Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Analysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula Sheet PDF
Caricato da
Amogh NarvekarTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Analysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula Sheet PDF
Caricato da
Amogh NarvekarCopyright:
Formati disponibili
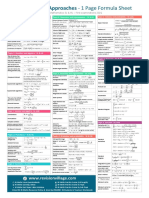
Analysis & Approaches - 1 Page Formula Sheet
IB Mathematics SL & HL – First examinations 2021
Prior Learning SL & HL Topic 3: Geometry and trigonometry – SL & HL Topic 4: Statistics and probability – HL only
P(𝐵)P(𝐴|𝐵)
Area: Parallelogram 𝐴 = 𝑏ℎ , 𝑏 = base, ℎ = height Distance between 2 points distance (𝑑) = P(𝐵|𝐴) =
P(𝐵)P(𝐴|𝐵) + P(𝐵′ )P(𝐴|𝐵′ )
1 (𝒙𝟏 , 𝒚𝟏 , 𝒛𝟏 ) , (𝒙𝟐 , 𝒚𝟐 , 𝒛𝟐 ) √(𝑥1 − 𝑥2 )2 + (𝑦1 − 𝑦2 )2 + (𝑧1 − 𝑧2 )2 Bayes’ theorem
Area: Triangle 𝐴 = 2 (𝑏ℎ) , 𝑏 = base, ℎ = height P(𝐵𝑖 |𝐴) =
Coordinates of the P(𝐵𝑖 )P(𝐴|𝐵𝑖 )
1 𝑥1 + 𝑥2 𝑦1 + 𝑦2 𝑧1 + 𝑧2 P(𝐵1 )P(𝐴|𝐵1 ) + P(𝐵2 )P(𝐴|𝐵2 ) + P(𝐵3 )P(𝐴|𝐵3 )
Area: Trapezoid 𝐴 = 2 (𝑎 + 𝑏)ℎ , 𝑎, 𝑏 = parallel sides, ℎ =height midpoint with endpoints ( , , )
(𝒙𝟏 , 𝒚𝟏 , 𝒛𝟏 ) , (𝒙𝟐 , 𝒚𝟐 , 𝒛𝟐 ) 2 2 2 ∑𝑘
𝑖=1 𝑓𝑖 (𝑥𝑖 −𝜇)
2 ∑𝑘
𝑖=1 𝑓𝑖 𝑥𝑖
2
Area: Circle 𝐴 = 𝜋𝑟 2 , 𝑟 = radius Variance 𝝈𝟐 𝜎2 = = − 𝜇2
1 𝑛 𝑛
Volume: Right-pyramid 𝑉 = 3 𝐴ℎ , 𝐴 = base area, ℎ =vertical height
Circumference of circle 𝐶 = 2𝜋𝑟, 𝑟 = radius
1 ∑𝑘
𝑖=1 𝑓𝑖 (𝑥𝑖 −𝜇)
2
Volume: Right cone 𝑉 = 3 𝜋𝑟 2 ℎ , 𝑟= radius, ℎ = height Standard Deviation 𝝈 𝜎=√
Volume: Cuboid 𝑉 = 𝑙𝑤ℎ , 𝑙 = length, 𝑤 = width, ℎ = height 𝑛
Volume: Cylinder 𝑉 = 𝜋𝑟 2 ℎ , 𝑟 = radius, ℎ = height Area: Cone curve 𝐴 = 𝜋𝑟𝑙 , 𝑟= radius, 𝑙 = slant height Linear transformation of E(𝑎𝑋 + 𝑏) = 𝑎E(𝑋) + 𝑏
4
Volume: Sphere 𝑉 = 3 𝜋𝑟 3 , 𝑟 = radius a single random variable Var(𝑎𝑋 + 𝑏) = 𝑎2 Var(𝑋)
Volume: Prism 𝑉 = 𝐴ℎ , 𝐴 = cross-section area, ℎ = height
Expected value: continuous ∞
Area: Cylinder curve 𝐴 = 2𝜋𝑟ℎ , 𝑟 = radius, ℎ = height Surface area: Sphere 𝐴 = 4𝜋𝑟 2 , 𝑟 = radius E(𝑋) = 𝜇 = ∫−∞ 𝑥𝑓(𝑥)d𝑥
