Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Reported Speech
Caricato da
NadheaDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Reported Speech
Caricato da
NadheaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Reported Speech/ Direct Indirect Speech
1. Reported Statements
When do we use reported speech? Sometimes someone says a sentence, for example "I'm
going to the cinema tonight". Later, maybe we want to tell someone else what the first person
said.
We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. (If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We
just put 'she says' and then the sentence:
Direct speech: She says,”“ I like ice cream”” .
Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
We don't need to change the tense, though probably we do need to change the 'person' from 'I'
to 'she', for example. We also may need to change words like 'my' and 'your'.
(As I'm sure you know, often, we can choose if we want to use 'that' or not in English. I've
put it in brackets () to show that it's optional. It's exactly the same if you use 'that' or if you
don't use 'that'.)
But, if the reporting verb is in the past tense, then usually we change the tenses in the
reported speech:
Direct speech: “ She said,’I like ice cream’.” .
Reported speech: She said (that) she liked ice cream.
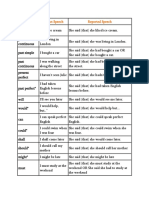
Tense Direct Speech Reported Speech
present
simple
She said (that) she liked ice
-V1/
I like ice cream cream.
V1+s/es
I am happy” She said (that) she was happy
-Do//does
I don’t like ice cream She said (that) she didn’t like ice
not
cream
-is, am, are
present She said (that) she was living in
I am living in London”
continuous London.
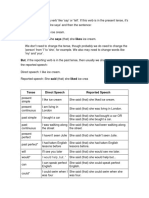
She said (that) she had bought a
past simple car
I bought a car”
-V2 She said (that) she had not
I didn’t buy a car
-did not V1 bought a car
I was happy
-was/were She said (that) she had been
happy
HAD + V3
past She said (that) she had been
I was walking along the street”
continuous walking along the street.
present She said (that) she hadn't seen
“ I haven't seen Julie”
perfect Julie.
She said (that) she had taken
past perfect* “ I had taken English lessons before”
English lessons before.
She said (that) she would see me
will “ I will see you later”
later.
She said (that) she would help
would* “ I would help, but..”
but...
She said (that) she could speak
can I can speak perfect English”
perfect English.
She said (that) she could swim
could* I could swim when I was four”
when she was four.
She said (that) she would come
shall I shall come later”
later.
She said (that) she should call
should*
I should call my mother” her mother
She said (that) she might be late
might* "I might be late"
She said (that) she might be late
may “I may be late”
She said (that) she must study at
must "I must study at the weekend" the weekend OR She said she
had to study at the weekend
* doesn't change.
Occasionally, we don't need to change the present tense into the past if the information in
direct speech is still true (but this is only for things which are general facts, and even then
usually we like to change the tense):
Direct speech: “ The sky is blue” .
Reported speech: She said (that) the sky is/was blue.
2. Reported Questions
a. WH Questios
Direct speech: "Where do you live?"
How can we make the reported speech here?
In fact, it's not so different from reported statements. The tense changes are the same, and we
keep the question word. The very important thing though is that, once we tell the question to
someone else, it isn't a question any more. So we need to change the grammar to a normal
positive sentence / stetement
Direct speech: "Where do you live?"
Reported speech: She asked me where I lived.
Do you see how I made it? The direct question is in the present simple tense. We make a
present simple question with 'do' or 'does' so I need to take that away. Then I need to change
the verb to the past simple.
Another example:
Direct speech: "where is Julie?"
Reported speech: She asked me where Julie was.
The direct question is the present simple of 'be'. We make the question form of the present
simple of be by inverting (changing the position of)the subject and verb. So, we need to
change them back before putting the verb into the past simple.
Here are some more examples:
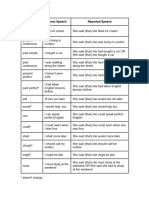
Direct Question Reported Question
“ Where is the Post Office, please?” She asked me where the Post Office was.
“ What are you doing?” She asked me what I was doing.
“ Who was that fantastic man?” She asked me who that fantastic man had been.
b. Yes/ No Questions
if you need to report a 'yes / no' question? We don't have any question words to help us.
