Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
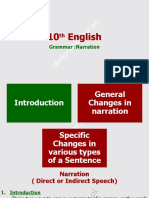
Narration Rules
Caricato da
Pushpendra SharmaqTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Narration Rules
Caricato da
Pushpendra SharmaqCopyright:
Formati disponibili
ENGLISH FOR PROFESSIONAL PURPOSES I (BELH 0003) 2019
SEMESTER III [APRM SHEET] TERM III
MODULE III: NARRATION
There are two ways of reporting something – Direct • The first person pronouns (I, me, my, mine,
Narration and Indirect Narration. Directly quoting the we, us, our, ours) change according to the
sentence spoken by some other person is called Direct subject of the reporting clause.
Narration whereas in Indirect Narration, you report the • The second person pronouns (you, your,
message in your language with minimum linguistic yours) change according to the object of the
changes. reporting clause.
• Third person pronouns (he, him, his, she, her,
Direct Narration: Prof. Ahuja said to the students, hers, it, its, they, them, their, theirs) are not
“Have you completed your assignments?” changed.
Indirect Narration: Prof. Ahuja asked the students if Note: The change in pronouns can be easily
they had completed their assignments. remembered with a simple mnemonic code 123/SON.
It means that the first person changes according to the
Some Defining Terms: subject, the second person changes according to the
object and the third person does not change.
• Reporting Verb: The verb that reports a
message to somebody is called the Reporting Change in Tense:
Verb. In a sentence in direct narration, the • If the reporting verb is in the present or future
reporting verb comes outside the quotation tense, the tense of the reported speech does not
marks in Direct Speech. change in indirect narration.
Nina said, “It is going to rain today”. • If the reported speech is a universal truth or a
“Fire and water do not agree”, said the old proverb, its tense does not change in indirect
priest. narration.
• If the reporting verb is in the past tense and the
• Reporting Clause: Clause consisting of a tense in the reported speech changes according
reporting verb is called Reporting to the following table:
Clause/Speech.
• Reported Speech: Reported Speech occurs in Changes from Changes into
the following contexts: Present indefinite Past indefinite
a. Subordinate Clause(s) in Indirect speech or Present continuous Past continuous
narration. Present perfect Past perfect
e.g. Rohan told Mukesh that he had sung a Present perfect Past perfect
song in the party. continuous continuous
b. Within quotation marks in direct narration. Past indefinite Past perfect
e.g. Rohan told Mukesh, “I have sang a song
Past continuous Past perfect
in the party”.
continuous
• Reported Verb: Reported Verb occurs in the
following contexts:
• Some important changes take place according
a. The finite verb/-s in subordinate clause in
to the following table:
indirect narration.
Changes from Changes into
e.g. Rohan told Mukesh that he had sung a
song in the party. Is, am was
b. The finite verb/-s within quotation marks in Are were
direct narration. Do, does Did
e.g. Rohan told Mukesh, “I have sang a song Has, have Had
in the party”. Can Could
Will Would
• Subject of Reporting Clause Shall Should
• Object of Reporting Clause May Might
• Subject of Reported Clause Must Had to
• Object of Reported Clause Should Should have
Could Could have
Some Basic Rules of Transformation: Might Might have
Would Would have
Change in pronoun This That
These those
Here There
[FOR B TECH II YEAR STUDENTS] Page 1
ENGLISH FOR PROFESSIONAL PURPOSES I (BELH 0003) 2019
SEMESTER III [APRM SHEET] TERM III
MODULE III: NARRATION
Come Go c) The question mark is replaced by a full stop.
Thus So Note: Any sentence that starts with a question word
Now Then may not essentially be a question. It may be an
Today That day exclamation also. But a question always has a question
Tonight That night mark at the end.
Yesterday The previous day
Tomorrow The next day When the reported speech is an imperative sentence
(order/request/advice)
• Conversion of Direct into Indirect Narration For changing an imperative sentence into indirect
when the reporting verb is in the Past Tense speech, the following rules are used:
a) “Said/ said to” is changed into “ordered/
When the reported speech is a statement- requested/advised/asked” according to sense.
a) the reporting verb changes according to b) Both the clauses are joined by using ‘to’.
the following rules: c) Negative reported speech is joined by using
Says to = tells ‘not to/never to’.
Say to = tell
Said to = told
Say/says/said = no change (when object of the When the reported speech is an exclamatory
reporting verb is not given) sentence
b) The reporting clause and the reported clause In an exclamatory sentence, intense feelings of joy,
are joined by using ‘that’ sorrow, surprise, happiness, etc. are expressed. These
c) When object of the reporting verb is not given, sentences generally have a sign of exclamation (!).
it can be understood as first person (me) or When the reported speech is an exclamatory sentence,
third person (him/her). the following rules are used for changing it into
indirect narration:
When the reported speech is a Yes-No Question- a) ‘Said’ is changed into ‘exclaimed with
When the reported speech is a question sorrow/joy/surprise.
starting with an auxiliary verb, we can change b) If feeling is not correctly identifiable, only
it into indirect narration by using the following ‘exclaimed’ should be used.
rules: c) Exclamatory sentence is written like a
a) ‘Said or said to’ is changed into ‘asked’. common statement.
