Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
International Human Resource Management 2167 0358 1000203
Caricato da
Samriddhi KrishnaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
International Human Resource Management 2167 0358 1000203
Caricato da
Samriddhi KrishnaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
l of Socialo
na
m
r
Jou
ics
Journal of Socialomics Mulang, J Socialomics 2017, 6:3
ISSN: 2167-0358 DOI: 10.1472/2167.0358.1000203
Mini Review Open Access
International Human Resource Management
Astuti Mulang*
Indonesia Timur University of Makassar, Indonesia
*Corresponding author: Astuti Mulang, Indonesia Timur University of Makassar, Indonesia, Tel: 0411421974; E-mail: eccetriana@yahoo.com
Rec date: Apr 28, 2017; Acc date: May 29, 2017; Pub date: June 05, 2017
Copyright: © 2017 Mulang A. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use,
distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Abstract
Global competition multinational companies can not only be faced with providing a reliable Human Resources.
More than that the company should have a strategy and valuables sets, namely Human Resources who has
committed, knowledgeable about the company in other countries, unable to compete face challenges and adapt
quickly to new environments. Human Resources should be distributed and allocated in a way that can provide a
competitive advantage. Management of Foreign Workers in this regard through expatriate assignments outside the
country must be done by a company Manpower Indonesia, and with the right choice of strategy is an attempt to
achieve corporate objectives.
Keywords: Strategies; Assignment; Expatriate company's goals can be achieved, then the function of Human
Resources should be integrated with the company's strategic
Introduction management process, meaning that a Human Resources manager
should:
Global competition faced by the nations of the world have
implications in life. Both in the business world, political, social and • Have a strategic planning input, whether it be human issues related
cultural and ideological transformation. The various implications, to business and disability in describing certain strategic
could not be addressed by each country to accelerate and adapt on the alternatives.
global changes. For business organizations, global business will have a • Have knowledge of the purpose of corporate strategy.
tendency on the activities of financial transactions, but has led to social • Understand the types of skills, behaviour patterns and attitudes
interaction such as the establishment of international business needed to support the strategic plan.
alliances, cooperation between two or more multinational companies • Develop a program to ensure that employees or existing workers
that are designed to benefit collectively. have the skills, behaviours and attitudes required by the company.
Regarding the above description [1] said that Indonesia as the Associated with the above description, the subject matter that is
country with the fourth largest population in the world, Indonesia has discussed in the Human Resource Management Human Resource
provided a meaningful opportunity for foreign companies that Management International is the possibility of employment outside the
traditionally rely on the expatriate her to mobilize and maintain country who automatically have differences such as differences in
operating companies the in Indonesia. The presence of expatriates in culture, climate and values that become trust.
Indonesia is human capital (Human Capital) for the company. Attitude
The scope of International Human Resource Management in
to do to prepare themselves for global competition that the business
general, [2] limits the scope of the International Human Resource
world includes: the intensification of the activity of research and
Management includes the function, the type of workers and countries
development resources business organizations that are adaptive, re-
involved. The scope of the question is as follows:
engineering on the pattern of applied management, prompted the
government to deregulate and Debirokrasi rules and regulations for
the sustainability of a healthy business climate, and expand your Human resource management functions include:
business or the company's operations to various countries. Having • acquisition function, include: planning, withdrawal and
regard to the variety and complexity of the challenges facing the socializing,
attitude that should be done, it will be much needed human resources • function development, including: training, development and
superior quality and able to compete. The human resources are coaching,
committed to the company and ready to compete face challenges is a
• maintenance functions, including: health and safety and labour
treasure among other resources owned by the company, both tangible
relations,
and intangible.
• motivational functions, including: evaluation, rewards,
In addition, the management system is required Human Resources compensation and discipline.
global prospective, meaning that management practices are applied
must be flexible. Because it is not possible patterns applied Type workers or employees may differ according to country
management will go through various countries with different human
of origin, namely:
objects. Human Resources of the company should be distributed and
allocated in such a way in a way that can provide a competitive • Employees who come from countries where the company operates
advantage and is a form of strategic management objectives. For the (local national)
J Socialomics, an open access journal Volume 6 • Issue 3 • 1000203
ISSN: 2167-0358
Citation: Mulang A (2017) International Human Resource Management. J Socialomics 6: 203. doi:10.1472/2167.0358.1000203
Page 2 of 5
• Employees from the company's home country (expatriates) the failure of workers who are stationed abroad, especially in the
• Employees from third countries (third country national) context of environmental and attitudinal adjustment is not successful
• While the countries involved in the operation, namely: a. [5].
