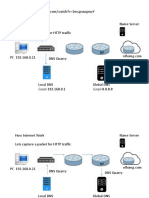
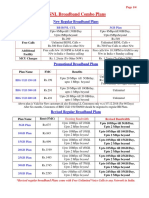
Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
WATM Reference Models, Protocol Architecture & Mobile ATM
Caricato da
SHRADDHA Vaishy0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
180 visualizzazioni13 pagineabout ATM
Titolo originale
Bluetooth Wireless ATM-converted
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoabout ATM
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
180 visualizzazioni13 pagineWATM Reference Models, Protocol Architecture & Mobile ATM
Caricato da
SHRADDHA Vaishyabout ATM
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 13
Submitted to Presented By
Mr. Parth Gautam Shraddha Vaishy
(Dept. Of Computer Science, DSVV) MCA 5th sem
Introduction
Wireless ATM Reference Models
Wireless ATM Protocol Architecture
Mobile ATM
WATM Projects
References
ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) has been advocated as an
important technology for all types of services and networks.
Most people believe that ATM will be the standard for the
future B-ISDN (Broadband Integrated Services Digital
Network).
From the service point of view, ATM combines both the data
and multimedia information into the wired networks while
scales well from backbones to the customer premises networks.
Figure 1 WATM reference model
The overall system consists of a fixed ATM network
infrastructure and a radio access segment.
In the fixed ATM network, the switches, which
communicate directly with wireless station or wireless
end user devices, are mobility enhanced ATM switches.
They serve as the "entrance" to the infrastructure wired
ATM networks.
Based on the different types of wireless applications,
the radio access segment falls into a number of areas
which may need different solutions.
Fixed Wireless Components
Mobile End Users
Mobile Switches with Fixed End Users
Mobile Switches with Mobile End Users
Interworking with PCS
Wireless Ad Hoc Networks
Media Access Control (MAC) -WATM MAC is responsible
for providing functionally point to point links for the higher
protocol layer to use.
Data Link Control (DLC)-Data Link Control is responsible
for providing service to ATM layer. Mitigating the effect of
radio channel errors should be done in this layer before cells
are sent to the ATM layer.
Radio Resource Control (RRC)- RRC is needed for
support of control plane functions related to the radio access
layer. It should support radio resource control and
management functions for PHY, MAC, and DLC layers.
To support mobility, new higher layer control/signaling
functions are needed to handling handover, location
management, routing, addressing, and traffic
management.
The item, which defines the design the functions of
control/signaling, are called Mobile ATM.
Handover-In WATM networks, a mobile end user
establish a virtual circuit (VC) to communicate with
another end user (either mobile or ATM end user).
When the mobile end user moves from one AP (access
point) to another AP, proper handover is required.
Location Management-When a connection is needed
to be established between an mobile ATM end point
and another ATM end point, the mobile ATM end point
is needed to be located. There are two basic location
management schemes: the mobile PNNI scheme and
the location register scheme
Routing-Due to the mobility feature of mobile ATM,
routing signaling is a little bit different from that for the
wired ATM network. First, mapping of mobile terminal
routing-id's to paths in the network is necessary. Also
rerouting is needed to re-establish connection when the
mobiles move around.
Wireless Network Management- In wireless networks,
the topology is changing in time. This, as well as other
mobility feature, present a unique set of network
management challenges. A specific methods must be
designed to maintain the dynamic nature of the network
topology.
Wireless ATM is a topic that raises a lot of interest at the
moment and there are a lot of research activities going
on. Many of the activities are done within the
universities and corporate research laboratories.
