Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Length and Time-Notes
Caricato da
Balasbramani ThangavelDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Length and Time-Notes
Caricato da
Balasbramani ThangavelCopyright:
Formati disponibili
GAAFU DHAAL ATOLL EDUCATION CENTRE
Notes- Length and time
S tr ive to S ur pass
Grade : 9 Sub: Physics
Learning outcomes
Use and describe the use of rules and measuring cylinders to find a length or a volume
Use and describe the use of clocks and devices, both analogue and digital, for
measuring an interval of time
Obtain an average value for a small distance and for a short interval of time by
measuring multiples (including the period of a pendulum).
Understand that a micrometer screw gauge is used to measure very small distances.
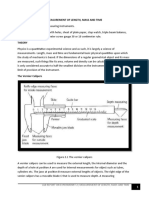
Measurement of length
Length measurements are made using a ruler, measuring tape, vernier calipers,
micrometer screw gauge…
Correct way to measure with ruler is to keep the eye right over the mark on the scale.
The line of sight should be perpendicular to the reading in order to avoid Parallax
error in measurement
Measuring instruments for length
Length to be Example Instrument to be used Accuracy
measured
Very short Diameter of a metal wire Micrometer screw 0.01mm
length gauge
Short Diameter of a measuring Vernier calipers 0.01cm
length cylinder
Medium Image distance of a lens Metre rule 0.1cm
length
Long length Length of physics laboratory Measuring tape 0.1cm
Grade 9/ Physics/ General physics/ Length and Time 1
AREA
Area of a rectangle = length x breadth
1
Area of a triangle = x base x height
2
Area of a circle = 𝑟2
SI unit of area is square-metre (m2)
1 𝒄𝒎𝟐 = 10-4 m2
VOLUME
It is the amount of space occupied by an object.
SI unit of volume is cubic-metre (m3)
1cm3 = 10-6m3
Volume of a regularly shaped solid
Volume of rectangular block = length x breadth x height
4
Volume of a sphere = 3
x (radius)3
Volume of a cylinder = x (radius)2 x height
Volume of a liquid
Volume of liquid is expressed in litres (l)
1 litre (l) = 1000ml
1millilitre (ml) = 1cm3
1 litre (l) = 1000cm3
Pour the liquid into the measuring cylinder and the level on the scale gives the volume
The measuring cylinder should be kept upright on a horizontal smooth surface.
Eye level should be perpendicular to the lower meniscus so as to avoid Parallax error
Volume of an irregularly shaped solid
Pour the liquid into the measuring cylinder. Note the initial volume(V1)
corresponding to the lower meniscus.
Immerse the solid into the measuring cylinder.
The liquid level rises.
Note the new scale reading as the final reading or the final volume(V2).
Grade 9/ Physics/ General physics/ Length and Time 2
Volume of the irregularly shaped solid = V2 – V1
Mass
It is the measure of the amount of matter present in an object.
SI unit of mass is kilogram(kg)
1 tonne(t) = 1000kilogram(kg)
1 kilogram(kg) = 1000gram(g)
1 gram(g) = 1000milligram(mg)
1milligram(mg) = 10-6kg
Mass of an object is found using various kinds of Balance.
1. Beam balance: An unknown mass is placed in one pan and balanced
against the unknown masses in the other pan. The beam balances when
the gravitational pull on the material in each pan is the same. Each pan
then contains the same mass of the material
Beam balance
Grade 9/ Physics/ General physics/ Length and Time 3
2. Top-pan balance: A direct reading is obtained from the position on the scale of a
pointer joined to the lever system or the
reading can be directly read in a top-pan balance.
Top-pan balance
Time
SI unit is second (s)
Stopwatches and stopclocks are used to measure time.
Time Period of oscillation of simple pendulum
- Note the time for 20 oscillations of simple pendulum
- Repeat for 3 times and take the average time ‘tavg’
𝑡𝑎𝑣𝑔
- Time period , T = 20
Questions:
1. A student measures the time taken for 20 swings of a pendulum. He finds that the
time taken in 55 seconds.
a) What time does the pendulum take for one wing?
b) How could the student have found the time for one swing more accurately.
2. A student measures the diameter of a sphere three times. His values are: 3.46
cm, 3.49 cm and 3.47 cm.
Find the average diameter.
Grade 9/ Physics/ General physics/ Length and Time 4
Micrometer screw gauge
Reading = MSR + (HSR x LC )
Where,
MSR = Main scale reading
HSR = Head scale reading
LC = 0.01 mm
Questions
1. The diameter of a copper wire is thought to be approximately 0.3mm.
Which instrument should be used to obtain a more accurate measurement of the
diameter of the wire?
