Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Power Systems Problem Set Version2 PDF
Caricato da
Vineel PanakalaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Power Systems Problem Set Version2 PDF
Caricato da
Vineel PanakalaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
For
Doubts/Clarifications Email us at gate.knrao@gmail.com
For Regualr Updates Telegram Channel: GATE Lectures by KN Rao https://t.me/knrao123
Power Systerms
Per Unit Systems:
1. What
is
the
per
unit
reactance
of
an
alternator
if
the
capacity
is
doubled
and
voltage
is
halved?
a) Increases
by
4
times
b)
reduces
by
8
times
c) Increases
by
8
times
d)
decreases
by
4
times
(Ans:
C)
2. The
per
unit
impedance
of
a
synchronous
machine
is
0.242.
If
the
base
voltage
in
increased
by
1.1
times
then
per
unit
impedance
value
will
be
a) 0.266
b)
0.244
c)
0.220
d)
0.2
(Ans:
d)
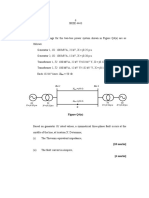
3. Two
identical
generators
of
100
MVA,
33
kV
are
connected
in
parallel
as
shown
in
the
figure,
they
are
interconnected
through
reactor,
Faults
occur
at
F1
and
F2
at
two
different
locations.
The
ratio
of
equivalent
fault
reactance
at
F1
w.r.t
F2
is
_________
a) 1.8 b) 0.55 c) 3.6 d) 0.27 (Ans: a)
4. For the power system shown in the fig below, the specifications of the components are the
following :
G1
=
25
kV,
100
MVA,
X
=
9%
G2
=
25
kV,
100
MVA,
X
=
9%
T1
=
25
kV/220
kV,
90
MVA,
X
=
12%
T2
=
220
kV/25
kV,
90
MVA,
X
=
12%
Line
1
:
200
kV,
X
=
150
ohms
Choose
25
kV
as
the
base
voltage
at
the
generator
G1,
and
200
MVA
as
the
MVA
base.
The
impedance
diagram
is
YouTube Channel Playlist for Machines: www.bit.ly/knraomcs
YouTube Channel Playlist for Power Systems: www.bit.ly/knraops
For Doubts/Clarifications Email us at gate.knrao@gmail.com
For Regualr Updates Telegram Channel: GATE Lectures by KN Rao https://t.me/knrao123
(Ans:b)
5.
A
3
–
phase
star
connected
load
is
drawing
power
at
a
voltage
of
0.9
pu
and
0.8
power
factor
lagging.
The
three
phase
base
power
and
base
current
are
100
MVA
and
437.38A
respectively.
The
line
–
to
–line
load
voltage
in
kV
is
______
(Ans
:
118.8)
6.
A
sustained
3-‐phase
fault
occurs
in
the
power
system
shown
in
the
fig.
The
current
and
voltage
phasors
during
the
fault
(on
a
common
reference),
after
the
natural
transients
have
died
down,
are
also
shown.
Where
is
the
fault
located?
YouTube Channel Playlist for Machines: www.bit.ly/knraomcs
YouTube Channel Playlist for Power Systems: www.bit.ly/knraops
For Doubts/Clarifications Email us at gate.knrao@gmail.com
For Regualr Updates Telegram Channel: GATE Lectures by KN Rao https://t.me/knrao123
a) Location
P
b)
Location
Q
c)
Location
R
d)
Location
S
(Ans:
b)
7. Three – phase to ground fault takes place at locations F1 and F2 in the system shown in the fig.
If
the
fault
takes
place
at
location
F1,
then
the
voltage
and
the
current
at
bus
A
are
Vf1
and
IF1
respectively.
If
the
fault
takes
place
at
location
F2,
then
the
voltage
and
the
current
at
bus
A
are
VF2
and
IF2
respectively.
