Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Purchasing and Procurement Strategy
Caricato da
Moccha Ling100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
140 visualizzazioni3 pagineThe document discusses a purchasing and procurement strategy, which is a long-term plan to obtain necessary supplies in a cost-effective manner from efficient suppliers who meet procurement terms and deadlines. It notes that a robust strategic procurement approach covers five areas: procurement and contract management, supplier management, process management, transaction management, and organizational structure. Each area is then described in terms of characteristics of traditional, emerging, advanced, and world-class approaches.
Descrizione originale:
purchasing
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThe document discusses a purchasing and procurement strategy, which is a long-term plan to obtain necessary supplies in a cost-effective manner from efficient suppliers who meet procurement terms and deadlines. It notes that a robust strategic procurement approach covers five areas: procurement and contract management, supplier management, process management, transaction management, and organizational structure. Each area is then described in terms of characteristics of traditional, emerging, advanced, and world-class approaches.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
140 visualizzazioni3 paginePurchasing and Procurement Strategy
Caricato da
Moccha LingThe document discusses a purchasing and procurement strategy, which is a long-term plan to obtain necessary supplies in a cost-effective manner from efficient suppliers who meet procurement terms and deadlines. It notes that a robust strategic procurement approach covers five areas: procurement and contract management, supplier management, process management, transaction management, and organizational structure. Each area is then described in terms of characteristics of traditional, emerging, advanced, and world-class approaches.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 3
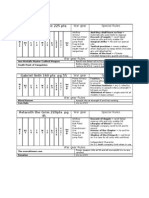
PURCHASING AND PROCUREMENT STRATEGY
The term purchasing and procurement strategy is a long-term plan to obtain the
necessary supplies cost-effectively from an efficient list of suppliers who will comply
with procurement terms and deliver on time. In general, a purchasing strategy depends
on many factors, such as purchase schedules, available budgets, total cost of
ownership (TCO), possible risks, and so on. A robust strategic procurement approach
may cover at least five basic areas, including procurement management and contract
management, process management, supplier management, transaction management,
organization.
First, Procurement and contract management typically includes the selection of
suppliers, procurement of goods and contract negotiations, and companies may take
these characteristics into account when evaluating strategic procurement capabilities:
companies with traditional procurement and contract management practices often
have the following characteristics: local suppliers with multiple sources and minimal
purchasing power; Companies with emerging procurement and contract management
practices often have the following characteristics: the usual use of domestic suppliers
with multiple or dual sources, some cross-functional procurement practices, focusing
on the lowest delivery costs, annual contract negotiations, bidding to obtain good
prices, and reliance on suppliers for cost data and basic cost analysis. Companies with
advanced procurement and contract management practices typically establish supplier
relationships, conduct global assessments or negotiate procurement, decide on a single
purchase of standard materials by a formal, cross-functional material group, leverage
the procurement of critical goods, focusing on overall value and overall cost
management, and use multi-year contract agreements with service levels. Companies
with world-class procurement and contract management practices typically use
strategic procurement for most or all of their materials, adopt a multi-faceted
approach to procurement, establish strategic alliances, select suppliers based in the
same location, coordinate and coordinate supply chain activities, establish lifecycle
procurement agreements, network-based negotiations (e.g. on-going bids/ask supms,
reverse auctions), and manage their own expenses, suppliers, and material data.
Second, Supplier management typically includes process such as supplier relationship
management, supplier development, and supplier performance management. When
evaluating strategic sourcing capabilities, companies can consider the following
characteristics. Traditional supplier management behaviour usually includes a large
number of dispersed suppliers with few specific relationships; emerging supplier
management behaviour typically includes preference for suppliers with limited
relationship structure, supplier evaluation systems and two-way communication,
product certification from key suppliers, on-site inspection, survey, review of
suppliers, and limited joint suppliers. Advanced supplier management typically
includes formal supplier certification, service-level agreements, including codes of
conduct and formal evaluation, and understanding of supplier cost composition.
