Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
EE 171 Take Home Chapter Test 4and Final Exam and Removal Exam
Caricato da
Aisha Zaleha LatipDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
EE 171 Take Home Chapter Test 4and Final Exam and Removal Exam
Caricato da
Aisha Zaleha LatipCopyright:
Formati disponibili
EE 171 Take Home Chapter Test 4 (d) reverse-biased
Field Effect Transistors 10. A certain JFET datasheet gives VGS(off ) = -4 V.The pinch-off
voltage, VP,
Instructions: Please use the answer sheet to answer. E- (a) cannot be determined
mail a photo or a scanned version of your answer sheet (b) is -4 V
to the given e-mail below.
(c) depends on VGS
(d) is +4 V
Shade the letter of the best answer.
11. The JFET in Question 10
(a) is an n channel
1. The JFET is
(b) is a p channel
(a) a unipolar device
(c) can be either
(b) a voltage-controlled device
12. For a certain JFET, IGSS =10 nA at VGS =10 V. The input
(c) a current-controlled device
resistance is
(d) answers (a) and (c)
(a) 100 M Ω (b) 1MΩ
(e) answers (a) and (b) (c) 1000MΩ (d) 1000M
2. The channel of a JFET is between the 13. For a certain p-channel JFET, VGS(off ) = 8 V. The value of
(a) gate and drain VGS for an approximate midpoint bias is
(b) drain and source (a) 4 V (b) 0 V
(c) gate and source (c) 1.25 V (d) 2.34 V
(d) input and output 14. In a self-biased JFET, the gate is at
3. A JFET always operates with (a) a positive voltage
(a) the gate-to-source pn junction reverse-biased (b) 0 V
(b) the gate-to-source pn junction forward-biased (c) a negative voltage
(c) the drain connected to ground (d) ground
(d) the gate connected to the source 15. The drain-to-source resistance in the ohmic region
4. For VGS = 0 V, the drain current becomes constant when depends on
VDS exceeds (a) VGS
(b) the Q-point values
(a) cutoff
(b) VDD (c) the slope of the curve at the Q-point
(c) VP (d) all of these
(d) 0 V 16. To be used as a variable resistor, a JFET must be
5. The constant-current region of a FET lies between (a) an n-channel device
(a) cutoff and saturation (b) a p-channel device
(b) cutoff and pinch-off (c) biased in the ohmic region
(c) 0 and IDSS (d) biased in saturation
(d) pinch-off and breakdown 17. When a JFET is biased at the origin, the ac channel
6. IDSS is resistance is determined by
(a) the drain current with the source shorted (a) the Q-point values (b) VGS
(b) the drain current at cutoff (c) the transconductance (d) answers (b) and (c)
(c) the maximum possible drain current 18. A MOSFET differs from a JFET mainly because
(d) the midpoint drain current (a) of the power rating
SELF-TEST ◆ 439
(b) the MOSFET has two gates
7. Drain current in the constant-current region increases
(c) the JFET has a pn junction
when
(d) MOSFETs do not have a physical channel
(a) the gate-to-source bias voltage decreases
19. A D-MOSFET operates in
(b) the gate-to-source bias voltage increases
(a) the depletion mode only
(c) the drain-to-source voltage increases
(b) the enhancement mode only
(d) the drain-to-source voltage decreases
(c) the ohmic region only
8. In a certain FET circuit, VGS = 0 V, VDD = 15 V, IDSS = 15 mA,
(d) both the depletion and enhancement modes
and RD = 470 Ω. If RD is decreased to
20. An n-channel D-MOSFET with a positive VGS is operating
(a) 19.5 mA (b) 10.5 mA
in
(c) 15 mA (d) 1 mA
(a) the depletion mode
9. At cutoff, the JFET channel is
(b) the enhancement mode
(a) at its widest point
(c) cutoff
(b) completely closed by the depletion region
(d) saturation
(c) extremely narrow
e-mail at: a.zaleha.latip@msumain.edu.ph
21. A certain p-channel E-MOSFET has a VGS(th) = -2 V. If VGS = 33. A certain common-drain (CD) amplifier with RS = 1.0 kΩ
0 V, the drain current is has a transconductance of 6000 mS. The voltage gain is
(a) 0 A (b) ID(on) (a) 1 (b) 0.86 (c) 0.98 (d) 6
(c) maximum (d) IDSS 34. The datasheet for the transistor used in a CD amplifier
22. In an E-MOSFET, there is no drain current until VGS specifies IGSS = 5 nA at VGS = 10 V. If the resistor from gate
