Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
EEA101L Lab Report - VALENTON-E08
Caricato da
Jan ValentonDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
EEA101L Lab Report - VALENTON-E08
Caricato da
Jan ValentonCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Experiment 3: Mesh Analysis
Interpretation of Results
The basis of the Mesh Analysis experiment was reflected from the theories and
equations. Mesh analysis is a technique used to find the current circulating in a loop/s or
mesh with in any closed path of a circuit. As a further matter, it depends on the voltage
source that is available. It uses the concepts from Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law and the Ohm’s
Law. In the application of the mesh analysis, there must be observations that must be
followed. One is the direction of the loops must be uniform either all loops in clockwise or
counterclockwise direction and determine if it is a supermesh--current source between
two meshes.
MESH CURRENTS VOLTAGES (V)
(mA)
I1 I2 V1 V2 V3 V4 V5
Simulated 1.22 20.45 0.264 0.473 4.26 6.72 4.01
Values
Calculated 1.2 20.45 0.260 0.465 4.02 6.72 4.01
Values
Actual 1.9 19.8 0.401 0.714 3.874 7.06 4.22
Values
Table 1. Data for Mesh Analysis
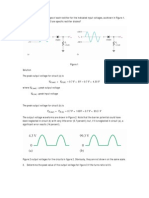
Figure 1. Simulation using Tina Pro
It was presented in Table 1 the gathered values from computations and simulation
using Tina Pro seen in figure 1. It was observed that the computed values from the
simulated values were likely the same to each other. However, gathered values from the
actual values has a slightly changes. Using Tina Pro, the measured values were
determined and is used as the values for the application of Mesh analysis that is reflected
in the calculated values.
The slightly changes were due to some of the following errors. The sources error
encountered in this experiment were instrumental drift, hysteresis and parallax error. The
instruments used may not have their readings accurate because the accuracy of the
multimeter may possibly drift over time that could cause different effects to the data. And
the next is hysteresis of the multimeter that shows the output voltage of the circuit
connected. And lastly parallax error wherein exact and correct reading in the ammeter
was not directly what you see with the naked eye.
Conclusion
The objectives of this experiment were first, to investigate the effects of mesh
analysis on multiple active linear source and to verify that the linear response at any point
in a mesh circuit is similar to Kirchhoff's Voltage Law. These objectives were observed
and determined all throughput the experiment. Mesh is a loop which does not contain
any loop within. In using the mesh analysis, planar circuits are best suited for this kind of
method. Moreover, voltage sources are the main sources that is utilized in a mesh
analysis method while current sources are converted into their equivalent voltage source.
Mesh analysis is the application of Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law [3] hence, it creates
similarities with KVL. In the process of mesh analysis, closed loops should be determined
these loops will be the representation of each mesh forming the mesh equations. Then,
KVL is applied through these equations, and Ohm’s law is practically used to find the
unknowns. Hence, it enables a simpler option of finding a solution into a certain
network. Furthermore, it is to take note that the direction of the flow present in the mesh
analysis are uniform. [2] For paths and electrical elements shared by the same loop the
actual current connotes to the difference between the two opposing mesh currents.
References
ARTICLES et al., "Mesh Current Method and Analysis | DC Network Analysis | Electronics
Textbook", Allaboutcircuits.com. Retrieved from:
https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/textbook/direct-current/chpt-10/mesh-current-method/.
[Accessed: 03- Sep- 2019].
Gupta, 2019. "Mesh Current Analysis or Method Explained with Examples", Circuitdigest.com.
Retrieved from https://circuitdigest.com/tutorial/mesh-current-analysis. [Accessed: 03- Sep-
2019].