World-class supplier management behaviours are usually self-certified by suppliers,
key vendor account management, strategic relationships and in-business supply
networks, systematic behavioural assessment feedback, simultaneous two-way
communication, and definition of supplier rationalization procedures.
Third, Processing management typically includes the following procedures: design
management, component/product standardization, cost management, capital usage
performance. In evaluating processing management capabilities, enterprises may take
these characteristics into account: enterprises with traditional processing management
practices often do not have the involvement of suppliers in design and manufacture as
required. Companies with emerging processing management practices often exhibit a
supply-to-buy joint processing movement, with suppliers providing higher value-
added content; Merchants with advanced processing management practices often have
interactive (design/procurement/re-design) procedures with technology transfer
forums; Companies with world-class processing management behaviour sit in the
supply-buyer design team to jointly design and share full design responsibilities with
suppliers, coordinate design with suppliers over the network, and share content
management and decision support tools.
Forth, Transaction management usually includes requesting orders, placing purchase
orders, tracking orders, and receiving orders. In evaluating transaction management
capabilities, companies can consider these characteristics: traditional transaction
management practices are often paper-based, including requiring multiple layers of
approval, requiring the buyer to select a supplier, purchasing products for delivery,
paper catalogues, tracking by phone or fax. Emerging transaction management
behaviour softens with technical point solutions, which are related to purchase and
planning, place orders online, and track through EDI. Advanced transaction
management practices typically use internal integration systems/technology, check
items online and request orders, pre-approve purchases, and check shipments through
the supplier's website. World-class transaction management behaviour typically
includes electronic contact with suppliers, real-time coordination, electronic
acquisition capabilities, dynamic online trading engines and catalogues, and visually
coordinated orders.
Lastly, Organizational structures and the ability to support strategic procurement
procedures include organizational design, behaviour planning, code of conduct, and
cost measurement. "In assessing organizational competence, firms may consider the
following characteristics: companies with traditional organizational structures and
competencies often focus on functional and narrow job descriptions, and the
organization's charter revolves around a formal buying organization that measures
performance against internal criteria." Companies with emerging organizational
structures and capabilities tend to have commercial-level buying behaviours, matrix
organizations, some commodity procurement plans, formal behavioural management
procedures and norms, succession and career plans, and shareholder awareness.
Merchants with advanced organizational structure and capabilities often have
procurement strategies that are linked to the entire business strategy, strong
administrative-level support, central coordination and local procurement management,
and cross-functional coordination. Companies with world-class organizational
structures and capabilities have a global supply chain vision, pre-emptively change
management processes, business-oriented functions and procedures, focus on
innovation, and strong communication and change management capabilities. It is the
companies that can win in the global economy to constantly assess their behaviour to
ensure that they are not at the forefront. Strategic procurement is an important element
of today's competitive business environment. Using the assessment criteria outlined
above can help identify areas for improvement.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Lect 5 What Is Strategic ProcurementDocumento3 pagineLect 5 What Is Strategic ProcurementAqsa FarooqNessuna valutazione finora
- Procurement Manager - ResponsibilitiesDocumento3 pagineProcurement Manager - ResponsibilitiesAsif ChougleNessuna valutazione finora
