Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Folliculitis Authored by DR Laurence Knott
Caricato da
Laica Nadine Pedronio0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
30 visualizzazioni13 pagineTitolo originale
Folliculitis Authored by Dr Laurence Knott
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
30 visualizzazioni13 pagineFolliculitis Authored by DR Laurence Knott
Caricato da
Laica Nadine PedronioCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 13
Folliculitis Authored by Dr Laurence Knott,
Reviewed by Dr Helen Huins |Last edited 6 Jul
2017 |
Certied by The Information Standard
Folliculitis means an inammation or infection of
the hair follicles of the skin. Most of the skin is
covered with tiny hairs which grow out of hair
follicles. In folliculitis, many hair follicles in one
area of the skin are affected. Folliculitis can be a
mild, short-lived condition or a severe long-term
problem that can literally take over your life.
Unfortunately, this variation in severity can lead
to the notion that it is nothing more than a
passing inconvenience. This can be very
frustrating if you have the more persistent form.
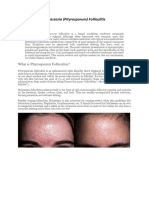
What does folliculitis look like? When hair
follicles become infected, they swell into small
pus-lled pimples. Each individual pimple looks
like a small, rounded, yellow-red spot. SKIN
RASHES 11/9/2019 Folliculitis & Pseudo-
Folliculitis | Prevention, Treatment | Patient
https://patient.info/skin-conditions/skin-
rashes/folliculitis 2/6
Folliculitis can occur anywhere on hair-
bearing skin. (It could not, for example, occur on
the palms of the hands where there is no hair.)
There are a few specic types of folliculitis that
deserve a mention: Sycosis barbae - this is the
medical name for a long-term (chronic)
folliculitis in the beard area of the face in men
(and some women). It often affects the upper lip
and it can be difcult to treat.
The skin is painful and crusted, with burning
and itching on shaving. Numerous pustules
develop in the hair follicles. Some men grow a
beard to solve the problem. Hottub folliculitis -
as the name suggests, this tends to affect people
who use hot tubs a lot. The hot water
encourages germs (bacteria) called
Pseudomonas spp. to grow (particularly if there
is not enough chlorine in the water to keep it
clean).
Bathing in this 'soup' of bacteria can increase
your risk of folliculitis. This type of folliculitis is
generally harmless and is prevented by proper
maintenance of hot tubs. Showering after using
the hot tub does not seem to reduce the chance
of folliculitis. Gram-negative folliculitis - this is a
type of folliculitis that may occur after acne has
been treated with long-term antibiotics.
Different bacteria are involved (not
staphylococci).
Gram-negative refers to a type of stain that
is used in a laboratory to identify different types
of bacteria. What is pseudo-folliculitis? Pseudo-
folliculitis is not really a true folliculitis. It does
look similar, as little lumps form at the bases of
hairs. These lumps do not contain pus. They are
actually due to ingrowing hairs. Sometimes this
problem causes scarring.
Pseudo-folliculitis is more common in people
with curly or Afro-Caribbean hair. As mentioned
above, these can cause a condition that looks
like folliculitis. They are hairs that have curled
around and grown back into the skin. Anyone
can have ingrowing hairs (also called ingrown
hairs), but they are more common in people
who have very curly or coarse hair. Curly hair is
more likely to bend back and re-enter the skin,
especially after it's been shaved or cut.
Ingrowing hairs may also be caused by dead skin
cells blocking the hair growing as normal.
Ingrowing hairs often irritate the skin and
make a raised, red bump (or group of bumps)
that looks like a little pimple. Sometimes the
bump(s) can be painful. In men, ingrowing hairs
often pop up as a bunch of little bumps on the
chin, cheeks, or neck after they've shaved. In
women they often occur on the legs or bikini
area. 11/9/2019 Folliculitis & Pseudo-Folliculitis
| Prevention, Treatment |Patient
https://patient.info/skin-conditions/skin-
rashes/folliculitis 3/6
Often an ingrowing hair will go away on its
own. If it doesn't go away, an ingrowing hair can
become infected, make the skin dark, or leave a
scar. This is more likely if you've been scratching
or picking the hair. Why does folliculitis occur?
Most cases of folliculitis are due to an infection
with a germ (bacterium) called Staphylococcus
aureus(S. aureus).
This bacterium is carried harmlessly in the
noses of many people, without causing any
problems. Occasionally, other germs (bacteria)
are the cause of folliculitis. Folliculitis usually
occurs at sites where hair follicles are damaged
by friction or shaving, or where there is blockage
of the follicle.
Excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis) due to
overactivity of the sweat glands can be another
cause. Sometimes, using a steroid cream on the
face can trigger a bout of folliculitis. The most
common site affected is the beard area of men
although women with facial hair can get it in this
area too. Other common sites for folliculitis are
the arms, legs, armpits and buttocks. Are there
other infections similar to folliculitis? Other
conditions involving hair follicles can occur.
Furuncles and carbuncles are the medical
names for what you would call a boil. Both are
skin infections caused by germs (bacteria) -
usually S. aureus. A furuncle is a skin infection
that involves the hair follicle and surrounding
skin. Clusters of furuncles can join together
under the surface of the skin, forming a
carbuncle. A carbuncle means the infection has
spread more deeply in the skin and scarring is
more likely.
Carbuncles and furuncles are generally much
bigger and more painful than the tiny pustules
you get in folliculitis. They may need to be cut
into (incised) and drained (lanced) to let the pus
out. Sometimes acne can look similar to
folliculitis too. The main difference is that in
acne, the hair follicles become plugged with oils
(from glands in the skin) and dead skin cells.
There may also be an overgrowth of certain
bacteria that can live in hair follicles. What is the
treatment for folliculitis?
Wherever the folliculitis occurs, the
treatment principle is broadly the same. General
measures involve avoiding things that aggravate
the condition. It is important to shave in the
direction of hair growth. Sometimes it is worth
taking a break from shaving for a few days, to let
the folliculitis 11/9/2019 Folliculitis & Pseudo-
Folliculitis | Prevention, Treatment | Patient
https://patient.info/skin-conditions/skin-
rashes/folliculitis 4/6
settle down by itself. Tight clothing over the
affected area, particularly if it makes you sweat,
will not help either. Keeping cool and keeping
folliculitis exposed to the fresh air will also help.
If you have folliculitis you should not share
towels, annels or razors. Mild cases Most cases
or folliculitis are mild and do not need any
treatment. It often clears without any treatment
within 7-10 days. It may be helpful to use a
moisturiser (emollient) which contains an
antibacterial agent - for example, Dermol®
cream or lotion or Emulsiderm®.
This will improve the condition of the skin
and soothe it. It may help the folliculitis to clear
more quickly and reduce the risk of it becoming
worse. You can use one of these emollients as a
soap substitute until the folliculitis has cleared.
Specic preparations for the bath or shower are
available - for example, Dermol® 200 Shower
Emollient, Dermol 600® Bath Emollient and
Oilatum® Plus bath additive. If simple measures
over a few days do not allow the folliculitis to
improve, you should probably see your GP for
further advice and treatment. Localised
folliculitis.
For localised areas of folliculitis, an antibiotic
cream may be useful. Fusidic acid is a suitable
antibiotic cream that can be applied 3-4 times
per day to affected areas. More severe cases If
the folliculitis is more severe or widespread then
a course of antibiotic tablets may be needed.
Recurrent or long-term (chronic) folliculitis
Recurrent folliculitis occurs when the infection
keeps coming back, although it disappears with
treatment. The gaps between episodes may get
shorter and, eventually, chronic folliculitis is the
result. In these cases, your GP may take a sample
(swab) from the skin where the folliculitis is. This
swab can show what germs (bacteria) are
responsible for the infection. If the swab conrms
S. aureus, it is a good idea to take some more
swabs, usually from the nose, to see if you are a
carrier of this germ (bacterium).
If you do carry staphylococci in the nose and
you get recurrent folliculitis (or if you have
chronic folliculitis), this is likely to be the reason
behind it. Treatment is to destroy (eradicate) the
staphylococci and prevent further folliculitis.
This will usually involve three forms of
treatment to be used at the same time. First, a
course of antibiotic tablets. Second, a course of
an antibiotic nasal cream. Because the
staphylococci may also be on other parts of the
body, not just where the 11/9/2019 Folliculitis &
Pseudo-Folliculitis
| Prevention, Treatment | Patient
https://patient.info/skin-conditions/skin-
rashes/folliculitis 5/6
folliculitis is, it is also advisable to use an
antiseptic skin wash or shower gel. Products
containing chlorhexidine (for example,
Hibiscrub® 4% solution or Hydrex® 4% surgical
scrub) or Ster-Zac Bath Concentrate®) are
suitable. You should also launder clothing, bed
linens and towels on a hot wash. This will
prevent you getting re-infection and also reduce
the risk of passing the infection to others.
Finally, you will need to have repeat swabs
to conrm that you are clear of the bacteria -
three clear swabs over a three-week period will
conrm the staphylococcal infection has been
eradicated. How can folliculitis be prevented?