(a) reaches VGS(th) (b) is positive to ground, RG, is 50 MΩ, the total input resistance is
(c) is negative (d) equals 0 V approximately
23. All MOS devices are subject to damage from (a) 50 MΩ (b) ) 200 MΩ (c) ) 40 MΩ (d) ) 20.5 MΩ
(a) excessive heat 35. The common-gate (CG) amplifier differs from both the CS
(b) electrostatic discharge and CD configurations in that it has a
(c) excessive voltage (a) much higher voltage gain (b) much lower voltage gain
(d) all of these (c) much higher input resistance (d) much lower input
24. A certain D-MOSFET is biased at VGS = 0 V. Its datasheet resistance
specifies IDSS = 20 mA and VGS(off) = -5 V. The value of the 36. If you are looking for both good voltage gain and high
drain current input resistance, you must use a
(a) is 0 A (a) CS amplifier (b) CD amplifier (c) CG amplifier
(b) cannot be determined 37. A cascode amplifier consists of
(c) is 20 mA (a) a CD and a CS amplifier (b) a CS and a CG amplifier
25. In a common-source amplifier, the output voltage is (c) a CG and a CD amplifier (d) two CG amplifiers
(a) 180°out of phase with the input 38. The class D amplifier is similar to
(b) in phase with the input (a) class C (b) class B (c) class A (d) none of these
(c) taken at the source 39. The class D amplifier uses
(d) taken at the drain (a) frequency modulation (b) amplitude modulation
(e ) answers (a) and (d) (c) pulse-width modulation (d) duty cycle modulation
26. In a certain common-source (CS) amplifier, Vds = 3.2 V rms 40. E-MOSFETs are generally used for switching applications
and Vgs = 280 mV rms. The voltage gain is because of their
(a) 1 (b) 11.4 (c) 8.75 (d) 3.2 (a) threshold characteristic (b) high input resistance
27. In a certain CS amplifier, RD = 1.0 kΩ, RS = 560 Ω, VDD = 10 (c) linearity (d) high gain
V, and gm = 4500 μS. If the source resistor is completely 41. A sampling circuit must sample a signal at a minimum of
bypassed, the voltage gain is (a) one time per cycle (b) the signal frequency
(a) 450 (b) 45 (c) 4.5 (d) 2.52 (c) twice the signal frequency (d) alternate cycles
28. Ideally, the equivalent circuit of a FET contains 42. The value of resistance emulated by a switched-capacitor
(a) a current source in series with a resistance circuit is a function of
(b) a resistance between drain and source terminals (a) voltage and capacitance (b) frequency and capacitance
(c) a current source between gate and source terminals (c) gain and transconductance (d) frequency and
(d) a current source between drain and source terminals transconductance
29. The value of the current source in Question 28 is 43. A basic CMOS circuit uses a combination of
dependent on the (a) n-channel MOSFETs (b) p-channel MOSFETs
(a) transconductance and gate-to-source voltage (c) pnp and npn BJTs (d) an n-channel and a p-channel
(b) dc supply voltage MOSFET
(c) external drain resistance 44. CMOS is commonly used in
(d) answers (b) and (c) (a) digital circuits (b) linear circuits (c) RF circuits (d) power
30. A certain common-source amplifier has a voltage gain of circuits
10. If the source bypass capacitor is removed, 45. If there is an internal open between the drain and source
(a) the voltage gain will increase in a CS amplifier, the drain voltage is
(b) the transconductance will increase equal to
(c) the voltage gain will decrease (a) 0 V (b) VDD (c) VGS (d) VGD
(d) the Q-point will shift
31. A CS amplifier has a load resistance of 10 kΩ and RD =
820 Ω. If gm = 5 mS and Vin = 500 mV, the output signal
voltage is
(a) 1.89 V (b) 2.05 V (c) 25 V (d) 0.5 V
32. If the load resistance in Question 31 is removed, the
output voltage will
(a) stay the same (b) decrease (c) increase (d) be zero
e-mail at: a.zaleha.latip@msumain.edu.ph
EE 171 Take Home Final Examination 4. Determine AVNL, Zi, Zo, AVL, and AVS. Sketch the two-port
Field Effect Transistors model with the parameters determined in place (such as
gmVgs).