Instead, we use 'if':
Direct speech: "Do you like chocolate?"
Reported speech: She asked me if I liked chocolate.
Here are a few more examples:
Direct Question Reported Question
“ Do you love me?” He asked me if I loved him.
“ Have you ever been to Mexico?” She asked me if I had ever been to Mexico.
“ Are you living here?” She asked me if I was living here.
3. Reported Requests
What if someone asks you to do something (in a polite way)? For example:
Direct speech: "Close the window, please"
Or: "Could you close the window please?"
Or: "Would you mind closing the window please?"
All of these requests mean the same thing, so we don't need to report every word when we
tell another person about it. We simply use 'ask me + to + infinitive':
Reported speech: She asked me to close the window.
Here are a few more examples:
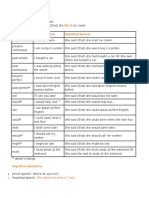
Direct Request Reported Request
“ Please help me” . She asked me to help her.
“ Please don't smoke” . She asked me not to smoke.
“ Could you bring my book tonight?” She asked me to bring her book that night.
“ Could you pass the milk, please?” She asked me to pass the milk.
“ Would you mind coming early tomorrow?” She asked me to come early the next day.
To report a negative request, use 'not':
Direct speech: "Please don't be late."
Reported speech: She asked us not to be late.
4. Reported Orders
And finally, how about if someone doesn't ask so politely? We can call this an 'order' in
English, when someone tells you very directly to do something. For example:
Direct speech: "Sit down!"
In fact, we make this into reported speech in the same way as a request. We just use 'tell'
instead of 'ask':
Reported speech: She told me to sit down.
Direct Order Reported Order
“ Go to bed!” He told the child to go to bed.
“ Don't worry!” He told her not to worry.
“ Be on time!” He told me to be on time.
“ Don't smoke!” He told us not to smoke.
Time Expressions with Reported Speech
Sometimes when we change direct speech into reported speech we have to change time
expressions too. We don't always have to do this, however. It depends on when we heard the
direct speech and when we say the reported speech.
For example:
It's Monday. Julie says "I'm leaving today".
If I tell someone on Monday, I say "Julie said she was leaving today".
If I tell someone on Tuesday, I say "Julie said she was leaving yesterday".
If I tell someone on Wednesday, I say "Julie said she was leaving on Monday".
If I tell someone a month later, I say "Julie said she was leaving that day".
So, there's no easy conversion. You really have to think about when the direct speech was
said.
Here's a table of some possible conversions:
now then / at that time
today yesterday / that day / Tuesday / the 27th of June
the day before yesterday / the day before / Wednesday / the 5th of
yesterday
December
last night the night before, Thursday night
last week the week before / the previous week
tomorrow today / the next day / the following day / Friday
Reported Speech
Direct Speech
Here There
the month/year before
the preceding month/year
last month/year
the previous month/year
a month/year later
the following month/year
next month/year
the next month/year
now at that time
then
today that day
a day later
tomorrow the following/next day
the day before
yesterday the previous day
two days/weeks before
two days/weeks
two days/weeks earlier
ago
Contoh Kalimat Direct Speech Contoh Kalimat Reported Speech
“Will I receive the packet tomorrow?” He asked if he would receive the packet the following day.
(Akankah saya menerima paket tsb (Dia bertanya apakah dia akan menerima paket tersebut
besok?) hari berikutnya.)
“I have to return the book two days
She said that she had to return the book two days earlier.
ago.”
(Dia berkata bahwa dia harus mengembalikan buku tersebut
(Saya harus mengembalikan buku tsb
dua hari sebelumnya.)
dua hari lalu.)
Menambahkan Whether atau If
Whether atau if ditambahkan untuk menyampaikan kembali kalimat yes-no question yang telah
didengar sebelumnya.
Contoh Kalimat Reported Speech
Contoh Direct Speech Contoh Kalimat Reported Speech
He asked me if I had a little time.
(Dia bertanya pada saya apakah saya memiliki sedikit waktu.)
“Do you have a little time?”
Keterangan:
(Apa kamu punya sedikit waktu?)
