Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Complete Cycle
Caricato da
Md Suzon MahmudTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Complete Cycle
Caricato da
Md Suzon MahmudCopyright:
Formati disponibili
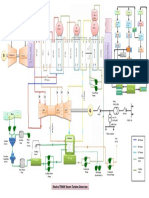
Complete cycle
of an ion exchange unit
In water treatment
The cycle of an ion exchange column used for water treatment consists of the following steps:
1. Exhaustion (production) step
2. Backwash
3. Regeneration
4. Rinse
The picture shows a cycle with co-flow regeneration.
Exhaustion step
The solution to be treated (feed water) passes through the ion exchange resin bed, exhausting the
resin progressively. At the breakthrough point, i.e. at the point where the ion leakage reaches a
pre-determined value, the exhaustion step is stopped.
Backwash
Before regeneration, the resin bed is backwashed
a) to loosen it and prevent excessive compaction
b) to remove accumulated suspended solid and possible broke resin particles from the bed
surface
The bed expansion should be 50 to 100 % and the time of backwash is a few minutes.
Backwashing the resin bed is not performed in case of reverse flow regeneration so as not to
disturb the distribution of resin layers, except whan the pressure drop increases excessively, or
every 30 cycles or so.
Regeneration
The regenerant solution is then slowly introduced into the column. The regeneration time is
usually 20 to 60 minutes. Full details about regeneration procedure are shown in a separate page.
Rinse
Rinsing the resin after regeneration is done in two steps:
1. The regenerant must be displaced with water from the resin bed until only traces of the
chemical are left. This displacement rinse is done at a low flow rate, the same as the
regeneration flow rate.
2. Finally, the resin bed is submitted to a fast rinse at service flow rate to remove the last
traces of regenerant. The end of this final rinse is reached when the outlet water quality
meets the treated water quality specification.
Special applications
In several applications other than water treatment, the solution treated by resins must be
displaced before regeneration, to recover as much treated solution as possible, avoiding losses in
the regeneration waste. This additional step is called "sweetening-off" because it was first
introduced in sugar treatment processes. Similarly, a "sweetening-on" step is carried out after
regeneration and rinse before feeding the raw solution to be treated, to avoid dilution of the
treated solution. The complete regeneration process consists then of the following steps:
1. Backwash with the raw solution (optional)
2. Sweetening-off: displacement of the solution with water
3. Regenerant injection
4. Displacement of the regenerant with water
5. Fast rinse with water
6. Sweetening-on with the solution to be treated
The sweetening-off fraction is sometimes recycled, particularly when the solution contains
valuable components (precious metals, expensive chemical compounds).
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Finding The GrooveDocumento6 pagineFinding The GrooveaingerutNessuna valutazione finora
- Telepathy. The Respectable Phenomenon by Sybil LeekDocumento53 pagineTelepathy. The Respectable Phenomenon by Sybil LeekTimothy BusseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Happpy Jacks Funhouse Ver 14a ColorDocumento65 pagineHapppy Jacks Funhouse Ver 14a ColorΔημητρης τιτος100% (7)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- RCM ARCT Analysis SampleDocumento47 pagineRCM ARCT Analysis SampleKalen Wu100% (1)
- Cortot Edition Chopin Etudes Alexander Technique Facilitate PerformanceDocumento102 pagineCortot Edition Chopin Etudes Alexander Technique Facilitate PerformanceMiguel Angel Aguirre Igoa50% (2)
- Appreciating Different Types of PoetryDocumento29 pagineAppreciating Different Types of PoetryJoy Mariette Cristo100% (1)