The
correct
statement
about
voltages
and
currents
during
faults
at
F1
and
F2
is
a) VF1 leads IF1 and VF2 leads IF2 b) VF1 leads IF1 and VF2 lags IF2
C) VF1 lags IF1 and VF2 leads IF2 d) VF1 lags IF1 and VF2 lags IF2 (Ans: c)
8.
Five
alternators
each
rated
5
MVA,
13.2
kV
with
25%
of
reactance
on
its
own
base
are
connected
in
parallel
to
a
busbar.
The
short-‐circuit
level
in
MVA
at
the
busbar
is
_______
(Ans:
100)
9.
For
the
configuration
shown
in
the
fig.
the
breaker
connecting
a
large
system
to
bus
2
is
initially
open.
The
system
3-‐phase
fault
level
at
bus
3
under
this
condition
is
not
known.
After
closing
the
system
breaker,
the
3-‐phase
fault
level
at
bus
1
was
found
to
be
5.0
pu
.
What
will
be
the
new
3-‐
phase
fault
level
at
system
bus
3
after
the
interconnection?
All
per
unit
values
are
on
common
base.
Prefault
load
currents
are
neglected
and
prefault
voltages
are
assumed
to
be
1.0
p.u
at
all
buses.
Eg = 1.0 p.u., XT = 0.2 p.u., XLine = 0.3 p.u., Xd = 0.2 p.u. (Ans: 11.4285)
YouTube Channel Playlist for Machines: www.bit.ly/knraomcs
YouTube Channel Playlist for Power Systems: www.bit.ly/knraops
For Doubts/Clarifications Email us at gate.knrao@gmail.com
For Regualr Updates Telegram Channel: GATE Lectures by KN Rao https://t.me/knrao123
Statement for Linked Answer Question: (10 and 11 only)
Two
generator
units
G1
and
G2
are
connected
by
15
kV
line
with
a
bus
at
the
mid-‐point
as
shown
below,
G1
=
250
MVA,
15
kV,
positive
sequence
reactance
X
=
25%
on
its
own
base.
G2 = 100 MVA, 15 kV, positive sequence reactance X = 10% on its own base.
L1 and L2 = 10 km, positive sequence reactance X = 0.225 ohms/km.
10.
For
the
above
system,
the
positive
sequence
diagram
with
the
p.u
values
on
the
100
MVA
common
base
is
YouTube Channel Playlist for Machines: www.bit.ly/knraomcs
YouTube Channel Playlist for Power Systems: www.bit.ly/knraops
For Doubts/Clarifications Email us at gate.knrao@gmail.com
For Regualr Updates Telegram Channel: GATE Lectures by KN Rao https://t.me/knrao123
(Ans:
a)
11. In the above system, the three-‐phase fault MVA at the bus 3 is
a) 82.55 MVA b) 85.11 MVA c) 170.91 MVA d) 181.82 MVA (Ans: d)
12.
In
the
circuit
shown,
the
switch
is
closed
at
t
=
0.
The
value
of
Ɵ
in
degrees
which
will
give
the
maximum
value
of
DC
offset
of
the
current
at
the
time
of
switching
is
a) -‐30 b) 60 c) -‐45 d) 90 (Ans: c)
13.
The
reference
voltage
for
phase
a
is
defined
as
V
(t)
=𝑉! cosωt.
A
symmetrical
3-‐Φ
fault
occurs
at
centre
of
the
line
i.e.at
point
F.
The
wave
form
corresponding
to
phase
a
fault
current
from
bus
X
reveals
that
decaying
D.C.
offset
current
is
negative
and
in
magnitude
at
its
maximum
initial
value.
(𝑍! = 0.006+j0.06 p.u. and f=50 hz ). The instant (t0) of the fault will be
a)
4.682
ms
b)
9.667
ms
c)
14.667
ms
d)
19.667
ms
(Ans:
a)
14.
A
50
Hz
alternator
is
rated
500
MVA,
20
kV,
with
Xd
=
1.0
per
unit
and
𝑋!!! =
0.2
per
unit.
