal MatematikSiti Norbaya GhazaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Bmaw2016pomdp RtiDocumento8 pagineBmaw2016pomdp Rtiapi-251716146Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sunday Dare Post Field Defence Slide PresentationDocumento19 pagineSunday Dare Post Field Defence Slide PresentationSikiru Issa NuhuNessuna valutazione finora
- 33-Article Text-100-1-10-20200617Documento6 pagine33-Article Text-100-1-10-20200617Lihnie Joy BoyoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Mastering Reasoning Skills in Learning Differentiation Using The Marzano's StrategyDocumento8 pagineMastering Reasoning Skills in Learning Differentiation Using The Marzano's StrategyNorhapidah Mohd SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal Penelitian Pendidikan IPA (JPPIPA)Documento16 pagineJurnal Penelitian Pendidikan IPA (JPPIPA)Raden HamidiNessuna valutazione finora
- Artikel JMEDocumento16 pagineArtikel JMErenny wahyuniNessuna valutazione finora
- Pengembangan Desain Pembelajaran Topik Peluang Berbasis Realistic Mathematics EducationDocumento11 paginePengembangan Desain Pembelajaran Topik Peluang Berbasis Realistic Mathematics EducationmegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Saefudin 2019 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1254 012083Documento7 pagineSaefudin 2019 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1254 012083Ulan MaulanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Effectiveness of Computer Based Concept Mapping Strategy On Self Regulation at Secondary School LevelDocumento4 pagineEffectiveness of Computer Based Concept Mapping Strategy On Self Regulation at Secondary School LevelIOSRjournalNessuna valutazione finora
- Developing Simulation ExercisesDocumento15 pagineDeveloping Simulation ExercisesCarlitos999999100% (1)
- 862-Article Text-2984-1-10-20230105 2Documento14 pagine862-Article Text-2984-1-10-20230105 2reza novrizalNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessing The Quality of Problems in Problem-Based Learning: Nachamma Sockalingam Jerome Rotgans Henk SchmidtDocumento9 pagineAssessing The Quality of Problems in Problem-Based Learning: Nachamma Sockalingam Jerome Rotgans Henk SchmidtalhanunNessuna valutazione finora
- Mind Map Learning Technique: An Educational Interactive ApproachDocumento6 pagineMind Map Learning Technique: An Educational Interactive ApproachrobinNessuna valutazione finora
- IJPR2019Documento6 pagineIJPR2019Anh Hồ Thị MinhNessuna valutazione finora
- The Problem and Its BackgroundDocumento6 pagineThe Problem and Its Background꾹태Nessuna valutazione finora
- FINAL VERSION ENGLISH ABSTRACT PROOFREAD Hayati Binti Hashim Mohd - 19 Mac 2023Documento1 paginaFINAL VERSION ENGLISH ABSTRACT PROOFREAD Hayati Binti Hashim Mohd - 19 Mac 2023HAYATI BTE HASHIM MOHD. MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Validating The Academic Self-Regulated Learning Scale With The Motivated Strategies For Learning Questionnaire (MSLQ) and Learning and Study Strategies Inventory (LASSI)Documento18 pagineValidating The Academic Self-Regulated Learning Scale With The Motivated Strategies For Learning Questionnaire (MSLQ) and Learning and Study Strategies Inventory (LASSI)Carlo MagnoNessuna valutazione finora
- STUDY NOTES 3 For PYC4807Documento3 pagineSTUDY NOTES 3 For PYC4807mikayla dreyerNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.metacognitive STRATEGIES AND TEST PERFORMANCEDocumento37 pagine10.metacognitive STRATEGIES AND TEST PERFORMANCEStephenNessuna valutazione finora
- Abstract Jhon Benedick R. DiomampoDocumento1 paginaAbstract Jhon Benedick R. DiomampoJhon Benedick DiomampoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Level of Learners' Performance in Mathematics Through Mind Mapping StrategyDocumento9 pagineThe Level of Learners' Performance in Mathematics Through Mind Mapping StrategyPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment No1 Writes by SohaibDocumento5 pagineAssignment No1 Writes by SohaibAsad UmairNessuna valutazione finora
- Synopsis Education Data Analysis and Prediction of Student Performance Using MLDocumento3 pagineSynopsis Education Data Analysis and Prediction of Student Performance Using MLVshala VtechcodersNessuna valutazione finora