A measuring tape B metre rule
C micrometer D ruler 25
2. Which measurement can be made using a micrometer screw gauge?
A the air pressure of a tyre B the diameter of a wire
C the turning effect of a spanner D the wavelength of microwaves
Grade 9/ Physics/ General physics/ Length and Time 5
Vernier calipers
Reading = MSR + (VSR x LC )
Where,
MSR = Main scale reading
VSR = Vernier scale reading
LC = 0.01 cm or 0.1mm
MSR is the value before the vernier scale zero. VSR is the value in line with the main
scale. LC is the smallest value that can be read from an instrument.
In vernier caliper, least count is 0.01cm if it is measured in cm. Least count is 0.1mm if
the value is measured in mm.
Example-1
Reading = MSR + (VSR x LC)
= 2.1 + (5X0.01)
= 2.1 + 0.05
= 2.15cm
Example-2
Grade 9/ Physics/ General physics/ Length and Time 6
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Physics: Chapter 1 - MeasurementsDocumento19 paginePhysics: Chapter 1 - Measurementsanwar9602020Nessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankDa EverandMeasurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To PhysicsDocumento135 pagineIntroduction To PhysicsDennis CheruiyotNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 MeasurementsDocumento13 pagine03 MeasurementsDOPPLER LIBRARY SERIES (DOLIS) EDUCATION SERVICES50% (2)
- Physics Core 2023Documento102 paginePhysics Core 2023Zaps ClapsNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - MeasurementsDocumento40 pagine1 - Measurementsmkedawat09Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics - 1 Iit MaterialDocumento1.438 paginePhysics - 1 Iit MaterialSHK sirasapalliNessuna valutazione finora
- The Study of Matter, Energy, and The Interactions Between ThemDocumento50 pagineThe Study of Matter, Energy, and The Interactions Between ThemAllyna BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Making Measurements CMDocumento37 pagineMaking Measurements CMelezabethNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 3 Physics-Measurement-1 PDFDocumento19 pagineForm 3 Physics-Measurement-1 PDFMichael NdambaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 1 MeasurementDocumento24 pagineLab 1 MeasurementRichard SerquinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Chap1Documento19 paginePhysics Chap1dela2Nessuna valutazione finora
- EXPERIMENT-2: Measurements of Mass, Volume and Density: ObjectivesDocumento8 pagineEXPERIMENT-2: Measurements of Mass, Volume and Density: ObjectivesElam KibetNessuna valutazione finora
- AP - Lab 01 - Measurement Using Vernier CalliperDocumento4 pagineAP - Lab 01 - Measurement Using Vernier Callipersaliha50% (4)
- Chapter 1 Notes (Physics)Documento65 pagineChapter 1 Notes (Physics)ronniego100% (3)
- Unit 1Documento94 pagineUnit 1uibikunNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 9th NBF 2022 (CH 1 2 3 4 5 6 7) Conceptual QuestionsDocumento65 pagineClass 9th NBF 2022 (CH 1 2 3 4 5 6 7) Conceptual QuestionsQasim Humdani100% (3)
- IGCSE Physics Paper 6Documento53 pagineIGCSE Physics Paper 6nexusdrops1Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 PhysicalQuantities NDocumento9 pagine1 PhysicalQuantities NImran ZafarNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 1 - Measurement of Length, Mass and TimeDocumento11 pagineExperiment 1 - Measurement of Length, Mass and TimeKAPEMBWA MAPALO100% (1)
- Measurement and UnitsDocumento10 pagineMeasurement and UnitsHanan MdSomNessuna valutazione finora
- SFL3011 Physic Laboratory Report Experiment 1Documento13 pagineSFL3011 Physic Laboratory Report Experiment 1Liyana Hamdan85% (13)
- Science Form1 Chapter 1Documento56 pagineScience Form1 Chapter 1Halizah Ramthan88% (16)
- Complete Olevel Physics Notes by Iftikhar PDFDocumento50 pagineComplete Olevel Physics Notes by Iftikhar PDFSufyaansufi100% (1)
- MeasurementsDocumento17 pagineMeasurementsadieshmukh150209Nessuna valutazione finora
- Measurements: General PhysicsDocumento19 pagineMeasurements: General Physicsmaram asharfNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy. Book - IgcseDocumento171 paginePhy. Book - IgcseRayyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 10 Physics Week 2 Lesson 1Documento5 pagineGrade 10 Physics Week 2 Lesson 1Daniel DowdingNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Physics MeasurementsDocumento15 pagine01 Physics MeasurementsAli SalamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Report Physics (Exp 1) EDITEDDocumento24 pagineLab Report Physics (Exp 1) EDITEDirdinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics O LevelDocumento30 paginePhysics O LevelPower of OneNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 9th NBF 2022 (CH 1 2 3 4 5 6 7) Conceptual QuestionsDocumento67 pagineClass 9th NBF 2022 (CH 1 2 3 4 5 6 7) Conceptual QuestionsGhalib khattakNessuna valutazione finora