Countries where the company operates (host country) b. The
company's home country (home country), c. Other countries Definition of foreign workers
• Schuler [2] divides the scope of the International Human Resource Talking about the International Human Resource Management
Management Home Host. means we are talking about the workforce or employees who come
from other countries, and matters relating to the preparation work in
Nationals local countries expatriates third country nationals the destination country. Workers coming from other countries called
type of employees the Foreign Workers for the country in which the foreign workers
employed. Minister of manpower and transmigration [3] concerning
Given the breadth of the operating area of International Human
procedures for utilization of foreign workers. What is meant by
Resource Management, functions and activities performed in
Expatriates are foreign nationals visa holder to work in Indonesia [6]
International Human Resource Management and a lot more wide-
defines that a person who left his home country to the other country to
ranging than the domestic Human Resource Management. There are
work, referred to as the Expatriate [4] categorizes people living outside
activities conducted International Human Resource Management but
their own country to work called Expatriate. While [7] in relation to
is not carried by the domestic Human Resource Management. These
Human Resource Management, in more detail to explain that:
activities include adjustments to the rules and regulations or
employees who work in an office or a company of which he is not a
international law or the law of the country inhabited including the
citizen of a country where the office or enterprise is located, but is a
rules governing taxation, administration related to the expatriates,
citizen of the country where the central office or the company is
such as a passport/visa and other required documents, as well as the
referred to as the Expatriate.
implementation of orientations for the expatriate.
From the above it can be concluded that not all foreign labour can
These adjustments are applicable in any country in which the
be referred to as expatriate, but an expatriate is a foreign worker. This
foreign worker will work. According to the Regulation of the Minister
paper is more focused towards foreign labour status as an Expatriate.
of Manpower and Transmigration [3] requirements that must be
owned by foreign labour employed by the company in Indonesia is:
Understanding of strategic management
Have the education or work experience of at least five (5) years in
accordance with the position that would be occupied. Before defining management strategy, it is necessary to define the
word strategy. The word strategy comes from the ancient Greek that
Willing to make a statement to transfer the skills to Indonesian strategies. In military circles said the strategy is intended to win a
Manpower especially companion. What is meant by the Labour battle. Mathis [7] defines strategy as the process of identifying the
Companion (Candy, 2008) is a manpower Indonesia designated state organization's goals and actions necessary to achieve that goal.
and prepared as the companion of Foreign Workers.
Strategic management is a process or an approach to dealing with
Can communicate in Indonesian. In the case of positions that would competitive challenges and opportunities faced by the company, in
be occupied by Foreign Workers. Already have work competency other words the management strategy is the number of decisions and
standards, then that will be employed must meet those standards. actions or efforts that led to the formulation of an effective strategy to
• Indonesian Manpower assistants must have a background in the help achieve the company's goals. Management strategy is basically a
field of education in accordance with the position that would be set shapes strategy, a process to analyse the competitive situation of
occupied. companies in developing corporate strategy objectives and devise a
plan of action and the allocation of resources that could improve the
• Employers of foreign workers are required to report the use of
chances tangible achievement of organizational goals [6]. The choice of
foreign labour, and the companion of foreign workers in the
strategy is a response to substantial questions regarding the
company periodically every 6 (six) months to the director
competition, which is how companies will compete to achieve the goals
controlling use of foreign workers.
and mission. The decision in this selection is often associated with the
• Director controlling use of foreign workers, reported permit use of
underlying problem, for example, where it will compete, how to
foreign workers issued periodically every 3 (three) months to the
compete and in what manner will compete. In practice, the decision
Minister with a copy to the director general.
maker little or no attention to the problem "by what means will
• Besides those described above, International Human Resource compete".