Keeping your skin clean, dry and free from
abrasions or irritations can help to prevent
folliculitis. Certain people are more prone to
infections, such as people with diabetes. If you
have a medical problem that makes you more
likely to get infections, these precautions may be
more important.
Using antiseptic washes routinely is not
generally recommended, as they can make the
skin sore and dry. Keeping the skin moisturised
can help protect it from damage. Take care
when shaving (especially if you wet shave), using
a shaving gel, foam or soap to lubricate the
blades across the skin and prevent nicks and
cuts. Most cases of folliculitis are not contagious
but if you have been identied as carrying the S.
aureus germ (bacterium), this infection can
occasionally be transferred to other people.
This risk can be minimised by normal
hygiene measures and laundering clothing, bed
linens and towels on a hot wash. Do not share
razors. You should also avoid sharing hot tubs
and Jacuzzis® until the infection has been
treated. Join our weekly wellness digest from
the best health experts in the business Enter
your email By clicking ‘Join now’ you agree to
our Terms and conditions and Privacy policy.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- FolliculitisDocumento5 pagineFolliculitisShreya BasakNessuna valutazione finora
- Folliculitis, A Simple Guide To the Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesDa EverandFolliculitis, A Simple Guide To the Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesNessuna valutazione finora
- Folliculitis Decalvans Update July 2019 - Lay Reviewed July 2019Documento4 pagineFolliculitis Decalvans Update July 2019 - Lay Reviewed July 2019sjeyarajah21Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is FolliculitisDocumento2 pagineWhat Is Folliculitisaashwini kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Folliculitis Demystified: Doctor's Secret GuideDa EverandFolliculitis Demystified: Doctor's Secret GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- Viral and Bacterial Infections of The SkinDocumento200 pagineViral and Bacterial Infections of The SkinKarla Jane100% (1)
- Acne: The nutritional approach for clear skin (A simple and suitable diet to totally cure Acnes in your body)Da EverandAcne: The nutritional approach for clear skin (A simple and suitable diet to totally cure Acnes in your body)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Folliculitis Barbae Update April 2017 - Lay Reviewed March 2017Documento4 pagineFolliculitis Barbae Update April 2017 - Lay Reviewed March 2017rahul jindalNessuna valutazione finora
- A Simple Guide to Fungal Acne, (Pityrosporum folliculitis) Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsDa EverandA Simple Guide to Fungal Acne, (Pityrosporum folliculitis) Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Acne vulgaris, (Updated) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandAcne vulgaris, (Updated) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsValutazione: 2 su 5 stelle2/5 (1)
- Homoeopathic Management of BoilsDocumento14 pagineHomoeopathic Management of BoilsVANSHRAJ AMALIYARNessuna valutazione finora
- Staph Skin Infections: Pictures, Causes, Risk Factors & TypesDocumento12 pagineStaph Skin Infections: Pictures, Causes, Risk Factors & Typesrunv25Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pityrosporum Folliculitis: Yeast Overgrowth Causes Itchy BumpsDocumento6 paginePityrosporum Folliculitis: Yeast Overgrowth Causes Itchy BumpsAndy Sugiharto WonodiharjoNessuna valutazione finora
- Skin DiseasesDocumento11 pagineSkin DiseasesMuhamad RidhoNessuna valutazione finora
- Superficial FolliculitisDocumento6 pagineSuperficial FolliculitisSauZen SalaZarNessuna valutazione finora
- Furuncles and Carbuncles: Bacterial Skin InfectionsDocumento19 pagineFuruncles and Carbuncles: Bacterial Skin InfectionsKylie GolindangNessuna valutazione finora
- Acne Success: The Essential Guide to Curing Acne for LifeDa EverandAcne Success: The Essential Guide to Curing Acne for LifeNessuna valutazione finora
- Homeopathic treatment and management of boilsDocumento24 pagineHomeopathic treatment and management of boilsVANSHRAJ AMALIYARNessuna valutazione finora
- TypesDocumento2 pagineTypesShreya BasakNessuna valutazione finora
- A Simple Guide To Miliaria, (Prickly Heat) Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandA Simple Guide To Miliaria, (Prickly Heat) Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Warts (Verruca) : Local Growth SurfaceDocumento4 pagineWarts (Verruca) : Local Growth SurfaceIbrahim AbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Subcorneal Pustular Dermatosis Draft Update January 2017 - Lay Review January 2017Documento3 pagineSubcorneal Pustular Dermatosis Draft Update January 2017 - Lay Review January 2017Andi Hardianti SucitraNessuna valutazione finora