random variable X
𝑎 𝑏 𝑐
Distance between two Sine rule = = Variance Var(𝑋) = E(𝑋 − 𝜇)2 = E(𝑋 2 ) − [E(𝑋)]2
𝑑 = √(𝑥1 − 𝑥2 )2 + (𝑦1 − 𝑦2 )2 sin𝐴 sin𝐵 sin𝐶
points (𝒙𝟏 , 𝒚𝟏 ) , (𝒙𝟐 , 𝒚𝟐 )
𝑐 2 = 𝑎2 + 𝑏2 − 2𝑎𝑏 cos 𝐶 Variance of a discrete Var(𝑋) = ∑(𝑥 − 𝜇)2 P(𝑋 = 𝑥)
𝑥1+𝑥2 𝑦1 +𝑦2
Coordinates of midpoint ( , ), for endpoints (𝑥1 , 𝑦1), (𝑥2 , 𝑦2 ) Cosine rule 𝑎2 + 𝑏2 − 𝑐 2 random variable X = ∑ 𝑥 2 P(𝑋 = 𝑥) − 𝜇2
2 2 cos 𝐶 = ∞
2𝑎𝑏 Var(𝑋) = ∫−∞(𝑥 − 𝜇)2 𝑓(𝑥)d𝑥
1 Variance of a continuous
Area: Triangle 𝐴 = 𝑎𝑏 sin 𝐶 random variable X ∞
Topic 1: Number and algebra - SL & HL 2 = ∫−∞ 𝑥 2 𝑓(𝑥)d𝑥 − 𝜇2
The 𝒏th term of an Length of an arc 𝑙 = 𝜃𝑟 , 𝜃 = angle in radians, 𝑟 = radius
𝑢𝑛 = 𝑢1 + (𝑛 − 1)𝑑 1
Topic 5: Calculus - SL & HL
arithmetic sequence Area of a sector 𝐴 = 2 𝑟 2 𝜃 , 𝜃 = angle in radians, 𝑟 = radius
Sum of 𝒏 terms of an 𝑛 𝑛 sin 𝜃 Derivative of 𝒙𝒏 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 𝑛 → 𝑓′(𝑥) = 𝑛𝑥 𝑛−1
𝑠𝑛 = (2𝑢1 + (𝑛 − 1)𝑑) = (𝑢1 + 𝑢𝑛 ) Identity for 𝐭𝐚𝐧 𝜽 tan 𝜃 =
arithmetic sequence 2 2 cos 𝜃
𝑥 𝑛+1
Pythagorean identity 2
cos 𝜃 + sin 𝜃 = 1 2 Integral of 𝒙𝒏 ∫ 𝑥 𝑛 𝑑𝑥 = + 𝐶 , 𝑛 ≠ −1
The 𝒏th term of a 𝑛+1
𝑢𝑛 = 𝑢1 𝑟 𝑛−1 sin 2𝜃 = 2 sin 𝜃 cos 𝜃 𝑏
geometric sequence Area enclosed by a
cos 2𝜃 = cos 2 𝜃 − sin2 𝜃 𝐴 = ∫ 𝑦 𝑑𝑥 , where 𝑓(𝑥) > 0
Double angle identities curve and the 𝒙-axis
Sum of 𝒏 terms of a 𝑢1 (𝑟 𝑛 − 1) 𝑢1 (1 − 𝑟 𝑛 ) = 2 cos 2 𝜃 − 1
𝑎
𝑠𝑛 = = ,𝑟 ≠ 1 Derivative of 𝐬𝐢𝐧 𝒙 𝑓(𝑥) = sin 𝑥 → 𝑓′(𝑥) = cos 𝑥
finite geometric seq. 𝑟−1 1−𝑟 = 1 − 2 sin2 𝜃
𝑟 𝑘 𝑛 Derivative of 𝐜𝐨𝐬 𝒙 𝑓(𝑥) = cos 𝑥 → 𝑓′(𝑥) = − sin 𝑥
𝐹𝑉 = 𝑃𝑉 × (1 + ) Topic 3: Geometry and trigonometry – HL only
100𝑘 1
Reciprocal trigonometric 1 1 Derivative of 𝐭𝐚𝐧 𝒙 𝑓(𝑥) = tan 𝑥 → 𝑓′(𝑥) =
Compound interest 𝐹𝑉 is future value, 𝑃𝑉 is present value, 𝑛 is sec 𝜃 = ; cosec 𝜃 = cos 2 𝑥
identities cos 𝜃 sin 𝜃
the number of years, 𝑘 is the number of Derivative of 𝒆𝒙 𝑥
𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑒 → 𝑓′(𝑥) = 𝑒 𝑥
2 2 2 2
compounding periods per year, 𝑟% is the Pythagorean identities 1 + tan 𝜃 = sec 𝜃 ; 1 + cot 𝜃 = cosec 𝜃
nominal annual rate of interest 1
sin(𝐴 ± 𝐵) = sin 𝐴 cos 𝐵 ± cos 𝐴 sin 𝐵 Derivative of 𝐥𝐧 𝒙 𝑓(𝑥) = ln 𝑥 → 𝑓′(𝑥) =
𝑥
Exponents & logarithms 𝑎 𝑥 = 𝑏 ↔ 𝑥 = log 𝑎 𝑏 , 𝑎, 𝑏 > 0, 𝑎 ≠ 1 Compound angle cos(𝐴 ± 𝐵) = cos 𝐴 cos 𝐵 ∓ sin 𝐴 sin 𝐵
𝑑𝑦 𝑑𝑦 𝑑𝑢
identities tan 𝐴 ± tan 𝐵 Chain rule 𝑦 = 𝑔(𝑢) , 𝑢 = 𝑓(𝑥) → = ×
log 𝑎 𝑥𝑦 = log 𝑎 𝑥 + log 𝑎 𝑦 tan(𝐴 ± 𝐵) = 𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑢 𝑑𝑥
𝑥 1 ∓ tan 𝐴 tan 𝐵
log 𝑎 = log 𝑎 𝑥 − log 𝑎 𝑦 𝑑𝑦 𝑑𝑣 𝑑𝑢
𝑦 Double angle identity 2 tan 𝜃 Product rule 𝑦 = 𝑢𝑣 → =𝑢 +𝑣
Exponents & logarithms tan 2𝜃 = 𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑥
log 𝑎 𝑥 𝑚 = 𝑚 log 𝑎 𝑥 for tan 1 − tan2 𝜃
𝑑𝑢 𝑑𝑣
log𝑏 𝑥 Magnitude of a vector |𝒗| = √𝑣1 2 + 𝑣2 2 + 𝑣3 2 Quotient rule 𝑢 𝑑𝑦 𝑣 𝑑𝑥 − 𝑢 𝑑𝑥
log 𝑎 𝑥 = 𝑦= → =
log 𝑏 𝑎 𝑣 𝑑𝑥 𝑣2
𝒗 ∙ 𝒘 = 𝑣1 𝑤1 + 𝑣2 𝑤2 + 𝑣3 𝑤3
𝑑𝑣 𝑑 2 𝑠 𝑑𝑣
The sum of an infinite 𝑢1 Scalar product 𝒗 ∙ 𝒘 = |𝒗||𝒘| cos 𝜃 Acceleration 𝑎= = 2=𝑣
𝑠∞ = , |𝑟| < 1 where 𝜃 is the angle between 𝒗 and 𝒘 𝑑𝑡 𝑑𝑡 𝑑𝑠
geometric sequence 1−𝑟 𝑡2 𝑡2
Angle between two 𝑣1 𝑤1 + 𝑣2 𝑤2 + 𝑣3 𝑤3 Distance; Displacement
(𝑎 + 𝑏)𝑛 = cos 𝜃 = dist = ∫ |𝑣(𝑡)| 𝑑𝑡 ; disp = ∫ 𝑣(𝑡) 𝑑𝑡
travelled from 𝒕𝟏 to 𝒕𝟐
Binomial theorem vectors |𝒗||𝒘| 𝑡1 𝑡1
𝑎𝑛 + (𝑛1 )𝑎𝑛−1 𝑏+. . . +(𝑛𝑟)𝑎𝑛−𝑟 𝑏𝑟 +. . . + 𝑏𝑛
Vector equ. of a line 𝒓 = 𝒂 + 𝜆𝒃 1
𝑛 𝑛! ∫ 𝑑𝑥 = ln|𝑥| + 𝐶 , 𝑥 > 0
Binomial coefficient ( ) = nC r = Parametric form of the 𝑥
𝑟 𝑟!(𝑛−𝑟)! 𝑥 = 𝑥0 + 𝜆𝑙, 𝑦 = 𝑦0 + 𝜆𝑚, 𝑧 = 𝑧0 + 𝜆𝑛
equation of a line ∫ sin 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = − cos 𝑥 + 𝐶
Topic 1: Number and algebra - HL only Cartesian equations of 𝑥 − 𝑥0 𝑦 − 𝑦0 𝑧 − 𝑧0
= =
Standard integrals
𝑛! a line 𝑙 𝑚 𝑛 ∫ cos 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = sin 𝑥 + 𝐶
Combinations nCr =
𝑟!(𝑛−𝑟)!