- Medieval Christian Dualist Perceptions and Conceptions of Biblical ParadiseDocumento18 pagineMedieval Christian Dualist Perceptions and Conceptions of Biblical ParadiseDositheus SethNessuna valutazione finora
- 93 Valentines-Day High-Int USDocumento11 pagine93 Valentines-Day High-Int USVika Harnaha100% (1)
- Ion Exchange Design - Hand Calculation: Brian Windsor (Purolite International LTD)Documento43 pagineIon Exchange Design - Hand Calculation: Brian Windsor (Purolite International LTD)Octiva100% (4)
- 75 MW Lab Test InfoDocumento295 pagine75 MW Lab Test InfoMd Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- Ion Exchange Resins - Water Conditioning ManualDocumento93 pagineIon Exchange Resins - Water Conditioning Manualm9m2070Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bangalore Business Samples 250Documento18 pagineBangalore Business Samples 250dpkraja100% (3)
- Love knows no boundsDocumento4 pagineLove knows no boundsraj94555123681334Nessuna valutazione finora
- 351 F248C S02 02 14.03.23 Id R0 PDFDocumento1 pagina351 F248C S02 02 14.03.23 Id R0 PDFMd Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- PDF Created With Pdffactory Pro Trial VersionDocumento1 paginaPDF Created With Pdffactory Pro Trial VersionMd Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- 351 F248S H0101 2015.2.25 Id R0Documento23 pagine351 F248S H0101 2015.2.25 Id R0Md Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- 351 F248C S01 02 14.03.23 Id R0 PDFDocumento1 pagina351 F248C S01 02 14.03.23 Id R0 PDFMd Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- 351 F248S J0101 2015.07.22 Id R1Documento77 pagine351 F248S J0101 2015.07.22 Id R1Md Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- ST Overview - FinalF PDFDocumento1 paginaST Overview - FinalF PDFMd Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 启动锅炉运维规程 Startup Boiler Operation and Maintenance Manual -2016-5Documento12 pagine5 启动锅炉运维规程 Startup Boiler Operation and Maintenance Manual -2016-5Md Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 启动锅炉运维规程 Startup Boiler Operation and Maintenance Manual -2016-5Documento12 pagine5 启动锅炉运维规程 Startup Boiler Operation and Maintenance Manual -2016-5Md Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- 351 F248S H0101 2015.2.25 Id R0Documento23 pagine351 F248S H0101 2015.2.25 Id R0Md Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- B 库尔那化学Documento133 pagineB 库尔那化学Md Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- B 库尔那化学Documento133 pagineB 库尔那化学Md Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- Consume Large ChemicalDocumento1 paginaConsume Large ChemicalMd Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- 351 F248C S01 04 14.03.23 Id R0 PDFDocumento1 pagina351 F248C S01 04 14.03.23 Id R0 PDFMd Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- 351 F248S D0201 02 2015.03.27 Id R0 PDFDocumento1 pagina351 F248S D0201 02 2015.03.27 Id R0 PDFMd Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- 351 F248C S01 02 14.03.23 Id R0 PDFDocumento1 pagina351 F248C S01 02 14.03.23 Id R0 PDFMd Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- Joe Woolley Process DesignDocumento53 pagineJoe Woolley Process DesignpgcedzovNessuna valutazione finora
- 351 F248C S01 03 14.03.23 Id R0 PDFDocumento1 pagina351 F248C S01 03 14.03.23 Id R0 PDFMd Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- K0502-05 Condenser Circulating Cooling Water System p&ID PDFDocumento1 paginaK0502-05 Condenser Circulating Cooling Water System p&ID PDFMd Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- K0501-04-HRSG HP FWP System P&ID PDFDocumento1 paginaK0501-04-HRSG HP FWP System P&ID PDFMd Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- K0501-07-08-HPFW Pump Oil Station System P&ID PDFDocumento2 pagineK0501-07-08-HPFW Pump Oil Station System P&ID PDFMd Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- TN5Documento57 pagineTN5OlgalycosNessuna valutazione finora