Instructions: Show a step-by-step solution with a
supporting statement for each step. Use the textbook for
references. If you choose to use another book, just state
the theorem, definition, or any other to support your
solution. E-mail a photo or a scanned version of your
answer sheets to the given e-mail below.
Note: If there are any similarities with your solution and
a classmate, both of your exams will be deemed invalid
and thus an automatic grade of 5.0.
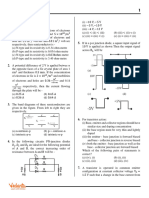
1.Determine VG, IDQ, VGSQ, VD, VS, and VDSQ.
5. Determine Vo if Vi = 4mV.
2. For the self-bias configuration, determine IDQ, VGSQ, VD,
and VDS.
6. Determine the output voltage of the network if Vi =
0.8mV and rd = 40kΩ.
3. For the voltage-divider circuit, find IDQ, VGSQ, VD, and VS.
e-mail at: a.zaleha.latip@msumain.edu.ph
EE 171 Take Home Removal Examination
Prelim and Midterm
Instructions: Show a step-by-step solution with a
supporting statement for each step. Use the textbook for
references. If you choose to use another book, just state
the theorem, definition, or any other to support your
solution. E-mail a photo or a scanned version of your
Midterm:
answer sheets to the given e-mail below.
For the network given below :
Your score will be multiplied by 60% of the total score
a. Determine AvNL, Z i , and Z o .
which will be your removal score for either your Prelim
b. Sketch the two-port model with the values determined
or Midterm Exam.
in part (a).
c. Determine AvL and Avs.
Prelim:
d. Change R s to 1 kΩ and determine AvL and Avs. What
1. Sketch Vo for the network and determine the dc
is the effect of increasing levels of R s
voltage available.
on the voltage gains?
e. Change R s to 1 k_ and determine AvNL, Z i , and Z o .
What is the effect of increasing levels of R s on the
parameters?
f. Change R L to 5.6 k_ and determine AvL and Avs. What
is the effect of increasing levels of RL on the voltage
gains? Maintain R s at its original level of 0.6 k_.
g. Determine Ai =Io/Ii with RL = 2.7 kΩ and Rs = 0.6 kΩ.
2. Sketch Vo for the network.
3. Design a clamper that performs the function.
4. a. Design the network of the given circuit to maintain
V L at 12 V for a load variation ( I L ) from 0 mA to 200
mA. That is, determine R S and V Z .
b. Determine P Z max for the Zener diode of part (a).
