Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Process Engineering Short Course
Caricato da
rutuja0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
229 visualizzazioni7 paginecourse
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentocourse
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
229 visualizzazioni7 pagineProcess Engineering Short Course
Caricato da
rutujacourse
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 7
SUBJECT: Process Engineering Short Course Syllabus
1) Introduction to Various Types of Project Contracts (4 hours)
Meaning of Engineering Procurement and Construction (EPC)
Typical Organization Chart of EPC Company
Work Flow in EPC Companies
FEED Stage Work Flow
EPC Contract Types
Procurement Procedure
Types of Tenders
Tender Procurement Process Flow Chart
2) Basic Engineering Design Package (BEDP or FEED Package) (10 hours)
Scope and Title
Contents of BEDP
Contents of Table 1
General Design Data
Project Specifications
Manuals and Drawings
Contents of Table 2
General Design Data
Specifications & Data Sheets
Drawings
Developments of Table 1 Contents
General information
Basic Engineering Design Data
Complex/Plant material balance
Utility summary tables
Flare Load Summary Tables
Effluent summary tables
Winterizing & heat conservation and insulation data
Safety
Resins, Chemicals, Solvents and Catalysts
Hazardous area classification
Licensor’s Proprietary Items
Project Specifications
Different Types of Manuals
Developments of Table 2 Contents
General Information
Unit Design Basis
Equipment Item Index
Heat & material balance tables
Utility Summary Tables
Review of Detailed Design
Specifications & Data Sheets
Fired heaters
Storage tanks
Towers, reactors and vessels
Heat exchangers
Machinery
Instruments
Drawings
Preliminary unit plot plan
Piping & instrumentation diagrams (P&IDs)
Utility distribution flow diagrams (UDFDs)
Emergency shut-down block diagram and/or logic diagram.
Cause & effect tables/diagrams.
Single line diagrams.
3) Detail Design and Engineering (6 hours)
Scope
Work Sequence and Procedures
Process and Utilities Engineering
Piping Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
Instrumentation Engineering
Electrical Engineering
Civil and Structural Engineering
List of Softwares used During Detail Engineering (Name and Application)
4) Introduction to Key Process Engineering Deliverables (5 hours)
5) Preparation of Key Process Engineering Summaries (5 hours)
Fluid List- Sample
Line List-Sample
Line List- Preparation
Tie-in-Point List-Sample
Tie-in-Point List-Preparation
Catalyst Summary-Sample
Chemicals Summary-Sample
Catalyst & Chemical Summary-Preparation
Hazardous Source List-Sample
Hazardous Source List-Preparation
Equipment List- Sample
Equipment List- Preparation
Utility Consumption Summary – Sample
Utility Consumption Summary - Preparation
Preparation of Flare Load Summary
Effluent Summary-Sample
Effluent Summary-Preparation
6) Typical Oil and Gas Production Facilities (6 hours)
Oil Production Facilities
Artificial Lift
Crude Oil Treatment
Produced Water Treatment
Natural Gas Processing
Amine Process (Flow Diagram)
Dehydration using Glycol (Flow Diagram)
Dehydration using Solid Desiccants (Flow Diagram)
NGL Recovery
LNG Supply Chain
7) Introduction to Crude Oil Refinery Processes (6 hours)
Introduction
Typical Block Flow Diagram for Refinery
Various processes PFD.