𝑣2 𝑤3 − 𝑣3 𝑤2
𝒗 × 𝒘 = (𝑣3 𝑤1 − 𝑣1 𝑤3 ) ∫ 𝑒 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = 𝑒 𝑥 + 𝐶
𝑛!
Permutations nPr = Vector product 𝑣1 𝑤2 − 𝑣2 𝑤1
(𝑛−𝑟)! 𝑏
|𝒗 × 𝒘| = |𝒗||𝒘| sin 𝜃 Area enclosed by a
𝐴 = ∫ |𝑦| 𝑑𝑥
Complex numbers 𝑧 = 𝑎 + 𝑏𝑖 where 𝜃 is the angle between 𝒗 and 𝒘 curve and 𝒙-axis 𝑎
Modulus-argument (polar) Area of a 𝐴 = |𝒗 × 𝒘| , where 𝒗 and 𝒘 form two Topic 5: Calculus – HL only
& Exponential (Euler) form
𝑧 = 𝑟(cos 𝜃 + 𝑖 sin 𝜃) = 𝑟𝑒 𝑖𝜃 = 𝑟cis𝜃
parallelogram adjacent sides of a parallelogram
Derivative of 𝒇(𝒙) d𝑦 𝑓(𝑥 + ℎ) − 𝑓(𝑥)
[𝑟(cos 𝜃 + 𝑖 sin 𝜃)]𝑛 = Vector equ. of a plane 𝒓 = 𝒂 + 𝜆𝒃 + 𝜇𝒄 = 𝑓′(𝑥) = lim ( )
De Moivre’s theorem from first principles d𝑥 ℎ→0 ℎ
𝑛 (cos 𝑛 𝑖𝑛𝜃 𝑛
𝑟 𝑛𝜃 + 𝑖 sin 𝑛𝜃) = 𝑟 𝑒 = 𝑟 cisn𝜃 Equation of a plane 𝒓 ∙ 𝒏 = 𝒂 ∙ 𝒏 (using the normal vector)
𝑓(𝑥) = tan 𝑥 ⇒ 𝑓 ′ (𝑥) = sec 2 𝑥
Cartesian equ. of a plane 𝑎𝑥 + 𝑏𝑦 + 𝑐𝑧 = 𝑑 𝑓(𝑥) = sec 𝑥 ⇒ 𝑓 ′ (𝑥) = sec 𝑥 tan 𝑥
Topic 2: Functions – SL & HL 𝑓(𝑥) = cosec 𝑥 ⇒ 𝑓 ′ (𝑥) = −cosec 𝑥 cot 𝑥
Topic 4: Statistics and probability - SL & HL 𝑓(𝑥) = cot 𝑥 ⇒ 𝑓 ′ (𝑥) = −cosec 2 𝑥
Equations of a 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑐, 𝑎𝑥 + 𝑏𝑦 + 𝑑 = 0
Interquartile range IQR = 𝑄3 − 𝑄1 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑎 𝑥 ⇒ 𝑓 ′ (𝑥) = 𝑎 𝑥 (ln 𝑎)
straight line 𝑦 − 𝑦1 = 𝑚(𝑥 − 𝑥1 ) 1
̅ , of a set of
Mean, 𝒙 ∑𝑘 Standard 𝑓(𝑥) = log𝑎 𝑥 ⇒ 𝑓 ′ (𝑥) =
rise 𝑦2 − 𝑦1 𝑖=1 𝑓𝑖 𝑥𝑖
Gradient formula 𝑚= = data 𝑥̅ = , where 𝑛 = ∑𝑘𝑖=1 𝑓𝑖 derivatives 𝑥 ln 𝑎
run 𝑥2 − 𝑥1 𝑛 1
Probability of an event 𝑛(𝐴) 𝑓(𝑥) = arcsin 𝑥 ⇒ 𝑓 ′ (𝑥) =
Axis of symmetry of a 𝑏 P(𝐴) = √1 − 𝑥 2
𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐 → 𝑥 = − 𝑨 𝑛(𝑢) 1
quadratic function 2𝑎 𝑓(𝑥) = arccos 𝑥 ⇒ 𝑓 ′ (𝑥) = −
Complementary events P(𝐴) + P(𝐴′ ) = 1 √1 − 𝑥 2
Solutions of a
−𝑏 ± √𝑏2 − 4𝑎𝑐 Combined events P(𝐴 ∪ 𝐵) = P(𝐴) + P(𝐵) − P(𝐴 ∩ 𝐵) 1
