Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
42nd Amendment of Indian Constitution Indian Polity
Caricato da
jaivik_ce7584Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
42nd Amendment of Indian Constitution Indian Polity
Caricato da
jaivik_ce7584Copyright:
Formati disponibili
UPSC Civil Services Examination
Political Science & International Relations for IAS Prelims and Mains
Topic: 42nd Amendment of Indian Constitution- Indian Polity Notes
42nd Amendment Act, 1976 is one of the most important amendments to the Indian Constitution. It was
enacted by Indian National Congress headed by Indira Gandhi then. The topic ‘42nd Amendment Act’
also called The Constitution Act, 1976 is significant for IAS Exam as it is an essential part of UPSC
Political Science for both Prelims and Mains GS-II papers.
What is 42nd Amendment Act?
The act also called The Constitution Act, 1976 is termed as one of the most controversial acts in the history of
amendments to Indian Constitution. It amended/ introduced various provisions given below:
Attempted to reduce the power of the Supreme Court and High Courts
Laid down Fundamental Duties for citizens
Terms- Socialist, Secular and Integrity added to the Preamble
Similar to the 42nd amendment act, there are several other important amendments in the Indian Constitution for
UPSC that you may like to read from the linked article for civil services exam preparation.
Why is 42nd Amendment called Mini Constitution?
The forty-second amendment attempted to alter the basic structure of Indian Constitution. Check the table below to
read what all amendments were brought by the constitution act, 1976 because of which it was called the mini-
constitution:
Amendments by 42nd Details of the Amendments
Amendment Act
Changes to Preamble Words Socialist, Secular and Integrity added
Changes to 7th Schedule Transferred five subjects from the state list to the concurrent list:
1. Education
2. Forests
3. Weights & Measures
4. Protection of Wild Animals and Birds
5. Administration of Justice
Added Article 51A 10 Fundamental Duties added for the citizens (Read below about the
amendments registered in Article 51A)
Parliamentary 1. Made President bound to the advice of the cabinet
Amendments 2. Allowed Centre to deploy central forces in State to deal with the
conflicting situations of law and order (Article 257A)
3. Gave special discriminatory powers to the speaker of Lok Sabha
and Prime Minister (Article 329A)
4. Directive Principles were given precedence over Fundamental
Rights and any law made to this effect by the Parliament was kept
beyond the scope of judicial review by the Court
Changes to the judicial Curtailed the judicial review power of the high courts
powers of HC
Added Articles 323A and Part XIV-A added entitled as Tribunals dealing with Administrative
323B XIV-A to the Tribunals and tribunals for other matters
Constitution.
Added 4 new DPSPs to list 1. To secure opportunities for the healthy development of children
(Article 39)
2. To promote equal justice and to provide free legal aid to the poor
(Article 39 A)
3. To take steps to secure the participation of workers in the
management of industries (Article 43 A)
4. To protect and improve the environment and to safeguard forests
and wildlife (Article 48 A)
How many duties are registered in 51st article of Indian Constitution by 42nd
Amendment?