Physical Processes
Thermal Processes
Catalytic Processes
Conversion of Heavy Residues
Treatment of Refinery Streams
Lube base stock preparation
Other processes (Common Facilities)
8) Guidelines for Preparation of Majors Process and Piping Drawings (6
hours)
Process Work Flow
Process Equipments Symbols for P&ID
Block Flow Diagram (BFD)
Process Flow Diagrams (PFD)
Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&ID)
Process Control Diagrams (PCD)
Plot Plan
Guidelines for Preparation of Plot Plan
Elevation Drawings
Guidelines for Preparation of Equipment Layout
9) Fluid Flow and Line Sizing (5 hours)
Types of Fluid Flow
Equation of Continuity
Bernoulli's Equation
Friction Losses in Pipes
Minor Losses Calculation
Equivalent Length of Fittings
Pressure Drop Formula
Step Wise Procedure for Single Phase Pipeline Sizing
Line Sizing Criteria – Allowable Velocity & Pressure Drop
Line Sizing – Two Phase Flow
Types of Two Phase Flows
Flow Regimes
Pressure Drop Calculation Procedure
10) Pumps and Hydraulic Calculations (8 hours)
Part 1
Introduction
Types of Pumps
Positive Displacement Pumps
Positive Displacement Pumps (Strengths/Concerns)
Roto Dynamic Pumps
Roto Dynamic Pumps (Strengths/Concerns)
Head & Typical Performance Curves
Selection Guidelines
Centrifugal v/s Reciprocating Pumps
Capacity /Pressure
Pressure/Flow/ Fluid Handling
Cost
Affinity Laws
Part 2
Terminology in Hydraulics
NPSHA Calculations
Hydraulics Calculations Procedure
Solved Example
Hydraulic Calculations – Reciprocating Pump
Rule of Thumb for Pumps
Excel Calculation Sheet
11) Compressors (5 hours)
Introduction
Type of Compressors
Positive Displacement Compressors
Centrifugal Compressors
Compressors
Lubricating System
Lube Oil Cooling
Comparison
Basic Calculations – Head/Power/Discharge Temperature
Compressor Operation
Surge & Anti surge
Surge Controls
Thumb Rules for Compressors
Codes & Standards
12) Introduction to Process Vessel Design (4 hours)
Process Design Conditions
Codes and Standards
Low Temperature Requirements
Pressure Testing
Separators / Pressure Vessel Sizing
Vertical Separator Design
Separator Sizing
Horizontal Separator Sizing
Thumb Rules (Separators)
Thumb Rules (Storage Tanks)
13) Heat Exchangers and Thermal Design Procedure (12 hours)
Part 1
Classification of Exchangers
Exchangers Nomenclature
Types of Heat Exchangers
Double Pipe Heat Exchanger
Shell and Tube Exchanger
Major Components of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
Plate and Frame Exchanger
Spiral Plate Exchanger
Spiral Tube and Helical Flow Exchanger
Air Cooled Exchanger
Plate Fin Exchanger
Categories of Shell and Tube Exchanger
Fouling Factors
Log Mean Temperature Difference Correction Factor
Overall Heat Transfer Coefficients
Energy Balance and Heat duty
Pressure Drop Calculations
Data Required for Thermal Design
Thermal Design Procedure
Thermal Design Parameters
Thumb Rules for Heat Exchangers
Codes and Standards
Part 2
Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
Allocation of Fluids
Flow Arrangements
Problem Statement
Design of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
General Design Steps
Thermal Design
Hydraulic Design
Part (A) - General Design Steps of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
Part (B) - Thermal Design of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
Physical Properties
How Should I Start
How to calculate heat duty of heat exchanger?
Calculating LMTD
Calculation Of Heat Transfer Area
Select A Suitable Size Tube
1 – 1 Pass Arrangement Calculation
1 – 4 Pass Arrangement Calculation
Read jH Factor from Graph-Tube
Summary of Tube Side Calculation...
Shell Side Calculations
Read jH Factor from Graph-Shell
Calculation Of Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient
Calculation of LMTD Correction Factor
Heat Transfer Area Verification
Part (C) – Hydraulic Design
Pressure Drop Calculations across Tube side…
Pressure Drop Calculations across shell side…
Single Phase Exchanger-Formulas
Codes & Standards
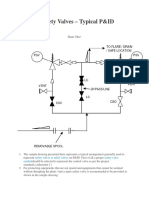
14) Pressure Safety Valves and Sizing / Calculation Procedures (6 hours)
Introduction
PSV Types
Chattering Problems
Sizing Calculations
Example and Procedures
Codes, Standards and Simulators
15) Control Valves and Sizing Calculations (5 hours)
Introduction
Features
Flow Characteristics
Cavitation
Flashing
Piping Influence & Choked Flow
Typical Control Valve Data Sheet
Construction Features
Classification & Types
Types of Actuators
Symbology in P&ID
Bonnet & Accessories
Major Vendors
Interface
Body & Trim Material
Codes & Standards
Sizing & Selection
16) Cost Estimation Methods (4 hours)
Fixed Capital Investment
Cost Estimate Types and Accuracy
Capital Cost Estimate Classifications
Capital Cost Estimate Definition
Cost Estimation Methods
Factors Affecting Capital Cost
Direct Project Expenses
Indirect Project Expenses
Contingency and Fee
Auxiliary Facilities
Pumps and Electric Motors
Fans
Blowers
Compressors
Heat Exchangers
Fired Heaters
Pressure Vessels
Distillation Columns
Packed Distillation Columns
17) HAZOP Analysis Fundamental (8 hours)
What is HAZOP?