Similarly, ‘say or says’ is changed into d) Both the clauses are joined with the help of
‘ask/asks’. ‘that’.
b) Both the clauses are joined by using ‘if e) ‘What or how’ is changed into ‘very’.
/whether’. ‘That’ is not used. f) Sign of exclamation is replaced by full stop.
c) The question is written as a statement with
helping verb after the subject. When the reported speech is a wish-
d) Question mark is replaced by a full stop. When the reported speech is a wish, greeting or prayer,
Note: In most cases, ‘if’ and ‘whether’ are the following rules are used while changing it into
interchangeable and one can be used in lace of the indirect narration:
other. However, the use of ‘whether’ is preferred when a) Sad is changed into wished/cursed/prayed
possibility of negative reply is high. according to meaning
b) The reported speech is added with the help of
When the reported speech is a Wh-Question- ‘that’.
When the reported speech is a question starting with a c) If wish is a phrase, it can be placed as an
question word, such as, what, when, where, why, object to the reporting verb
who, how, etc., we can change it into indirect narration Note: some greetings are not wishes but simply
by using the following rules: spoken for acknowledging the presence, such greetings
a) No additional conjunction is used for joining are reported by using ‘bade’. Some of these greetings
the clauses. Only the question word functions are hi, hello, tata, bye- bye, etc.
like a subordinating conjunction.
b) The reported speech is written as a statement,
put a helping verb after the subject.
[FOR B TECH II YEAR STUDENTS] Page 2
ENGLISH FOR PROFESSIONAL PURPOSES I (BELH 0003) 2019
SEMESTER III [APRM SHEET] TERM III
MODULE III: NARRATION
When the reported speech is a proposal or
suggestion-
When the reported speech is a proposal or suggestion,
the following rules are used:
a) The reporting verb is changed into ‘suggested’
or ‘proposed’.
Note:
• If first person pronouns (I, me, we, us) are
used with the reporting verb, we should use
“that we should”. If first person pronoun is not
there outside the inverted comma, “that they
should” can be used.
• In proposals and suggestions, gerund or noun
phrases can be used just after proposed or
suggested.
[FOR B TECH II YEAR STUDENTS] Page 3
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Narration 9345691 PowerpointDocumento17 pagineNarration 9345691 PowerpointSUBHADIP PALNessuna valutazione finora
- Seventh Class-ICSE Revision Notes For Second TermDocumento5 pagineSeventh Class-ICSE Revision Notes For Second TermShalinee App Deepo BhavNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct and Indirect Speech: He Said To Them, "I Will Help You."Documento2 pagineDirect and Indirect Speech: He Said To Them, "I Will Help You."English from BabylonNessuna valutazione finora
- Narration 2Documento30 pagineNarration 2vikram100% (2)
- Reported SpeechDocumento1 paginaReported SpeechDaniel Ovalle 10Nessuna valutazione finora
- Direct Indirect SpeechDocumento10 pagineDirect Indirect SpeechAbhimanyu Singh100% (2)
- Basic Rules For Indirect SpeechDocumento14 pagineBasic Rules For Indirect SpeechjoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Class X Lesson 6 Narrations or Direct and Indirect RulesDocumento4 pagineClass X Lesson 6 Narrations or Direct and Indirect RulesMAREEZ E ISHQ MAREEZ E ISHQNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec File Narration PrintDocumento9 pagineLec File Narration Printteshosta123Nessuna valutazione finora
- I D SDocumento5 pagineI D SJesica VariasNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes On Direct and Indirect SpeechDocumento5 pagineNotes On Direct and Indirect Speechkanaya khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct and indirect speech rulesDocumento7 pagineDirect and indirect speech rulesRoshan UpadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- Reporting Speech Chapter NotesDocumento4 pagineReporting Speech Chapter NotesBilisuma AmanteNessuna valutazione finora
- DirectindirectDocumento1 paginaDirectindirectWaleedNessuna valutazione finora
- Centre of Excellence in Economics and Finance Language and Communication DepartmentDocumento25 pagineCentre of Excellence in Economics and Finance Language and Communication DepartmentmariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation 13Documento11 paginePresentation 13gkjhkjhNessuna valutazione finora
- SSC Eng Direct and Indirect SpeechDocumento39 pagineSSC Eng Direct and Indirect Speechstatebankofindia sbiNessuna valutazione finora