Article 51A under Part IV-A of the Constitution (which consists of only one Article—51A) was added by the 42nd
amendment act. It introduced 10 Fundamental Duties:
S.No Fundamental Duties under Article 51A
1 to respect the Constitution, national flag and national anthem
2 To cherish and follow the noble ideals which inspired our national freedom struggle
3 to protect the sovereignty, unity and integrity of the country
4 To defend the country and render national service
5 to promote harmony and the spirit of common brotherhood amongst all the people
6 to preserve the rich heritage of our composite culture
7 To protect and improve the natural environment and have compassion for living creatures
8 To develop the scientific temper, humanism and spirit of enquiry
9 To safeguard public property
10 To strive towards excellence in all spheres of individual and collective activity
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Amendments in Indian Constitution:: First Amendment Act, 1951Documento16 pagineAmendments in Indian Constitution:: First Amendment Act, 1951zahawaahmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Constitution of India MCQ CollectionDocumento14 pagineConstitution of India MCQ CollectionultracetNessuna valutazione finora
- Minerva Mills Vs UOI - PerspectiveDocumento19 pagineMinerva Mills Vs UOI - Perspectivemd4mahesh100% (2)
- Indian Polity OnelinerDocumento5 pagineIndian Polity OnelinerKiran PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Doctrine of Colourable Legislation SeverabilityDocumento5 pagineDoctrine of Colourable Legislation SeverabilitysandeepNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Federal System ExplainedDocumento9 pagineIndian Federal System ExplainedAmrinder SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To The Constitution of IndiaDocumento40 pagineIntroduction To The Constitution of IndiaBhavya Goswami100% (1)
- Constitutional Law - I Question Bank: Detailed Questions: Unit IDocumento4 pagineConstitutional Law - I Question Bank: Detailed Questions: Unit Isravani ravinuthalaNessuna valutazione finora
- RTI NotesDocumento30 pagineRTI NotesRamanah VNessuna valutazione finora
- Legal GK PDF For CLAT 2020 PDFDocumento20 pagineLegal GK PDF For CLAT 2020 PDFAnil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Pith and Substance Doctrine ExplainedDocumento13 paginePith and Substance Doctrine ExplainedPrerak RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Constitution: Key Features and NatureDocumento7 pagineIndian Constitution: Key Features and NatureShobha RajputNessuna valutazione finora
- Important Articles in Indian Constitution for UPSC ExamsDocumento17 pagineImportant Articles in Indian Constitution for UPSC ExamsAditya SuriNessuna valutazione finora
- Case EvaluationDocumento11 pagineCase EvaluationKushagra AmritNessuna valutazione finora
- State of Punjab v. Tehal Singh (2002) 2 SCC 7Documento5 pagineState of Punjab v. Tehal Singh (2002) 2 SCC 7Kabir VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Union Executive: The President of IndiaDocumento16 pagineUnion Executive: The President of IndiaShiny ShinyNessuna valutazione finora
- RTI Act-2005 Important PointsDocumento63 pagineRTI Act-2005 Important PointsGurmeet SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Sankari Prasad Deo V Union of IndiaDocumento6 pagineSankari Prasad Deo V Union of IndiaSachin LohiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Article 368 - Constitution of IndiaDocumento27 pagineArticle 368 - Constitution of IndiaHarman SainiNessuna valutazione finora
- No. Amendments Enforced Since Objectives: Amendments To The Constitution of IndiaDocumento8 pagineNo. Amendments Enforced Since Objectives: Amendments To The Constitution of IndiaPrashant SuryawanshiNessuna valutazione finora
- R.C. Cooper v. Union of India (Bank Nationalisation Case) - Case SummaryDocumento13 pagineR.C. Cooper v. Union of India (Bank Nationalisation Case) - Case SummarymitaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Emergency Provisions Under The Indian ConstitutionDocumento11 pagineEmergency Provisions Under The Indian ConstitutionShardendu Pandey100% (1)
- Lokpal and Lokayukta Act ExplainedDocumento3 pagineLokpal and Lokayukta Act ExplainedShyam kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Right To Information Why?Documento24 pagineRight To Information Why?shakthivelNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Summary - Sheela BarseDocumento4 pagineCase Summary - Sheela BarsePragyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Right To Information RTI Act 2005: Dr. Monika Dubey Faculty, MBA Program Rajasthan Technical University, KotaDocumento31 pagineRight To Information RTI Act 2005: Dr. Monika Dubey Faculty, MBA Program Rajasthan Technical University, Kotamani100% (1)
