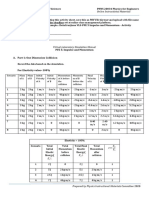
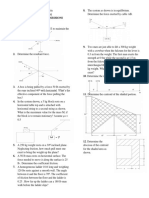
Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Fact Sheet
Caricato da
daniel0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
15 visualizzazioni1 paginaThe reaction rate is defined as the change in concentration of reactants or products per unit time. Factors that affect the reaction rate include the surface area of solids, concentration or pressure of reactants, temperature, nature of reactants, and presence of a catalyst. Specifically, increasing the surface area, concentration, pressure, or temperature will increase the reaction rate, while different reactants or catalysts can impact the rate in different ways.
Descrizione originale:
Fact sheets in Reaction Rate
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThe reaction rate is defined as the change in concentration of reactants or products per unit time. Factors that affect the reaction rate include the surface area of solids, concentration or pressure of reactants, temperature, nature of reactants, and presence of a catalyst. Specifically, increasing the surface area, concentration, pressure, or temperature will increase the reaction rate, while different reactants or catalysts can impact the rate in different ways.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
15 visualizzazioni1 paginaFact Sheet
Caricato da
danielThe reaction rate is defined as the change in concentration of reactants or products per unit time. Factors that affect the reaction rate include the surface area of solids, concentration or pressure of reactants, temperature, nature of reactants, and presence of a catalyst. Specifically, increasing the surface area, concentration, pressure, or temperature will increase the reaction rate, while different reactants or catalysts can impact the rate in different ways.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 1
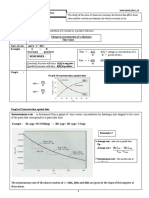
Definition of Reaction Rate
The Reaction Rate for a given
chemical reaction is the measure of the Factors that affect Reaction Rate.
change in concentration of the Chemical reactions proceed at different rates. The factors that affect
reactants or the change in reaction rates are:
concentration of the products per unit surface area of a solid reactant
time. The speed of a chemical reaction concentration or pressure of a reactant
may be defined as the change in
concentration of a substance divided by
temperature
the time interval during which this nature of the reactants
change is observed: presence/absence of a catalyst.
Surface Area
rate=ΔconcentrationΔtime(4) Surface area is the exposed matter of a solid substance.
(4)rate=ΔconcentrationΔtime Concentration
The concentration of a substance can be expressed in a
For a reaction of the variety of ways depending on the nature of a substance.
form A+B→CA+B→C, the rate can be
Aqueous solutions typically have their concentrations
expressed in terms of the change in
concentration of any of its components expressed in mol/L. For example, a solution made by
dissolving sodium hydroxide in water has its
rate=−Δ[A]Δt(5)(5)rate=−Δ[A]Δt concentration expressed as moles of NaOH per litre of
rate=−Δ[B]Δt(6)(6)rate=−Δ[B]Δt
solution. Gases can also have their concentrations
expressed in mol/L.
rate=Δ[C]Δt(7)(7)rate=Δ[C]Δt Pressure
The concentration of a gas is a function of the pressure
in which Δ[A]Δ[A] is the difference on the gas. Increasing the pressure of a gas is exactly
between the concentration of AA over
the time interval t2–t1t2–t1:
the same as increasing its concentration. If you have a
certain number of gas molecules, you can increase the
Δ[A]=[A]2–[A]1(8)(8)Δ[A]=[A]2–[A]1 pressure by forcing them into a smaller volume.
Temperature
Notice the minus signs in the first two With the exception of some precipitation reactions
examples above. The concentration of a involving ionic compounds in solution, just about all
reactant always decreases with time, chemical reactions take place at a faster rate at higher
so Δ[A]Δ[A] and Δ[A]Δ[A] are both temperatures. The question is why? Temperature (in
negative. Since negative rates do not
make much sense, rates expressed in
Kelvin degrees) is proportional to the kinetic energy of
terms of a reactant concentration the particles in a substance. For example, if the Kelvin
are always preceded by a minus temperature of a substance is doubled, then the
sign to make the rate come out average kinetic energy of the particles in that substance
positive. is doubled.