- Reference Notes For Igcse Physics PDFDocumento18 pagineReference Notes For Igcse Physics PDFpappadakunduNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics: Is The Science That Idea of Idea of Energy Can Be StudiedDocumento6 paginePhysics: Is The Science That Idea of Idea of Energy Can Be StudiedSadia Rahman, MonaliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Complete Olevel PhysicsDocumento105 pagineComplete Olevel PhysicsSarim AbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap No.1Documento3 pagineChap No.1Abu JamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 11 Physics Revision Notes Units and MeasurementDocumento17 pagineClass 11 Physics Revision Notes Units and MeasurementVedanth.KNessuna valutazione finora
- Sec 3E Science (Physics) : Physical Quantities, Units and MeasurementDocumento53 pagineSec 3E Science (Physics) : Physical Quantities, Units and MeasurementKoh Seok Hwee100% (1)
- Measurement and Units WorksheetDocumento3 pagineMeasurement and Units WorksheetYoNessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement Physics NotesDocumento6 pagineMeasurement Physics NotesAhmed OmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Session E112Documento96 pagineSession E112maryam.essam.ketNessuna valutazione finora
- Tushars NoteDocumento25 pagineTushars Notevbg6v42dypNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 2 Measuring Instruments and Density: Name/s: 1) 2) 3) 4)Documento15 pagineExperiment 2 Measuring Instruments and Density: Name/s: 1) 2) 3) 4)Kylie EralinoNessuna valutazione finora
- CSEC Physics Manual - 074634Documento114 pagineCSEC Physics Manual - 074634Reyugi AisukaNessuna valutazione finora
- Laporan Praktikum Fisika Geografi Alat Ukur DasarDocumento16 pagineLaporan Praktikum Fisika Geografi Alat Ukur DasarAnonymous grrnqvrXNNessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement and Experimentation Class 9 IcseDocumento28 pagineMeasurement and Experimentation Class 9 Icseabhishek_sinha100% (2)
- Quantities, Units, and MeasurementDocumento8 pagineQuantities, Units, and MeasurementTriacute80% (5)
- Topic: Measurement:, andDocumento25 pagineTopic: Measurement:, andCarl BlakeNessuna valutazione finora
- Combined Science - S3NADocumento240 pagineCombined Science - S3NAMuhammad Dzul Akrom Nasaruddin (Manjusriss)Nessuna valutazione finora
- PHY110 CHAPTER 1-Week 1Documento49 paginePHY110 CHAPTER 1-Week 1SOFIAH NAJWA BINTI SHAMSUDDINNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Masurment and UncertainlyDocumento29 pagineBasic Masurment and UncertainlyHelny LydarisboNessuna valutazione finora
- Adventures in Practical Physics: Physics in Our Lives: Jasdeep Kaur, Avinash KaurDocumento5 pagineAdventures in Practical Physics: Physics in Our Lives: Jasdeep Kaur, Avinash KaurRifkaa LatiffahNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Form1 Chapter 1Documento41 pagineScience Form1 Chapter 1Che Norasiykin89% (9)
- 1.1 Understanding That Science Is Part of Everyday LifeDocumento57 pagine1.1 Understanding That Science Is Part of Everyday LifeGunalan SubramaniamNessuna valutazione finora
- S1 S.1 Phys From JicoDocumento106 pagineS1 S.1 Phys From JicoIsaiah KruzNessuna valutazione finora
- NOTES - XI - Units and Measurement - Docx-1Documento8 pagineNOTES - XI - Units and Measurement - Docx-1manomani007123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Laporan Amali FizikDocumento7 pagineLaporan Amali FizikTeo Hui pingNessuna valutazione finora
- Report of PracticumDocumento27 pagineReport of PracticumIrdayani HamidNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 - Physical QuantitiesDocumento24 pagineChapter 1 - Physical QuantitiesSafwan MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- Building Hadrons from Quarks: ψ = ψ (space) ψ (spin) ψ (flavor) ψ (color)Documento36 pagineBuilding Hadrons from Quarks: ψ = ψ (space) ψ (spin) ψ (flavor) ψ (color)Balasbramani ThangavelNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Energy Physics by SachaDocumento100 pagineIntroduction To Energy Physics by SachaBalasbramani ThangavelNessuna valutazione finora
- The Maury Project: Shallow-Water Ocean WavesDocumento19 pagineThe Maury Project: Shallow-Water Ocean WavesBalasbramani ThangavelNessuna valutazione finora
- Provisional: June 2021 Examination TimetableDocumento22 pagineProvisional: June 2021 Examination TimetableBalasbramani ThangavelNessuna valutazione finora