- Cleaning Method For IX ResinDocumento8 pagineCleaning Method For IX Resinjoshua gomezNessuna valutazione finora
- K0501-04-HRSG HP FWP System P&ID PDFDocumento1 paginaK0501-04-HRSG HP FWP System P&ID PDFMd Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- K0501-09-10 - HPFW Pump Itself System P&ID PDFDocumento2 pagineK0501-09-10 - HPFW Pump Itself System P&ID PDFMd Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- 351-F248S-D0101-02 (Rev.1) PDFDocumento1 pagina351-F248S-D0101-02 (Rev.1) PDFMd Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- K0503-02-EH Oil Supply System P&ID Diagram PDFDocumento1 paginaK0503-02-EH Oil Supply System P&ID Diagram PDFMd Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- 1278 V Data 7835Documento1 pagina1278 V Data 7835Md Suzon MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- Bicol University College of Education Daraga, AlbayDocumento2 pagineBicol University College of Education Daraga, AlbayAbegail Terillano InfanteNessuna valutazione finora
- Levis HistoryDocumento17 pagineLevis HistoryAsha SampatNessuna valutazione finora
- WCS Panel PDFDocumento25 pagineWCS Panel PDFbhaskarNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation: On Industrial Visit of NOMAN WEAVING MILLS LTDDocumento30 paginePresentation: On Industrial Visit of NOMAN WEAVING MILLS LTDMehzabeen ShahidyNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Galeri Luxton Layout Plans 3D Perspectives Furniture DimensionsDocumento16 pagineMarketing Galeri Luxton Layout Plans 3D Perspectives Furniture DimensionsYustisia KatriniNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Grids An A List Apart ArticleDocumento12 pagineFluid Grids An A List Apart ArticlenilasonaNessuna valutazione finora
- Angiosperm or GymnospermDocumento2 pagineAngiosperm or Gymnospermtuti_ron_007100% (1)
- Automotive-Maintenance Merit Badge WorksheetDocumento10 pagineAutomotive-Maintenance Merit Badge WorksheetgivenjwNessuna valutazione finora
- Cbse 10TH NotesDocumento2 pagineCbse 10TH NotesManoj KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Dear YouDocumento6 pagineDear YouSue SandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Materials Overwing Aircraft NozzlesDocumento3 pagineMaterials Overwing Aircraft NozzlesLucio Falbi FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- History Capsule SSC 2014Documento20 pagineHistory Capsule SSC 2014mkiriti0% (1)
- The Future Tenses 1: 1. It's Likely It ... SoonDocumento8 pagineThe Future Tenses 1: 1. It's Likely It ... SoonDublea BogdanNessuna valutazione finora
- NayeonieejeongyeonsanajihyooooominadahyuuuuuunyyyDocumento5 pagineNayeonieejeongyeonsanajihyooooominadahyuuuuuunyyyNayeon LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Rules for reading Sri Sri ChandiDocumento2 pagineRules for reading Sri Sri Chandiviky24100% (1)
- A Timeline for the History of Public Art The United Kingdom and the United States of America, 1900–2005 Cameron Cartiere, Rosemary Shirley, and Shelly Willis.Pages from The Practice of Public Art Edited by Cameron CartiereDocumento16 pagineA Timeline for the History of Public Art The United Kingdom and the United States of America, 1900–2005 Cameron Cartiere, Rosemary Shirley, and Shelly Willis.Pages from The Practice of Public Art Edited by Cameron CartiererobotchilangoNessuna valutazione finora
- Disputers of The Tao-Kwong-Loi ShunDocumento4 pagineDisputers of The Tao-Kwong-Loi Shunlining quNessuna valutazione finora
- ENGINEERING GRAPHICS TITLEDocumento39 pagineENGINEERING GRAPHICS TITLEsugunay123Nessuna valutazione finora
- AllDocumento30 pagineAllYass CosmeticsNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept Car With GM and Frank O. GehryDocumento32 pagineConcept Car With GM and Frank O. GehryFabian MosqueraNessuna valutazione finora