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Experiment #2 Final - Report - CO PDFDocumento6 pagineExperiment #2 Final - Report - CO PDFEisen Jaylord100% (1)
- Review in Matrix and Determinants PDFDocumento89 pagineReview in Matrix and Determinants PDFJan ValentonNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics ProblemsDocumento6 pagineElectronics ProblemsOsama AlviNessuna valutazione finora
- Construction of Alternator - Electrical4uDocumento5 pagineConstruction of Alternator - Electrical4uM Kumar MarimuthuNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 6 Import Design and FloorplanDocumento54 pagineLecture 6 Import Design and FloorplanVamsi KrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mapua Institute of Technology: The Superposition Theorem and LinearityDocumento6 pagineMapua Institute of Technology: The Superposition Theorem and LinearityAngel MallariNessuna valutazione finora
- The Electronic Experimenter's Manual FindlayDocumento176 pagineThe Electronic Experimenter's Manual FindlayTEDY-RNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2 - Introduction To Ac CircuitDocumento49 pagineModule 2 - Introduction To Ac CircuitScrappy WellNessuna valutazione finora
- Acdc - DC Generator - Lecture Notes 3Documento27 pagineAcdc - DC Generator - Lecture Notes 3Cllyan ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculation of Electrical Induction Near Power LinesDocumento22 pagineCalculation of Electrical Induction Near Power LinesalpcruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Acckt Single PhaseDocumento6 pagineAcckt Single Phaseken peligrinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 8 Series and Parallel Circuits Physics LabDocumento7 pagineExperiment 8 Series and Parallel Circuits Physics Labvada_soNessuna valutazione finora
- Geas Complete Naka PDFDocumento389 pagineGeas Complete Naka PDFMarvin SinuesNessuna valutazione finora
- Mod. 1 Basic ElectricalDocumento21 pagineMod. 1 Basic Electricalderping lemon100% (1)
- Experiment 9 Analysis and Conclusion PDFDocumento5 pagineExperiment 9 Analysis and Conclusion PDFQuirino Arzadon IV50% (2)
- Mapúa Institute of Technology: Analysis of Resistive Network: Series-Parallel CircuitsDocumento10 pagineMapúa Institute of Technology: Analysis of Resistive Network: Series-Parallel CircuitsJohn FerreNessuna valutazione finora
- EXPERIMENT 3 4 and 5 - LINGAODocumento9 pagineEXPERIMENT 3 4 and 5 - LINGAOairaNessuna valutazione finora
- EE21L Experiment 8Documento12 pagineEE21L Experiment 8Jian TumaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Current Electricity DoneDocumento36 pagineCurrent Electricity DonewhyreadNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 10Documento18 pagineChapter 10farah haniNessuna valutazione finora
- Test 7esasDocumento13 pagineTest 7esasMichael GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Simulation of Power Supply Circuit (Paloma)Documento16 pagineSimulation of Power Supply Circuit (Paloma)Emmanuel PalomaNessuna valutazione finora
- Eelab - Exp2Documento6 pagineEelab - Exp2Corps LaroprocNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz No. 2.2: InstructionsDocumento20 pagineQuiz No. 2.2: Instructionsjaja caburnay100% (1)
- Thevenin's Theorem and Maximum Power TransferDocumento26 pagineThevenin's Theorem and Maximum Power TransferNathaniel PanganibanNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 4: Mesh Analysis, Nodal Analysis and Superposition TheoremDocumento23 pagineActivity 4: Mesh Analysis, Nodal Analysis and Superposition Theoremjian cool dudeNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 7 ArtDocumento8 pagineLab 7 ArtCharles SiringanNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp 04Documento13 pagineExp 04Zharlene SasotNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 3 (Nodal Analysis)Documento8 pagineLab 3 (Nodal Analysis)anon_938313424Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Circuits For Biological Engineering Laboratory: BE154L/A43/4Q1920Documento34 pagineElectronic Circuits For Biological Engineering Laboratory: BE154L/A43/4Q1920Kylle SaligumbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Solved Problems in Mechanics 2016Documento28 pagineSolved Problems in Mechanics 2016Debbie TonogNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 1 DiodeApplicationDocumento4 pagineLab 1 DiodeApplicationAlissandra ClaveriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Set Circuits 2Documento1 paginaProblem Set Circuits 2Vien Ysabel JasaNessuna valutazione finora