- Impetigo, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandImpetigo, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Pseudofolliculitis barbae (Razor Bumps), A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandPseudofolliculitis barbae (Razor Bumps), A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Scabies PeduculosisDocumento35 pagineScabies PeduculosisSean MercadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pityriasis VersicolorDocumento3 paginePityriasis VersicolorJamalul AdilNessuna valutazione finora
- A Simple Guide to Pilonidal Sinus, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsDa EverandA Simple Guide to Pilonidal Sinus, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitiligo, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandVitiligo, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsValutazione: 2 su 5 stelle2/5 (1)
- Pit VeriscolorDocumento5 paginePit VeriscolorNida Fithria FadhilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pityrosporum FolliculitisDocumento3 paginePityrosporum Folliculitisshivam18Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ringworm Types and Treatment in ChildrenDocumento9 pagineRingworm Types and Treatment in ChildrenPapitas FritasNessuna valutazione finora
- A Simple Guide to Butterfly Skin Disease (Epidermolysis Bullosa), Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsDa EverandA Simple Guide to Butterfly Skin Disease (Epidermolysis Bullosa), Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Fish Scale Disease, (Ichthyosis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandFish Scale Disease, (Ichthyosis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Fungal AcneDocumento54 pagineFungal AcneMellia BeautycareNessuna valutazione finora
- Eczema No More: The Complete Guide to Natural Cures for Eczema and a Holistic System to End Eczema & Clear Your Skin Naturally & PermanentlyDa EverandEczema No More: The Complete Guide to Natural Cures for Eczema and a Holistic System to End Eczema & Clear Your Skin Naturally & PermanentlyValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Seborrheic Dermatitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandSeborrheic Dermatitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Herbal Products For Acne Vulgaris A ReviewDocumento19 pagineHerbal Products For Acne Vulgaris A ReviewSilvester HendryNessuna valutazione finora
- Skin Care Tips: Some Suggestions On Taking Care Of Your Body's Largest OrganDa EverandSkin Care Tips: Some Suggestions On Taking Care Of Your Body's Largest OrganNessuna valutazione finora
- I. Overview:: Acne (Acne Vulgaris) Is A Skin Condition That Occurs When Your Hair Follicles Become Pilosebaceous UnitDocumento14 pagineI. Overview:: Acne (Acne Vulgaris) Is A Skin Condition That Occurs When Your Hair Follicles Become Pilosebaceous UnitTruong DangNessuna valutazione finora
- AcneDocumento12 pagineAcneAli RizgarNessuna valutazione finora
- Miliaria (Heat Rash), A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandMiliaria (Heat Rash), A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- GENOVE, ERICKA IS-Module2Documento11 pagineGENOVE, ERICKA IS-Module2Ericka GenoveNessuna valutazione finora
- Get Rosacea Under Control Immediately: Practical GuideDa EverandGet Rosacea Under Control Immediately: Practical GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- SKIN DISORDERS AND DISEASES HandoutsDocumento9 pagineSKIN DISORDERS AND DISEASES HandoutsMARIALUPE ESTOQUENessuna valutazione finora
- Acne to a Clear Skin: Saying Goodbye to all Skin Blemishes in 7 DaysDa EverandAcne to a Clear Skin: Saying Goodbye to all Skin Blemishes in 7 DaysNessuna valutazione finora
- Keratosis Pilaris Updated Nov 2021 Lay Reviewed Oct 2021 1Documento4 pagineKeratosis Pilaris Updated Nov 2021 Lay Reviewed Oct 2021 1Bhavani KirthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Acne: Learn the Most Effective Methods to Get Rid of Acne (Nature and Science Together Help You to Get Rid of Pimples)Da EverandAcne: Learn the Most Effective Methods to Get Rid of Acne (Nature and Science Together Help You to Get Rid of Pimples)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Supplementary MaterialsDocumento22 pagineSupplementary MaterialsMARIA CECILIA TAPIRONessuna valutazione finora
- Hair Loss In Women: The Ultimate Hair Loss Book For Every WomanDa EverandHair Loss In Women: The Ultimate Hair Loss Book For Every WomanNessuna valutazione finora
