Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Yow
Caricato da
Sarahfay Ashley TingCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Yow
Caricato da
Sarahfay Ashley TingCopyright:
Formati disponibili
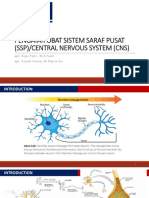
The Cell of the Nervous System
The nervous system comprises of two group of cells, glial cells and neurons.
Neurons are responsible for sensing change and communicating with other neurons.
Glial cells work to support, nourish, insulate neurons and remove waste products.
A neuron is a nerve cell that is the basic building block of the nervous
system. Neurons are similar to other cells in the human body in a number of ways,
but there is one key difference between neurons and other cells. Neurons are
specialized to transmit information throughout the body.
The human body contains some 100 billion neurons, which form a part of
the nervous tissue (the brain, the spinal cord and the nerves).
Nervous system cells are called neurons. They have three distinct parts, including
a cell body, axon, and dendrites. These parts help them to send and receive
chemical and electrical signals.
Parts of a Nerve Cell
Cell body- The cell body, also called the soma, is the spherical part of the neuron
that contains the nucleus. The cell body connects to the dendrites, which bring
information to the neuron, and the axon, which sends information to other neurons.
Axon- An axon, or nerve fiber, is a long slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron,
that conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body or
soma. Axons are in effect the primary transmission lines of the nervous system, and
as bundles they help make up nerves.
Dendrites- Dendrites also dendrons, are branched protoplasmic extensions of a
nerve cell that propagate the electrochemical stimulation received from other neural
cells to the cell body, or soma, of the neuron from which the dendrites project.
The one who received the message is a form of stimulus.
For communication between neurons to take place, an electrical impulse triggers
the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters are released
into the space between the two neurons. This space is called the synapse. ...
Receptors receive and process the message, then send it on to the next neuron.
Cs will travel to the cell.
NCS- this nerve will release a chemical that called Neuro Transmitter.
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that enable neurotransmission. It is
a type of chemical messenger which transmits signals across a chemical synapse,
such as a neuromuscular junction, from one neuron (nerve cell) to another "target"
neuron, muscle cell, or gland cell.
The nervous system is made up of nerves. A nerve is a bundle of nerve cells. A nerve cell that
carries messages is called a neuron (Figure below). The messages carried by neurons are
called nerve impulses. Nerve impulses can travel very quickly because they are electrical
impulses.
Myelin is an insulating layer, or sheath that forms around nerves, including those in the brain
and spinal cord. It is made up of protein and fatty substances. This myelin sheath allows
electrical impulses to transmit quickly and efficiently along the nerve cells.
One part of cell it releases a New Transmitter signal.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Sleep PowerpointDocumento10 pagineSleep PowerpointTravisHarringtonNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 6Documento37 pagineGroup 6LohithNessuna valutazione finora
- Electroencephalography (EEG) : Dr. Altaf Qadir KhanDocumento65 pagineElectroencephalography (EEG) : Dr. Altaf Qadir KhanAalia RanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscarinic Jones Concert: Skeletal Muscle Contraction Analogy WorksheetDocumento5 pagineMuscarinic Jones Concert: Skeletal Muscle Contraction Analogy WorksheetCharles VollmersNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurotransmitters: Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA)Documento12 pagineNeurotransmitters: Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA)Kay RandhawaNessuna valutazione finora
- N, N-Dimethyltryptamine and The Pineal Gland: Separating Fact From Myth - David NicholsDocumento7 pagineN, N-Dimethyltryptamine and The Pineal Gland: Separating Fact From Myth - David NicholsIno MoxoNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution of Cell SignalingDocumento3 pagineEvolution of Cell SignalingkatakanNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurotransmitters PDFDocumento23 pagineNeurotransmitters PDFБакытNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuroscience NotesDocumento35 pagineNeuroscience NotesAnna Conigrave100% (4)
- Cellular Signal Transduction: The Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Department of CMUDocumento98 pagineCellular Signal Transduction: The Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Department of CMUKrisda JitrakbumrungNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.1 One Pager Reflex Action - MEMODocumento1 pagina5.1 One Pager Reflex Action - MEMORudzi UdziNessuna valutazione finora
- VMAT2 Gene Molecular Study of 2,000 Peoples in The Religious Behavior and Belief in God of The Citizens of The City of Tabriz in IRANDocumento10 pagineVMAT2 Gene Molecular Study of 2,000 Peoples in The Religious Behavior and Belief in God of The Citizens of The City of Tabriz in IRANcipinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharma 2nd LEDocumento3 paginePharma 2nd LEkimberly abianNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug-Receptor Interactions AND Pharmacodynamics: Ramla KashifDocumento36 pagineDrug-Receptor Interactions AND Pharmacodynamics: Ramla KashifRamla KashifNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding PharmacodynamicsDocumento27 pagineUnderstanding PharmacodynamicsHansNessuna valutazione finora
- Axon ReflexDocumento38 pagineAxon ReflexKamalakannanNessuna valutazione finora
- NERVOUS SYSTEM CHEMICAL INTERMEDIARIESDocumento40 pagineNERVOUS SYSTEM CHEMICAL INTERMEDIARIESPopa NicuNessuna valutazione finora
- Autonomic & Systemic Pharmacology Exam QuestionsDocumento5 pagineAutonomic & Systemic Pharmacology Exam QuestionsG S RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- GABRIEL JONATHAN 22010323140059 E6a4Documento6 pagineGABRIEL JONATHAN 22010323140059 E6a4RIfki ARYANANDA ajiNessuna valutazione finora
- IB Psychology: Neuroplasticity and NeurotransmittersDocumento2 pagineIB Psychology: Neuroplasticity and NeurotransmittersSayana GramalNessuna valutazione finora
- Sleep Circuits and Functions PDFDocumento247 pagineSleep Circuits and Functions PDFSupratik ChakrabortyNessuna valutazione finora
- Purves Neuroscience Website Questions CH 7 AnswersDocumento4 paginePurves Neuroscience Website Questions CH 7 AnswersPK32145987100% (1)
- Mechanism of Action of QuetiapineDocumento4 pagineMechanism of Action of QuetiapineThoha AlbaarNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOKIMIA Regulation of Neurotransmitters in Neuropsychiatric SystemDocumento83 pagineBIOKIMIA Regulation of Neurotransmitters in Neuropsychiatric SystemAndi Suchy Qumala SarieNessuna valutazione finora
- Pex 03 09Documento5 paginePex 03 09Kinea1100% (3)
- 1-Obat Sistem Saraf Pusat-Parkinson Dan Alzheimer DDocumento57 pagine1-Obat Sistem Saraf Pusat-Parkinson Dan Alzheimer DFarhan AshsiddiqiNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurotransmitter Cell CommunicationDocumento25 pagineNeurotransmitter Cell CommunicationOtnil DNessuna valutazione finora
- PYC1501 Unit 1 Human Nervous System OERDocumento18 paginePYC1501 Unit 1 Human Nervous System OERjulia.mokoenadjNessuna valutazione finora
- K10 Opioid AnalgesicsDocumento30 pagineK10 Opioid AnalgesicsLa Lydia TampubolonNessuna valutazione finora
- Cobra VenomDocumento29 pagineCobra VenomJohn ShaprioNessuna valutazione finora