Objective of HAZOP
How and Why HAZOP is used.
Purpose of HAZOP
HAZOP – Hazard and Operability Study
Features of HAZOP Study
HAZOP Phasing
HAZOP Study Procedure
HAZOP Study Flow Chart
Guidelines for division into Sections (Nodes)
Guide Words
HAZOP Study Form
HAZOP Study
Strength of HAZOP
Weakness of HAZOP
Planning for HAZOP
Documents to be kept ready
Team Characteristics
Responsibility of HAZOP Team Members
Sample Process Documents
Sample HAZOP Work Sheet
Sample HAZOP Close Out Report
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Inspire Science Overview BrochureDocumento16 pagineInspire Science Overview BrochureJeffery Rafael Zeledon Tinoco0% (1)
- Oxygen Generation Plant For HospitalDocumento4 pagineOxygen Generation Plant For Hospitalrutuja100% (1)
- Deliverables and Estimated Man-Hours: Detail DesignDocumento10 pagineDeliverables and Estimated Man-Hours: Detail DesignkingNessuna valutazione finora
- Construction Schedule With S-CurveDocumento23 pagineConstruction Schedule With S-CurveJp Gallardo100% (2)
- EPC For ASAB Phase-II Stage-2-LatestDocumento2 pagineEPC For ASAB Phase-II Stage-2-LatestGokulprabhuNessuna valutazione finora
- P&ID ChecklistDocumento4 pagineP&ID ChecklistMeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Equipment Design BasisDocumento4 pagineEquipment Design BasisAnjani GantiNessuna valutazione finora
- PFD ChecklistDocumento1 paginaPFD ChecklistNguyen Anh TungNessuna valutazione finora
- Piping Material Take Off-MTO, BOM, BOQ & MTO Stages (With PDFDocumento5 paginePiping Material Take Off-MTO, BOM, BOQ & MTO Stages (With PDFDhiren PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Column Piping: Study Layout, Nozzle Orientation & Platforms RequirementsDocumento23 pagineColumn Piping: Study Layout, Nozzle Orientation & Platforms Requirementsreach_arindomNessuna valutazione finora
- Rebar ArrangmentDocumento116 pagineRebar ArrangmentJesusBlasVitangcol100% (2)
- Guideline - Pump - System - Designers (Pump Fundamentals) PDFDocumento16 pagineGuideline - Pump - System - Designers (Pump Fundamentals) PDFyyukin1100% (1)
- P&ID Check ListDocumento3 pagineP&ID Check Listankur2061Nessuna valutazione finora
- Test Plan TemplateDocumento11 pagineTest Plan Templateapi-3806986100% (8)
- Geotechnical Manual For SlopesDocumento303 pagineGeotechnical Manual For SlopesMarcel Toruño Mendez100% (19)
- P&id PDFDocumento36 pagineP&id PDFSterling GordianNessuna valutazione finora
- en - O.1 - 8131 38Documento61 pagineen - O.1 - 8131 38yones83% (72)
- Pressure Safety ValvesDocumento11 paginePressure Safety Valveschianhho100% (1)
- Introduction To Engineering in Oil&Gas Facilitlities (For Distribution)Documento26 pagineIntroduction To Engineering in Oil&Gas Facilitlities (For Distribution)henryhh111100% (2)
- Process MaddahDocumento263 pagineProcess MaddahparykoochakNessuna valutazione finora
- Line SizingDocumento14 pagineLine SizingSaif MujawarNessuna valutazione finora
- PSV SizingDocumento18 paginePSV SizingGo IELTSNessuna valutazione finora
- General Deliverable of Piping Industry All DepartmentDocumento3 pagineGeneral Deliverable of Piping Industry All Departmentsujay Avati100% (1)
- Line Sizing CalculationsDocumento21 pagineLine Sizing Calculationsjabar sathikNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Engineering Plant Design (Che-441) : Dr. Imran HassanDocumento24 pagineChemical Engineering Plant Design (Che-441) : Dr. Imran HassanHassan KhalidNessuna valutazione finora
- Brief About Atlas CopcoDocumento17 pagineBrief About Atlas CopcorutujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2 Process Engineering-1Documento95 pagineLecture 2 Process Engineering-1ahmed.ayoob.abdNessuna valutazione finora
- Flowsheet LectureDocumento23 pagineFlowsheet LectureAdolfo Perez MonteroNessuna valutazione finora
- MMP-CKL-0007 PID Check ListDocumento5 pagineMMP-CKL-0007 PID Check ListQWAS111Nessuna valutazione finora
- KIL3012 - WEEK 1 - 10.9.19 (Student Copy)Documento61 pagineKIL3012 - WEEK 1 - 10.9.19 (Student Copy)Ed100% (1)
- Flare Line Stress AnalysisDocumento7 pagineFlare Line Stress Analysisdhurjatibhutesh100% (1)
