Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Philosohical Thoughts/Doctorines Vis-Avis Education
Caricato da
Eddie Jr Sadamo0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
11 visualizzazioni3 pagineAbout philosophy of teaching education
Titolo originale
Review
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoAbout philosophy of teaching education
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
11 visualizzazioni3 paginePhilosohical Thoughts/Doctorines Vis-Avis Education
Caricato da
Eddie Jr SadamoAbout philosophy of teaching education
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 3
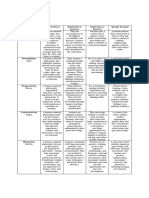
PHILOSOHICAL THOUGHTS/DOCTORINES VIS-AVIS EDUCATION
Goal of Role of Role of Teaching Subjects
Education Students Teacher Methods Studied
Existentialism Develop authentic Develop Encourage studentsDiscussion and Drama
individualism who independence, to philosophize
analysis, Art
exercise freedom of self-discipline, set about life and to examination of Literature
choices and take challenges and recognize and fulfill
choice-making in Social Science
responsibility for solve problems personal freedom. own and others’ History
their actions lives
Marxism Shape people and Live and work Lead and advocate Scientific Emphasis on
institutions; change harmoniously change methodology, science and
material conditions with others, practical activity history
of society, producing acquire and use (problem solving)
classless society knowledge that
will enable them
to transform
natural and social
world.
Behaviorism Engineer Respond to Manipulate the Programmed Learning tasks in
environments that environmental learning instruction that which behavior
efficiently maximize and behavioral environment and provides feedback can be directly
learning. stimuli: become present stimuli, on performance observed,
self-regulated. using conditioning behavioral measured, and
and social learning contracts evaluated.
to shape student reinforcement.
behavior.
Cognitivism Develop thinking Construct Stimulate cognitive Use of Integrated
skills for lifelong self- meaningful development; manipulatives curricula;
directed learning. knowledge mediate student and real-life emphasis on
through learning and learning thinking and
experience and monitor thought opportunities critical thinking
interaction. processes. relevant to skills, study
students prior skills, and
experiences. problem solving
skills.
Pragmatism Develop and apply Active learning
Teach inductive and Hand-on Emphasis on
practical knowledge and participation.
deductive curricula; group citizenship,
and skills for life in a reasoning, the work; knowledge and
progressive scientific method, experimental. skills applicable
democratic society. and the powers of to daily life, and
observation and career or job
practice. preparation.
Perennialism Acquisition of Receive Guide to the Teacher-centered Emphasis on
timeless principles of knowledge and classics; teach basic direct instruction Great Books and
reality, truth, and academic skills. skills. core curricula in
value; learning for the arts and
the sake of learning. sciences.
Essentialism Acquisition of Receive Deliver a standard Subject-centered Uniform
culture; cultural knowledge; curriculum. direct instruction curriculum for
literacy for personal demonstrate all students that
benefit. minimum emphasizes the
competencies. essence of
traditional
cunture
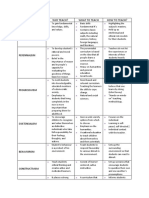
DEFFERENT PHILOSOPHIES AS APPLIED IN EDUCATION
Philosophies Idealism Realism Humanism Pragmatism Reconstruction Existentialism Democracy
1. Aims of Development Development Culture Individual Social Philosophical Welfare of
Education of mind & of mind & bod balance growth thru awareness analysis of the
body thru the sense physical and processes, reforms & human individual &
& reason Mental experience construct of a experience, society
growth & construct new society. life, love &
of a new death
society
2. Nature of Subject Subject Individual & Child & Child, subject Child & Child &
Curriculum matter- matter- society – process – &human subject society-
centered centered centered centered reaction- matter- centered
centered centered
3. Role/ Dispenser of Initiator & Dispenser of Facilitator/ Aware of Facilitator, Facilitator,
character of knowledge/ facilitator/ knowledge, dynamic dominant moderator, liberal, open-
teacher active, practical, facilitator/ good social values, consultant, minded,
imposing, organizer, tradition classroom issue & adviser provides for
serious, strict authoritarian when manager problems, goal individual
emphasizing Result & &future differences.
values process- oriented
oriented
4. Role/ Receives Discover of Discover of Problem- Organizer, Curious, Free- seekers
character of knowledge, knowledge knowledge Solvers, lead, future & assertive of
learning passive, thru sensation thru the arts observe the goal- oriented, inquiry, knowledge,
dependent & abstraction, & literature scientific, socially aware expressive inquisitive,
good at method, & responsible articulate, adventurous,
classifying & curious personally & indencent.