Nature of Reactants
Consider now a reaction in which the Individual properties of substances also affect reaction
coefficients are different:
rates. The scope of these properties is broad and there
A+3B→2D(9)(9)A+3B→2D are few generalizations that you can apply consistently.
Some of the properties in this category are state of
It is clear that [B][B] decreases three matter, molecular size, bond type and bond strength.
times as rapidly as [A][A], so in order to Catalyst
avoid ambiguity when expressing the A catalyst is a species that speeds up a chemical
rate in terms of different components, reaction without being chemically changed upon
it is customary to divide each change in
completion of the reaction. In other words, the mass of
concentration by the appropriate
coefficient: a catalyst is the same before and after a reaction
occurs.
rate=−Δ[A]Δt=−Δ[B]3Δt=Δ[D]2Δt(1
0)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 8 - PDFsam - Conceptual Physics, Global EditionDocumento13 pagine8 - PDFsam - Conceptual Physics, Global EditionΒανικιώτης Νικήτας100% (1)
- Edmund Shaftesbury - Universal Magnetism and Magnetic Control of OthersDocumento590 pagineEdmund Shaftesbury - Universal Magnetism and Magnetic Control of OthersJohnette Ricchetti100% (9)
- Kinetics (Filled)Documento36 pagineKinetics (Filled)MarikNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 6 Elevate Science Workbook - 86500313 - 225 - 2022519533Documento63 pagineGrade 6 Elevate Science Workbook - 86500313 - 225 - 2022519533satbooks30Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical KineticsDocumento64 pagineChemical Kineticssmudgegaming4989Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical KineticsDocumento77 pagineChemical KineticsDipu RokayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical KineticsDocumento31 pagineChemical Kineticsakbar azamNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical KineticsDocumento72 pagineChemical KineticsSiddhartha KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical KineticsDocumento21 pagineChemical Kineticsdipankargh48Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Kinetics & Reactor DesignDocumento134 pagineChemical Kinetics & Reactor DesignShakoor MalikNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical KineticsDocumento6 pagineChemical KineticsespinosajennywayneNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical KineticsDocumento18 pagineChemical KineticsPankaj JindamNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinetics of Chemical Reactions, James KeelerDocumento51 pagineKinetics of Chemical Reactions, James Keelerm222000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Equilibruim - 1Documento24 pagineChemical Equilibruim - 1Vinod AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- 2023-24 XII Chem UNIT 04. 02 Oct 2023Documento13 pagine2023-24 XII Chem UNIT 04. 02 Oct 2023GayatriNessuna valutazione finora
- 22 00 14 11 12 2023 Doc-20220901-Wa0007.Documento9 pagine22 00 14 11 12 2023 Doc-20220901-Wa0007.hmegm123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical KineticDocumento40 pagineChemical KineticHamzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Kinetics: Rate of A ReactionDocumento49 pagineChemical Kinetics: Rate of A ReactionVijay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Kinetics - NotesDocumento15 pagineChemical Kinetics - NotesEspace NuvemNessuna valutazione finora
- Reactor Technology 6Documento13 pagineReactor Technology 6Sami WhiteNessuna valutazione finora
- Instantaneous Rate: Is Determined From A Graph of Time Versus Concentration by Drawing A Line Tangent To The CurveDocumento13 pagineInstantaneous Rate: Is Determined From A Graph of Time Versus Concentration by Drawing A Line Tangent To The CurveSupia NazmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Chemical KineticsDocumento47 pagine6 Chemical KineticsAlthea Angela BulaclacNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Kinetics Lecture 1 2Documento59 pagineChemical Kinetics Lecture 1 2BaNcHoNessuna valutazione finora