e-mail at: a.zaleha.latip@msumain.edu.ph
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- BL Thereja QA FULLDocumento15 pagineBL Thereja QA FULLAishaNessuna valutazione finora
- Field-Effect Transistors (FETs) - Print - QuizizzDocumento6 pagineField-Effect Transistors (FETs) - Print - QuizizzRASHMI RANI SAMANTARAYNessuna valutazione finora
- Field Effect TransistorsDocumento2 pagineField Effect TransistorsJonabelle MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- MOSFET QuestionsDocumento23 pagineMOSFET QuestionsSure Avinash100% (2)
- BJT ProblemsDocumento11 pagineBJT ProblemsRajesh PerlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Term Exam - BK192 / 2019-2020: CE C (Sat)Documento5 pagineFinal Term Exam - BK192 / 2019-2020: CE C (Sat)Hào NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- B.V.Raju Institute of Technology: IV B.Tech Comprehensive Viva Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocumento3 pagineB.V.Raju Institute of Technology: IV B.Tech Comprehensive Viva Electronic Devices and Circuitsniladridey12345Nessuna valutazione finora
- Notes PDFDocumento24 pagineNotes PDFkalyanNessuna valutazione finora
- ELET1500 FET Tutorial: NP P - NP PDocumento3 pagineELET1500 FET Tutorial: NP P - NP PCadane CodnerNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electrical and Electronics 225 MCQ: Answer Have Given by Bold OptionDocumento17 pagineBasic Electrical and Electronics 225 MCQ: Answer Have Given by Bold OptionaishwaryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Electronics Sample PaperDocumento5 pagineAnalog Electronics Sample PaperVarsha WaingankarNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory 11th Edition Boylestad Test Bank 1Documento13 pagineElectronic Devices and Circuit Theory 11th Edition Boylestad Test Bank 1julia100% (34)
- Analog Fina - Docx - 1480304487181Documento31 pagineAnalog Fina - Docx - 1480304487181manutalakalmathNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch-8 Analog MCQ and MSQDocumento43 pagineCh-8 Analog MCQ and MSQRintu MukherjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- SEMICONDUCTORSDocumento7 pagineSEMICONDUCTORSBHOOMI BNessuna valutazione finora
- Electroncs Devices and Circuits PDFDocumento36 pagineElectroncs Devices and Circuits PDFpriya dharshiniNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ6 AC MOSFET Amplifier PDFDocumento3 pagineMCQ6 AC MOSFET Amplifier PDFaamir shahzadNessuna valutazione finora
- Certcdavao: Instruction: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingDocumento4 pagineCertcdavao: Instruction: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingJj JumawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuit Debugging Questions 2Documento2 pagineCircuit Debugging Questions 2Charan ChandrasekaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Eee MCQ 2Documento5 pagineEee MCQ 2Roshnal BluestacksNessuna valutazione finora
- Cmos QuestionsDocumento10 pagineCmos Questionsmeenakshimani996Nessuna valutazione finora
- HT TP: //qpa Pe R.W But .Ac .In: 2009 Solid State DevicesDocumento7 pagineHT TP: //qpa Pe R.W But .Ac .In: 2009 Solid State DevicesSoumitra BhowmickNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Electronics & Telecom Engineering EDC-1 Question Bank For IA-02 A.Y 2021-22Documento7 pagineDepartment of Electronics & Telecom Engineering EDC-1 Question Bank For IA-02 A.Y 2021-22Pratik BhalakeNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics Devices and Circuits 1 Figueroa, Raed A. August 31, 2010 B.S. Cpe Engr. Jason Rex H. AgustinDocumento4 pagineElectronics Devices and Circuits 1 Figueroa, Raed A. August 31, 2010 B.S. Cpe Engr. Jason Rex H. AgustinRa-ed FigueroaNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Have Given by Bold OptionDocumento9 pagineAnswer Have Given by Bold OptionKarthi Keyan RNessuna valutazione finora
- PunjabDocumento6 paginePunjabshailiayushNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic ElectronicsDocumento31 pagineBasic ElectronicsPiyushsinhNessuna valutazione finora