sorting critical socially
objects based result & aware
on the process-
characteristics oriented
DEFFERENT PHILOSOPHIES AS APPLIED IN EDUCATION
Philosophies Idealism Realism Humanism Pragmatism Reconstruction Existentialism Democracy
5. Method Lecture Grouping or Traditional, Scientific Group Group Group
of teaching deductive classifying lecture method & activities & dynamics dynamics
method objects method, experimental dynamics
appreciation
of the arts
6. Nature of Traditional, Traditional Artistic with Flexible, rich Modern, Democratic/
Classroom rigid, but with plenty of in needs-based liberal
inflexible little reading opportunities
flexibility in material for students
the to experience
arrangement what they’re
of seats learning
7. Source of Books Objects, Working of Challenging Social, issues, Books, Books,
Knowing nature arts and experience problems and experience, environment,
theology current issues society, experience,
environment society
current issues
8. Plato, Aquinas, Dewey, Brameld, Sartre,
Proponents Froebel, Aristotle, James, Pierce James, Pierce Marcel,
Herbert, Broudy, Mowes,
Buther, Martin, Soderquist
Hegel, Pestalozzi
Berkeley
9. Values, Use of realia Humanities Learning by Politics and The use of Social
Influences GMRC as a course, experience social work group sciences,
on the arts, dynamics anthropology,
Present architecture, sociology
Educational painting
System
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- ASSIGNMENT #3 -Matrix of the different PhilosophiesDocumento6 pagineASSIGNMENT #3 -Matrix of the different Philosophiesngitngit.jjtNessuna valutazione finora
- Idealism Realism Pragmatism/ Experimentalism Essentialism Perennialism Progressivism Social Reconstructionism ExistentialismDocumento2 pagineIdealism Realism Pragmatism/ Experimentalism Essentialism Perennialism Progressivism Social Reconstructionism ExistentialismRey Pineda100% (1)
- ProEd 6Documento1 paginaProEd 6Jirah Joy PeañarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ice Task 3 Foed7411Documento2 pagineIce Task 3 Foed7411melengnvsnNessuna valutazione finora
- Educ 2Documento5 pagineEduc 2Jhonalyn ManubagNessuna valutazione finora
- ED101Documento2 pagineED101Rodie lyn SueltoNessuna valutazione finora
- Philosophy in EducationDocumento2 paginePhilosophy in EducationTamarha Natalie VillarealNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 2Documento2 pagineAssignment 2Marianne ParohinogNessuna valutazione finora
- Six Contemporary Educational PhilosophiesDocumento2 pagineSix Contemporary Educational PhilosophiesRickyJeciel100% (7)
- Tugasan Kuliah - Perkembangan Falsafah Pendidikan BaratDocumento5 pagineTugasan Kuliah - Perkembangan Falsafah Pendidikan BaratFiona TiehNessuna valutazione finora
- NRepublic Act No. 9293Documento6 pagineNRepublic Act No. 9293JAY TAGBUYAWANNessuna valutazione finora
- Why Teach What To Teach How To Teach: EssentialismDocumento2 pagineWhy Teach What To Teach How To Teach: EssentialismSunako Claes0% (1)
- Curriculum DevelopmentDocumento7 pagineCurriculum DevelopmentStephanie Joy Delos SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3 Philosophies of EducationImplication To Teachinglearning Process Short NewDocumento8 pagineLesson 3 Philosophies of EducationImplication To Teachinglearning Process Short NewMae Therese TaguriganNessuna valutazione finora
- Five Major Philosophies of EducationDocumento2 pagineFive Major Philosophies of Educationeunice nikki tavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sir AdaDocumento2 pagineSir AdaNai JoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparing Learning TheoriesDocumento8 pagineComparing Learning Theoriesfimmee2006Nessuna valutazione finora
- Philosophy of Education Goals and MethodsDocumento2 paginePhilosophy of Education Goals and MethodsJemima joy antonioNessuna valutazione finora
- Adult Education Philosophies ComparedDocumento3 pagineAdult Education Philosophies ComparedunknownNessuna valutazione finora
- EDUC 11A 1st Exam and Activity1-4 ExercisesDocumento3 pagineEDUC 11A 1st Exam and Activity1-4 ExercisesDanilo Malbueso Ebol Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bachelor in Technology and Livelihood EducationDocumento15 pagineBachelor in Technology and Livelihood EducationMikee SantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Kapu YaaaaDocumento6 pagineKapu YaaaaJenny Rose BaculadNessuna valutazione finora