quadratic equation in 𝑥= ,𝑎 ≠ 0 𝑓(𝑥) = arctan 𝑥 ⇒ 𝑓 ′ (𝑥) =
2𝑎 1 + 𝑥2
the form 𝒂𝒙𝟐 + 𝒃𝒙 + 𝒄 Mutually exclusive
P(𝐴 ∪ 𝐵) = P(𝐴) + P(𝐵) 1
events ∫ 𝑎 𝑥 d𝑥 = ln 𝑎 𝑎 𝑥 + 𝐶
Discriminant ∆ = 𝑏2 − 4𝑎𝑐
P(𝐴 ∩ 𝐵) Standard 1 1 𝑥
Conditional probability P(𝐴|𝐵) = ∫ 𝑎2 +𝑥2 d𝑥 = 𝑎 arctan (𝑎) + 𝐶
Exponential and 𝑎 𝑥 = 𝑒 𝑥 ln 𝑎 ; log 𝑎 𝑎 𝑥 = 𝑥 = 𝑎 log𝑎 𝑥 P(𝐵) integrals
1 𝑥
logarithmic functions where 𝑎, 𝑥 > 0 , 𝑎 ≠ 1 ∫ √𝑎2 +𝑥2 d𝑥 = arcsin (𝑎) + 𝐶 , |𝑥| < 𝑎
Independent events P(𝐴 ∩ 𝐵) = P(𝐴)P(𝐵)
Topic 2: Functions – HL only Expected value of a
E(𝑋) = ∑ 𝑥 P(𝑋 = 𝑥) Integration by parts
d𝑣
∫ 𝑢 d𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = 𝑢𝑣 − ∫ 𝑣 d𝑥 𝑑𝑥
d𝑢
𝑛 discrete random variable
Area enclosed by a 𝑏
Sum & product of the ∑ 𝑎𝑟 𝑥 𝑟 = 0 Binomial distribution 𝑋~B(𝑛, 𝑝) 𝐴 = ∫𝑎 |𝑥| 𝑑𝑦
curve and 𝒚-axis
roots of polynomial 𝑟=0 Mean ; Variance E(𝑋) = 𝑛𝑝 ; Var(𝑋) = 𝑛𝑝(1 − 𝑝)
−𝑎𝑛−1 (−1) 𝑎0 𝑛 Volume of revolution 𝑏 𝑏
equations of the form ⇒ Sum is ; product is 𝑥−𝜇
about 𝒙 or 𝒚-axes 𝑉 = ∫𝑎 𝜋𝑦 2 𝑑𝑥 or 𝑉 = ∫𝑎 𝜋𝑥 2 𝑑𝑦
𝑎𝑛 𝑎𝑛 Standardized normal variable 𝑧=
𝜎
𝑦𝑛+1 = 𝑦𝑛 + ℎ × 𝑓(𝑥𝑛 , 𝑦𝑛 ); 𝑥𝑛+1 = 𝑥𝑛 + ℎ
Euler’s method
where ℎ is a constant (step length)
www.revisionvillage.com Integrating factor for
𝒚′ + 𝑷(𝒙)𝒚 = 𝑸(𝒙) 𝑒 ∫ 𝑃(𝑥)d𝑥
𝑥 2 ′′
IB Maths Exam Questionbanks IB Maths Practice Exams (Full Length) Maclaurin series 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑓(0) + 𝑥𝑓 ′ (0) + 𝑓 (0)+ . ..
2!
IB Maths Learning Videos IB Maths Practice Exams by Topic 2
∙ 𝑒 𝑥 = 1 + 𝑥 + 𝑥2! + ... ∙ ln(1 + 𝑥) = 𝑥 − 𝑥2 + 𝑥3 − ...
2 3
IB Maths Past Paper Video Solutions IB Maths Practice Exams by Sub-Topic Maclaurin series for 3 5
∙ sin 𝑥 = 𝑥 − 𝑥3! + 𝑥5! − ... ∙ cos 𝑥 = 1 − 𝑥2! + 𝑥4! − ...
2 4
special functions
Voted #1 IB Maths Resource Online & Used by 250,000+ IB Students & Teachers Worldwide ∙ arctan 𝑥 = 𝑥 − 𝑥3! + 𝑥5! − ...