- Korf BrochureDocumento1 paginaKorf Brochurelhphong021191Nessuna valutazione finora
- Technology SelectionDocumento5 pagineTechnology SelectionrutujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculation of Relief Load On ColumnDocumento5 pagineCalculation of Relief Load On Columnnghiemta18Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computation of Dead LoadsDocumento10 pagineComputation of Dead LoadsSyrille Reyes75% (4)
- (SKP) PFD & P&idDocumento43 pagine(SKP) PFD & P&idSuresh Haldipur100% (1)
- Safety in OverpressureDocumento27 pagineSafety in OverpressurevrajakisoriDasiNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Definitions of Overall Engineering PhasesDocumento12 pagineBasic Definitions of Overall Engineering PhasesTamka76100% (1)
- August 2012 IssueDocumento56 pagineAugust 2012 IssueGas, Oil & Mining Contractor Magazine100% (1)
- Industrial: Western European Energy Conservation Technologies For EvaporatorsDocumento33 pagineIndustrial: Western European Energy Conservation Technologies For EvaporatorsPhoe ChitNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Skid TrainingDocumento5 pagineProcess Skid TrainingrutujaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.1 Working Principle of Equipment:: 6.2.1 Steady State Heat TransferDocumento35 pagine6.1 Working Principle of Equipment:: 6.2.1 Steady State Heat TransferAthar IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Design EngineeringDocumento3 pagineProcess Design EngineeringSHIVAM GUPTANessuna valutazione finora
- How Do You Carry Out Estimation? Ans: 1. Input From BidDocumento21 pagineHow Do You Carry Out Estimation? Ans: 1. Input From BidSunil ShaNessuna valutazione finora
- P&id SeminarDocumento30 pagineP&id SeminaryasirvazhikkadavuNessuna valutazione finora
- 10a - Pressure Relief SystemsDocumento3 pagine10a - Pressure Relief SystemsIslam SolimanNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Coolers Versus Shell-And-tube Water CoolersDocumento8 pagineAir Coolers Versus Shell-And-tube Water CoolersDefenceDog67% (3)
- Epcm Services For Installation of "Indresid " Demonstration Plant at PanipatDocumento19 pagineEpcm Services For Installation of "Indresid " Demonstration Plant at Panipatrutuja100% (2)
- Introducers Agreement O.I.L.Ahmedabad and AEC PuneDocumento4 pagineIntroducers Agreement O.I.L.Ahmedabad and AEC PunerutujaNessuna valutazione finora
- 01b. - Design Phases & InformationDocumento9 pagine01b. - Design Phases & InformationAna Carrasco MartínezNessuna valutazione finora
- Procurement of Piping SP Item PDFDocumento1 paginaProcurement of Piping SP Item PDFDinda Putri AmaliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Technology Selection For A Chemical Process GuidelinesDocumento9 pagineTechnology Selection For A Chemical Process GuidelinesrutujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Safeguarding - PSE02Documento2 pagineProcess Safeguarding - PSE02Sarfraz AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Eclipse HandbookDocumento118 pagineEclipse Handbook23Otter100% (1)
- Presentation For PSA Medical Oxygen GeneratorsDocumento10 paginePresentation For PSA Medical Oxygen GeneratorsrutujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Model Review Process X5axp5bsDocumento8 pagineModel Review Process X5axp5bsNadi Jothidan KLNessuna valutazione finora
- Equipment SizingDocumento5 pagineEquipment SizingPandu RockingNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Design Engineering Test-1Documento6 pagineProcess Design Engineering Test-1Vague FruitsNessuna valutazione finora
- Erification Omment Heet: ALPHA ECC-Dehydration Skids Package For Tien Hai Thai Binh ProjectDocumento2 pagineErification Omment Heet: ALPHA ECC-Dehydration Skids Package For Tien Hai Thai Binh ProjectLê Đức ThiệnNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Engineering Course by IfluidsDocumento81 pagineProcess Engineering Course by IfluidsirfichemNessuna valutazione finora