- Philosophies of Education: Perennialism, Essentialism, Progressivism & MoreDocumento3 paginePhilosophies of Education: Perennialism, Essentialism, Progressivism & MoreErika Parungao100% (1)
- Six Contemporary Educational PhilosophiesDocumento1 paginaSix Contemporary Educational PhilosophiesAshley Adams100% (14)
- Curriculum FoundationDocumento9 pagineCurriculum FoundationEsme EncalladoNessuna valutazione finora
- EDUC 103 Module 2 2T 2018 2019Documento4 pagineEDUC 103 Module 2 2T 2018 2019Pau CervantesNessuna valutazione finora
- AJENTH JACEL ARO EDUC103 Philosophy of EducationDocumento2 pagineAJENTH JACEL ARO EDUC103 Philosophy of EducationajenthjacelramosaroNessuna valutazione finora
- PHILOS and EDUCATIONAL IMPLICATIONSDocumento5 paginePHILOS and EDUCATIONAL IMPLICATIONSmarnylieNessuna valutazione finora
- STI - Explore - TasksDocumento5 pagineSTI - Explore - TasksSandra IsraelNessuna valutazione finora
- Different Type of Educ PhilosophyDocumento6 pagineDifferent Type of Educ PhilosophyThet SalazarNessuna valutazione finora
- The Teaching Profession - Activity 2 - Pbte1-1 - CaladDocumento2 pagineThe Teaching Profession - Activity 2 - Pbte1-1 - CaladJohn Michael Alejandro CaladNessuna valutazione finora
- EDUC 122 - Lesson 1 To 5Documento17 pagineEDUC 122 - Lesson 1 To 5Webster III M. OpiasaNessuna valutazione finora
- Philosophies of Education Comparison ChartDocumento6 paginePhilosophies of Education Comparison ChartJake FundalNessuna valutazione finora
- EDUC 3 LECTURE SEVEN PHILOSOPHIES of EDUCATIONDocumento5 pagineEDUC 3 LECTURE SEVEN PHILOSOPHIES of EDUCATIONAlexie Anne MariñoNessuna valutazione finora
- Philosophy Theory of Truth Methodolog y To Arrive at The Truth Theory of What Is Available/ Good Goal of Teaching and LearningDocumento4 paginePhilosophy Theory of Truth Methodolog y To Arrive at The Truth Theory of What Is Available/ Good Goal of Teaching and LearningIan Dante Arcangeles73% (15)
- Online Learning Module Synapse StrengthenersDocumento10 pagineOnline Learning Module Synapse StrengthenersKaren Kate DumulagNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Profession Activity 1 - Realyn D. TanecaDocumento5 pagineTeaching Profession Activity 1 - Realyn D. TanecaEya Delos Santos TañecaNessuna valutazione finora
- THE RELEVANCE OF EDUCATIONAL PHILOSOPHIESDocumento4 pagineTHE RELEVANCE OF EDUCATIONAL PHILOSOPHIESFrancis KatigmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Philosophy Theory of Truth Methodology To Arrive at The Truth Theory of What Is Valuable/Goo D Goal of Teaching-LearningDocumento4 paginePhilosophy Theory of Truth Methodology To Arrive at The Truth Theory of What Is Valuable/Goo D Goal of Teaching-LearningVerlyn ReynesNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Philosophies of EducationDocumento3 pagine7 Philosophies of EducationZaib Rehman73% (11)
- Seven Philosophies - Rocel NavajaDocumento3 pagineSeven Philosophies - Rocel NavajaRocel NavajaNessuna valutazione finora
- Foundations of Curriculum Development: PhilosophiesDocumento32 pagineFoundations of Curriculum Development: PhilosophiesKisha Trixie FernandoNessuna valutazione finora
- EDUC 90 Task 1 & 2Documento7 pagineEDUC 90 Task 1 & 2Gliecy OletaNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 1 Matrix of Major PhilosophiesDocumento2 pagineActivity 1 Matrix of Major PhilosophiesHeart Wp100% (1)
- ANSCHAPTER 1 - Module 1 - The Philosophical HeritageDocumento5 pagineANSCHAPTER 1 - Module 1 - The Philosophical HeritageDivine CardejonNessuna valutazione finora
- School of Arts and Sciences Vision, Goals and ObjectivesDocumento1 paginaSchool of Arts and Sciences Vision, Goals and Objectivesmarklouie budiasNessuna valutazione finora
- The 7 Philosophies of Education: A Comparison of Teacher-Centered and Student-Centered ApproachesDocumento4 pagineThe 7 Philosophies of Education: A Comparison of Teacher-Centered and Student-Centered ApproachesJonamay CarantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment - Philosophy in LifeDocumento8 pagineAssignment - Philosophy in LifeArjay PascuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Theories Comparison Table 1Documento3 pagineLearning Theories Comparison Table 1api-296917124Nessuna valutazione finora
- Activity Philosophical Foundations of CurriculumDocumento4 pagineActivity Philosophical Foundations of Curriculumjoan arreolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Profession AssignmentDocumento2 pagineTeaching Profession Assignmentjunjun gallosa100% (6)