3 5
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Analysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula SheetDocumento1 paginaAnalysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula SheetFN6012021 RAVICHANDRAN GOKULNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula SheetDocumento1 paginaAnalysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula SheetYusufAliBahrNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula Sheet PDFDocumento1 paginaAnalysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula Sheet PDFZia SilverNessuna valutazione finora
- IB Maths 1-Page Formula SheetDocumento1 paginaIB Maths 1-Page Formula SheetGenesis Norbert Alconaba100% (1)
- Analysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula Sheet PDFDocumento1 paginaAnalysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula Sheet PDFRia ChopraNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula SheetDocumento1 paginaAnalysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula SheetAmanda PoetirayNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula SheetDocumento1 paginaAnalysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula SheetrheaNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Analysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula Sheet PDFDocumento1 paginaMath Analysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula Sheet PDFTiberiuNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis & Approaches - 1 Page Formula Sheet: IB Mathematics SL & HL - First Examinations 2021Documento1 paginaAnalysis & Approaches - 1 Page Formula Sheet: IB Mathematics SL & HL - First Examinations 2021Kathryn Tian100% (1)
- Analysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula Sheet V1.3Documento1 paginaAnalysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula Sheet V1.3Chantal TockeNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula Sheet V1.3Documento1 paginaAnalysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula Sheet V1.3AyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Applications and Interpretation 1 Page Formula Sheet V1.1 PDFDocumento1 paginaApplications and Interpretation 1 Page Formula Sheet V1.1 PDFIsmaila MbodjiNessuna valutazione finora
- Applications & Interpretation - 1 Page Formula Sheet: IB Mathematics SL & HL - First Examinations 2021Documento1 paginaApplications & Interpretation - 1 Page Formula Sheet: IB Mathematics SL & HL - First Examinations 2021Zia Silver100% (1)
- Applications and Interpretation 1 Page Formula Sheet V1.1Documento1 paginaApplications and Interpretation 1 Page Formula Sheet V1.1talahamayel07Nessuna valutazione finora
- Formula SheetDocumento1 paginaFormula SheetNoemi LayogNessuna valutazione finora
- Formula Sheet For Free VibrationDocumento5 pagineFormula Sheet For Free VibrationCesar MolinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acst356 Class Test 1 FinalDocumento1 paginaAcst356 Class Test 1 FinalJoshua AlexanderNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch.4 - Two-Dimensional KinematicsDocumento48 pagineCh.4 - Two-Dimensional Kinematicsnoriegak94Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hysical Quantities Vectors and Otion: Standards and Units The International Standard, or SI (Système International) UnitsDocumento11 pagineHysical Quantities Vectors and Otion: Standards and Units The International Standard, or SI (Système International) UnitsSamyak JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch. 03 - Kinematics in Two DimensionsDocumento22 pagineCh. 03 - Kinematics in Two Dimensionssthembisosthera992Nessuna valutazione finora
- Formula Sheet - Phys 131Documento1 paginaFormula Sheet - Phys 131eNessuna valutazione finora
- Euclidean Vector Space: Geophysics UiDocumento9 pagineEuclidean Vector Space: Geophysics Uifdla rhmahNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytic Geometry FormulasDocumento6 pagineAnalytic Geometry FormulasHanie FordNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulas in Business MathDocumento1 paginaFormulas in Business MathGeraldo MejillanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulas for Business Math CalculationsDocumento1 paginaFormulas for Business Math CalculationsGeraldo MejillanoNessuna valutazione finora
- STEAM AND GAS TURBINE FORMULA SHEETDocumento2 pagineSTEAM AND GAS TURBINE FORMULA SHEEThamza ahmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Accuracy and precision in physics formulasDocumento2 pagineAccuracy and precision in physics formulasMadrid Jay RowellNessuna valutazione finora
- MIE100H1 - 20195 - 631572298320MIE 100 CheatsheetDocumento2 pagineMIE100H1 - 20195 - 631572298320MIE 100 CheatsheetSCR PpelusaNessuna valutazione finora
- Topsis PDFDocumento31 pagineTopsis PDFLetsplay GamesNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytic Geometry 1Documento2 pagineAnalytic Geometry 1Wayne VillarozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistics Sheet I (Descriptive Statistics)Documento3 pagineStatistics Sheet I (Descriptive Statistics)Priyanka ShanbhagNessuna valutazione finora