- DIRECT and Indirect Word Doc PDF 1636913196542Documento6 pagineDIRECT and Indirect Word Doc PDF 1636913196542md.muzzammil shaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- The International School - Agra: Homework Assignment For 4 January 2022Documento3 pagineThe International School - Agra: Homework Assignment For 4 January 2022anuradha TiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocumento15 pagineDirect and Indirect SpeechDiosalette W. FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes of Reported Speech (Class 10 & 9)Documento14 pagineNotes of Reported Speech (Class 10 & 9)Naren KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Narration Notes (Class 11-12)Documento12 pagineNarration Notes (Class 11-12)Anugrah Stanley67% (3)
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocumento18 pagineDirect and Indirect SpeechSangay DemaNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentación Reported Speech 1Documento19 paginePresentación Reported Speech 1Juan Antonio Mochales San VicenteNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech (El Estilo Indirecto) : A) DefiniciónDocumento19 pagineReported Speech (El Estilo Indirecto) : A) DefiniciónRaquel Marcos-alberca Calonge100% (2)
- Tema 9-EOI-Ingles (Estilo Directo Indirecto) (WWW Preparadores Punto EuDocumento14 pagineTema 9-EOI-Ingles (Estilo Directo Indirecto) (WWW Preparadores Punto EuenglishvideoNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct & Indirect SlidesDocumento14 pagineDirect & Indirect Slidesshayanali1682003Nessuna valutazione finora
- Example: He Says, "I Write Poems." - He Says That He Writes EnglishDocumento4 pagineExample: He Says, "I Write Poems." - He Says That He Writes EnglishRita QuispeNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct Indirect Speech: English GrammarDocumento8 pagineDirect Indirect Speech: English GrammarSalman LeghariNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct and Indirect Speech NewDocumento4 pagineDirect and Indirect Speech NewPandora EvergardenNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech (Full)Documento6 pagineReported Speech (Full)kaustubhchoudhary2005Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Narration?: Some of The Rules For Changing "Direct Speech" Into "Indirect Speech" AreDocumento5 pagineWhat Is Narration?: Some of The Rules For Changing "Direct Speech" Into "Indirect Speech" AreArif HasnatNessuna valutazione finora
- Eng 7 Quarter 4 W4Documento4 pagineEng 7 Quarter 4 W4Jan Philip AbellonNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct and Indirect NarrationDocumento9 pagineDirect and Indirect NarrationPrashant Tiwari100% (1)
- Notes On Direct and Indirect SpeechDocumento4 pagineNotes On Direct and Indirect SpeechCrampey UmaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 7 Speech/NarrationDocumento18 pagineUnit 7 Speech/NarrationMohammad AshfaqNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct To Indirect SpeechDocumento31 pagineDirect To Indirect SpeechHINA NAAZ KHANNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech (Statements)Documento11 pagineReported Speech (Statements)Dishu SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocumento10 pagineDirect and Indirect SpeechNur Asfiya KhustinaNessuna valutazione finora
- NARRATIONS (Recovered)Documento7 pagineNARRATIONS (Recovered)Debashish Paul100% (1)
- Reported SpeechDocumento4 pagineReported SpeechNiranjan SNessuna valutazione finora
- Let's Learn About... : Reported SpeechDocumento9 pagineLet's Learn About... : Reported SpeechevilNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech RulesDocumento6 pagineReported Speech RulesJahnvi KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct & Indirect Speech Gr10-1Documento18 pagineDirect & Indirect Speech Gr10-1joshdevree3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Direct & Indirect NarrationDocumento8 pagineDirect & Indirect NarrationMusdiq AwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct and Indirect Speech BasicsDocumento4 pagineDirect and Indirect Speech BasicsnatashaNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct-Indirect - Perfect TensesDocumento26 pagineDirect-Indirect - Perfect TensesSheena Mae de OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- Narration RulesDocumento2 pagineNarration RulesRajesh Kumar Duggal68% (25)
- Quoted and Reported SpeechDocumento6 pagineQuoted and Reported SpeechPRECIOUS KAYE MARIE BANTIGUENessuna valutazione finora
- Ingles Instrumental IV - Clase 6Documento46 pagineIngles Instrumental IV - Clase 6Nicolás LaraNessuna valutazione finora
- 4-L2 Oblique (Indirect) Translation TechniquesDocumento9 pagine4-L2 Oblique (Indirect) Translation TechniquesDaniel DuarteNessuna valutazione finora