Jawaban dari pertanyaan pada direct speech: Yes, I do atau No, I
don’t.
She wanted to know whether I had heard the news.
“Have you heard the news?” (Dia ingin tahu apakah saya telah mendengar berita tersebut.)
(Sudahkah kamu mendengar berita
tsb?) Keterangan:
Jawaban dari pertanyaan pada direct speech: Yes, I
have atau No, I haven’t.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Reported SpeechDocumento4 pagineReported Speechmaria estevezNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech PDFDocumento12 pagineReported Speech PDFYoNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech: But, If The Reporting Verb Is in The Past Tense, Then Usually We Change The Tenses in The ReportedDocumento5 pagineReported Speech: But, If The Reporting Verb Is in The Past Tense, Then Usually We Change The Tenses in The ReportedHamalahamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech: Here's How It WorksDocumento8 pagineReported Speech: Here's How It WorksMarina PeshovskaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento3 pagineReported SpeechMacarena Berdugo MenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento5 pagineReported SpeechSandra SilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento10 pagineReported SpeechAlbertoyJavier Sancho CamposNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5 Lesson 2: Reported Speech: Statements/ SentencesDocumento7 pagineUnit 5 Lesson 2: Reported Speech: Statements/ SentencesJesus PonceNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech: But, If The Reporting Verb Is in The Past Tense, Then Usually We Change The Tenses inDocumento4 pagineReported Speech: But, If The Reporting Verb Is in The Past Tense, Then Usually We Change The Tenses inamalia9bochisNessuna valutazione finora
- ENCGW1 Reported Speech PDFDocumento2 pagineENCGW1 Reported Speech PDFImane MegzariNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento14 pagineReported SpeechBryan Anthony Aranda CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- But, If The Reporting Verb Is in The Past Tense, Then Usually We Change The Tenses in TheDocumento9 pagineBut, If The Reporting Verb Is in The Past Tense, Then Usually We Change The Tenses in TheRenatoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tense Direct Speech Reported SpeechDocumento2 pagineTense Direct Speech Reported SpeechAnano KiziriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento10 pagineReported SpeechNicole ConsuegraNessuna valutazione finora
- Pref - 5 - Grammar 3.5 - Revisión Del IntentoDocumento5 paginePref - 5 - Grammar 3.5 - Revisión Del IntentoGamerMExXNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento1 paginaReported Speechvuckovicpetra2004Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tense Direct Speech Reported Speech: ObservaçãoDocumento3 pagineTense Direct Speech Reported Speech: ObservaçãoAssunção BarbosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento3 pagineReported SpeechLeticia FornaciariNessuna valutazione finora
- U3 Reported SpeechDocumento4 pagineU3 Reported SpeechJorge PiñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tense Direct Speech Reported SpeechDocumento3 pagineTense Direct Speech Reported SpeechmauvedandelionNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech RulesDocumento6 pagineReported Speech Rulesliziana zaharieNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech HandoutDocumento6 pagineReported Speech HandoutMabikane.C. ArnaldoNessuna valutazione finora
- Click Here For More About Using 'Say' and 'Tell'Documento2 pagineClick Here For More About Using 'Say' and 'Tell'Taty UrdanetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento4 pagineReported SpeechSaNe. i.L.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento6 pagineReported Speechsara berrahalNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech: Prepared BY Mr. Meyphalla OudomDocumento7 pagineReported Speech: Prepared BY Mr. Meyphalla Oudomphalla oudomNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech WorksheetDocumento3 pagineReported Speech WorksheetMangasi SinagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech 8th GradeDocumento4 pagineReported Speech 8th Gradecosac raczNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento4 pagineReported SpeechnataNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech: Click Here For A List of Reported Speech Exercises. Click Here To Download This Explanation in PDFDocumento35 pagineReported Speech: Click Here For A List of Reported Speech Exercises. Click Here To Download This Explanation in PDFArabic&English NonoooNessuna valutazione finora