Management also has a broader perspective than the domestic
Human Resource Management, it is very possible because they This decision has a broad impact on the company. Failure to
must deal with a very heterogeneous group of employees. anticipate problems above can lead companies do not know how they
can compete, either in their own country where the parent company's
Therefore, it is often in the practice of the International Human operations and in other countries with which branch it operates.
Resource Management allows for further participation in the life of the International Human
employee [4]. It is necessary in the activities of selection, training and
effective management. Because the International Human Resource Resource management strategies is a link between the international
Management in practice is more influenced by external factors, such as Human Resource Management with strategic goals and objectives that
the form of government, economy, and business practices host the are intended to improve business performance and develop corporate
International Human Resource Management has a very high risk of the culture, to encourage and help to create, innovate more flexible.
failure of the implementation of the strategy. This failure was caused by Strategic International Human Resource Management can also be
J Socialomics, an open access journal Volume 6 • Issue 3 • 1000203
ISSN: 2167-0358
Citation: Mulang A (2017) International Human Resource Management. J Socialomics 6: 203. doi:10.1472/2167.0358.1000203
Page 3 of 5
interpreted as a pattern of human resource deployment planned and sought to be recruited and selected by the company. The process of
an act intended to assure and increase that the company can achieve its recruitment and selection of candidates for expatriate done more
objectives. rigorously selective Danlebih. Prospective workers required is truly
ready for Reviews their cross-cultural challenge, has a highly
In connection with the above description, the presence of the
competent and experienced in their field, have extensive knowledge
candidate expatriates Expatriate in this case, it must be properly
about the major companies Similar in other countries, preferably from
managed by large companies that have international networks (MNCs
executive groups. The models that can be applied in the recruitment
= Multinational Corporations) if the company it wants workers to
and selection by the companies that operate and on an international
succeed in their foreign assignments. Reviews These companies should
scale by [8,9] Among others:
be aware that high-performing employees in their own country can
Easily Become a low-performing employee in other countries [2]. To • Selected from the group of the national executive that is in the
Anticipate the possibility that the company must have a plan and what parent company (home country), to be placed in the company
the right selection strategy used for corporate purposes and to equip branch (host country) in other countries.
workers in the work in other countries where the conditions are • Recruiting executives from countries where labour in the country
different situations and with the parent company or the company's or locally.
home (home country). • Trying to adopt executives who have an international perspective
Strategies in the application of International Human Resource without restricting citizenship.
Management is done through a variety of activities, namely: From the survey on expatriate selection, [5,10] reported that as
many as 1,750 organizations representing 20 million employees and
Planning in international human resource management 175,000 professionals Human Resources policies using a selection of
international assignments are as follows: pre-assignment using the visit
According to [2] Human Resource planning in general were
as much as 60%; their language training as much as 34%; family
properly requires certain measures relating to the activities of Human
readiness evaluation as much as 26%; evaluation of cultural
Resource planners towards a competitive company. These steps are:
understanding as much as 15%.
• Collection and analysis of data to forecast the demand and supply
of human resources for the expected future business planners Settings or management staff
• Develop Human Resources planning purposes
In the framework of the arrangement or management staff must
• Design and implement programs that can Facilitate the
consider a variety assumptions as following: at the same position, but
achievement of the company in Human Resources planning
in a different place then would require specific skills, cultural and
purposes
physical environment influences locals must be carefully Considered
• Supervision and Evaluate programs that are running. and should be avoided estimates that wrong, besides than it according
The fourth stage can be implemented for the achievement of short- [11,12] in the settings or managing staff should use a variety of criteria
term goals < 1 year, 2-3 years medium, and long term > 3 years. As well International, Among others:
as planning activities, Human Resources in general above, in • Prospective employees must have a personality that is patient,
International Human Resource planning is required an external labour persevering, full of initiative and flexible accept or to experiment
market analysis from, whether they are local or domestic or on new things in the job.
international. This analysis is Necessary to Determine the needs or in
• Prospective employees should have high technical skills and
the provision of labour associated with the skills and expertise required
appropriate technology with progress. In addition to technical
in international business. In the framework of this plan need to
skills, prospective employees must have the skills of
consider several aspects, Including:
communication also in the which includes mastery of the
• Determination as well as the identification of potential or criteria language.
that must be met at each level of the management. • Prospective employees should have a high tolerance for differences
• Process of identifying crucial factors in bisnis International. of race, creed or religion, color, values, habits, and customs and
• Formulation of steps that must be done to Streng then the traditions.
commitment to the development of an international career. • Prospective employees must be highly motivated and defended.