- Sorsogon City: Education, Accountancy, and Entrepreneurship DepartmentDocumento13 pagineSorsogon City: Education, Accountancy, and Entrepreneurship DepartmentEmily Despabiladeras DulpinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Research 2 Quantitative Research: Inferential Statistics Reference of Formulas Hypothesis-Testing ProcessDocumento4 paginePractical Research 2 Quantitative Research: Inferential Statistics Reference of Formulas Hypothesis-Testing Processjessa barbosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 11 Sheet #11 Week 3 Find The Domain and Range of A Rational FunctionDocumento2 pagineActivity 11 Sheet #11 Week 3 Find The Domain and Range of A Rational FunctionJoel LeriosNessuna valutazione finora
- Measures of Central TendencyDocumento3 pagineMeasures of Central TendencyAlishba NadeemNessuna valutazione finora
- MA20226 Statistics 2A CourseworkDocumento3 pagineMA20226 Statistics 2A CourseworkVlad BrebeanuNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022 - SynthèseDocumento9 pagine2022 - SynthèseThéo MélotteNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Package - EPDocumento178 pagineFull Package - EPretterateNessuna valutazione finora
- Core Subject: Semester:: Second Semester - Quarter 4 - Week 1 and 2Documento23 pagineCore Subject: Semester:: Second Semester - Quarter 4 - Week 1 and 2Edeth SubongNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Formula Sheet For ExamsDocumento2 paginePhysics Formula Sheet For ExamsRubicoNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of Finite Element Analysis FEM-StudentsDocumento64 pagineOverview of Finite Element Analysis FEM-StudentsCadet Muhammad Musawir AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Multivector Review Center Co.: Analytic GeometryDocumento22 pagineMultivector Review Center Co.: Analytic GeometryJohn Elver VeriNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 and 2 - Solving Quadratic Equations by Extracting Square Roots and FactoringDocumento21 pagineLesson 1 and 2 - Solving Quadratic Equations by Extracting Square Roots and FactoringRosalyn CalapitcheNessuna valutazione finora
- Motion in 2D: Projectiles and VectorsDocumento9 pagineMotion in 2D: Projectiles and VectorsChan LieslNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 6Documento4 pagineTutorial 6azurebirble12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Functions of Several VariablesDocumento25 pagineChapter 4 Functions of Several VariablesMostafa IbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Polar Coordinates LESSONDocumento10 paginePolar Coordinates LESSONHawraa HawraaNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 1.3. Optimazation of Learning AlgorithmsDocumento14 paginePart 1.3. Optimazation of Learning AlgorithmsViệt HoàngNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2. The ParabolaDocumento12 pagineLesson 2. The ParabolaAlanbert BangloNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 04 - Supervised Learning by Computing Distances (2) - PlainDocumento16 pagineLecture 04 - Supervised Learning by Computing Distances (2) - PlainRajaNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied Mathematics II-Multiple IntegralsDocumento27 pagineApplied Mathematics II-Multiple IntegralsTadesse100% (1)
- Data Collection and SummationDocumento4 pagineData Collection and SummationJet jet GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytic Geometry 1Documento2 pagineAnalytic Geometry 1Lemuel TeopeNessuna valutazione finora
- Formula B.SC (CS& AI)Documento2 pagineFormula B.SC (CS& AI)gracesachinrockNessuna valutazione finora
- Relative Velocity Reduction with Special RelativityDocumento5 pagineRelative Velocity Reduction with Special RelativityTathaNessuna valutazione finora
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDa EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (8)
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankDa EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsDa EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Gender Theory Textual AnalysisDocumento4 pagineGender Theory Textual AnalysisAmogh NarvekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Growth Evolution Economies Scale Globalization BusinessesDocumento5 pagineGrowth Evolution Economies Scale Globalization BusinessesjencpicNessuna valutazione finora
- HardwareDocumento74 pagineHardwareAmogh NarvekarNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.2 B PDFDocumento2 pagine3.2 B PDFAmogh NarvekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Task Sheet PDFDocumento2 pagineBusiness Task Sheet PDFAmogh NarvekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Solutions UNITS 1-4 PDFDocumento337 paginePhysics Solutions UNITS 1-4 PDFAmogh Narvekar80% (5)