It
supplies
a
purely
resistive
load
of
400
MW
at
20
kV.
The
load
is
connected
directly
across
the
generator
terminals
when
a
symmetrical
fault
occurs
at
the
load
terminals.
The
initial
rms
current
in
the
generator
in
per
unit
is
a) 7.22 b) 5.05 c) 3.22 d) 2.25 (Ans: b)
YouTube Channel Playlist for Machines: www.bit.ly/knraomcs
YouTube Channel Playlist for Power Systems: www.bit.ly/knraops
For Doubts/Clarifications Email us at gate.knrao@gmail.com
For Regualr Updates Telegram Channel: GATE Lectures by KN Rao https://t.me/knrao123
15.
A
50
MVA,
10
kV,
50
Hz,
star-‐connected,
unloaded
three-‐phase
alternator
has
a
synchronous
reactance
of
1
p.u.
and
a
sub-‐transient
reactance
of
0.2
p.u.
If
a
3-‐phase
short
circuit
occurs
close
to
the
generator
terminals,
the
ratio
of
initial
and
final
values
of
the
sinusoidal
component
of
the
short
circuit
current
is
________
(Ans:
5.0)
16.
The
magnitude
of
3-‐phase
fault
currents
at
buses
A
and
B
of
a
power
system
are
10
pu
and
8
pu,
respectively.
Neglect
all
resistances
in
the
system
and
consider
the
pre-‐fault
system
to
be
unloaded.
The
pre-‐fault
voltage
at
all
buses
in
the
system
is
1.0
pu.
The
voltage
magnitude
at
bus
B
during
a
three-‐phase
fault
at
bus
A
is
0.8
pu.
The
voltage
magnitude
at
bus
A
during
a
three-‐phase
fault
at
bus
B,
in
pu,
is
____________?
(Ans:
0.84)
17.
A
500
MVA,
20
kV,
60
Hz
synchronous
generator
having
𝑋!" =0.2pu
is
supplying
a
passive
load
of
400MW
at
20
Kv.
The
load
is
purely
resistive.
Then
the
value
of
post
fault
current
at
the
generator
terminals
is
(Ans
:
5.06∠-‐80.9
pu
)
18. A 2-‐bus system and corresponding zero sequence network are shown in the figure.
The transformer T1 and T2 are connected
(Ans: b)
19.
For
the
network
as
shown
in
the
fig.
the
zero
sequence
reactance
in
p.u
are
indicated.
The
Zero
sequence
driving
point
reactance
of
the
node
3
is
a) 0.12 pu b) 0.30 pu c) 0.10 pu d) 0. 20 pu (Ans: c)
20.
In
an
unbalanced
three-‐phase
system,
phase
current
Ia
=
1∠(-‐900)
pu,
negative
sequence
current
Ib2
=
4∠
(-‐1500)
pu,
zero
sequence
current
Ic0
=
3∠900.
The
magnitude
of
phase
current
Ib
in
pu
is
a) 1.00 b)7.81 c) 11.53 d) 13.00 (Ans: c)
21)
Three
identical
star
connected
resistors
of
1.0
p.u
are
connected
to
an
unbalanced
3
phase
supply.
The
load
neutral
is
isolated.
The
symmetrical
components
of
the
line
voltages
in
p.u
are:
YouTube Channel Playlist for Machines: www.bit.ly/knraomcs
YouTube Channel Playlist for Power Systems: www.bit.ly/knraops
For Doubts/Clarifications Email us at gate.knrao@gmail.com
For Regualr Updates Telegram Channel: GATE Lectures by KN Rao https://t.me/knrao123
Vab1 = X∠Ɵ1, Vab2 = Y∠Ɵ2
If
all
the
p.u
calculations
are
with
the
respective
base
values,
the
phase
to
neutral
sequence
voltages
are
a) Van1 = X∠(Ɵ1 + 300), Van2 = Y∠(Ɵ2 – 300)
b) Van1 = X∠(Ɵ1 -‐ 300), Van2 = Y∠(Ɵ2 + 300)
! !
c) Van1 = 𝑋∠(Ɵ1 -‐ 300), Van2 = 𝑌∠(Ɵ2 + 300)
! !