• Linking Human Resources planning by strengthening the skills • Prospective employees should have a good behaviour in the
required by the executive using strategic business planning. membership of a larger community.
• Expansion of opportunities for self- development workers.
• Distribution of units in the business held by focusing efforts on Orientation or Debriefing
international business goal achievement.
This activity is done to equip prospective employees who will go to
other countries where he is assigned. Besides debriefing in their
Recruitment and Selection respective sectors, supply is also given with the aim to adapt, by
Recruitment prospective employer/employee is the process studying the pattern of life and culture of the country that will be
undertaken by the company to find workers potential, while the addressed. Here is intended as a characteristic cultural understanding
selection of related to the process where companies seek to identify job in their behaviour or way of doing something wherewith formed by the
seekers/applicants using the knowledge, skills, abilities and other surrounding environment within a long time. This In the case of
features to help the company Achieve its goals. The strategy of the companies should help employees who will be placed in the other state
company will have an impact directly on the type of workers who were to be a part of world culture and have an identity as an expatriate.
J Socialomics, an open access journal Volume 6 • Issue 3 • 1000203
ISSN: 2167-0358
Citation: Mulang A (2017) International Human Resource Management. J Socialomics 6: 203. doi:10.1472/2167.0358.1000203
Page 4 of 5
Enterprises become part of the culture of other countries is not Compensation system is carried out depends on the rules and
intended as an effort to be like living in other countries, but also as an agreements with the company's home early in countries where the
effort to improve the ability to understand strangers through reviews company operates.
their attitudes and behaviour, including emphasis on language
acquisition. Mastery of the language includes both mastery Conclusion
communicate orally and in writing and mastery of communication
ethics. Mastery of communicating important ethics for ethics in Global competition in the business world for companies that have
communication between countries differ from one another with that. an international network of very influential on the need for quality
Unfamiliarity in the ethics of communication may cause failure or human resources and the company's efforts in determining what the
workers repatriated to the country of origin before the work is right strategy is used to deal with competitors. Human Resources
completed. Orientation activities carried out next, when it has arrived (expatriate) quality is that committed, ready to compete face the
in the country of destination. Orientation is meant to do an challenge, have high competence in the field as well as fast-adapt.
introduction to the environment, introduction to the unit of work and Companies large companies that assign workers to other countries
workers, as well as the orientation of the work that became the main where the company operates, should know that the workers/employees
tasks of workers who concerned. The workers who can understand who perform well in the country can change be under-performing in
Reviews their culture, language and patterns of another state is other countries.
considered as a worker a cosmopolitan item, namely workers who have To address this the company must have a plan and choosing the
high sensitivity to cultural differences, language and patterns of life right strategy. Strategies can be done through various activities items,
and be able to accept and adjust to the peculiarities of foreign people's namely: planning, recruitment and selection, settings and management
behaviour. staff, providing orientation or debriefing, training and development,
and compensation and rewards. in the plan required prospective
Training and development expatriate workforce needed for the external analysis determine the
Training is defined as a business that is planned with the learning skills and labour requirements associated with membership.
providing facilities work associated with the knowledge, skills and Obtained needs through the recruitment and selection process, the
behaviour of the workers/employees. While the development about the which subsequently prepared given a briefing or orientation. Pre-
way to gain the skills and patterns of behaviour that can improve and assignment is an options strategy that is often done in the process of
increase of their ability so that work can overcome the challenges faced training and development. The provision of compensation and rewards
today or job come. In the future the company will change strategy to the expatriate aims to attract and retain qualified workers, ease of
often generally require changes in behaviour patterns, types, levels and transfer between branches, the maintenance of the relationship
skills mix through recruitment, selection, training and development between the parent company and branches and support for efforts to
workers/employees, so the company is able to describe the strategy of excel in competition. Compensation and rewards system depends on
what is appropriately applied to change In practice, education and the rules and the initial agreement between the parent company and
training program is a comprehensive coverage, starting from the subsidiary companies.