- Privileged Class DevianceDocumento2 paginePrivileged Class Devianceएम. के. झा0% (1)
- Notes On Union ParliamentDocumento8 pagineNotes On Union ParliamentOnline SubsNessuna valutazione finora
- Nistar Patrak and Regulation of FishingDocumento39 pagineNistar Patrak and Regulation of FishingVinod JuariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Constitutional Law of India Course OverviewDocumento27 pagineConstitutional Law of India Course OverviewMahima SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Press Council Act establishes media oversightDocumento15 paginePress Council Act establishes media oversightVipul PartapNessuna valutazione finora
- Module - 2: Indian Constitutional Law The New ChallengesDocumento164 pagineModule - 2: Indian Constitutional Law The New ChallengesSameerLalakiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1703 4444 1 PBDocumento8 pagine1703 4444 1 PBvijaya choudhary100% (1)
- 65 Important Judgments of 2020Documento55 pagine65 Important Judgments of 2020Utkarrsh MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Constitution of India NotesDocumento197 pagineConstitution of India Noteselangovankc100% (1)
- Minerva Mills CaseDocumento17 pagineMinerva Mills Casemayankmarwahascribd50% (2)
- List of Important Articles in Indian Constitution Indian PolityDocumento6 pagineList of Important Articles in Indian Constitution Indian PolitySai KiranNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Constitution QuizDocumento67 pagineIndian Constitution QuizAshokkumar GanesanNessuna valutazione finora
- LLB 5 Semester Criminal Procedure CodeDocumento26 pagineLLB 5 Semester Criminal Procedure CodeRams Wizdom100% (2)
- Union of India Vs Alok Kumar 2010Documento7 pagineUnion of India Vs Alok Kumar 2010KHUSHI KATRENessuna valutazione finora
- Kerala Education BillDocumento11 pagineKerala Education BillAditya AnandNessuna valutazione finora
- Powers and Functions of President in IndiaDocumento6 paginePowers and Functions of President in IndiavarshiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Doctrine of Colourable LegislationDocumento15 pagineDoctrine of Colourable LegislationUditanshu MisraNessuna valutazione finora
- CPC NotesDocumento107 pagineCPC NotesAlpha Emperor100% (1)
- I R CoheloDocumento5 pagineI R CoheloHarsh PathakNessuna valutazione finora
- Article 16 of Constitution of IndiaDocumento36 pagineArticle 16 of Constitution of IndiaRvi MahayNessuna valutazione finora
- Mis Conduct CaseDocumento9 pagineMis Conduct CaseBandana Pha Go LimbooNessuna valutazione finora
- Settlement Act 1781Documento9 pagineSettlement Act 1781Dinesh PK100% (1)
- LB-203 - Law of Crimes - II Full Material Jan 2018Documento261 pagineLB-203 - Law of Crimes - II Full Material Jan 2018Arihant RoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Rights: Previous Year's MCQs of Tripura University and Answers with Short ExplanationsDa EverandHuman Rights: Previous Year's MCQs of Tripura University and Answers with Short ExplanationsNessuna valutazione finora
- 42nd Amendment Act 1976: Understanding India's Mini ConstitutionDocumento3 pagine42nd Amendment Act 1976: Understanding India's Mini ConstitutionJyotishna MahantaNessuna valutazione finora
- Significance of Preamble and Amendment 42nd-1Documento3 pagineSignificance of Preamble and Amendment 42nd-1Saiby KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- 42nd AMENDMENT OF THE CONSTITUTION OF INDIADocumento17 pagine42nd AMENDMENT OF THE CONSTITUTION OF INDIASonia SabuNessuna valutazione finora
- Judicial Activism On Environment in IndiaDocumento15 pagineJudicial Activism On Environment in IndiaGagandeepNessuna valutazione finora
- Raus CSP21T14S POLDocumento17 pagineRaus CSP21T14S POLprakharmishra902Nessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Chapter 3Documento49 pagine12 Chapter 3harsh0987636fbbjnNessuna valutazione finora
- Ammendments Made Under 42nd Constitutional Amendment ActDocumento2 pagineAmmendments Made Under 42nd Constitutional Amendment Actvivek bhagatNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamental Duties India ConstitutionDocumento4 pagineFundamental Duties India Constitutionsudip48Nessuna valutazione finora