- Ques AnswerDocumento8 pagineQues AnswerRafeek makramNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electronics QDocumento18 pagineBasic Electronics QShivam KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Devices 9th Edition - CHP 2 Basic ProblemsDocumento9 pagineElectronic Devices 9th Edition - CHP 2 Basic ProblemsThivhulawi MukondeleliNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz1 AnalogIC ECE4A - SetADocumento8 pagineQuiz1 AnalogIC ECE4A - SetANiel Joshua I. LozadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-I: Diode Circuits: PES's Modern College of Engineering, Department of Electronics & Telecommunication EngineeringDocumento23 pagineUnit-I: Diode Circuits: PES's Modern College of Engineering, Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering1514VARAD DUDHALMALNessuna valutazione finora
- Question BankDocumento5 pagineQuestion BankDhaya VNessuna valutazione finora
- Semiconductor and Digital Circuit 1693007493Documento4 pagineSemiconductor and Digital Circuit 1693007493samsuzzaman sahinNessuna valutazione finora
- Elec MidtermDocumento8 pagineElec MidtermRichster LofrancoNessuna valutazione finora
- MOS Transistors As Inverters - Print - QuizizzDocumento2 pagineMOS Transistors As Inverters - Print - QuizizzRASHMI RANI SAMANTARAYNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5Documento5 pagineUnit 5Raj PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz1 AnalogIC ECE4A - SetBDocumento8 pagineQuiz1 AnalogIC ECE4A - SetBNiel Joshua I. LozadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Field Effect TransistorsDocumento15 pagineField Effect TransistorsAnonymous eWMnRr70qNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Engineering Paper III IofDocumento9 pagineElectrical Engineering Paper III IofSebastianNessuna valutazione finora
- AicDocumento6 pagineAicSatwik JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics Devices and Circuits SET 1,2,3Documento24 pagineElectronics Devices and Circuits SET 1,2,3Avinash PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Nesative: Lna If TapDocumento3 pagineNesative: Lna If TapAman AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Important MCQ-P.N Junction Diode WWW - Allexamreview.com 2Documento3 pagineImportant MCQ-P.N Junction Diode WWW - Allexamreview.com 2arijitlgsp100% (1)
- Field Effect Transistors (FETs)Documento58 pagineField Effect Transistors (FETs)ksreddy2002100% (1)
- Unit Test 8: (Electronic Devices)Documento7 pagineUnit Test 8: (Electronic Devices)padhi8480Nessuna valutazione finora
- Edc MCQ Unit 1 PN Junction DiodeDocumento3 pagineEdc MCQ Unit 1 PN Junction DiodeUma100% (1)
- Electronics Devices & Material PDFDocumento36 pagineElectronics Devices & Material PDFEthanNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER NO.12.1 Electrostatics: SESSION 2020-21 PhysicsDocumento2 pagineCHAPTER NO.12.1 Electrostatics: SESSION 2020-21 PhysicsFarid AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic CircuitDocumento2 pagineElectronic CircuitAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Beee BitsDocumento5 pagineBeee BitsSurya TejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Semiconductors - DPP 02Documento3 pagineSemiconductors - DPP 02mv7602456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ch. 7 ACDocumento8 pagineCh. 7 ACAawesh BackupsNessuna valutazione finora
- Eec 234 Electronics 2 PracticalDocumento39 pagineEec 234 Electronics 2 Practicalblessingmonday2199Nessuna valutazione finora
- Test 7 Chap 17 (PHY 2)Documento2 pagineTest 7 Chap 17 (PHY 2)Hira RubabNessuna valutazione finora
- EDCDocumento5 pagineEDCGiri KandeNessuna valutazione finora
- Tunnel Field-effect Transistors (TFET): Modelling and SimulationDa EverandTunnel Field-effect Transistors (TFET): Modelling and SimulationNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesDa EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Matrix Analysis and Synthesis: With Applications to Electronic EngineeringDa EverandBasic Matrix Analysis and Synthesis: With Applications to Electronic EngineeringNessuna valutazione finora
- Node-B Wcdma EricssonDocumento54 pagineNode-B Wcdma Ericssonfalberto08100% (3)
- TDA7498MV: 100 W Mono BTL Class-D Audio AmplifierDocumento26 pagineTDA7498MV: 100 W Mono BTL Class-D Audio AmplifierDan TeodorescuNessuna valutazione finora