- Hasan Sayginel: Edexcel IAL Physics Unit 2Documento34 pagineHasan Sayginel: Edexcel IAL Physics Unit 2Balasbramani ThangavelNessuna valutazione finora
- Melissinos Photoelectric Effect 1966Documento5 pagineMelissinos Photoelectric Effect 1966Balasbramani ThangavelNessuna valutazione finora
- Education Policy PDFDocumento5 pagineEducation Policy PDFBalasbramani ThangavelNessuna valutazione finora
- Veljko Milkovic - Two-Stage Mechanical Oscillator - 9 - 1 Overunity and Antigravity..Documento26 pagineVeljko Milkovic - Two-Stage Mechanical Oscillator - 9 - 1 Overunity and Antigravity..Erwin BlancoNessuna valutazione finora
- PH1O2 Experiment 2Documento12 paginePH1O2 Experiment 2wallace kitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan in EnergyDocumento23 pagineLesson Plan in EnergyJesse100% (1)
- Test Bank For Physics 5th Edition Alan GiambattistaDocumento32 pagineTest Bank For Physics 5th Edition Alan Giambattistaanthonyelliscnjswramob100% (23)
- 2013 Iepc PolkDocumento24 pagine2013 Iepc PolkmgNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Harmonic Motion: Physics 1425 Lecture 28Documento15 pagineSimple Harmonic Motion: Physics 1425 Lecture 28Anthony Wijaya, S.Pd., M.Si.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Accleration Due To Gravity by Bar PendulumDocumento3 pagineAccleration Due To Gravity by Bar PendulumSumit BagdeNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper 6 Tips (Physics IGCSE) Centre of Mass Experiment (With The LaminaDocumento6 paginePaper 6 Tips (Physics IGCSE) Centre of Mass Experiment (With The LaminavexinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7Documento81 pagineChapter 7nida batoolNessuna valutazione finora
- A Level Practical PDFDocumento3 pagineA Level Practical PDFRafsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Aerodynamics and Flight Control Design For Hovering Micro Air VehiclesDocumento3 pagineAerodynamics and Flight Control Design For Hovering Micro Air VehiclesRitesh SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- DrivePac eDocumento363 pagineDrivePac eCharoon SuriyawichitwongNessuna valutazione finora
- Leybold Didactic GMBH Instruction Sheet 401 20 - 24: Physics Chemistry Biology TechnicsDocumento4 pagineLeybold Didactic GMBH Instruction Sheet 401 20 - 24: Physics Chemistry Biology Technicstmya06Nessuna valutazione finora
- AP Physics 1 FinaleDocumento188 pagineAP Physics 1 FinaleEvan ThompsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Nota Padat Fizik F5 WavesDocumento28 pagineNota Padat Fizik F5 Wavesslokkro98% (102)
- Large Amplitude PendulumDocumento12 pagineLarge Amplitude PendulumagnesNessuna valutazione finora
- The Proportional Levelling System: General DescriptionDocumento7 pagineThe Proportional Levelling System: General DescriptionAlanNessuna valutazione finora
- Time and Frequency MeasurementDocumento143 pagineTime and Frequency MeasurementJBSfan100% (2)
- Philip R. Kesten and David L. Tauck - Instructor's Solution Manuals To University Physics For The Physical and Life Sciences (2012, W.H.Freeman) PDFDocumento1.510 paginePhilip R. Kesten and David L. Tauck - Instructor's Solution Manuals To University Physics For The Physical and Life Sciences (2012, W.H.Freeman) PDFhiromy100% (1)
- Tugas 1Documento31 pagineTugas 1arock15Nessuna valutazione finora
- 588 801 STM PhysicsDocumento30 pagine588 801 STM PhysicsthaisubNessuna valutazione finora
- Coopertitchener Trifilar1Documento30 pagineCoopertitchener Trifilar1api-24490620450% (2)
- 1st Year Physics According To COVID-19 Syllabus PDFDocumento334 pagine1st Year Physics According To COVID-19 Syllabus PDFMohsin HayatNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No:08 Compound Pendulum: Kinematics and Dynamics Lab Manual (ME406ES)Documento3 pagineExperiment No:08 Compound Pendulum: Kinematics and Dynamics Lab Manual (ME406ES)madhavNessuna valutazione finora
- Pendulum Lab - Basic VersionDocumento6 paginePendulum Lab - Basic VersionTeachLABScINessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematical ModellingDocumento12 pagineMathematical ModellingAnirvan ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Harmonic Motion Worksheet 3: X (T) (7.8 CM) Cos (T)Documento3 pagineSimple Harmonic Motion Worksheet 3: X (T) (7.8 CM) Cos (T)NadeenMohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/31Documento12 pagineCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/31sangdeepNessuna valutazione finora
- VERpg 33Documento102 pagineVERpg 33Miguel Áttilla GouveiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Torque PendulumDocumento5 pagineTorque PendulumAhmed AlaminNessuna valutazione finora