Example-
Magic WAND (Wireless ATM Network Demonstrator)
MEDIAN (Wireless Broadband CPN/LAN for
Professional and Residential Multimedia Application
AWACS (ATM Wireless Access Communication
System)
https://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cis788-97/ftp/wireless_atm/index.html
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- ATM Simulator Project ReportDocumento71 pagineATM Simulator Project ReportSuchi Usha100% (1)
- Atm 141210010458 Conversion Gate01Documento33 pagineAtm 141210010458 Conversion Gate01Shashank ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- OmnykeyDocumento55 pagineOmnykeytorito2691Nessuna valutazione finora
- 8.3. Developing Use-Case DiagramsDocumento8 pagine8.3. Developing Use-Case DiagramsDeep AdhikaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Selfserv32 PrepareDocumento38 pagineSelfserv32 PrepareChristian Buelna NavarroNessuna valutazione finora
- Literature Survey (1) Smart Atm Security System Using FPR, GSM, GpsDocumento2 pagineLiterature Survey (1) Smart Atm Security System Using FPR, GSM, GpsRAMADEVI KESANANessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced ATM Security System by Using Smart Card and IOT TechnologyDocumento69 pagineAdvanced ATM Security System by Using Smart Card and IOT Technologykota naikNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar Report On ATM With An Eye 2011-12Documento21 pagineSeminar Report On ATM With An Eye 2011-12Vinod Kumar100% (1)
- Machine-to-Machine M2M Communications Third EditionDa EverandMachine-to-Machine M2M Communications Third EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Auto Car Lock Using Cell PhoneDocumento25 pagineAuto Car Lock Using Cell PhoneAmadi E. UchennaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCR ATMs and The ADA Final RuleDocumento4 pagineNCR ATMs and The ADA Final RuleDamian RamirezNessuna valutazione finora
- 93.ATM SecurityDocumento3 pagine93.ATM SecurityAjith manjuNessuna valutazione finora
- The ATM SystemDocumento7 pagineThe ATM Systemmanoum2Nessuna valutazione finora
- ATM Project FinalDocumento65 pagineATM Project FinalSaurabh0% (1)
- GSM Based Smart Information System For Lost ATM CardsDocumento3 pagineGSM Based Smart Information System For Lost ATM Cardsadzri_azahariNessuna valutazione finora
- Personas 86 Site PrepDocumento264 paginePersonas 86 Site PrepFree FortestNessuna valutazione finora
- Chipless RFID based on RF Encoding Particle: Realization, Coding and Reading SystemDa EverandChipless RFID based on RF Encoding Particle: Realization, Coding and Reading SystemNessuna valutazione finora
- ATM Reporting SystemDocumento3 pagineATM Reporting SystemSrikanth Jalam80% (5)
- Atm SecurityDocumento22 pagineAtm SecurityEr. Amar KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Secure ATM Door Locking System Using RFIDDocumento8 pagineSecure ATM Door Locking System Using RFIDImranNessuna valutazione finora
- Embedded Security in ATMsDocumento15 pagineEmbedded Security in ATMsSam Raj0% (1)
- Bluejacking (PP, P4)Documento20 pagineBluejacking (PP, P4)Harshada KoliNessuna valutazione finora
- 1122 DatasheetDocumento10 pagine1122 Datasheetneethurj9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Technologies for Emerging Markets: 2G, 3G and BeyondDa EverandCellular Technologies for Emerging Markets: 2G, 3G and BeyondNessuna valutazione finora
- Uml (Atm)Documento29 pagineUml (Atm)Henu Sharma100% (1)
- ATM Machine ManagementDocumento5 pagineATM Machine ManagementDannyNessuna valutazione finora
- Broadband Network Management: ATM NetworksDocumento40 pagineBroadband Network Management: ATM NetworksAnuvrat ChaturvediNessuna valutazione finora
- Java Ring Seminar ReportDocumento22 pagineJava Ring Seminar ReportSugam KatariaNessuna valutazione finora
- ATM Design Specification BreakdownDocumento9 pagineATM Design Specification BreakdownEminaTopalovićNessuna valutazione finora