- When The Reporting Verb Is in The Past TenseDocumento3 pagineWhen The Reporting Verb Is in The Past TenseGlobal Learners' ProgrammesNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of NarrationDocumento8 pagineTypes of NarrationVikas ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Narrations: Reporting Speech: Reported SpeechDocumento3 pagineNarrations: Reporting Speech: Reported SpeechFozia ArshadNessuna valutazione finora
- Shift in TenseDocumento15 pagineShift in TenseMarium naeemNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct & Indirect SpeechDocumento18 pagineDirect & Indirect Speechadindanur302Nessuna valutazione finora
- Língua Inglesa: Reported SpeechDocumento3 pagineLíngua Inglesa: Reported SpeechPatrick AlmeidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct & Indirect SpeechDocumento2 pagineDirect & Indirect SpeechHendrikus FJ100% (1)
- Legwrit DraftDocumento72 pagineLegwrit DraftJohn Kayle BorjaNessuna valutazione finora
- Prototext-metatext translation shifts: A model with examples based on Bible translationDa EverandPrototext-metatext translation shifts: A model with examples based on Bible translationNessuna valutazione finora
- Econometrics PaperDocumento24 pagineEconometrics PaperPam Ramos0% (1)
- 232 SpdaDocumento4 pagine232 SpdaGerard Sierr BarboNessuna valutazione finora
- 20 Reefer Container Ij ContainerDocumento32 pagine20 Reefer Container Ij ContainerElvisor Visor100% (1)
- Experiment 6Documento7 pagineExperiment 6sajithNessuna valutazione finora
- Glencoe Mcgraw Hill Geometry Homework Practice Workbook Answer KeyDocumento8 pagineGlencoe Mcgraw Hill Geometry Homework Practice Workbook Answer Keybodinetuzas2100% (1)
- CSD Full TermDocumento29 pagineCSD Full TermNishat Farha SharmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Bending Moment Due To Live Load:: A) IRC Class 70R Load (Tracked Vehicle)Documento9 pagineBending Moment Due To Live Load:: A) IRC Class 70R Load (Tracked Vehicle)Tashi TamangNessuna valutazione finora
- Copia de JOISTDocumento44 pagineCopia de JOISTOscar SanabriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Human ActivityDocumento53 pagineHuman ActivityabiramanNessuna valutazione finora
- Discretization Methods of Fractional Parallel PIDDocumento4 pagineDiscretization Methods of Fractional Parallel PIDBaherNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical behavior of gases explained by kinetic theory and gas lawsDocumento12 paginePhysical behavior of gases explained by kinetic theory and gas lawsPAUL KOLERENessuna valutazione finora
- RNC2600 DatasheetDocumento2 pagineRNC2600 DatasheetShaikh Tariq100% (1)
- Mercury Pollution A Threat To Agusan MarshDocumento25 pagineMercury Pollution A Threat To Agusan MarshKalambuan Foundation, Inc.50% (4)
- RFPO55 G.8263: SpecificationsDocumento5 pagineRFPO55 G.8263: SpecificationsullascsNessuna valutazione finora
- SHK Error CodesDocumento7 pagineSHK Error CodesmmlipuNessuna valutazione finora
- ICAO Flight PlanDocumento4 pagineICAO Flight Planrmpilot2012Nessuna valutazione finora
- Trampas de Vapor AmstrongDocumento113 pagineTrampas de Vapor Amstrongjeyjo_64Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ericsson Training PDFDocumento118 pagineEricsson Training PDFNuwan100% (1)
- 4th Quarter Science 9 Impulse and MomentumDocumento45 pagine4th Quarter Science 9 Impulse and MomentumApple SamoyNessuna valutazione finora
- FVM - CFDDocumento44 pagineFVM - CFDgrkguptaNessuna valutazione finora
- What is a Neutron Star? Facts About These Ultradense Remnants of Dead StarsDocumento3 pagineWhat is a Neutron Star? Facts About These Ultradense Remnants of Dead StarsYoo YoungNessuna valutazione finora
- Sweater Consumption CostingDocumento2 pagineSweater Consumption Costingapi-214283679Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fourier SeriesDocumento16 pagineFourier Seriesvolly666Nessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 11 RevisionDocumento26 pagineTopic 11 RevisionYun Ho CHONessuna valutazione finora
- II Year Civil Engineering Syllabus and Evaluation SchemeDocumento12 pagineII Year Civil Engineering Syllabus and Evaluation SchemeSheezan KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple HTTP Client for Reading RSS Feeds on MobileDocumento6 pagineSimple HTTP Client for Reading RSS Feeds on MobileMarcel LefterNessuna valutazione finora
- Welding ErrorsDocumento42 pagineWelding ErrorsNDTInstructorNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiments On Partial Replacement of Coconut Shell As Coarse Aggregate in ConcreteDocumento10 pagineExperiments On Partial Replacement of Coconut Shell As Coarse Aggregate in ConcreteIJIRSTNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Notes Schwarzschild GeometryDocumento27 pagineLecture Notes Schwarzschild Geometryga.simplicio2Nessuna valutazione finora
- SssDocumento24 pagineSssSaFdaR QaZiNessuna valutazione finora