- Narration Gyan ArpanDocumento10 pagineNarration Gyan ArpanAnu KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech: 'Say' and 'Tell'Documento5 pagineReported Speech: 'Say' and 'Tell'Kristina DolinskaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported StatementsDocumento7 pagineReported StatementsEduardo RacuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Indirect Speech in EnglishDocumento4 pagineIndirect Speech in EnglishDaniela CraciunNessuna valutazione finora
- Indirect and Direct SpeechDocumento5 pagineIndirect and Direct SpeechLaura VillarroelNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech: But, If The Reporting Verb Is in The Past Tense, Then Usually We Change The Tenses in TheDocumento5 pagineReported Speech: But, If The Reporting Verb Is in The Past Tense, Then Usually We Change The Tenses in TheNicoleta LipanNessuna valutazione finora
- Here's How It Works:: Click Here For More About Using 'Say' and 'Tell'Documento6 pagineHere's How It Works:: Click Here For More About Using 'Say' and 'Tell'Ceci PecheNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech 2Documento7 pagineReported Speech 2Diana HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocumento7 pagineDirect and Indirect SpeechRadu IonelNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech: Reported Speech Is Often Also Called Indirect Speech in English. When We Use Reported Speech, We AreDocumento4 pagineReported Speech: Reported Speech Is Often Also Called Indirect Speech in English. When We Use Reported Speech, We AreLoredanaNessuna valutazione finora
- REPORTED SPEECH UsageDocumento7 pagineREPORTED SPEECH Usagesamria 2005Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento13 pagineReported SpeechОльгаNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento6 pagineReported SpeechJopa FebiolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech: Click Here For A List of Reported Speech Exercises. Click Here To Download This Explanation in PDFDocumento28 pagineReported Speech: Click Here For A List of Reported Speech Exercises. Click Here To Download This Explanation in PDFIVAN ANDRE AGUILAR ALVARADONessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento5 pagineReported Speechadriana884Nessuna valutazione finora
- Indirect Statements: For More ExplanationDocumento5 pagineIndirect Statements: For More ExplanationWinnieNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech LENGUA INGLESA UADEDocumento22 pagineReported Speech LENGUA INGLESA UADEMaru CottNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento6 pagineReported SpeechΓεωργία ΤζανάκουNessuna valutazione finora
- Sem 2 BBA-Bcom Class Notes 2Documento12 pagineSem 2 BBA-Bcom Class Notes 2Anil Shenoy KNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproted Speech BackshiftDocumento2 pagineReproted Speech Backshifteliseofernandezrojas40Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento9 pagineReported SpeechSubashini ChryshanthusNessuna valutazione finora
- Tense Direct Speech Reported Speech: Click Here To Practise Reported StatementsDocumento4 pagineTense Direct Speech Reported Speech: Click Here To Practise Reported StatementsSlimaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento3 pagineReported Speechmohamed el bahiNessuna valutazione finora
- Grammar Basics-Reported SpeechDocumento2 pagineGrammar Basics-Reported SpeechSilvia TripodiNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento1 paginaReported SpeechFreixel RamsésNessuna valutazione finora