! !
d) Van1
=
𝑋∠(Ɵ1
-‐
600),
Van2
=
𝑌∠(Ɵ2
-‐
600)
(Ans:
b)
! !
22)
A
three-‐phase
alternator
generating
unbalanced
voltages
is
connected
to
an
unbalanced
load
through
a
3-‐phase
transmission
line
as
shown
in
fig.
The
neutral
of
the
alternator
and
the
star
point
of
the
load
are
solidly
grounded.
The
phase
voltages
of
the
alternator
are
Ea=10∠00V,
Eb
=
10∠-‐900V,
Ec
=
10∠1200
V.
The
+ve
sequence
component
of
the
load
current
is
a) 1.310∠-‐1070
A
b)
0.332∠-‐1200
A
c)
0.996∠-‐1200
A
d)
3.510∠-‐810
A
(Ans:
d)
23) The parameters of transposed overhead transmission lie are given as:
Self-‐reactance
Xs
=
0.4
Ω/km
and
Mutual
reactance
Xm
=
0.1
Ω/km
The
positive
sequence
reactance
x1
and
zero
sequence
reactance
x0,
respectively,
in
Ω/km
are
a) 0.3, 0.2 b) 0.5, 0.2 c) 0.5, 0.6 d) 0.3, 0.6 (Ans: d)
24) The series impedance matrix of a short three-‐phase transmission line in phase coordinate is
.
If
the
positive
sequence
impedance
is
(1+j10)
Ω,
and
the
zero
sequence
is
(4+j31)
Ω,
then
the
imaginary
part
of
Zm
(in
Ω)
is
_____
(up
to
2
decimal
places).
(Ans:
7)
25) Suppose we define a sequence transformation between “a-‐b-‐c” and “p-‐n-‐o” variables as follows:
YouTube Channel Playlist for Machines: www.bit.ly/knraomcs
YouTube Channel Playlist for Power Systems: www.bit.ly/knraops
For Doubts/Clarifications Email us at gate.knrao@gmail.com
For Regualr Updates Telegram Channel: GATE Lectures by KN Rao https://t.me/knrao123
Where and k is a constant now, if it is given that:
And then,
a) b)
C) d) (Ans: b)
26) A 3-‐phase transmission line is shown in figure:
Voltage
drop
across
the
transmission
line
is
given
by
the
following
equation:
Shunt
capacitance
of
the
line
can
be
neglect.
If
the
line
has
positive
sequence
impedance
of
15Ω
and
zero
sequence
impedance
of
48Ω,
then
the
values
of
Zs
and
Zm
will
be
a) Zs = 31.5 Ω; Zm = 16.5Ω b) Zs = 26 Ω; Zm = 11Ω
c) Zs = 16.5 Ω; Zm = 31.5Ω d) Zs = 11 Ω; Zm = 26Ω (Ans: b)
27)
The
positive,
negative
and
zero
sequence
reactance’s
of
a
wye-‐connected
synchronous
generator
are
0.2
p.u,
0.2
p.u
and
0.1
p.u
respectively.
The
generator
is
on
open
circuit
with
a
YouTube Channel Playlist for Machines: www.bit.ly/knraomcs
YouTube Channel Playlist for Power Systems: www.bit.ly/knraops
For Doubts/Clarifications Email us at gate.knrao@gmail.com
For Regualr Updates Telegram Channel: GATE Lectures by KN Rao https://t.me/knrao123
terminal
voltage
of
1
p.u.