- RMW Rqs Rules RegulationsDocumento8 pagineRMW Rqs Rules RegulationsBoy EggieNessuna valutazione finora
- Principle of Communication QuestionsDocumento3 paginePrinciple of Communication Questionsceazar padillaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Series Inductance-Capacitance (L-C) CircuitDocumento7 pagineThe Series Inductance-Capacitance (L-C) Circuitzed coz100% (1)
- Mse SW2CDocumento11 pagineMse SW2CmarkkkkkNessuna valutazione finora
- This Study Resource Was: EE 201 Experiment (4) Section: 052Documento5 pagineThis Study Resource Was: EE 201 Experiment (4) Section: 052Johnjoseph VeraNessuna valutazione finora
- ThermodynamicsDocumento23 pagineThermodynamicsRennel MallariNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics Laboratory Simulation of DC Power Supply CircuitDocumento18 pagineElectronics Laboratory Simulation of DC Power Supply CircuitIvan Mark LucasNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Set No. 1 in Circuits 1Documento6 pagineProblem Set No. 1 in Circuits 1pinedajianneNessuna valutazione finora
- Review Problems in Ac FundamentalsDocumento2 pagineReview Problems in Ac FundamentalsHubert SemenianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Math and ESAT Questions - ECE Quiz BeeDocumento7 pagineMath and ESAT Questions - ECE Quiz BeeJeremy Lorenzo Teodoro VirataNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment Open and Closed Thermodynamic SystemDocumento1 paginaAssignment Open and Closed Thermodynamic SystemJenellie BahintingNessuna valutazione finora
- Impedance of A Series RLC CircuitDocumento12 pagineImpedance of A Series RLC Circuit2XWinNessuna valutazione finora
- EE21L Experiment 7Documento4 pagineEE21L Experiment 7Filbert SaavedraNessuna valutazione finora
- Signature Over Full Name Valcos, John Louis R. Student Number 2019165101 Program (EE or ECE) : ECE ECE Prelims Ece107LDocumento2 pagineSignature Over Full Name Valcos, John Louis R. Student Number 2019165101 Program (EE or ECE) : ECE ECE Prelims Ece107Lyuwee yiiiNessuna valutazione finora
- Parallel and Series Parallel ConfigurationsDocumento3 pagineParallel and Series Parallel Configurationssean ballocanagNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 3,4 and 5Documento10 pagineExperiment 3,4 and 5airaNessuna valutazione finora
- B. Electricity - Basic PrinciplesDocumento4 pagineB. Electricity - Basic PrinciplesXyxy LofrancoNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory No. 1 - Familiarization of Electrical Measuring Instruments DevicesDocumento11 pagineLaboratory No. 1 - Familiarization of Electrical Measuring Instruments DevicesJames Patrick Torres0% (1)
- Assignment 6 PDFDocumento2 pagineAssignment 6 PDFAhmed AttallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3Documento23 pagineModule 3streetranpuNessuna valutazione finora
- Power at AC given by P = VI cosθDocumento4 paginePower at AC given by P = VI cosθJohn Paul BaquiranNessuna valutazione finora
- Sinusoidal AC Circuit MeasurementsDocumento17 pagineSinusoidal AC Circuit MeasurementsComputer Guru100% (4)
- Circuit 2: Admittance: I. Applying Complex Numbers To Parallel Ac CircuitsDocumento22 pagineCircuit 2: Admittance: I. Applying Complex Numbers To Parallel Ac CircuitsShaina MabborangNessuna valutazione finora
- BJT Ac AnalysisDocumento18 pagineBJT Ac AnalysisjjeongdongieeNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Exercise 4 Ohms LawDocumento5 pagineLaboratory Exercise 4 Ohms Lawjaine ylevrebNessuna valutazione finora
- m1 Act1 Thermo David, RoieDocumento2 paginem1 Act1 Thermo David, Roieroie david100% (1)
- Activity 2Documento5 pagineActivity 2Pastrano Andria KrytieNessuna valutazione finora
- EEA101L Lab Report - VALENTON-E08Documento2 pagineEEA101L Lab Report - VALENTON-E08Jan ValentonNessuna valutazione finora
- E104-Mesh Analysis and Nodal AnalysisDocumento11 pagineE104-Mesh Analysis and Nodal AnalysisjoebreakerNessuna valutazione finora