- Levels of SMC - Ced Students' Computational Skills in Solving Rational NumbersDocumento32 pagineLevels of SMC - Ced Students' Computational Skills in Solving Rational NumbersMarlon Cabanilla BaslotNessuna valutazione finora
- Hommes Van Der MolenDocumento11 pagineHommes Van Der MolenHamdy RagbNessuna valutazione finora
- CE-7 Implementation of Jigsaw Model With Lesson-Study-Based On Strategy and Method of Chemistry Instruction Subject (SMPK)Documento8 pagineCE-7 Implementation of Jigsaw Model With Lesson-Study-Based On Strategy and Method of Chemistry Instruction Subject (SMPK)Firda AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- A Model of Classroom Assessment in Action: Using Assessment To Improve Student Learning and Statistical ReasoningDocumento4 pagineA Model of Classroom Assessment in Action: Using Assessment To Improve Student Learning and Statistical ReasoningAgi B BossNessuna valutazione finora
- MSLQ ReviewDocumento24 pagineMSLQ ReviewDelikanliX100% (1)
- Validating The Academic Self-Regulated L PDFDocumento18 pagineValidating The Academic Self-Regulated L PDFJerrie Mae GutierrezNessuna valutazione finora
- Telaah JurnalDocumento7 pagineTelaah JurnalAremia VaneshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Meta-Analysis Chapter 2Documento2 pagineMeta-Analysis Chapter 2Dianne DucosNessuna valutazione finora
- The Problem and Its BackgroundDocumento7 pagineThe Problem and Its BackgroundNiña Anne Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- MSLQ (Pintrich Et Al. 1993) CompletoDocumento24 pagineMSLQ (Pintrich Et Al. 1993) CompletoFrancisco J. SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Unpacking Pedagogical KnowledgeDocumento0 pagineUnpacking Pedagogical Knowledgeafham.muflihinNessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis Module 7Documento6 pagineThesis Module 7Lianne Grace Basa BelicanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Clements - BB - JRME - MatemáticaDocumento28 pagineClements - BB - JRME - MatemáticaMarisa CostaNessuna valutazione finora
- GROUP 4 MASEIS 4 Evaluation Study ProposalDocumento19 pagineGROUP 4 MASEIS 4 Evaluation Study ProposalJENNY VERZOSANessuna valutazione finora
- Assessing Students' Reading Comprehension Ability: The Comparison of Two Test Item Formats inDocumento7 pagineAssessing Students' Reading Comprehension Ability: The Comparison of Two Test Item Formats inrafiqa putriNessuna valutazione finora
- Applsci 10 00090Documento27 pagineApplsci 10 00090cafexarmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment 1Documento8 pagineAssessment 1Beberly Kim AmaroNessuna valutazione finora
- Of The Undergraduate Students in Oman. Dhofar UniversityDocumento10 pagineOf The Undergraduate Students in Oman. Dhofar UniversityVanessa Pangan KellerNessuna valutazione finora
- The Revised Two Factor Study Process Questionnaire: R-SPQ-2FDocumento20 pagineThe Revised Two Factor Study Process Questionnaire: R-SPQ-2FCedie YganoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ijpo 3 (3) 503-507Documento5 pagineIjpo 3 (3) 503-507Aarushi BNessuna valutazione finora
- Realistic Mathematics Education Untuk Siswa Kelas Vii SMP: Pengembangan Alur Pembelajaran Perbandingan BerbasisDocumento17 pagineRealistic Mathematics Education Untuk Siswa Kelas Vii SMP: Pengembangan Alur Pembelajaran Perbandingan Berbasisrefni ErlizaNessuna valutazione finora
- SLS PresentationDocumento2 pagineSLS PresentationBenjamin MulatyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analisis Pemahaman Konsep Dasar Geometri Dengan Pembelajaran Metode Penemuan Terbimbing Pada Mata Kuliah GeometriDocumento8 pagineAnalisis Pemahaman Konsep Dasar Geometri Dengan Pembelajaran Metode Penemuan Terbimbing Pada Mata Kuliah Geometrisitiaminah 27Nessuna valutazione finora
- Continued Intentions of Adopting E-Learning System in Blended Learning Instruction in CTU Construct ReferenceDocumento30 pagineContinued Intentions of Adopting E-Learning System in Blended Learning Instruction in CTU Construct ReferenceStrange MagicNessuna valutazione finora
- An Applied Research of Rasch GSP For Evaluating Difficulty of Test QuestionsDocumento10 pagineAn Applied Research of Rasch GSP For Evaluating Difficulty of Test QuestionsInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNessuna valutazione finora