- Weele 5th Ed - Chapter 03Documento17 pagineWeele 5th Ed - Chapter 03Neha SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sourcing & ProcurementDocumento2 pagineSourcing & ProcurementShyamsundar RNessuna valutazione finora
- Is Procurement Category Management Right For Your BusinessDocumento7 pagineIs Procurement Category Management Right For Your BusinessTanuj BhattacharyyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.principle Unit 1Documento18 pagine1.principle Unit 1musonza murwiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Sourcing and ProcurementDocumento14 pagineSourcing and Procurementgeorge aarthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 1 Purchasing and Supplies ManagementDocumento13 pagineTopic 1 Purchasing and Supplies Managementtashabriana86Nessuna valutazione finora
- Purchasing and Vendor Management Lecture 6Documento34 paginePurchasing and Vendor Management Lecture 6dinesh9936115534100% (4)
- SCM301 MDocumento19 pagineSCM301 MHà My NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- Responsiveness Is The Ability To Respond To Customers' Requirements in EverDocumento25 pagineResponsiveness Is The Ability To Respond To Customers' Requirements in EverDương Xuân NamNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 - Procurement & SourcingDocumento7 pagineChapter 4 - Procurement & SourcingMaham ShaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- The Challenge of Purchasing and Supply ManagementDocumento48 pagineThe Challenge of Purchasing and Supply ManagementWaseem Ahmed HingorjoNessuna valutazione finora
- SCM ch05Documento84 pagineSCM ch05Hasan RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Procurement ManagementDocumento32 pagineProcurement ManagementmemeNessuna valutazione finora
- An Introduction To Strategic SourcingDocumento29 pagineAn Introduction To Strategic SourcingAdeen ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Procurement Management Lecture Notes by Bagaya Ramathan PDFDocumento11 pagineStrategic Procurement Management Lecture Notes by Bagaya Ramathan PDFFatmata Sheriff KamaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Improving Warehouse Productivity: WarehousingDocumento14 pagineImproving Warehouse Productivity: WarehousingEllah Mae Cao - CasitasNessuna valutazione finora
- Procurement ManagementDocumento8 pagineProcurement ManagementManoj AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Supply Chain Chapter 3Documento55 pagineSupply Chain Chapter 3Youssef Ait zahraNessuna valutazione finora
- The Purpose of Operations FunctionDocumento3 pagineThe Purpose of Operations FunctionSaleem RomeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Materials Management - Class NotesDocumento76 pagineMaterials Management - Class NotesKarthick Sivaraman84% (31)
- MODULE-II Sourcing ManagementDocumento14 pagineMODULE-II Sourcing ManagementumeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Procurement Manual Group WorkDocumento7 pagineProcurement Manual Group WorkEnock MaunyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 LogisticsDocumento8 pagineChapter 6 Logisticseviegonzalez21175% (4)
- Supply Chain ManagementDocumento23 pagineSupply Chain ManagementSri Sarveentaran100% (1)
- S&VM Practice Questions Piyush - GautamDocumento8 pagineS&VM Practice Questions Piyush - GautamPIYUSH GAUTAMNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategy 2.0Documento28 pagineStrategy 2.0takudzwa kunakaNessuna valutazione finora
- Purchasing and Procurement1234Documento11 paginePurchasing and Procurement1234ekojamichaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Project and Sourcing ManagementDocumento28 pagineProject and Sourcing ManagementDEEPANSHI SONI100% (1)
- ISP-purchasing Cycle-Procurement Cycle 2021Documento9 pagineISP-purchasing Cycle-Procurement Cycle 2021Nic chicNessuna valutazione finora
- I. Describe of Definition or Content of Items: 1. Supply ChainDocumento14 pagineI. Describe of Definition or Content of Items: 1. Supply ChainlctrinhNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Procurement ManagementDocumento30 pagineWhat Is Procurement Managementcompiler&automataNessuna valutazione finora
- Sourcing Management: Post Graduate Diploma in Supply Chain ManagementDocumento6 pagineSourcing Management: Post Graduate Diploma in Supply Chain ManagementEnamul Huque SarkerNessuna valutazione finora