interpersonal relationships, understanding of local culture or local,
understanding the values and consumer behaviour through to References
operational global company, the transfer of the corporate culture,
values in the culture of pluralistic, business systems , international 1. Baert H, Govaerts N (2012) Learning patterns of teams at the workplace. J
strategy, socialization and other techniques. In the expatriate training Workplace Learning 24: 538-550.
and development process often tests also try to understand the culture 2. Savelsbergh C (2012) Team role stress: Relationships with team learning
of another country by way of sending it to other countries during a and performance in project teams. Dev Learning Org Int J 26: 67- 100.
certain time (pre-assignment) to learn to adapt to new environments. 3. Cross R, Gray P, Cunningham S, Showers M, Thomas R (2010) The
collaborative organization: How to make employee networks really work.
MIT Sloan Manag Rev Fall 52: 83-90.
Provision of compensation and rewards 4. Hendrickson J (2012) The capable utility company: Redefining
Compensation and rewards practice at the expatriate has a performance for the new business environment, booz & company.
significant role in defining a strategy. The compensation is intended to 5. Coghlan D, Rigg C (2012) Action learning as praxis in learning and
changing. Res Org Change Dev 20: 59-89.
attract and retain qualified workers in business between countries,
facilitate movement between branches in different countries, the 6. Garvin D (2000) Learning in Action: A guide to putting the learning
organization to work. Harvard School Business Press, Boston,
maintenance relationship that is consistent and keep the compensation Massachusetts, USA.
provided is rational and supports efforts to excel in minimal
7. Horwitz SK, Horwitz IB, Barshes N (2011) Addressing dysfunctional
competition with competitors terdekatnya. In the achievement the relations among health care teams: Improving team cooperation through
purpose, there are two principles in Determining remuneration system applied organizational theories. Adv Health Care Manag 10:173-197.
compensation or International company’s items, namely: 8. Nahrgang J, DeRue DS, Hollenbeck JR, Spitzmuller M, Jundt D, et al.
(2013) Goal setting in teams: The impact of learning and performance
• The concept of remuneration in accordance with the central
goals on process and performance. Organ Behav Hum Decis Process
company/the company's home (home country) 122:12-21.
• The concept of remuneration with the remuneration referred 9. Edmondson A (1999) Psychological safety and learning behaviour in
modular. That approach with a modular approach is separated work teams. Admin Sci Q 2: 350.
from the compensation package that regulations of the country of 10. Maurer I (2010) How to build trust in inter-organizational projects: The
origin or adapted to the regulations in the countries where the firm impact of project staffing and project rewards on the formation of trust,
operates (host country)
J Socialomics, an open access journal Volume 6 • Issue 3 • 1000203
ISSN: 2167-0358
Citation: Mulang A (2017) International Human Resource Management. J Socialomics 6: 203. doi:10.1472/2167.0358.1000203
Page 5 of 5
knowledge acquisition and product innovation. Int J Proj Manag 28: 12. Edmondson A (2012) Teaming: How organizations learn, innovate, and
629-637. compete in the knowledge economy, Jossey-Bass Publishing, San
11. Edmondson A, Carroll J (2002) Leading organisational learning in health Francisco, CA, USA.
care. Qual Saf Health Care 11: 51-56.