- Process EngineeringDocumento2 pagineProcess EngineeringSuvidya Institute of TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ammonia B PDFDocumento9 pagineAmmonia B PDFmehrdad_k_rNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of PipingDocumento51 pagineDesign of PipingLuisRiosQNessuna valutazione finora
- P&IDDocumento38 pagineP&IDHưng Luca100% (1)
- SAMSUNG SEM-9471E - Process Design Manual - Health and Design Safety Specification Rev0 2004Documento7 pagineSAMSUNG SEM-9471E - Process Design Manual - Health and Design Safety Specification Rev0 2004d_mazieroNessuna valutazione finora
- Automated Valves - GeneralDocumento19 pagineAutomated Valves - Generalhafizi07Nessuna valutazione finora
- 312013145817piping Design Engineering With PDMS Training CourseDocumento4 pagine312013145817piping Design Engineering With PDMS Training CourseAsan IbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Design of Process EquipmentsDocumento2 pagineMechanical Design of Process EquipmentsSuvidya Institute of TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- General Arrangement Drawing: Pump DataDocumento1 paginaGeneral Arrangement Drawing: Pump DataJwardNessuna valutazione finora
- Junín Upgrader Hydrocracking Unit (14) Overall Material BalanceDocumento11 pagineJunín Upgrader Hydrocracking Unit (14) Overall Material BalancegarciahoNessuna valutazione finora
- BepDocumento4 pagineBepkashifwarsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Final PrintDocumento5 pagineFinal PrintMustafa AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Massive Open Online CourseDocumento44 pagineMassive Open Online CourseAdegunju Adedayo SulaimonNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Audit Report (Sample)Documento4 pagineTechnical Audit Report (Sample)रविन्द्र मरघड़ेNessuna valutazione finora
- NSPR Ipp Ac 001Documento1 paginaNSPR Ipp Ac 001rutujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Comments On Equinox - BuHasa Project ScopeDocumento4 pagineComments On Equinox - BuHasa Project ScoperutujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Site Conditions Considered : (The Site Pressure and Pvs Values Are Taken From Vapour Pressure Chart)Documento1 paginaSite Conditions Considered : (The Site Pressure and Pvs Values Are Taken From Vapour Pressure Chart)rutujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Overview: Hazard and Operability (HAZOP) Studies For Supervisors-Team LeadersDocumento3 pagineCourse Overview: Hazard and Operability (HAZOP) Studies For Supervisors-Team LeadersrutujaNessuna valutazione finora
- SVN Process Capability Strength ListDocumento1 paginaSVN Process Capability Strength ListrutujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Enhanced-Gravity-Sizing PackDocumento1 paginaEnhanced-Gravity-Sizing PackrutujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Risk Assessment & Risk Management Outline: Course OverviewDocumento2 pagineProcess Risk Assessment & Risk Management Outline: Course OverviewrutujaNessuna valutazione finora
- HS 08 Working Safely Course OutlineDocumento2 pagineHS 08 Working Safely Course OutlinerutujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Enlistment Form For Engineering Sub-Contractor: L&T-ChiyodaDocumento3 pagineEnlistment Form For Engineering Sub-Contractor: L&T-ChiyodarutujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sour Water Stripper 2Documento2 pagineSour Water Stripper 2rutujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tech Clarification No.1 VaangdenDocumento1 paginaTech Clarification No.1 VaangdenrutujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Design, Fabrication, Supply & Commissioning of Stainless Steel Chemical SkidsDocumento2 pagineDesign, Fabrication, Supply & Commissioning of Stainless Steel Chemical SkidsrutujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vaangden Pte LTD: MOU Strictly ConfidentialDocumento9 pagineVaangden Pte LTD: MOU Strictly ConfidentialrutujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reply E-102 Bottoms Feed Heat ExchangerDocumento1 paginaReply E-102 Bottoms Feed Heat ExchangerrutujaNessuna valutazione finora