- Large-Scale 3D Chips: Challenges and Solutions For Design Automation, Testing, and Trustworthy IntegrationDocumento18 pagineLarge-Scale 3D Chips: Challenges and Solutions For Design Automation, Testing, and Trustworthy Integrationyunfan yNessuna valutazione finora
- DTMF Controlled Robot Using Arduino: Sushma Ronanki, Divya Tandra, Prasanth Pogiri, Dilleswara Rao TDocumento8 pagineDTMF Controlled Robot Using Arduino: Sushma Ronanki, Divya Tandra, Prasanth Pogiri, Dilleswara Rao Tsantiago pablo albertoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitsubishi F700 VFD Instruction Manual-BasicDocumento149 pagineMitsubishi F700 VFD Instruction Manual-BasicMROstop.comNessuna valutazione finora
- B.E E&C Seventh Semester Syllabus Microwaves and AntennasDocumento15 pagineB.E E&C Seventh Semester Syllabus Microwaves and AntennasKausthubha BkNessuna valutazione finora
- EC335 Power Electronics & Instrumentation Lab PDFDocumento33 pagineEC335 Power Electronics & Instrumentation Lab PDFAnu RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Quanta Zd1 Re SchematicsDocumento38 pagineQuanta Zd1 Re SchematicsPREVISTONessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12 - P-N JunctionDocumento69 pagineChapter 12 - P-N JunctionShelly RismawatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Acer Aspire 4320 4720 4720G 4720Z - QUANTA ZO1 - REV 1ASecDocumento25 pagineAcer Aspire 4320 4720 4720G 4720Z - QUANTA ZO1 - REV 1ASecBudi Ono100% (1)
- Guia de Diagramas de Turbina SolarDocumento102 pagineGuia de Diagramas de Turbina SolarbillitusNessuna valutazione finora
- Analogue DialogueDocumento56 pagineAnalogue DialoguetorinomgNessuna valutazione finora
- Xpol 1710 2170Mhz 90°17dbi Fixed Tilt X Sector Panel AntennaDocumento1 paginaXpol 1710 2170Mhz 90°17dbi Fixed Tilt X Sector Panel AntennaIkap DarkNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Equipment Solutions DatasheetDocumento7 pagineTest Equipment Solutions DatasheetAnonymous 60esBJZIjNessuna valutazione finora
- sszb130d PDFDocumento19 paginesszb130d PDFMohammad HBNessuna valutazione finora
- 01-Terminologi IC DigitalDocumento15 pagine01-Terminologi IC DigitalDonaDoniAntoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Playful Puppy Robot Instruction ManualDocumento22 paginePlayful Puppy Robot Instruction ManualHenry RiosNessuna valutazione finora
- Kistler - AcelerômetroDocumento3 pagineKistler - Acelerômetromarco.valentimNessuna valutazione finora
- Using A Digital Potentiometer To Optimize A Precision Single-Supply Photo Detection CircuitDocumento8 pagineUsing A Digital Potentiometer To Optimize A Precision Single-Supply Photo Detection CircuitYossy RyanantaNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Factor Improvement in Ac-Dc Converter PDFDocumento46 paginePower Factor Improvement in Ac-Dc Converter PDFBny HdyNessuna valutazione finora
- Rotary Encoder Basics: If Both Switches Are ClosedDocumento7 pagineRotary Encoder Basics: If Both Switches Are ClosedMohammed El-AwamryNessuna valutazione finora
- KPI ImprovementDocumento3 pagineKPI ImprovementSandyan YanNessuna valutazione finora
- 8086 Assembler Tutorial For Beginners (Part 1)Documento3 pagine8086 Assembler Tutorial For Beginners (Part 1)Mayank Khan Singh D'souza100% (1)
- Gulf Alpha 70 CM Circular Polarized Satellite YagiDocumento3 pagineGulf Alpha 70 CM Circular Polarized Satellite YagiScott GillisNessuna valutazione finora
- SK 1-Waterproof Dual-Relay Access Control: User ManualDocumento1 paginaSK 1-Waterproof Dual-Relay Access Control: User Manualjose pastenNessuna valutazione finora
- PS40Documento14 paginePS40BASEER AHMADNessuna valutazione finora
- Getting Started With Icarus VerilogDocumento6 pagineGetting Started With Icarus VerilogZohebMasoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Ldoms Io Best Practices PDFDocumento34 pagineLdoms Io Best Practices PDFKuswahyudi UtomoNessuna valutazione finora
- Intel® Server Chassis SC5650: Technical Product SpecificationDocumento148 pagineIntel® Server Chassis SC5650: Technical Product SpecificationSaiful RizamNessuna valutazione finora
- FR151 - FR157-STR: Fast Recovery Rectifier Diodes PRV: 50 - 1000 Volts Io: 1.5 AmperesDocumento2 pagineFR151 - FR157-STR: Fast Recovery Rectifier Diodes PRV: 50 - 1000 Volts Io: 1.5 AmperesJOHN BRICCO A. MATACSILNessuna valutazione finora