- 10th Worksheet July 20th-24th - Docx 3 Reported SpeechDocumento6 pagine10th Worksheet July 20th-24th - Docx 3 Reported SpeechDanny MontoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento3 pagineReported SpeechAndrei HanNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Chinese (BOOK 2) – Learn Chinese in a Simple and Successful Way – Series BOOK 1, 2, 3, 4Da EverandModern Chinese (BOOK 2) – Learn Chinese in a Simple and Successful Way – Series BOOK 1, 2, 3, 4Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Life 2E Pre-Intermediate Unit 1 TBDocumento16 pagineLife 2E Pre-Intermediate Unit 1 TBAnonymous J2egZ4A100% (2)
- NOUN CountVsNonCountDocumento22 pagineNOUN CountVsNonCountBagasWicaksanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Modal Aux. LessonDocumento36 pagineModal Aux. LessonNikko Manio100% (1)
- Writing Task 1 - Sentence TransformationsDocumento4 pagineWriting Task 1 - Sentence TransformationsPham Thi Thanh Thao100% (2)
- Stress in EnglishDocumento14 pagineStress in EnglishHussain LitonNessuna valutazione finora
- Line by Line PDFDocumento241 pagineLine by Line PDFQingsong GuoNessuna valutazione finora
- Used To and WouldDocumento2 pagineUsed To and WouldFabian GusgoNessuna valutazione finora
- AdjectivesDocumento38 pagineAdjectivesFOM YESCH100% (2)
- Combined Particles JapaneseDocumento5 pagineCombined Particles JapaneseChristian GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- MORPHOLOGYDocumento11 pagineMORPHOLOGYnguyenthikieuvanNessuna valutazione finora
- BBH - Ak 32 HophalStrongDocumento2 pagineBBH - Ak 32 HophalStrongCristóbal Ávalos RojasNessuna valutazione finora
- Inflectional Morphemes AwDocumento2 pagineInflectional Morphemes AwZayyani Mohd NoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Grammar 7 - Not - As As Not So As. Grammar, Exercises and Answer KeyDocumento4 pagineGrammar 7 - Not - As As Not So As. Grammar, Exercises and Answer Keyrosaroncero100% (2)
- Information Report Template and ScaffoldDocumento4 pagineInformation Report Template and Scaffoldapi-248888410Nessuna valutazione finora
- Participle Modifiers and Prepositions - English Exercises & Practice - Grammar QuizzesDocumento20 pagineParticiple Modifiers and Prepositions - English Exercises & Practice - Grammar QuizzesUriel MtzNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation For Grade 10 (Modals)Documento18 paginePresentation For Grade 10 (Modals)Raphael Auwee Rivas0% (1)
- New Teacher Training (Guide For Teachers)Documento71 pagineNew Teacher Training (Guide For Teachers)Edlyn Estopa Bueno100% (2)
- Anglais Examen 9emeDocumento1 paginaAnglais Examen 9emeJean Jerry100% (2)
- Catullus, Poem 3: On The Death of A Pet Sparrow: Lugete, O Veneres CupidinesqueDocumento6 pagineCatullus, Poem 3: On The Death of A Pet Sparrow: Lugete, O Veneres CupidinesqueDarkoIlinNessuna valutazione finora
- S1-Farmasi/Pertemuan Ke-11 Passive SentenceDocumento2 pagineS1-Farmasi/Pertemuan Ke-11 Passive SentenceMiminNessuna valutazione finora
- TRANSLATIONDocumento40 pagineTRANSLATIONSibghatullah MujadidiNessuna valutazione finora
- Nurul Mukaromah - Eka Laila Fikriani - Silvia Ira - Reza Dakwani - Dhia Fathi Attala - Alifya Pramesty A. (X Mipa I)Documento7 pagineNurul Mukaromah - Eka Laila Fikriani - Silvia Ira - Reza Dakwani - Dhia Fathi Attala - Alifya Pramesty A. (X Mipa I)nurulNessuna valutazione finora
- English: Lower Intermediate Salon 36 AdverbsDocumento5 pagineEnglish: Lower Intermediate Salon 36 AdverbsJose CarrizalesNessuna valutazione finora
- RUMUS Passive PoiceDocumento42 pagineRUMUS Passive PoiceMhare Haryadhyk The'EmergencyNessuna valutazione finora
- Mapa Conceptual InglesDocumento2 pagineMapa Conceptual InglesMario Alberto Pastenes RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Present Unreal ConditionalDocumento2 paginePresent Unreal ConditionalPatricia SandovalNessuna valutazione finora
- Future Perfect Progressive Story 1Documento8 pagineFuture Perfect Progressive Story 1jasnas750% (1)
- Polysemy: từ đa nghĩa (nhưng có chung nét nghĩa với nhau) Homonymy: đồng âm, đồng tự (cách viết), khác nghĩaDocumento11 paginePolysemy: từ đa nghĩa (nhưng có chung nét nghĩa với nhau) Homonymy: đồng âm, đồng tự (cách viết), khác nghĩabaphong593Nessuna valutazione finora
- Infinitive Gerund RulesDocumento5 pagineInfinitive Gerund RulesKumaresh AmulNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 20: The Cult of Celebrity TensesDocumento11 pagineUnit 20: The Cult of Celebrity TensesYaina IvanovaNessuna valutazione finora