- RFID Based Toll Collection SystemDocumento72 pagineRFID Based Toll Collection SystemGopalkrishnan Nadar67% (3)
- Technical Seminar On Automatic Teller Machine by Using BiometricsDocumento23 pagineTechnical Seminar On Automatic Teller Machine by Using BiometricsNAGMA SULTANANessuna valutazione finora
- 17fin8653 e NCR Selfserv 38 DsDocumento2 pagine17fin8653 e NCR Selfserv 38 DsAntonio SolisNessuna valutazione finora
- ATM Card OTP VerificationDocumento7 pagineATM Card OTP VerificationMansoorSulaiman100% (1)
- Door Locking Security System Using GSMDocumento130 pagineDoor Locking Security System Using GSMAnsumanNath100% (1)
- An Atm With An Eye2Documento18 pagineAn Atm With An Eye2Hacker4a4Nessuna valutazione finora
- ON Atm SecurityDocumento14 pagineON Atm SecurityShashankShekharNessuna valutazione finora
- NFC Tag ProtocolDocumento25 pagineNFC Tag ProtocolStefan IrovicNessuna valutazione finora
- SR-201 Network Relay Quick Start GuideDocumento7 pagineSR-201 Network Relay Quick Start GuideiakapoNessuna valutazione finora
- Automated Teller MachineDocumento20 pagineAutomated Teller MachineRathna Kumar SelvarajNessuna valutazione finora
- Bank System BANK Transaction ResponseDocumento3 pagineBank System BANK Transaction ResponseElle LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- RFID Antenna DesignDocumento8 pagineRFID Antenna DesignKevinValerTaiñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Book of AtmDocumento35 pagineProject Book of Atmpavan puppalaNessuna valutazione finora
- ATM ReportDocumento16 pagineATM Reportsoftware8832100% (1)
- MalwareDocumento17 pagineMalwareTarun NarulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Virtual SIM Solution enDocumento2 pagineVirtual SIM Solution entelephonicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Shodan Comandos PrincipalesDocumento1 paginaShodan Comandos PrincipalesmayraNessuna valutazione finora
- VisBCR (Systech)Documento54 pagineVisBCR (Systech)DExTERNessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis of Project To Interface Intercom System With (GSM) V-PhoneDocumento18 pagineThesis of Project To Interface Intercom System With (GSM) V-PhoneDecorate FutureNessuna valutazione finora
- Automated System in BankingDocumento67 pagineAutomated System in BankingRaj RamNessuna valutazione finora
- A Micro-Project Report ON: "Latest ATM Security''Documento19 pagineA Micro-Project Report ON: "Latest ATM Security''Kashyap PathakNessuna valutazione finora
- Atm ProcessingDocumento25 pagineAtm Processingbhargavi0850% (10)
- Immune-Inspired Adaptable Error Detection For Automated Teller MachinesDocumento15 pagineImmune-Inspired Adaptable Error Detection For Automated Teller Machinespearllover007Nessuna valutazione finora
- White Paper On Dingtalk SecurityDocumento31 pagineWhite Paper On Dingtalk Securitysean pulungtaNessuna valutazione finora
- SE Case StudyDocumento33 pagineSE Case StudyChirag SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Requirements For Example ATM SystemDocumento14 pagineRequirements For Example ATM Systemamel2910Nessuna valutazione finora
- Detecting and Characterizing Extremist Reviewer Groups in Online Product ReviewsDocumento11 pagineDetecting and Characterizing Extremist Reviewer Groups in Online Product ReviewsHEMALATHA SHANMUGAMNessuna valutazione finora
- Smart CardDocumento14 pagineSmart CardPraveen KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Training CheckpointDocumento63 pagineTraining Checkpointrajivmukherjee07Nessuna valutazione finora
- Streamline Area Monitoring with the G7 EXO Cloud-Connected Gas DetectorDocumento2 pagineStreamline Area Monitoring with the G7 EXO Cloud-Connected Gas DetectorMeesanNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Cisco'S Netflow Technology: Slide 1Documento29 pagineIntroduction To Cisco'S Netflow Technology: Slide 1jeffgrantinctNessuna valutazione finora