- SVN Commented 258A - Proposal - From FOCUS To SVNAIK - CRISIL REPORTDocumento6 pagineSVN Commented 258A - Proposal - From FOCUS To SVNAIK - CRISIL REPORTrutujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Typical PFD For Sour Water Stripper Column: Crude Oil Production Slug CatcherDocumento2 pagineTypical PFD For Sour Water Stripper Column: Crude Oil Production Slug CatcherrutujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 18 - Foundations and Retaining WallsDocumento32 pagineChapter 18 - Foundations and Retaining WallsShyamNessuna valutazione finora
- DEA GuidelinesDocumento2 pagineDEA GuidelinesKawsar AlamNessuna valutazione finora
- Slab With ReportsDocumento36 pagineSlab With ReportsER Manish MakhijaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gate Iitd Ac in EEKey PHPDocumento2 pagineGate Iitd Ac in EEKey PHPshagun gargNessuna valutazione finora
- High-Strength Concrete Structural Walls: Aci Structural Journal Technical PaperDocumento10 pagineHigh-Strength Concrete Structural Walls: Aci Structural Journal Technical PaperSiva GuruNessuna valutazione finora
- Abet Comm2 2015-2016 1Documento2 pagineAbet Comm2 2015-2016 1moneer1994Nessuna valutazione finora
- Residual Strength A N D Crack Propagation Tests O N C-130 Airplane Center Wings With Service-Imposed Fatigue DamageDocumento69 pagineResidual Strength A N D Crack Propagation Tests O N C-130 Airplane Center Wings With Service-Imposed Fatigue DamagemilindshettiNessuna valutazione finora
- Precast Piles For Route 40 Bridge in Virginia Using Concrete Filled FRP TubesDocumento14 paginePrecast Piles For Route 40 Bridge in Virginia Using Concrete Filled FRP TubesmarkicivanNessuna valutazione finora
- Attachment 01-Project Standards & Specifications-PearlDocumento8 pagineAttachment 01-Project Standards & Specifications-Pearlum erNessuna valutazione finora
- SBGH Corporate BrochureDocumento28 pagineSBGH Corporate Brochureomar14saifNessuna valutazione finora
- An Innovative RTM Providing Test Maintenance in An Automated Scripting New FrameworksDocumento5 pagineAn Innovative RTM Providing Test Maintenance in An Automated Scripting New FrameworksInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Fy 2018 Status of Contracts - Report For StakeholderDocumento266 pagineFy 2018 Status of Contracts - Report For StakeholderAngel MilitanteNessuna valutazione finora
- Cheemi SBWZ Temperature Transmitter PDFDocumento2 pagineCheemi SBWZ Temperature Transmitter PDFNguyen SonNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction - Types of BuildingDocumento15 pagineIntroduction - Types of BuildingOmar SakibNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Development PlanDocumento1 paginaDesign Development PlanRajNessuna valutazione finora
- 123 Electrical InspectorDocumento2 pagine123 Electrical InspectorFahimuddin QureshiNessuna valutazione finora
- B.tech (CSE) Curriculum 2015 2016 Final - June 4Documento6 pagineB.tech (CSE) Curriculum 2015 2016 Final - June 4Soumyadeep SenguptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Compression and Capillary Pipe FittingsDocumento2 pagineCompression and Capillary Pipe FittingsstarykltNessuna valutazione finora
- Profile of Dr. Premanand ShenoyDocumento1 paginaProfile of Dr. Premanand ShenoyPremanand ShenoyNessuna valutazione finora
- AcharyaInstitute of Management VS Dayananda Sagar College of EngineeringDocumento7 pagineAcharyaInstitute of Management VS Dayananda Sagar College of EngineeringAdmission DetailsNessuna valutazione finora
- Ucu 3102Documento2 pagineUcu 3102Ishak IshakNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of UPS With Customer Load Management Function Ko, Jae HunDocumento82 pagineDesign of UPS With Customer Load Management Function Ko, Jae HunArmandinho CaveroNessuna valutazione finora
- Fem Analysis of Anchored Sheet Pile Quay Wall: A Case Study On The Failure of Wq-7 Berth of Visakhapatnam PortDocumento7 pagineFem Analysis of Anchored Sheet Pile Quay Wall: A Case Study On The Failure of Wq-7 Berth of Visakhapatnam Portbasum matNessuna valutazione finora