- KineticsDocumento37 pagineKineticsJessika DorssersNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Kinetics REVISEDocumento62 pagineChemical Kinetics REVISEpriyapriyankan43Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Kinetics Neet MCQDocumento12 pagineChemical Kinetics Neet MCQmanan10jas1529Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Kinetics: The Rates and Mechanisms of Chemical ReactionsDocumento21 pagineChemical Kinetics: The Rates and Mechanisms of Chemical ReactionsOyinkansola OsiboduNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Kinetics - Reaction Orders: H° For This Reaction Is: H H HDocumento13 pagineChemical Kinetics - Reaction Orders: H° For This Reaction Is: H H HLinaGeneyReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- General Chemistry II Chapter 13 Lecture Notes Chemical KineticsDocumento11 pagineGeneral Chemistry II Chapter 13 Lecture Notes Chemical KineticsJacinta SamalengiNessuna valutazione finora
- 2) 2020 - Chemical - KineticsDocumento8 pagine2) 2020 - Chemical - KineticsFaizan AnsariNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical KineticsDocumento101 pagineChemical Kineticsec1412Nessuna valutazione finora
- Enzyme KineticsDocumento28 pagineEnzyme Kineticsghislain22.kevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Rate of A ReactionDocumento25 pagineRate of A ReactionLelouch V. BritaniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Essentials of Chemical KineticsDocumento49 pagineEssentials of Chemical KineticsJohn KanteNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinetics UkgvdWVDocumento17 pagineKinetics UkgvdWVMaica GarampilNessuna valutazione finora
- Che-Unit 2 Chemical KineticsDocumento26 pagineChe-Unit 2 Chemical Kineticsmuchakayala umeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Hsslive Xii CH 3 Chemical Kinetics AnilDocumento10 pagineHsslive Xii CH 3 Chemical Kinetics AnilFathima NithinshaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6-Chemical Kinetics-01 TheoryDocumento42 pagine6-Chemical Kinetics-01 TheoryRaju SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Kinetics..Documento26 pagineChemical Kinetics..Ayyan FerozNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical KineticsDocumento15 pagineChemical KineticsThara BijuNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Fifteen Chemical Kinetics: A + B C + DDocumento17 pagineChapter Fifteen Chemical Kinetics: A + B C + DanandyelwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinetics 2Documento98 pagineKinetics 2Hem Chandra ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12 Chemical KineticsDocumento70 pagineChapter 12 Chemical KineticsiB13eNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Kinetics: Module - 5Documento23 pagineChemical Kinetics: Module - 5TeachingTrainingCoaching KnowledgeSharingSessionNessuna valutazione finora
- A270134180 - 23715 - 17 - 2019 - Chemical Kinetics - 1Documento50 pagineA270134180 - 23715 - 17 - 2019 - Chemical Kinetics - 1omer faruqeNessuna valutazione finora
- XII CHEMICAL KINETICS - Module 1Documento4 pagineXII CHEMICAL KINETICS - Module 1Rahul Joseph ThomasNessuna valutazione finora
- C1 Reaction KineticsDocumento12 pagineC1 Reaction KineticsChloeNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Che - KinDocumento16 pagine4 Che - KinRoxanneNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Kinetics: T 0 ' o D (R) D (P) R DT DTDocumento12 pagineChemical Kinetics: T 0 ' o D (R) D (P) R DT DTVeerNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinetics LPDocumento41 pagineKinetics LPHarkritSinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical KineticsDocumento49 pagineChemical KineticsS KNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Kinetics - IITDocumento24 pagineChemical Kinetics - IITSiddu GowdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 1 and 2-ChemicalKineticsDocumento86 pagineTopic 1 and 2-ChemicalKineticsNOR AZAM BIN ENDOT / FSNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Term Study Guide Chemical KineticsDocumento5 pagineFinal Term Study Guide Chemical KineticsMarvin Villanueva LPTNessuna valutazione finora