- Directive Principles of State Policy Indian Polity NotesDocumento5 pagineDirective Principles of State Policy Indian Polity Notesjaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- UPSC DPSP NotesDocumento5 pagineUPSC DPSP Notesjaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- MCom Sem-IV (Reg) HPP Adv Ac & Audi 3-09-2020Documento1 paginaMCom Sem-IV (Reg) HPP Adv Ac & Audi 3-09-2020jaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- Notification of The Gujarat University No. Exam. 4-A' /89719/ of 2020Documento1 paginaNotification of The Gujarat University No. Exam. 4-A' /89719/ of 2020jaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- MDS Medical 14-07-2020Documento2 pagineMDS Medical 14-07-2020jaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- Time Table Online Exam - 2020 MLW PDFDocumento2 pagineTime Table Online Exam - 2020 MLW PDFjaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- Revised - BEd Sem-IV (New) 12-09-2020Documento1 paginaRevised - BEd Sem-IV (New) 12-09-2020jaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- Revised - BEd Sem-IV (New) 12-09-2020Documento1 paginaRevised - BEd Sem-IV (New) 12-09-2020jaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- Notification of The Gujarat UniversityDocumento1 paginaNotification of The Gujarat Universityjaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- MEd Sem-IV (New) 03-09-2020 PDFDocumento1 paginaMEd Sem-IV (New) 03-09-2020 PDFjaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- FOURTH BSC (Nursing) 01-09-2020Documento1 paginaFOURTH BSC (Nursing) 01-09-2020jaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
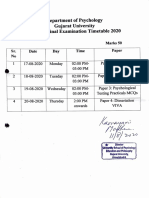
- Department of Psychology Gujarat University PGDCP Final Examination Timetable 2020Documento2 pagineDepartment of Psychology Gujarat University PGDCP Final Examination Timetable 2020jaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- P-G Dip Rehab. Psy 21-08-2020 PGDRPDocumento1 paginaP-G Dip Rehab. Psy 21-08-2020 PGDRPjaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- M.Sc. Semester IV Exam Schedule Sept 2020 Gujarat UniversityDocumento1 paginaM.Sc. Semester IV Exam Schedule Sept 2020 Gujarat Universityjaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- Revised - BEd Sem-IV (New) 12-09-2020Documento1 paginaRevised - BEd Sem-IV (New) 12-09-2020jaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- MSC Sem-IV (Inte,) 12-09-2020 PDFDocumento1 paginaMSC Sem-IV (Inte,) 12-09-2020 PDFjaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- MSC Sem-IV (Inte,) 12-09-2020 PDFDocumento1 paginaMSC Sem-IV (Inte,) 12-09-2020 PDFjaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- P-G Dip Rehab. Psy 21-08-2020 PGDRPDocumento1 paginaP-G Dip Rehab. Psy 21-08-2020 PGDRPjaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- Explain Fraudulent Transfer - Sec 53 With Decided Cases of Property ActDocumento1 paginaExplain Fraudulent Transfer - Sec 53 With Decided Cases of Property Actjaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- FOURTH BSC (Nursing) 01-09-2020Documento1 paginaFOURTH BSC (Nursing) 01-09-2020jaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Marketing ManagementDocumento37 pagineUnderstanding Marketing Managementpenusila69410% (1)
- Define Property and Transfer of Property and Explain in Detail The Kinds of Property Under The Transfer of Property ActDocumento3 pagineDefine Property and Transfer of Property and Explain in Detail The Kinds of Property Under The Transfer of Property Actjaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- LLB Sem-II 3-09-2020Documento1 paginaLLB Sem-II 3-09-2020jaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- LLBSEM2Documento53 pagineLLBSEM2jaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- LLB Sem-II 3-09-2020Documento1 paginaLLB Sem-II 3-09-2020jaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- Preamble of Indian Constitution Question For LLB ExamDocumento3 paginePreamble of Indian Constitution Question For LLB Examjaivik_ce7584Nessuna valutazione finora
- Airbus Aircraft AC A380 PDFDocumento327 pagineAirbus Aircraft AC A380 PDFLaura MoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Aircraft Structures Analysis and DesignDocumento71 pagineAircraft Structures Analysis and DesignMemyah AlNessuna valutazione finora
