Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Enzyme Kinetics 216370 1701736696
Caricato da
Hannah WilsonTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Enzyme Kinetics 216370 1701736696
Caricato da
Hannah WilsonCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Data Interpretation
The following data were obtained in studies on the effects of pH on the enzyme
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Studies were carried out at pH 7.6 and pH 9.0 and the reaction followed by measuring
the increase in absorbance of light at 340nm due to NADPH production.
Substrate concentration Increase in Absorbance in the first 5min
X 104 (M)
pH 7.6 pH 9.0
0.174 0.062 0.029
0.267 0.075 0.04
0.526 0.089 0.075
1.666 0.11 0.13
4.000 0.12 0.17
Questions
1. Construct a properly labeled lineweaver-Burk plot from the data.
Fig 1) Shows the two velocities of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase at both pH 7.6
& 9 at an Abs of 340nm and a substrate conc. of 1x10^4M. These figures show the
increase of the first 5 minutes and reciprocals were then taken to plot a linear graph.
2. Calculate the Km and Vmax values for both pH’s and comment on the effect of
pH on this enzyme.
pH 7.6
Vmax = 1/(1/V) = 1/8.2369 = 0.12150
Km = Km/V x Vmax =1.3834 x 0.12150 = 0.16795
pH 9.0
Vmax = 1/(1/V) = 1/4.3225 = 0.23134
Km = Km/V x Vmax =5.2907 x 0.23134 = 1.22399
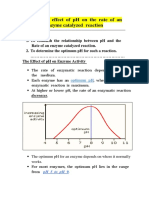
The optimum pH of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase is 7.4 and this due to this
being one of the enzymes used in the physiological glycolic pathway of glucose to
pyruvate.
Looking at normal bell-curve graph that relates the enzyme velocity related to pH, it
is noticed that pH 7 gives a better affinity and as the pH decreases or increases, the
affinity of the enzyme falls dramatically. The pH 7.6 in the experiment is closer to the
biological pH environment that it would usually reside in, providing a higher Km
value than that of pH9 which is too alkaline for the normal functionality of the
enzyme due to a disruption of the hydrogen ions becoming polarized and essentially
denaturing the enzyme.
pH 7.6 gives a lower Vmax value than that of pH 9 as the affinity of the enzyme is
greater in relation to the substrate as the conditions that the enzyme are present in are
optimal. pH 9 has a higher Vmax value and this is due to the fact that the enzyme has
a much harder time binding to the substrate mainly due to the deformation of the
structural binding sites which would require an increase in substrate resulting in a
lower affinity.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Enzyme Kinetics: Rapid-Equilibrium Applications of MathematicaDa EverandEnzyme Kinetics: Rapid-Equilibrium Applications of MathematicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Report On The PkaDocumento13 paginePractical Report On The PkaRohit50% (2)
- Fermentation Lab ReportDocumento8 pagineFermentation Lab ReportJoel ComanNessuna valutazione finora
- Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman Faculty of Science Bachelor of Science (Hons) ChemistryDocumento6 pagineUniversiti Tunku Abdul Rahman Faculty of Science Bachelor of Science (Hons) ChemistryKirthinee JegatheesanNessuna valutazione finora
- LSM1101 Practical 1Documento6 pagineLSM1101 Practical 1givena2ndchance100% (1)
- Y11 Biofuels Research ProjectDocumento12 pagineY11 Biofuels Research ProjectShental RohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Result Discussion Conclusion Exp 2 Physic ChemDocumento6 pagineResult Discussion Conclusion Exp 2 Physic Chemarif arifin100% (1)
- PKa Lab Report 3Documento14 paginePKa Lab Report 3Amanda Wang100% (2)
- Practical 3Documento9 paginePractical 3ARYSSA BINTI AZRINessuna valutazione finora
- Discussion On Potentiometric TitrationsDocumento16 pagineDiscussion On Potentiometric TitrationsKcirtap Zketh60% (5)
- Sample Chemistry Undergraduate Laboratory ReportDocumento14 pagineSample Chemistry Undergraduate Laboratory ReportApril TapayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Report 1Documento27 pagineLab Report 1szulkipeliNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of PH On EnzymesDocumento3 pagineEffect of PH On EnzymesJanick MallareNessuna valutazione finora
- Extraction of Invertase From Yeast and Effect of PH On Invertase ActivityDocumento6 pagineExtraction of Invertase From Yeast and Effect of PH On Invertase ActivityBea Trixia GalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Neutralization: Prepared by Michigan Department of Environmental Quality Operator Training and Certification UnitDocumento44 pagineNeutralization: Prepared by Michigan Department of Environmental Quality Operator Training and Certification UnitKhang TrầnNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Chemistry IADocumento13 pagineFinal Chemistry IASanjai AnanthNessuna valutazione finora