- The Theorem of Mesh and Nodal - DC CircuiDocumento3 pagineThe Theorem of Mesh and Nodal - DC CircuiJerry Arthur MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- The Theorem of Mesh and Nodal - DC Circuit.: Abstract: The Experiment Is About To DemonstrateDocumento3 pagineThe Theorem of Mesh and Nodal - DC Circuit.: Abstract: The Experiment Is About To DemonstrateJerry Arthur MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Questions and ProblemsDocumento1 paginaQuestions and ProblemsJan ValentonNessuna valutazione finora
- EEA101L Lab Report - VALENTON-E08Documento2 pagineEEA101L Lab Report - VALENTON-E08Jan ValentonNessuna valutazione finora
- Env021 - A1 - ValentonDocumento1 paginaEnv021 - A1 - ValentonJan ValentonNessuna valutazione finora
- System Oflinear EquationsDocumento138 pagineSystem Oflinear EquationsJan ValentonNessuna valutazione finora
- Coursework 1.1 PDFDocumento4 pagineCoursework 1.1 PDFJan ValentonNessuna valutazione finora
- ENVO21 Quiz1Documento3 pagineENVO21 Quiz1Jan ValentonNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Squirrel Cage Three (3) Phase Squirrel Cage Induction MotorDocumento12 pagineDesign of Squirrel Cage Three (3) Phase Squirrel Cage Induction MotorMuhammadZaydArattKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultrasonic Range Finder Using 8051Documento6 pagineUltrasonic Range Finder Using 8051Jason Hendricks100% (3)
- Ee 2022Documento9 pagineEe 2022LATIGAR, JEFFERSON 0.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Oled Seminar ReportDocumento25 pagineOled Seminar ReportVarun Pathak100% (8)
- CONSOLLEDocumento3 pagineCONSOLLEPeter YliNessuna valutazione finora
- Bistar - TP6L72M & TP6L72M (H) - 9BB - 20200701 - enDocumento2 pagineBistar - TP6L72M & TP6L72M (H) - 9BB - 20200701 - enObumpa TeyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ola Al QasemDocumento212 pagineOla Al QasemMadalina-Alexandra PuscasuNessuna valutazione finora
- PRE-73 JR: Vintage Style Pre AmplifierDocumento2 paginePRE-73 JR: Vintage Style Pre AmplifiercarboydratiNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical and Vocational Education Faculty: Engineering Education Department (JPK)Documento27 pagineTechnical and Vocational Education Faculty: Engineering Education Department (JPK)Farahnasuhaa JamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Dte Micro ProjectDocumento15 pagineDte Micro ProjectDanish AliNessuna valutazione finora
- I 0000035Documento20 pagineI 0000035jose antonioNessuna valutazione finora
- Canon Ipf 8000 Service ManualDocumento200 pagineCanon Ipf 8000 Service ManualMasandani Meisam100% (3)
- DC MachinesDocumento52 pagineDC MachinesArun Kumar100% (1)
- Transductor GefranDocumento2 pagineTransductor GefranMarco Martinez SantiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Railway Track Security System Report PDFDocumento26 pagineRailway Track Security System Report PDFeshu50% (2)
- EmbracoDocumento21 pagineEmbracoSukhee TserNessuna valutazione finora
- MFL49414507 M227WD-PZJDocumento41 pagineMFL49414507 M227WD-PZJmaxdornNessuna valutazione finora
- André-Marie Ampère Was: EncyclopédieDocumento5 pagineAndré-Marie Ampère Was: EncyclopédieAngela Monato de MesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Spd-Saltek SLP-275 V - 3+1Documento2 pagineSpd-Saltek SLP-275 V - 3+1MJNessuna valutazione finora
- Subject: Distribution Transformer Failure (B-06) Report: To, Executive Engineer, M.S.E.D.Co - Ltd. Karjat (R) DivisionDocumento1 paginaSubject: Distribution Transformer Failure (B-06) Report: To, Executive Engineer, M.S.E.D.Co - Ltd. Karjat (R) Divisionadhalgaon sectionNessuna valutazione finora
- Signals and Systems: Assignment-1 Monsoon 2020Documento3 pagineSignals and Systems: Assignment-1 Monsoon 2020NishkarshNessuna valutazione finora
- Alpha T10 DatasheetDocumento2 pagineAlpha T10 DatasheetMahmood TulveNessuna valutazione finora
- 2011 KICKER Catalog Rev1 WebDocumento44 pagine2011 KICKER Catalog Rev1 Webautoperi2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- Clap Counter Using 8051 Microcontroller (AT89C51) : Description Circuit Diagram Code ComponentsDocumento4 pagineClap Counter Using 8051 Microcontroller (AT89C51) : Description Circuit Diagram Code ComponentsKarthik Dm60% (5)
- General Notes of Seam SealingDocumento6 pagineGeneral Notes of Seam Sealingalokedas1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Denso Spark Plug Catalog 2015-CompressedDocumento12 pagineDenso Spark Plug Catalog 2015-CompressedFarrukh SharfiNessuna valutazione finora