J Socialomics, an open access journal Volume 6 • Issue 3 • 1000203
ISSN: 2167-0358
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Perkins 20 Kva (404D-22G)Documento2 paginePerkins 20 Kva (404D-22G)RavaelNessuna valutazione finora
- SPH4U Assignment - The Wave Nature of LightDocumento2 pagineSPH4U Assignment - The Wave Nature of LightMatthew GreesonNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Vibration Analysis Training-1Documento193 pagineBasic Vibration Analysis Training-1Sanjeevi Kumar SpNessuna valutazione finora
- G.R. No. 185449, November 12, 2014 Del Castillo Digest By: DOLARDocumento2 pagineG.R. No. 185449, November 12, 2014 Del Castillo Digest By: DOLARTheodore DolarNessuna valutazione finora
- Embedded Systems DesignDocumento576 pagineEmbedded Systems Designnad_chadi8816100% (4)
- DesalinationDocumento4 pagineDesalinationsivasu1980aNessuna valutazione finora
- Sourcing Decisions in A Supply Chain: Powerpoint Presentation To Accompany Powerpoint Presentation To AccompanyDocumento58 pagineSourcing Decisions in A Supply Chain: Powerpoint Presentation To Accompany Powerpoint Presentation To AccompanyAlaa Al HarbiNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Retrofit in Solution Manager 7.2Documento17 pagineWhat Is Retrofit in Solution Manager 7.2PILLINAGARAJUNessuna valutazione finora
- PCDocumento4 paginePCHrithik AryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fake PDFDocumento2 pagineFake PDFJessicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Elastic Modulus SFRCDocumento9 pagineElastic Modulus SFRCRatul ChopraNessuna valutazione finora
- Executive Summary - Pseudomonas AeruginosaDocumento6 pagineExecutive Summary - Pseudomonas Aeruginosaapi-537754056Nessuna valutazione finora
- Star Link SafetyDocumento2 pagineStar Link SafetyJeronimo FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- IdM11gR2 Sizing WP LatestDocumento31 pagineIdM11gR2 Sizing WP Latesttranhieu5959Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Motor DrivesDocumento24 pagineIntroduction To Motor Drivessukhbat sodnomdorjNessuna valutazione finora
- Dialog Suntel MergerDocumento8 pagineDialog Suntel MergerPrasad DilrukshanaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Rise of Populism and The Crisis of Globalization: Brexit, Trump and BeyondDocumento11 pagineThe Rise of Populism and The Crisis of Globalization: Brexit, Trump and Beyondalpha fiveNessuna valutazione finora
- Ss 7 Unit 2 and 3 French and British in North AmericaDocumento147 pagineSs 7 Unit 2 and 3 French and British in North Americaapi-530453982Nessuna valutazione finora
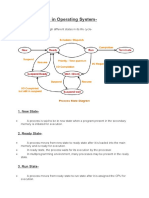
- Process States in Operating SystemDocumento4 pagineProcess States in Operating SystemKushal Roy ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Shubham RBSEDocumento13 pagineShubham RBSEShubham Singh RathoreNessuna valutazione finora
- SILABO 29-MT247-Sensors-and-Signal-ConditioningDocumento2 pagineSILABO 29-MT247-Sensors-and-Signal-ConditioningDiego CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Privacy: Based On Slides Prepared by Cyndi Chie, Sarah Frye and Sharon Gray. Fifth Edition Updated by Timothy HenryDocumento50 paginePrivacy: Based On Slides Prepared by Cyndi Chie, Sarah Frye and Sharon Gray. Fifth Edition Updated by Timothy HenryAbid KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Rofi Operation and Maintenance ManualDocumento3 pagineRofi Operation and Maintenance ManualSteve NewmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Portrait of An INTJDocumento2 paginePortrait of An INTJDelia VlasceanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Doterra Enrollment Kits 2016 NewDocumento3 pagineDoterra Enrollment Kits 2016 Newapi-261515449Nessuna valutazione finora
- Feasibility Study of Diethyl Sulfate ProductionDocumento3 pagineFeasibility Study of Diethyl Sulfate ProductionIntratec SolutionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Delta AFC1212D-SP19Documento9 pagineDelta AFC1212D-SP19Brent SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- (X-09485) XYLENE RECTIFIED Extra Pure (Mix Isomers)Documento9 pagine(X-09485) XYLENE RECTIFIED Extra Pure (Mix Isomers)Bharath KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 4th Sem Electrical AliiedDocumento1 pagina4th Sem Electrical AliiedSam ChavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Building Program Template AY02Documento14 pagineBuilding Program Template AY02Amy JaneNessuna valutazione finora