- Sourcing Management - 1Documento31 pagineSourcing Management - 1Sad FrogNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar Questions For Topic One Baf 2Documento23 pagineSeminar Questions For Topic One Baf 2Edgar WistonNessuna valutazione finora
- Logistics Management: Definition: Logistics Is The Process of StrategicallyDocumento9 pagineLogistics Management: Definition: Logistics Is The Process of StrategicallyashwinNessuna valutazione finora
- Great Links To Read:: All Necessary Components of Negotiation PreparationDocumento11 pagineGreat Links To Read:: All Necessary Components of Negotiation Preparationerinc bahceciNessuna valutazione finora
- Supply Chain Management SCMDocumento5 pagineSupply Chain Management SCMAce Shernyll Son GallanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Block 1: Supply Management and Procurement OverviewDocumento63 pagineLearning Block 1: Supply Management and Procurement OverviewBon-Boni Arnaiz100% (1)
- Assignment 2Documento4 pagineAssignment 2Anam ShoaibNessuna valutazione finora
- Materials Management Class Notes PDFDocumento76 pagineMaterials Management Class Notes PDFraum123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Procurement & Sourcing Strategy: Characteristics of World Class SuppliersDocumento7 pagineProcurement & Sourcing Strategy: Characteristics of World Class SuppliersaashanNessuna valutazione finora
- Benchmarking Study of Strategic Sourcing PracticesDocumento2 pagineBenchmarking Study of Strategic Sourcing PracticesPepe CMNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Procurement NotesDocumento58 paginePrinciples of Procurement Notesvincent nemadzivaNessuna valutazione finora
- ProcurementDocumento31 pagineProcurementfeteneNessuna valutazione finora
- Sourcing ManagementDocumento31 pagineSourcing Managementtipu azizNessuna valutazione finora
- Sourcing and ProcurementDocumento16 pagineSourcing and Procurementgeorge aarthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Retailer Supplier PartnershipDocumento12 pagineRetailer Supplier PartnershipSanjeev Bishnoi100% (1)
- Module 3Documento19 pagineModule 3Sanak Aditya MannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 1 - Fundamentals of ProcurementDocumento8 pagineTopic 1 - Fundamentals of ProcurementsimushiNessuna valutazione finora
- Procurement Challenges and Solutions - Fleet and Transport ManagementDocumento22 pagineProcurement Challenges and Solutions - Fleet and Transport Managementtonderai mangozheNessuna valutazione finora
- Category Management GTDocumento2 pagineCategory Management GTArun MaithaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Materials Management Ec IVDocumento92 pagineMaterials Management Ec IVshivashankaracharNessuna valutazione finora
- Ba AssisgnmentDocumento19 pagineBa Assisgnmentayshwarya sudheerNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 8Documento29 pagineTopic 8Mohamed K MarahNessuna valutazione finora
- Supplier Relationship ManagementDocumento6 pagineSupplier Relationship ManagementMadeleine TinteiaNessuna valutazione finora
- L7 Prodqua-1Documento2 pagineL7 Prodqua-1Catherine AborNessuna valutazione finora
- ERRC Grid and Blue Ocean StrategyDocumento2 pagineERRC Grid and Blue Ocean StrategyfereNessuna valutazione finora
- Tecson VS Glaxo LaborDocumento2 pagineTecson VS Glaxo LaborDanyNessuna valutazione finora
- Form Audit QAV 1&2 Supplier 2020 PDFDocumento1 paginaForm Audit QAV 1&2 Supplier 2020 PDFovanNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Amendment Form: 1 General InformationDocumento3 pagineFinancial Amendment Form: 1 General InformationRandolph QuilingNessuna valutazione finora
- Q1Documento16 pagineQ1satyamNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Angels Ref SheetsDocumento4 pagineBlood Angels Ref SheetsAndrew ThomasNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Seniority List of HM (High), I.s., 2013Documento18 pagineFinal Seniority List of HM (High), I.s., 2013aproditiNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes (Part 1) : Accounting Policies, Changes in Estimates and ErrorsDocumento13 pagineNotes (Part 1) : Accounting Policies, Changes in Estimates and ErrorsPaula Bautista100% (2)
- GHMC Results, 2009Documento149 pagineGHMC Results, 2009UrsTruly kotiNessuna valutazione finora