The
minimum
value
of
the
inductive
reactance,
in
Pu,
required
to
be
connected
between
neutral
and
ground
so
that
the
fault
current
does
not
exceed
3.75
Pu
if
a
single
line
to
ground
fault
occurs
at
the
terminals
is
_______.
(Assume
fault
impedance
to
be
zero).
(Give
the
answer
up
to
be
one
decimal
place).
(Ans:
0.1)
28) Two identical unloaded generators are connected in parallel as shown in the figure.
Both
the
generators
are
having
positive,
negative
and
zero
sequence
impedance
of
j0.4
p.u,
j0.3
p.u
and
j0.15
p.u.,
respectively.
If
the
pre-‐fault
voltage
is
1
p.u.,
for
a
line-‐to-‐ground
(L-‐G)
fault
at
the
terminals
of
the
generators,
the
fault
current,
in
p.u,.
is
______?
(Ans:
6)
29)
The
positive,
negative
and
zero
sequence
impedances
of
a
3-‐phase
generator
are
Z1,
Z2
and
Z0
respectively.
For
a
line-‐to-‐line
fault
with
fault
impedance
Zf,
the
fault
current
is
If1
=
kIf,
where
If
is
the
fault
current
with
zero
fault
impedance.
The
relation
between
Zf
and
k
is
a) b)
c) d) (Ans: a)
30)
A
30
MVA,
3-‐phase,
50
Hz,
13.8
kV,
star-‐connected
synchronous
generator
has
positive,
negative
and
zero
sequence
reactance’s,
15%,
15%
and
5%
respectively.
A
reactance
(Xn)
is
connected
between
the
neutral
of
the
generator
and
ground.
A
double
line
to
ground
fault
takes
place
involving
phases
‘b’
and
‘c’,
with
a
fault
impedance
of
j0.1
p.u.
The
value
of
Xn
(in
p.u)
that
will
limit
the
positive
sequence
generator
current
to
4270
A
is
______
(Ans:
1.07)
31)
A
30
kV,
50
Hz,
50
MVA
generator
has
the
positive,
negative
and
zero
sequence
reactance’s
of
0.25
pu,
0.15
pu,
0.05
pu,
respectively.
The
neutral
of
the
generator
is
grounded
with
a
reactance
so
that
the
fault
current
for
a
bolted
LG
fault
and
that
of
a
bolted
three-‐phase
fault
at
the
generator
terminal
are
equal.
The
value
of
grounding
reactance
in
ohms
(round
off
to
one
decimal
place)
is
___
(Ans:
1.8)
32)
The
sequence
components
of
the
fault
current
are
as
follows:
I
positive
=
j1.5
pu,
Inegative=
-‐j0.5
pu,
Izero=
-‐j1
pu.
The
type
of
fault
in
the
system
is
a) LG b) LL c) LLG d) LLLG (Ans: c)
33)
A
100
MVA,
11kV,
50Hz
turbo
generator
is
having
a
symmetrical
fault
at
its
terminals.
The
short-‐
circuit
capacity
is
500
MVA.
The
neutral
of
the
alternator
is
grounded
through
a
reactance
of
0.05
pu.
The
zero-‐sequence
reactance
of
the
generator
is
25%
of
its
positive-‐sequence.
The
short-‐circuit
capacity
for
a
line
to
ground
fault
is
_______
MVA.