- ACE Guide BufferSelectionDocumento20 pagineACE Guide BufferSelectionarcherofthestarsNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzymes and PH - The Effect of PH On The Activity of The Enzyme CatalaseDocumento1 paginaEnzymes and PH - The Effect of PH On The Activity of The Enzyme Catalasear404100% (1)
- Lab 4 - Soda Titrations 1Documento9 pagineLab 4 - Soda Titrations 1api-385516219Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lactase LabDocumento9 pagineLactase Labapi-527875218Nessuna valutazione finora
- Formal Report Expt 3 EnzymesDocumento4 pagineFormal Report Expt 3 EnzymesKat De LaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Universidad de Las Américas PueblaDocumento8 pagineUniversidad de Las Américas PueblaJesus Alfredo LMNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 160.1 Ex2 BufferDocumento8 pagineChem 160.1 Ex2 BufferAsi JenNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Report CHM 213 (Physical Chemistry)Documento6 pagineLaboratory Report CHM 213 (Physical Chemistry)Muhd Mirza HizamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Wrd-Ot-Neutralization 445273 7Documento44 pagineWrd-Ot-Neutralization 445273 7Sheik Abdullah BakrudeenNessuna valutazione finora
- Formal Report Experiment 3 EnzymesDocumento4 pagineFormal Report Experiment 3 Enzymesliezl_alvarez_1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Formal Report Experiment 3 EnzymesDocumento4 pagineFormal Report Experiment 3 EnzymesMonica Gamboa100% (3)
- BIO 1121 Unit 2 Assignment Updated-3Documento4 pagineBIO 1121 Unit 2 Assignment Updated-3Dank Idiomas TeresópolisNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrolisis and FlavorDocumento13 pagineHydrolisis and FlavorSara PalermoNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential Adsorption-Spectrophotometric Assay Method For NucleotidesDocumento3 pagineDifferential Adsorption-Spectrophotometric Assay Method For NucleotidesGökberk ÖzsakallıNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Report CHM 213 (Physical Chemistry) : 1. Muhammad Mirza Hizami Bin RajieiDocumento6 pagineLaboratory Report CHM 213 (Physical Chemistry) : 1. Muhammad Mirza Hizami Bin RajieiMuhd Mirza Hizami100% (2)
- Lactase Enzyme Activity Lab Bio10a FinalDocumento7 pagineLactase Enzyme Activity Lab Bio10a FinalRomero JunioNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell MolecreportDocumento8 pagineCell Molecreportapi-586722985Nessuna valutazione finora
- Paper 2250Documento1 paginaPaper 2250BrianNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of PH On Enzyme ActivityDocumento12 pagineEffect of PH On Enzyme ActivityAb AbNessuna valutazione finora
- Isolation of Invertase PHDocumento4 pagineIsolation of Invertase PHJohn Mark Flores VillenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Written Report Expt.8Documento5 pagineWritten Report Expt.8Nicole NatanauanNessuna valutazione finora
- Acyl ActivationDocumento6 pagineAcyl ActivationMel June FishNessuna valutazione finora
- CHM 2962 Report 3Documento13 pagineCHM 2962 Report 3Yun KiatNessuna valutazione finora
- BiochemistryDocumento10 pagineBiochemistryjohnny brooksNessuna valutazione finora
- S Determination of Phosphoric Acid Content in SoftdrinksDocumento5 pagineS Determination of Phosphoric Acid Content in SoftdrinksMike Anderson0% (1)
- Isolation of Active Invertase and Effect of PH On Enzymatic ActivityDocumento3 pagineIsolation of Active Invertase and Effect of PH On Enzymatic ActivityGerald SevillaNessuna valutazione finora
- WjceDocumento5 pagineWjceshmohiuddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 2 Enzyme Assays and Factors Affectingenzyme ActivityDocumento15 pagineExperiment 2 Enzyme Assays and Factors Affectingenzyme Activitymohamad ashaziq100% (4)
- Lab 19 - Elsa Tejada Acids Bases PH and BuffersDocumento2 pagineLab 19 - Elsa Tejada Acids Bases PH and BuffersPaul Stephen SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Extraction of InvertaseDocumento5 pagineExtraction of InvertaseDianne Joy Pascua100% (1)
- CBB 2093 Process Instrumentation Laboratory ReportDocumento13 pagineCBB 2093 Process Instrumentation Laboratory ReportZaid SalmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Report4#: PH MeasurementDocumento7 pagineReport4#: PH MeasurementTaha ShalabiNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzyme Kinetics Lab ReportDocumento8 pagineEnzyme Kinetics Lab ReportPriyanka TiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Set 1 BCDocumento4 pagineProblem Set 1 BCakshookannanNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp 3 Enzymology Part 1 Determination of Optimum ParametersDocumento5 pagineExp 3 Enzymology Part 1 Determination of Optimum ParametersNur Fadhilah75% (4)
- Expt 3&4 - Peroxidase From RadishDocumento9 pagineExpt 3&4 - Peroxidase From RadishLogeetha Geetha100% (1)
- Chemistry Laboratory (CY1094D) : Dr. Mausumi ChattopadhyayaDocumento18 pagineChemistry Laboratory (CY1094D) : Dr. Mausumi ChattopadhyayaSita kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- ITS Undergraduate 16946 Paper 1404058Documento10 pagineITS Undergraduate 16946 Paper 1404058Stephy Florez MenesesNessuna valutazione finora