- General Terms Conditions For Sales Purchases LPG and Chemical TankersDocumento34 pagineGeneral Terms Conditions For Sales Purchases LPG and Chemical TankersSally AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Sharmeen Obaid ChinoyDocumento5 pagineSharmeen Obaid ChinoyFarhan AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Testamentary Succession CasesDocumento69 pagineTestamentary Succession CasesGjenerrick Carlo MateoNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Enterprise Simulation Quarter 3 - Module 2 - Lesson 1: Analyzing The MarketDocumento13 pagineBusiness Enterprise Simulation Quarter 3 - Module 2 - Lesson 1: Analyzing The MarketJtm GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- General Concepts and Principles of ObligationsDocumento61 pagineGeneral Concepts and Principles of ObligationsJoAiza DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- DocumentDocumento2 pagineDocumentHP- JK7Nessuna valutazione finora
- List of Departed Soul For Daily PrayerDocumento12 pagineList of Departed Soul For Daily PrayermoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Medieval Societies The Central Islamic LDocumento2 pagineMedieval Societies The Central Islamic LSk sahidulNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER - 3 - Creating Responsive Supply ChainDocumento23 pagineCHAPTER - 3 - Creating Responsive Supply Chainsyazwani aliahNessuna valutazione finora
- Turtle Walk WaiverDocumento1 paginaTurtle Walk Waiverrebecca mott0% (1)
- CompTIA Network+Documento3 pagineCompTIA Network+homsom100% (1)
- Holiday/Vacation Policy: Annual HolidaysDocumento18 pagineHoliday/Vacation Policy: Annual HolidaysmalaysianheartNessuna valutazione finora
- Vayigash BookletDocumento35 pagineVayigash BookletSalvador Orihuela ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- History and Culture of The Indian People, Volume 10, Bran Renaissance, Part 2 - R. C. Majumdar, General Editor PDFDocumento1.124 pagineHistory and Culture of The Indian People, Volume 10, Bran Renaissance, Part 2 - R. C. Majumdar, General Editor PDFOmkar sinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Quranic Studies PDFDocumento19 pagineChapter 1 Introduction To Quranic Studies PDFtaha zafar100% (3)
- 14CFR, ICAO, EASA, PCAR, ATA Parts (Summary)Documento11 pagine14CFR, ICAO, EASA, PCAR, ATA Parts (Summary)therosefatherNessuna valutazione finora
- Comprehensive Problem Excel SpreadsheetDocumento23 pagineComprehensive Problem Excel Spreadsheetapi-237864722100% (3)
- Types of Business LettersDocumento11 pagineTypes of Business LettersernewstNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 GMC Individuals Round 1 ResultsDocumento2 pagine2016 GMC Individuals Round 1 Resultsjmjr30Nessuna valutazione finora
- Archbishop Averky Taushev - Stand Fast in The TruthDocumento14 pagineArchbishop Averky Taushev - Stand Fast in The Truthdorin_jambaNessuna valutazione finora
- Coursework Assignment: Graduate Job ImpactDocumento13 pagineCoursework Assignment: Graduate Job ImpactmirwaisNessuna valutazione finora
- The Coaching Habit: Say Less, Ask More & Change the Way You Lead ForeverDa EverandThe Coaching Habit: Say Less, Ask More & Change the Way You Lead ForeverValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (186)
- The Millionaire Fastlane: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeDa EverandThe Millionaire Fastlane: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Summary of Steven Bartlett's The Diary of a CEODa EverandSummary of Steven Bartlett's The Diary of a CEOValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (4)
- High Road Leadership: Bringing People Together in a World That DividesDa EverandHigh Road Leadership: Bringing People Together in a World That DividesNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of Noah Kagan's Million Dollar WeekendDa EverandSummary of Noah Kagan's Million Dollar WeekendValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- The First Minute: How to start conversations that get resultsDa EverandThe First Minute: How to start conversations that get resultsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (57)
- Billion Dollar Lessons: What You Can Learn from the Most Inexcusable Business Failures of the Last Twenty-five YearsDa EverandBillion Dollar Lessons: What You Can Learn from the Most Inexcusable Business Failures of the Last Twenty-five YearsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (52)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Da EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Summary: The 5AM Club: Own Your Morning. Elevate Your Life. by Robin Sharma: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandSummary: The 5AM Club: Own Your Morning. Elevate Your Life. by Robin Sharma: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (22)