(Ans:
500)
YouTube Channel Playlist for Machines: www.bit.ly/knraomcs
YouTube Channel Playlist for Power Systems: www.bit.ly/knraops
For Doubts/Clarifications Email us at gate.knrao@gmail.com
For Regualr Updates Telegram Channel: GATE Lectures by KN Rao https://t.me/knrao123
Problem Sets will keep on updated… For most
recent Problem Set Visit www.knrao.in
YouTube Channel Playlist for Machines: www.bit.ly/knraomcs
YouTube Channel Playlist for Power Systems: www.bit.ly/knraops
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Advanced Power System Anlaysis SyllabusDocumento2 pagineAdvanced Power System Anlaysis SyllabusKiran KunchamNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee 404 Problem Sets 1 Part 2 SolutionDocumento6 pagineEe 404 Problem Sets 1 Part 2 SolutionJohn Lloyd ComiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Timeline of Philippine HistoryDocumento6 pagineTimeline of Philippine HistoryCarlos Baul DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Electro MagsDocumento4 pagineElectro MagsVan Daryl C MonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Viscous Flow and Boundary LayerDocumento72 pagineViscous Flow and Boundary LayerBilal UsmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Elementary Differential Equations-BoyceDocumento39 pagineElementary Differential Equations-BoyceNurul HanifahNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Systems Lecture Series: Part Vii. Unsymmetrical Faults (Open Case)Documento26 paginePower Systems Lecture Series: Part Vii. Unsymmetrical Faults (Open Case)Joshua Roberto GrutaNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of QuestionsDocumento31 pagineSummary of QuestionsMacLife AlexNessuna valutazione finora
- Higher Order Differential Equations - Dr. M. A. MalequeDocumento54 pagineHigher Order Differential Equations - Dr. M. A. MalequeShadman Saqlain Rahman, 170021057Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electromagnetism Session 2 QuestionsDocumento80 pagineElectromagnetism Session 2 QuestionsJohn English100% (1)
- Approaches To School Curriculum: Prepared By: HAIFADocumento23 pagineApproaches To School Curriculum: Prepared By: HAIFAHaifa Mohammadsali AndilingNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering ChemistryDocumento2 pagineEngineering ChemistryssjatavNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Mechanics and Machinery - Lab ManualDocumento76 pagineFluid Mechanics and Machinery - Lab ManualSiva KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus in Fluid MechanicsDocumento9 pagineSyllabus in Fluid MechanicsAlan BalilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Density and Specific GravityDocumento76 pagineDensity and Specific GravityJireh Ann Mejino50% (2)
- ELEX1 Lecture 01 PDFDocumento10 pagineELEX1 Lecture 01 PDFBarn Go100% (1)
- Problem Solving Questions (Part I) PDFDocumento6 pagineProblem Solving Questions (Part I) PDFclainNessuna valutazione finora
- Algebra ReviewerDocumento2 pagineAlgebra Revieweresto_domingoNessuna valutazione finora
- AC Circuit 2 (Three-Phase)Documento2 pagineAC Circuit 2 (Three-Phase)marlon desaculaNessuna valutazione finora
- Questions On Single Phase Series CircuitsDocumento45 pagineQuestions On Single Phase Series Circuitskibrom atsbhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Book-2 - Physcis - 312 - Senior Secondary PDFDocumento386 pagineBook-2 - Physcis - 312 - Senior Secondary PDFNaren GujjarNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre Board Math B PDFDocumento6 paginePre Board Math B PDFAnjoe Mhar NocheNessuna valutazione finora
- Single Tuned Voltage Amplifier: Siddhartha Engineering CollegeDocumento11 pagineSingle Tuned Voltage Amplifier: Siddhartha Engineering CollegeChakri KamaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigo MCQsDocumento9 pagineTrigo MCQsShawn GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Stress, Strain and Young's ModulusDocumento2 pagineStress, Strain and Young's ModuluswahNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1Documento2 pagineAssignment 1Lourence Adriel DimaunahanNessuna valutazione finora