- Determination of Phosphoric Acid Content in Cola BeveragesDocumento13 pagineDetermination of Phosphoric Acid Content in Cola BeveragesNicole Pavlichich100% (1)
- Physicochemical Basis For Formation of RenalDocumento9 paginePhysicochemical Basis For Formation of Renaloctavieumba10Nessuna valutazione finora
- Enzyme LabDocumento3 pagineEnzyme Labjasonli2897Nessuna valutazione finora
- PI Exp9 CompiledDocumento12 paginePI Exp9 CompiledZaid SalmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 541l Lab Report 1 GLDDocumento9 pagineBio 541l Lab Report 1 GLDapi-604795842Nessuna valutazione finora
- Green 1933Documento6 pagineGreen 1933Rob Robbie RabuelNessuna valutazione finora
- CO2 & SelexolDocumento18 pagineCO2 & Selexolmihaileditoiu2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemicals Zetag DATA Powder Zetag 7650 - 0410Documento2 pagineChemicals Zetag DATA Powder Zetag 7650 - 0410PromagEnviro.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocumento35 pagineClass 12 Physics Chapter 11 Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterParvatham VijayNessuna valutazione finora
- Industial Chemistry IDocumento318 pagineIndustial Chemistry ItesfayeNessuna valutazione finora
- Explosion Safety in Ethoxylation Reactors: M Braithwaite & A PekalskiDocumento19 pagineExplosion Safety in Ethoxylation Reactors: M Braithwaite & A Pekalskikhali54Nessuna valutazione finora
- Semester Project Proposal: Galvanic CellDocumento7 pagineSemester Project Proposal: Galvanic CellHashir FurhanNessuna valutazione finora
- E C B E C B: Cathode Ca CathodeDocumento1 paginaE C B E C B: Cathode Ca CathodewilfreddelgadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Set-A: Bakliwal Tutorials-IITDocumento33 pagineSet-A: Bakliwal Tutorials-IITNeeravNessuna valutazione finora
- Perovskyt 5 ADocumento18 paginePerovskyt 5 ASegundo AcevedoNessuna valutazione finora
- NMR and EsrDocumento52 pagineNMR and EsrSenthil Sethu FvfcNessuna valutazione finora
- Bulletin 23 PDFDocumento20 pagineBulletin 23 PDFmanuelavfNessuna valutazione finora
- Prelim 1 2015 EXAMDocumento13 paginePrelim 1 2015 EXAMMichael YeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrochemistry and Chemical Sensors: Prasad V.A. PamidiDocumento32 pagineElectrochemistry and Chemical Sensors: Prasad V.A. PamidiRiskullah MakmurNessuna valutazione finora
- Electroless Plating28266Documento17 pagineElectroless Plating28266fsarfrazNessuna valutazione finora
- MCAT Organic ChemistryDocumento7 pagineMCAT Organic ChemistryjoNessuna valutazione finora
- MKKKLDocumento21 pagineMKKKLdaney67299Nessuna valutazione finora
- Report No 4 Identification of Liquid Substances Through Their Physical PropertiesDocumento8 pagineReport No 4 Identification of Liquid Substances Through Their Physical PropertiesrodneyperuNessuna valutazione finora
- Prediction of The Minimum Film Boiling Temperature Using Artificial Neural NetworkDocumento11 paginePrediction of The Minimum Film Boiling Temperature Using Artificial Neural Networkvane-16Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ab-Initio Simulations of Materials Using VASP PDFDocumento35 pagineAb-Initio Simulations of Materials Using VASP PDFjie shiNessuna valutazione finora
- A. Radiant B. Mechanical C. Thermal D. Electrical, andDocumento5 pagineA. Radiant B. Mechanical C. Thermal D. Electrical, andEuniceCareLanajaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2011 Enthalpy Tutorial (With Ans)Documento11 pagine2011 Enthalpy Tutorial (With Ans)kahwahcheong100% (1)
- Processing of Bopp FilmDocumento49 pagineProcessing of Bopp FilmHassan Ali Khan75% (8)
- Lecturer Chemistry Mcqs PSC Past PaperDocumento26 pagineLecturer Chemistry Mcqs PSC Past Paperlog man63% (8)
- Year 13 MTDocumento15 pagineYear 13 MTKissiedu YirenkyiNessuna valutazione finora
- Different Polymerization ProcessesDocumento6 pagineDifferent Polymerization ProcessesMarc Dennis Angelo UgoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Review On Adsorption of Heavy Metal in Wastewater by Using GeopolymerDocumento8 pagineReview On Adsorption of Heavy Metal in Wastewater by Using GeopolymerJanine Rose MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 01 91Documento4 pagine12 01 91antonioNessuna valutazione finora
- Arkema MP Chemical Process Industry Market PresentationDocumento17 pagineArkema MP Chemical Process Industry Market PresentationMarcelo PerettiNessuna valutazione finora
- Sri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: PhysicsDocumento10 pagineSri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: PhysicsAditya Raj SinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- SSC JE Syllabus Mechanical Engineering (ME) PDF Download PDFDocumento15 pagineSSC JE Syllabus Mechanical Engineering (ME) PDF Download PDFSajid AnsariNessuna valutazione finora