- Contoh 1 Journal Article Critique - Jamal Oman 2009Documento6 pagineContoh 1 Journal Article Critique - Jamal Oman 2009Adrian LohNessuna valutazione finora
- THE IMPACT STUDY ON EFFECTIVENESS OF AKEPT'S T& L TRAINING PROGRAMMESDocumento86 pagineTHE IMPACT STUDY ON EFFECTIVENESS OF AKEPT'S T& L TRAINING PROGRAMMEShanipahhussinNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison Between KEMP, SMITHRAGAB, DICK CAREYsDocumento8 pagineComparison Between KEMP, SMITHRAGAB, DICK CAREYsEskawatiNessuna valutazione finora
- EDS 541 Instructional Design: Week 4 AssignmentDocumento8 pagineEDS 541 Instructional Design: Week 4 AssignmentchandrikaNessuna valutazione finora
- RRL Sa Chapter 2Documento16 pagineRRL Sa Chapter 2HungryNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Management System Efficiency versus Staff ProficiencyDa EverandLearning Management System Efficiency versus Staff ProficiencyValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- Summary of Wolfram Rollett's Student Feedback on Teaching in SchoolsDa EverandSummary of Wolfram Rollett's Student Feedback on Teaching in SchoolsNessuna valutazione finora
- Panduan Lesson PlanDocumento55 paginePanduan Lesson PlanNorhapidah Mohd SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- ASL Copyright Transfer Agreement CTA NizamDocumento1 paginaASL Copyright Transfer Agreement CTA NizamNorhapidah Mohd SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Soalan Kertas 1 Sukatan Membulat - EditedDocumento15 pagineSoalan Kertas 1 Sukatan Membulat - EditedNorhapidah Mohd SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Modul Tudingan Kertas 1 Set 1 Fasa 2 2015Documento12 pagineModul Tudingan Kertas 1 Set 1 Fasa 2 2015Norhapidah Mohd SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Lampiran Pembetulan JSH NizamDocumento2 pagineLampiran Pembetulan JSH NizamNorhapidah Mohd SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Nota Math Form 1-3Documento8 pagineNota Math Form 1-3Norhapidah Mohd Saad100% (2)
- Mastering Reasoning Skills in Learning Differentiation Using The Marzano's StrategyDocumento8 pagineMastering Reasoning Skills in Learning Differentiation Using The Marzano's StrategyNorhapidah Mohd SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Modul Tudingan Kertas 1 Set 3Documento11 pagineModul Tudingan Kertas 1 Set 3Norhapidah Mohd SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Probability Distribution ReinforcementDocumento8 pagineProbability Distribution ReinforcementNorhapidah Mohd SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Vectors 1Documento19 pagineVectors 1Fazlina MustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Modul Tudingan Kertas 1 Set 1 Fasa 2 2015Documento12 pagineModul Tudingan Kertas 1 Set 1 Fasa 2 2015Norhapidah Mohd SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Mastering Reasoning Skills Among Form Four Students in The Topic of Differentiation Based On Marzano Dimensional Mastery Learning ModelDocumento1 paginaMastering Reasoning Skills Among Form Four Students in The Topic of Differentiation Based On Marzano Dimensional Mastery Learning ModelNorhapidah Mohd SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigo FunctionsDocumento17 pagineTrigo FunctionsNorhapidah Mohd SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper Work Math WeekDocumento9 paginePaper Work Math WeekNorhapidah Mohd SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- RPT Add Math Form 4Documento9 pagineRPT Add Math Form 4Norhapidah Mohd SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Prob DistributionDocumento13 pagineProb DistributionNorhapidah Mohd SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Motion Along A Straight LineDocumento16 pagineMotion Along A Straight LineNorhapidah Mohd SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Permutation & CombinationDocumento8 paginePermutation & CombinationNorhapidah Mohd SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear ProgrammingDocumento19 pagineLinear ProgrammingNorhapidah Mohd SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- DifferentiationDocumento21 pagineDifferentiationNorhapidah Mohd Saad100% (1)