- Aircraft Basic ConstructionDocumento22 pagineAircraft Basic ConstructioncongngthanhNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Pollution Control Measures: Table 6-1 Seven Categories of PollutionDocumento20 pagineEnvironmental Pollution Control Measures: Table 6-1 Seven Categories of PollutionMurthy MandalikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5Documento51 pagineChapter 5dayasanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Air PollutionDocumento217 pagineAir Pollutionفردوس سليمانNessuna valutazione finora
- Succession Reviewer - Lectures (4th Year)Documento53 pagineSuccession Reviewer - Lectures (4th Year)Ramon Miguel Rodriguez100% (3)
- Condescension - Defendant's Strategy RevealedDocumento3 pagineCondescension - Defendant's Strategy Revealedhansley cookNessuna valutazione finora
- Ge 02 - PPT Reporting The Philippine ConstitutionDocumento22 pagineGe 02 - PPT Reporting The Philippine ConstitutionChenee PeñalogaNessuna valutazione finora
- Money Laundering With Companies and Related Corporate ServicesDocumento2 pagineMoney Laundering With Companies and Related Corporate ServicesAlexbepsNessuna valutazione finora
- Webfil LTD V Abhishek Kumar 395868Documento13 pagineWebfil LTD V Abhishek Kumar 395868Vishwajit SawantNessuna valutazione finora
- Rti Revoke Dod 17-6-2019Documento10 pagineRti Revoke Dod 17-6-2019ChakNessuna valutazione finora
- JK Pay SysDocumento3 pagineJK Pay SysMir Mudasir RehmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Intentional Torts and Torts Impacting BusinessDocumento10 pagineChapter 4 Intentional Torts and Torts Impacting BusinessMark Adiel Fodra PalaruanNessuna valutazione finora
- 5158-LL T HandbookDocumento32 pagine5158-LL T HandbookEswar StarkNessuna valutazione finora
- CLEA Moot, 2016 - Best Memo - RespondentDocumento43 pagineCLEA Moot, 2016 - Best Memo - RespondentAmol Mehta100% (2)
- Data Privacy Act of 2012 overviewDocumento7 pagineData Privacy Act of 2012 overviewGodfrey ReverenteNessuna valutazione finora
- ERISA Employee Benefits Paralegal in Dallas, TX ResumeDocumento2 pagineERISA Employee Benefits Paralegal in Dallas, TX ResumeRCTBLPONessuna valutazione finora
- Case 31 35Documento13 pagineCase 31 35HadjieLimNessuna valutazione finora
- PLUNDERDocumento10 paginePLUNDERManilyn Beronia PasciolesNessuna valutazione finora
- Fihfc Kyc Aml Policy March 2020Documento23 pagineFihfc Kyc Aml Policy March 2020HarpreetNessuna valutazione finora
- Separation of Powers - WikipediaDocumento15 pagineSeparation of Powers - WikipediaSacredly YoursNessuna valutazione finora
- Stat Con Cases (1-4)Documento47 pagineStat Con Cases (1-4)Maricar BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- 5112 Law 4 AdminstrativeLawDocumento318 pagine5112 Law 4 AdminstrativeLawrmbj94_scribdNessuna valutazione finora
- CCTV in Delhi Schools PetitionDocumento107 pagineCCTV in Delhi Schools Petitionanon_378445473Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Juris Lesson 1: The Code of Ethics For Filipino NursesDocumento20 pagineNursing Juris Lesson 1: The Code of Ethics For Filipino Nursesinno so qtNessuna valutazione finora
- Mediation A Resolution To Complaints Under The Consumer Protection Act, 2019Documento3 pagineMediation A Resolution To Complaints Under The Consumer Protection Act, 2019Archman comethNessuna valutazione finora
- Meaning of FreedomDocumento2 pagineMeaning of FreedomMelody B. MiguelNessuna valutazione finora
- Melendres # 675 - MCSO Proposed Training ScheduleDocumento29 pagineMelendres # 675 - MCSO Proposed Training ScheduleJack RyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Boracay CaseDocumento2 pagineBoracay CaseyenNessuna valutazione finora
- COMMISSION ON AUDIT CIRCULAR NO. 92-391 November 25, 1992 TODocumento2 pagineCOMMISSION ON AUDIT CIRCULAR NO. 92-391 November 25, 1992 TOpaoloNessuna valutazione finora
- R.A. No. 10022Documento47 pagineR.A. No. 10022Sonny MorilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Part I. Prepare A Complaint Affidavit. Part Ii. Prepare A Counter Affidavit. Part Iii. Multiple ChoiceDocumento2 paginePart I. Prepare A Complaint Affidavit. Part Ii. Prepare A Counter Affidavit. Part Iii. Multiple ChoiceDoan BalboaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1705FA Certification Regarding Sex Offender RegistryDocumento3 pagine1705FA Certification Regarding Sex Offender RegistryLaura FrekiNessuna valutazione finora
- Maguan Vs CA - Patents - EibborDocumento2 pagineMaguan Vs CA - Patents - EibborPevi Anne Bañaga FetalveroNessuna valutazione finora
- Filed: Patrick FisherDocumento3 pagineFiled: Patrick FisherScribd Government DocsNessuna valutazione finora