- MWC Microproject ReportDocumento17 pagineMWC Microproject Report10 Durvesh PathakNessuna valutazione finora
- Dokumen - Tips - Huawei Smartax Ma5616 Configuration Guide v800r310c0003 PDFDocumento717 pagineDokumen - Tips - Huawei Smartax Ma5616 Configuration Guide v800r310c0003 PDFfelckieNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction NS2 SimulatorDocumento41 pagineIntroduction NS2 SimulatoralagiriNessuna valutazione finora
- SonicWALL 1⁄2 day hands-on workshopDocumento35 pagineSonicWALL 1⁄2 day hands-on workshopkingericcantonaNessuna valutazione finora
- Flatbush Internet Asifa Kintres EnglishDocumento22 pagineFlatbush Internet Asifa Kintres Englishדער בלאטNessuna valutazione finora
- Defend DissentDocumento131 pagineDefend DissentR. Tyler CroyNessuna valutazione finora
- ABB Drives Function Blocks For Siemens PLCs Quick-Start-Up Guide B A4Documento139 pagineABB Drives Function Blocks For Siemens PLCs Quick-Start-Up Guide B A4Automation WorksNessuna valutazione finora
- Starbridge 1531 Wireless ADSL Router User ManualDocumento35 pagineStarbridge 1531 Wireless ADSL Router User ManualJulio César RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- BSNL All Plans - BB LL FTTH Mobile Aseem Wings Amazon CashbackDocumento4 pagineBSNL All Plans - BB LL FTTH Mobile Aseem Wings Amazon Cashbackankushmangal83Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anti RapeDocumento9 pagineAnti Rapesumit patnaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Minor Project Report For Bba 3rd SemDocumento42 pagineMinor Project Report For Bba 3rd Semfromanshul88% (50)
- A6V10452678Documento7 pagineA6V10452678ABI RAJESH GANESHA RAJANessuna valutazione finora
- DIGITAL CommunicationsDocumento253 pagineDIGITAL CommunicationsRachelle TungolNessuna valutazione finora
- Propagation Unit 2Documento21 paginePropagation Unit 2KURRA UPENDRA CHOWDARYNessuna valutazione finora
- COC LEVEL 4 Exam IP Addressing and SubnettingDocumento11 pagineCOC LEVEL 4 Exam IP Addressing and Subnettingdave takeleNessuna valutazione finora
- Introductory Topics in Communication SystemsDocumento21 pagineIntroductory Topics in Communication SystemsMark Allan CalubNessuna valutazione finora
- Adsp PDFDocumento1 paginaAdsp PDFVishwajeet S BNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 03Documento32 pagineLesson 03LuisCantoralNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Telephone Number Codes For IndiaDocumento17 pagineMobile Telephone Number Codes For IndiaPalaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Especificaciones Tecnicas DS-2CD2683G2-IZS V5.5.113 20220601Documento6 pagineEspecificaciones Tecnicas DS-2CD2683G2-IZS V5.5.113 20220601RAMONGRANDE30Nessuna valutazione finora
- Adapting Voice For ATM Networks: A Comparison of AAL1 Versus AAL2Documento16 pagineAdapting Voice For ATM Networks: A Comparison of AAL1 Versus AAL2Control A60Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mang May Tinh 01 1 Tongquan (Cuuduongthancong - Com)Documento48 pagineMang May Tinh 01 1 Tongquan (Cuuduongthancong - Com)Vũ KhangNessuna valutazione finora
- Ofcom New Mobile Operator Guide For MNPDocumento31 pagineOfcom New Mobile Operator Guide For MNPsandeep755Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Communications Handbook: Hsu, H.P. "Sampling" Ed. Suthan S. Suthersan Boca Raton: CRC Press LLC, 1999Documento12 pagineMobile Communications Handbook: Hsu, H.P. "Sampling" Ed. Suthan S. Suthersan Boca Raton: CRC Press LLC, 1999openid_HsJaS0hjNessuna valutazione finora
- ME TERM 1 ReportDocumento5 pagineME TERM 1 ReportDeep GhoshNessuna valutazione finora
- DH-IPC-HFW2320R-ZS/VFS-IRE6 - 3MP IR Bullet CameraDocumento3 pagineDH-IPC-HFW2320R-ZS/VFS-IRE6 - 3MP IR Bullet Cameraesjomaba0% (1)
- ARTNET Receiver V3.inoDocumento4 pagineARTNET Receiver V3.inoESIN NISENessuna valutazione finora