- Trailblazers Student Enrolment Form - DomesticDocumento2 pagineTrailblazers Student Enrolment Form - DomesticAmogh NarvekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Validations, Verification & Testings - Amogh and Ishaan PDFDocumento3 pagineValidations, Verification & Testings - Amogh and Ishaan PDFAmogh NarvekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula SheetDocumento1 paginaAnalysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula SheetAmogh NarvekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory of Knowledge - Course Companion - Dombrowski, Rotenberg and Beck - Oxford 2013 PDFDocumento446 pagineTheory of Knowledge - Course Companion - Dombrowski, Rotenberg and Beck - Oxford 2013 PDFCaptian ProximaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula SheetDocumento1 paginaAnalysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula SheetAmogh NarvekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Institute of Actuaries of India: Solutions For ACET 2017Documento7 pagineInstitute of Actuaries of India: Solutions For ACET 2017Ananya KarmakarNessuna valutazione finora
- RMODocumento4 pagineRMOPavan Teja0% (1)
- Fpure ch3Documento34 pagineFpure ch3ShivamNessuna valutazione finora
- Panjab University Chandigarh BSc Mathematics SyllabusDocumento75 paginePanjab University Chandigarh BSc Mathematics Syllabusn0% (1)
- Carleton University: Final Examination Fall 2010Documento10 pagineCarleton University: Final Examination Fall 2010examkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- 26 MatricesDocumento26 pagine26 MatricesFazli KamawalNessuna valutazione finora
- BDA14103 Engineering Mathematics 2-Tutorial 4Documento2 pagineBDA14103 Engineering Mathematics 2-Tutorial 4KhaiNessuna valutazione finora
- C-GEC4 Module 7: Graphing Linear InequalitiesDocumento19 pagineC-GEC4 Module 7: Graphing Linear Inequalitiesfirestorm riveraNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Quarter Final Examination Mathematics 7Documento6 pagine1 Quarter Final Examination Mathematics 7Maria Martina Delos SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- 15.093J Optimization Methods: Lecture 4: The Simplex Method IIDocumento10 pagine15.093J Optimization Methods: Lecture 4: The Simplex Method IIAnup scribdNessuna valutazione finora
- Eric Mikida Fall 2011Documento34 pagineEric Mikida Fall 2011Avantika GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- LCC Course Descriptions for INDU, MNGM, MATH CoursesDocumento3 pagineLCC Course Descriptions for INDU, MNGM, MATH CoursesБогдан КулиничNessuna valutazione finora
- MIT8 09F14 Chapter 2Documento24 pagineMIT8 09F14 Chapter 2AnnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adding Subtracting Multiplying RadicalsDocumento4 pagineAdding Subtracting Multiplying RadicalsJacqueline TurciosNessuna valutazione finora
- Book Shahriar Shahriari AlgebraDocumento699 pagineBook Shahriar Shahriari Algebramehr1384100% (4)
- 2019 3N MatricesDocumento11 pagine2019 3N MatricesTeow JeffNessuna valutazione finora
- Extracted Pages From SSC Constable GD Exam Guide 2021-ArihantDocumento71 pagineExtracted Pages From SSC Constable GD Exam Guide 2021-Arihants saravanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Modeling With AlgebraDocumento4 pagineModeling With AlgebrapeueetNessuna valutazione finora
- DSP Final Exam Answers - 2017Documento9 pagineDSP Final Exam Answers - 2017AbadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Framework For California Public Schools: Kindergarten Through Grade TwelveDocumento37 pagineMathematics Framework For California Public Schools: Kindergarten Through Grade TwelveBin BinNessuna valutazione finora
- Greedy Approximation-Cambridge University Press (2011) Vladimir TemlyakovDocumento434 pagineGreedy Approximation-Cambridge University Press (2011) Vladimir TemlyakovOmonda Nii100% (1)
- Mathematics Volume 3 Class 12 JEEDocumento152 pagineMathematics Volume 3 Class 12 JEEMUTTA ADITHYA SAI SRINIVAS100% (1)
- Mathematic Question Paper Set ADocumento4 pagineMathematic Question Paper Set AADITHYA SUJINessuna valutazione finora
- MAT1102 - Course Unit No. 2 - Part 1Documento68 pagineMAT1102 - Course Unit No. 2 - Part 1shellaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2015 - 2008 Mathematics - All TopicsDocumento49 pagine2015 - 2008 Mathematics - All TopicsRickyNessuna valutazione finora
- 19 Scalar Products and Vector Products With ApplicationsDocumento32 pagine19 Scalar Products and Vector Products With ApplicationsKenton LamNessuna valutazione finora
- Evans, Kristian P. - Jacob, Niels - Course in Analysis, A - Volume II Differentiation and Integration of Functions of Several Variables, Vector Calculus-World Scientific Publishing Company (2016)Documento815 pagineEvans, Kristian P. - Jacob, Niels - Course in Analysis, A - Volume II Differentiation and Integration of Functions of Several Variables, Vector Calculus-World Scientific Publishing Company (2016)Бернард Баруч100% (1)
- 04 Quadratic EquationDocumento23 pagine04 Quadratic EquationmamunNessuna valutazione finora
- Solving Rational Equations and Inequalities LessonDocumento6 pagineSolving Rational Equations and Inequalities LessonDindin Oromedlav LoricaNessuna valutazione finora
- L3 - Differentiation RulesDocumento28 pagineL3 - Differentiation RulesAliah IzzahNessuna valutazione finora