- Internal and External Factors Affecting Achievement in Mathematics: Some Findings From TimssDocumento7 pagineInternal and External Factors Affecting Achievement in Mathematics: Some Findings From TimssNorhapidah Mohd SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Coordinate GeometryDocumento34 pagineCoordinate GeometryNorhapidah Mohd SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Disaster Management ResumeDocumento3 pagineDisaster Management ResumeStella FreskyNessuna valutazione finora
- National Symbols and Festivals of India-ExerciseDocumento4 pagineNational Symbols and Festivals of India-ExerciseVIVAANNessuna valutazione finora
- Muhammad Usman PDFDocumento1 paginaMuhammad Usman PDFSheraz IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Luați, Bre, de Vă Săturați!Documento3 pagineLuați, Bre, de Vă Săturați!nafetsboyNessuna valutazione finora
- International Law and The Use of Force by States: Ian Brownlie, Q.C., D.C.L., F.B.ADocumento6 pagineInternational Law and The Use of Force by States: Ian Brownlie, Q.C., D.C.L., F.B.Aarsalan ShahzadNessuna valutazione finora
- RPT Bi Ppki - Tahun 1Documento9 pagineRPT Bi Ppki - Tahun 1api-602922608Nessuna valutazione finora
- BLESSED BIRTH: The Birth of Huzoor Ghaus-e-Azam (Radiallahu Ta'ala Anh) Was A GreatDocumento1 paginaBLESSED BIRTH: The Birth of Huzoor Ghaus-e-Azam (Radiallahu Ta'ala Anh) Was A GreatmagillaniNessuna valutazione finora
- UNHCR Report On Minorities in Pakistan 2012Documento46 pagineUNHCR Report On Minorities in Pakistan 2012Aamir MughalNessuna valutazione finora
- The Effects of Socialization On Gender Discrimination and Violence: A Case Study From LebanonDocumento23 pagineThe Effects of Socialization On Gender Discrimination and Violence: A Case Study From LebanonOxfamNessuna valutazione finora
- Residential Schools and Truth and ReconciliationDocumento29 pagineResidential Schools and Truth and ReconciliationOmkar ThoratNessuna valutazione finora
- List Journal Scopus Dan Nasional Terakreditasi-1Documento13 pagineList Journal Scopus Dan Nasional Terakreditasi-1wimarakayanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lakan at LakambiniDocumento7 pagineLakan at LakambiniMheiiNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Is Islam A Complete Code of Life by DR S M IshtiaqDocumento8 pagine2 Is Islam A Complete Code of Life by DR S M IshtiaqFAREED AHMED KHANNessuna valutazione finora
- BSSP Course DescriptionsDocumento3 pagineBSSP Course DescriptionsJilliane LagusNessuna valutazione finora
- Simon Task 2Documento37 pagineSimon Task 2Hoàng LongNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Rights Report 2013 - Odhikar Report On BangladeshDocumento160 pagineHuman Rights Report 2013 - Odhikar Report On BangladeshFIDHNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Iii Understanding by Design (Ubd), A Curriculum ModelDocumento15 pagineUnit Iii Understanding by Design (Ubd), A Curriculum ModelMylene VillarNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 12 SHS - JHSDocumento7 pagineWeek 12 SHS - JHSCeasar Ryan AsuncionNessuna valutazione finora
- An Interview With A LawyerDocumento3 pagineAn Interview With A LawyerarielramadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Starbucks at The ShantyDocumento7 pagineStarbucks at The ShantyDrin Mendoza56% (9)
- Miss Julie and Hedda Gabler WorldLit1Documento5 pagineMiss Julie and Hedda Gabler WorldLit1Patricia Abeabe100% (2)
- Business Organization and ManagementDocumento4 pagineBusiness Organization and ManagementJoanaNessuna valutazione finora
- S. Robson Notes On The Early Kidung Literature: This PDF-file Was Downloaded From HTTP://WWW - Kitlv-Journals - NLDocumento24 pagineS. Robson Notes On The Early Kidung Literature: This PDF-file Was Downloaded From HTTP://WWW - Kitlv-Journals - NLDevan FirmansyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer in Oral Comm 2Documento39 pagineReviewer in Oral Comm 2Sam SammyNessuna valutazione finora
- Military EthicsDocumento5 pagineMilitary EthicsEli BondNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 1: Languages in Variation and Languages in Contact IdiolectDocumento4 pagineGroup 1: Languages in Variation and Languages in Contact IdiolectAlondra L. FormenteraNessuna valutazione finora