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelDa EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Leadership and Self-Deception: Getting out of the BoxDa EverandLeadership and Self-Deception: Getting out of the BoxValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (156)
- The 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDa EverandThe 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2567)
- Think Remarkable: 9 Paths to Transform Your Life and Make a DifferenceDa EverandThink Remarkable: 9 Paths to Transform Your Life and Make a DifferenceNessuna valutazione finora
- Extreme Ownership by Jocko Willink and Leif Babin - Book Summary: How U.S. Navy SEALS Lead And WinDa EverandExtreme Ownership by Jocko Willink and Leif Babin - Book Summary: How U.S. Navy SEALS Lead And WinValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (75)
- The Catalyst: How to Change Anyone's MindDa EverandThe Catalyst: How to Change Anyone's MindValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (276)
- How to Talk to Anyone at Work: 72 Little Tricks for Big Success Communicating on the JobDa EverandHow to Talk to Anyone at Work: 72 Little Tricks for Big Success Communicating on the JobValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (37)
- Brain Rules (Updated and Expanded): 12 Principles for Surviving and Thriving at Work, Home, and SchoolDa EverandBrain Rules (Updated and Expanded): 12 Principles for Surviving and Thriving at Work, Home, and SchoolValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (702)
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelDa EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Millionaire Mindset: Accept That Your Own Life Choices Led to Who You Are Today. If You Can Accept This Then You Can Learn to Change Your Mindset and Habits to Match Those of Today's Millionaires and Effortlessly Lead the Way to Your Own Success!Da EverandMillionaire Mindset: Accept That Your Own Life Choices Led to Who You Are Today. If You Can Accept This Then You Can Learn to Change Your Mindset and Habits to Match Those of Today's Millionaires and Effortlessly Lead the Way to Your Own Success!Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (17)
- How to Win Friends and Influence People: Updated For the Next Generation of LeadersDa EverandHow to Win Friends and Influence People: Updated For the Next Generation of LeadersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (151)
- How To Win Friends And Influence PeopleDa EverandHow To Win Friends And Influence PeopleValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (6521)
- How to Lead: Wisdom from the World's Greatest CEOs, Founders, and Game ChangersDa EverandHow to Lead: Wisdom from the World's Greatest CEOs, Founders, and Game ChangersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (95)
- The FBI Way: Inside the Bureau's Code of ExcellenceDa EverandThe FBI Way: Inside the Bureau's Code of ExcellenceNessuna valutazione finora
- TED Talks: The Official TED Guide to Public SpeakingDa EverandTED Talks: The Official TED Guide to Public SpeakingValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (211)
- Good to Great by Jim Collins - Book Summary: Why Some Companies Make the Leap...And Others Don'tDa EverandGood to Great by Jim Collins - Book Summary: Why Some Companies Make the Leap...And Others Don'tValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (64)
- The Five Temptations of A CEO: A Leadership FableDa EverandThe Five Temptations of A CEO: A Leadership FableValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (216)
- Summary of Leaders Eat Last: Why Some Teams Pull Together and Others Don't by Simon SinekDa EverandSummary of Leaders Eat Last: Why Some Teams Pull Together and Others Don't by Simon SinekValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (142)
- Superminds: The Surprising Power of People and Computers Thinking TogetherDa EverandSuperminds: The Surprising Power of People and Computers Thinking TogetherValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (7)