- Work Energy and Power1Documento13 pagineWork Energy and Power1E guruNessuna valutazione finora
- Pounds Mass and Pounds ForceDocumento11 paginePounds Mass and Pounds Forcewensley jethrou guzmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice QuizDocumento7 pagineMultiple Choice QuizMHLS68Nessuna valutazione finora
- Power System - Analysis, Stability & Computer TechniquesDocumento19 paginePower System - Analysis, Stability & Computer TechniquesSudip Mondal100% (1)
- Digital Electronics Ece 213 PDFDocumento15 pagineDigital Electronics Ece 213 PDFAlisha AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Iecep Compilation GeasDocumento4 pagineIecep Compilation Geasjanno2101100% (1)
- Lec2 Transformers IIDocumento17 pagineLec2 Transformers IIMohammed Dyhia AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Algebra 3 CP PDFDocumento1 paginaAlgebra 3 CP PDFJefferson Nolty GenoviaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Optional Method of Calculation For Dwelling Units Is Reserved ForDocumento17 pagineThe Optional Method of Calculation For Dwelling Units Is Reserved ForLem Eruel MabutasNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics and Experimental Methods PDFDocumento19 pagineElectronics and Experimental Methods PDFPhysicsNessuna valutazione finora
- Start Download - View PDF: 110 Top Most Control SYSTEMS Objective Questions and Answers PDFDocumento24 pagineStart Download - View PDF: 110 Top Most Control SYSTEMS Objective Questions and Answers PDFEj ParañalNessuna valutazione finora
- PHM 601 Question Bank-2018Documento4 paginePHM 601 Question Bank-2018Abhishek YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Day 01 - Algebra 1Documento19 pagineDay 01 - Algebra 1Ironfalcon101Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - Electrical+Basics+-+CircuitsDocumento36 pagine1 - Electrical+Basics+-+Circuitsareina75Nessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Mathematics 1Documento2 pagineEngineering Mathematics 1ofreneo_joshua4437Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Problems of EEDocumento9 pagineSample Problems of EEEdson MilanoNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ in Physics Part 1 ECE Board ExamDocumento9 pagineMCQ in Physics Part 1 ECE Board ExamJemmuel MamintaNessuna valutazione finora
- Capacitors & Energy StorageDocumento44 pagineCapacitors & Energy StoragearuunrsNessuna valutazione finora
- Three Types of Transistor Configuration: - : Common Emitter Common Base Common CollectorDocumento4 pagineThree Types of Transistor Configuration: - : Common Emitter Common Base Common CollectorMuhammad FitriNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics Engineering Pre-Board 1Documento12 pagineElectronics Engineering Pre-Board 1Rennel MallariNessuna valutazione finora
- Forward and Reverse Bias of PN JunctionDocumento9 pagineForward and Reverse Bias of PN JunctionHasin Ishrak HishamNessuna valutazione finora
- VillamorDocumento146 pagineVillamorzellepedranza100% (1)
- Practice Problems 1Documento5 paginePractice Problems 1Lanz de la Cruz100% (1)
- Mesl Set 1Documento8 pagineMesl Set 1RENE JOSHUA PECASONessuna valutazione finora
- Elec 3202 Chap 6Documento67 pagineElec 3202 Chap 6budi_ummNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 10 - ch2, 100Documento2 pagineGrade 10 - ch2, 100NayLinNessuna valutazione finora
- PPP Areas I - XDocumento151 paginePPP Areas I - XCleofe CaidicNessuna valutazione finora
- Session 4 - Electrical LayoutDocumento17 pagineSession 4 - Electrical LayoutCeino Rey QuimintanNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Machines Problem Set V2 PDFDocumento13 pagineElectrical Machines Problem Set V2 PDFVineel PanakalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Section A: 1 Choose/fill in The Blanks/match FollowingsDocumento4 pagineSection A: 1 Choose/fill in The Blanks/match Followingssurendra kumar kashyapNessuna valutazione finora
- Passed or Past - OxfordWords Blog PDFDocumento9 paginePassed or Past - OxfordWords Blog PDFMohamad SannanNessuna valutazione finora
- Symmetrical Fault AssignmentDocumento14 pagineSymmetrical Fault Assignmentsir isaNessuna valutazione finora