- Skin Infections, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandSkin Infections, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Treatment and Prevention of Pediculosis (Lice InfestationDocumento3 pagineTreatment and Prevention of Pediculosis (Lice InfestationAdrian MangahasNessuna valutazione finora
- AMA Manual 10th Edition PDFDocumento1.014 pagineAMA Manual 10th Edition PDFKannan Fangs S100% (2)
- Ko vs. Atty. Uy-LampasaDocumento1 paginaKo vs. Atty. Uy-LampasaMaria Janelle RosarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Dance Manual W. Learning Outcomes PDFDocumento8 pagineDance Manual W. Learning Outcomes PDFJoshua Quijano LamzonNessuna valutazione finora
- HDFDJH 5Documento7 pagineHDFDJH 5balamuruganNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal Entry DiscussionDocumento8 pagineJournal Entry DiscussionAyesha Eunice SalvaleonNessuna valutazione finora
- Treatise On Vocal Performance and Ornamentation by Johann Adam Hiller (Cambridge Musical Texts and Monographs) (2001)Documento211 pagineTreatise On Vocal Performance and Ornamentation by Johann Adam Hiller (Cambridge Musical Texts and Monographs) (2001)Lia Pestana RocheNessuna valutazione finora
- Ohp (2171912)Documento8 pagineOhp (2171912)rajushamla9927Nessuna valutazione finora
- HDFC Bank's Organizational Profile and BackgroundDocumento72 pagineHDFC Bank's Organizational Profile and Backgroundrohitkh28Nessuna valutazione finora
- An Empirical Study of Car Selection Factors - A Qualitative & Systematic Review of LiteratureDocumento15 pagineAn Empirical Study of Car Selection Factors - A Qualitative & Systematic Review of LiteratureadhbawaNessuna valutazione finora
- DDAL05-02 The Black RoadDocumento45 pagineDDAL05-02 The Black Roadlpokm100% (1)
- Preterite vs Imperfect in SpanishDocumento16 paginePreterite vs Imperfect in SpanishOsa NilefunNessuna valutazione finora
- Angel Turns 18 Debut ScriptDocumento2 pagineAngel Turns 18 Debut ScriptChristian Jorge Lenox100% (1)
- Reviewer in Intermediate Accounting IDocumento9 pagineReviewer in Intermediate Accounting ICzarhiena SantiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Download Test Bank For Macroeconomics 11th Edition Arnold PDF Full ChapterDocumento36 pagineFull Download Test Bank For Macroeconomics 11th Edition Arnold PDF Full Chaptervitalizefoothook.x05r100% (17)
- Corporate Process Management (CPM) & Control-EsDocumento458 pagineCorporate Process Management (CPM) & Control-EsKent LysellNessuna valutazione finora
- This Study Resource Was: Solving Problems Using Counting Techniques - TestDocumento5 pagineThis Study Resource Was: Solving Problems Using Counting Techniques - TestVisalini RagurajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Vaccination Consent Form: Tetanus, Diphtheria / Inactivated Polio Vaccine (DTP) & Meningococcal ACWY (Men ACWY)Documento2 pagineVaccination Consent Form: Tetanus, Diphtheria / Inactivated Polio Vaccine (DTP) & Meningococcal ACWY (Men ACWY)meghaliNessuna valutazione finora
- GUCR Elections Information 2017-2018Documento10 pagineGUCR Elections Information 2017-2018Alexandra WilliamsNessuna valutazione finora
- Lauritzen 1964Documento10 pagineLauritzen 1964Priyanka GandhiNessuna valutazione finora
- OF Ministry Road Transport Highways (Road Safety Cell) : TH THDocumento3 pagineOF Ministry Road Transport Highways (Road Safety Cell) : TH THAryann Gupta100% (1)
- Lecture 9-EVENT BUDGETDocumento19 pagineLecture 9-EVENT BUDGETAlbina AbilkairNessuna valutazione finora
- Crypt of Cthulhu 49 1987 Cosmic-JukeboxDocumento71 pagineCrypt of Cthulhu 49 1987 Cosmic-JukeboxNushTheEternal100% (3)
- Importance of Time Management To Senior High School Honor StudentsDocumento7 pagineImportance of Time Management To Senior High School Honor StudentsBien LausaNessuna valutazione finora
- E GCOct 2013 NsDocumento0 pagineE GCOct 2013 Nsvae2797Nessuna valutazione finora
- ExpressionismDocumento16 pagineExpressionismRubab ChaudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Review Activity For The Final Test - 6 Level: 1. Match Phrasal Verbs and Match To The MeaningDocumento3 pagineReview Activity For The Final Test - 6 Level: 1. Match Phrasal Verbs and Match To The MeaningGabrielle CostaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Revival Strategies of Vespa Scooter in IndiaDocumento4 pagineThe Revival Strategies of Vespa Scooter in IndiaJagatheeswari SelviNessuna valutazione finora
- Ds B2B Data Trans 7027Documento4 pagineDs B2B Data Trans 7027Shipra SriNessuna valutazione finora
- Swot AnalysisDocumento6 pagineSwot AnalysisSneha SinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Apexocardiograma Precizari PracticeDocumento12 pagineApexocardiograma Precizari PracticeDaniel VelciuNessuna valutazione finora