- Genchm280 KineticsDocumento28 pagineGenchm280 KineticsDelia BratzchNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter No 6 - Chemical KineticsDocumento45 pagineChapter No 6 - Chemical KineticsTanish SalviNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Kinetics: - : Types of Chemical ReactionsDocumento12 pagineChemical Kinetics: - : Types of Chemical ReactionsmanishNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Kinetics: Unit IDocumento43 pagineChemical Kinetics: Unit IEanna Jullienne UyvicoNessuna valutazione finora
- 3051 Chapter FiveDocumento51 pagine3051 Chapter FiveMalicha GalmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical EquilibriumDocumento112 pagineChemical EquilibriumAudreyNessuna valutazione finora
- E Electric Circuit PDFDocumento44 pagineE Electric Circuit PDFPam G.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 2 Module of Free Vibration Engineering 1st SEMESTER S.Y. 2016 - 2017Documento14 pagineAssignment 2 Module of Free Vibration Engineering 1st SEMESTER S.Y. 2016 - 2017Narry StrummerNessuna valutazione finora
- Rates of Evaporation From Swimming Pools in Active UseDocumento10 pagineRates of Evaporation From Swimming Pools in Active Useاحمد الجزار20070% (1)
- Chemistry JeopardyDocumento54 pagineChemistry Jeopardyohoegh8985Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Biophotonics PDFDocumento2 pagineIntroduction To Biophotonics PDFDebashish PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Damped Free VibrationDocumento6 pagineDamped Free Vibrationraffiq85Nessuna valutazione finora
- EE301Documento6 pagineEE301savithaNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Report On Industrial Training (Siwes) by Fagorola Eniitan OlawoleDocumento46 pagineTechnical Report On Industrial Training (Siwes) by Fagorola Eniitan OlawoleOkorie Victor100% (2)
- Paper - GST2012 - Understanding The Physics of Trim - Nikolaj Lemb LarsenDocumento10 paginePaper - GST2012 - Understanding The Physics of Trim - Nikolaj Lemb LarsenFernando Raúl LADINONessuna valutazione finora
- Vertical Curve DesignDocumento6 pagineVertical Curve DesignMidhun JosephNessuna valutazione finora
- Ceramic Fiber HeatersDocumento22 pagineCeramic Fiber HeatersElias100% (1)
- BTech Mechanical Engineering SyllabusDocumento190 pagineBTech Mechanical Engineering Syllabusprasaad7Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4 1 Alternating Current PDFDocumento24 pagine4 1 Alternating Current PDFmarizg piolNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics ProjectDocumento13 paginePhysics Projectvani sarohaNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Courses-SemV VIIDocumento2 pagineList of Courses-SemV VIIAakash VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Geochemistry IntroductionDocumento25 pagineGeochemistry Introductionkristiano97100% (1)
- Making Chemistry Logical and Relevant by Jessica AmesDocumento33 pagineMaking Chemistry Logical and Relevant by Jessica AmesPaul SchumannNessuna valutazione finora
- VLS-PFE 5 Impulse and Momentum Activity SheetDocumento5 pagineVLS-PFE 5 Impulse and Momentum Activity SheetMohammadrayyan MacasindilNessuna valutazione finora
- Docc 1996Documento8 pagineDocc 1996swchen100% (2)
- R Lake AnalyzerDocumento30 pagineR Lake AnalyzerMateo ParraNessuna valutazione finora
- Control DevicesDocumento19 pagineControl DevicesSuzaini SupingatNessuna valutazione finora
- Istalaciones Electricas de Vivienda PDFDocumento19 pagineIstalaciones Electricas de Vivienda PDFWilder Benites VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sterilization Validation and Routine Operation Handbook RadiationDocumento170 pagineSterilization Validation and Routine Operation Handbook RadiationSlavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tower DetailsDocumento1 paginaTower DetailsBalasubramanya Barkur100% (1)
- PHYSICSDocumento4 paginePHYSICSalmiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Rail Gun Project PresentationDocumento15 pagineRail Gun Project PresentationJohn SabuNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 2 - Analysis of Rect Sections (Ec2)Documento6 pagineTopic 2 - Analysis of Rect Sections (Ec2)RCdesign2012Nessuna valutazione finora