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)Da EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Beles1 701Documento2 pagineBeles1 701Arsh DeepNessuna valutazione finora
- ThermodynamicsDocumento14 pagineThermodynamicsRyan Trajano EspalmadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Atoms and Elements, Compounds and Mixtures - ExercisesDocumento8 pagineAtoms and Elements, Compounds and Mixtures - ExercisesLim Kok PingNessuna valutazione finora
- Ques - 14 55 PDFDocumento15 pagineQues - 14 55 PDFVosuMittalNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Project Report Format of 2020 Passout.Documento84 pagineSample Project Report Format of 2020 Passout.Prem sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- BNP C3015 PDFDocumento231 pagineBNP C3015 PDFAri Ercilio Farias FereirraNessuna valutazione finora
- Company ListDocumento1.314 pagineCompany ListCharles Williams0% (1)
- Load Dispatch Centre: By-Siddharth KumarDocumento16 pagineLoad Dispatch Centre: By-Siddharth KumarSIDDHARTHNessuna valutazione finora
- Engg CW DetailsDocumento26 pagineEngg CW DetailsMuhammad Sohail TariqNessuna valutazione finora
- 2013 04Documento110 pagine2013 04Jose Emmanuel Martinez CordovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sandvik 533: Technical Specification 533-Revision 2 1/9Documento9 pagineSandvik 533: Technical Specification 533-Revision 2 1/9ricardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Transmission Lines and NetworksDocumento18 pagineTransmission Lines and NetworkszgxfsbjbnNessuna valutazione finora
- An Efficient Microgrid Management System For Rural Area Using ArduinoDocumento7 pagineAn Efficient Microgrid Management System For Rural Area Using ArduinoRicha SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Siemons - Cello Bowing TechniqueDocumento15 pagineSiemons - Cello Bowing TechniqueMassa Awaj100% (2)
- 04 - Modul Simulasi Impetus Physics 2021Documento162 pagine04 - Modul Simulasi Impetus Physics 2021Doraemon Music100% (1)
- Sir. Abdul-Kareem: Stereoisomerism - Geometric IsomerismDocumento8 pagineSir. Abdul-Kareem: Stereoisomerism - Geometric IsomerismsaudNessuna valutazione finora
- Static Electricity in Fuel Handling FacilitiesDocumento29 pagineStatic Electricity in Fuel Handling Facilitiesbiondimigu100% (1)
- Mechanizing Philippine Agriculture For Food SufficiencyDocumento21 pagineMechanizing Philippine Agriculture For Food SufficiencyViverly Joy De GuzmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Sources of Energy Class 10Documento17 pagineSources of Energy Class 10Maan NmNessuna valutazione finora
- Research and Development: Applied Research IN Renewable Energy SystemsDocumento22 pagineResearch and Development: Applied Research IN Renewable Energy SystemsBilaljafraniNessuna valutazione finora
- Sneak WireDocumento36 pagineSneak WireMeraSultanNessuna valutazione finora
- M047 Service Manual: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineDocumento286 pagineM047 Service Manual: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineLH TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ci Ride Leader - Guide To Cycling On The Road PDFDocumento10 pagineCi Ride Leader - Guide To Cycling On The Road PDFΑυτός είμαι εγώNessuna valutazione finora
- Work Method StatementDocumento10 pagineWork Method StatementMdNasruddin shaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Theoretical Approaches Regarding The VENTURI EffectDocumento4 pagineTheoretical Approaches Regarding The VENTURI EffectJose A AbrahamNessuna valutazione finora
- Information & Operations Manual For Bavaria Cruiser 37Documento37 pagineInformation & Operations Manual For Bavaria Cruiser 37RDNessuna valutazione finora
- Leroy Somer D510C AVRDocumento54 pagineLeroy Somer D510C AVRabuzer1981Nessuna valutazione finora
- Coal Handling SystemDocumento56 pagineCoal Handling SystemPrudhvi RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Transistor (Ukr)Documento31 pagineTransistor (Ukr)Uday RaiNessuna valutazione finora
- PHD Thesis On Thermal Power PlantDocumento6 paginePHD Thesis On Thermal Power Plantafkneafpz100% (1)