- Challenge 3 Philophies of EducationDocumento3 pagineChallenge 3 Philophies of EducationDiane RomeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Title: Science in Early Childhood Education Course Code: ECED 300123 Course Credit: Three (3) Units Pre-Requisite: NoneDocumento9 pagineCourse Title: Science in Early Childhood Education Course Code: ECED 300123 Course Credit: Three (3) Units Pre-Requisite: NoneleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Asyncronous Assignment TTP...Documento17 pagineAsyncronous Assignment TTP...Kim alexandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Prof. Ed 13 - The Teaching Profession Modular Lesson No. 2Documento4 pagineProf. Ed 13 - The Teaching Profession Modular Lesson No. 2Mish LimNessuna valutazione finora
- NBCompetenciesDocumento1 paginaNBCompetenciesAlpha ZetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Philosophy TableDocumento2 paginePhilosophy Tablenestor villarosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Les Compétences de Vie AnglaisDocumento20 pagineLes Compétences de Vie AnglaisElma DavidsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary PresentationsDocumento3 pagineSummary PresentationsCielo Micaela Tomala MaciasNessuna valutazione finora
- Collins Little Learners - Art & Craft_LKGDa EverandCollins Little Learners - Art & Craft_LKGRani TNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of TeachingDocumento49 paginePrinciples of TeachingJoviner Yabres LactamNessuna valutazione finora
- Johann Friedrich Herbart - Founder of Modern Scientific PedagogyDocumento10 pagineJohann Friedrich Herbart - Founder of Modern Scientific PedagogyEddie Jr SadamoNessuna valutazione finora
- Johann Friedrich Herbart - Founder of Modern Scientific PedagogyDocumento10 pagineJohann Friedrich Herbart - Founder of Modern Scientific PedagogyEddie Jr SadamoNessuna valutazione finora
- A New Role For Linguistic Philosophy in Education With An Applica PDFDocumento85 pagineA New Role For Linguistic Philosophy in Education With An Applica PDFkarynNessuna valutazione finora
- International Human Resource ManagementDocumento20 pagineInternational Human Resource ManagementAziz UllahNessuna valutazione finora
- The Alchemical Role of Fire in Transformation and the Great WorkDocumento2 pagineThe Alchemical Role of Fire in Transformation and the Great WorkZeteticus100% (2)
- Analyzing the structure and meaning of wordsDocumento9 pagineAnalyzing the structure and meaning of wordsJL CuonoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sapiens Ubique Civis II - Szeged 2014Documento1 paginaSapiens Ubique Civis II - Szeged 2014Classica Mediaevalia et ceteraNessuna valutazione finora
- Mba (HRM-322) ch-1Documento25 pagineMba (HRM-322) ch-1Shubhi ShubhamNessuna valutazione finora
- Religion Board Game RubricDocumento1 paginaReligion Board Game Rubricapi-193794856Nessuna valutazione finora
- Shull, D. (2003) - Neurobiology of Repetition Compulsion. Annals of Modern Psychoanalysis, 2 (1), 21-46.Documento26 pagineShull, D. (2003) - Neurobiology of Repetition Compulsion. Annals of Modern Psychoanalysis, 2 (1), 21-46.Shawn A. Wygant100% (1)
- New Era University: Integrated School Senior High School No. 9 Central Avenue, New Era, Quezon CityDocumento9 pagineNew Era University: Integrated School Senior High School No. 9 Central Avenue, New Era, Quezon CityBechay PallasigueNessuna valutazione finora
- EAPPDocumento3 pagineEAPPJed Riel Balatan50% (4)
- Violence of Children EppDocumento4 pagineViolence of Children EppBayu Yudha SamudraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ford Pinto Case StudyDocumento3 pagineFord Pinto Case StudyTou Joon HauNessuna valutazione finora
- HRPDocumento27 pagineHRPPriyanka Sharma33% (3)
- Test 5 - QUIZDocumento9 pagineTest 5 - QUIZClaudia Lucía Zuñiga Guevara67% (6)
- Aesthetic Experience, Interpretation and PleasureDocumento4 pagineAesthetic Experience, Interpretation and PleasureStephen GarrettNessuna valutazione finora
- Carswell Checklist 10Documento15 pagineCarswell Checklist 10api-400442112Nessuna valutazione finora
- Arno Gruen War or PeaceDocumento7 pagineArno Gruen War or PeaceAlexandre BanquetNessuna valutazione finora
- Orchid ChildrenDocumento10 pagineOrchid ChildrenAndie LurveNessuna valutazione finora
- New Vocabulary of Unit 7 SUMMIT 2Documento2 pagineNew Vocabulary of Unit 7 SUMMIT 2Rosmery RiberaNessuna valutazione finora
- Edtpa Lesson PlansDocumento9 pagineEdtpa Lesson Plansapi-405758157100% (1)
- Daft 7e - PPT - Ch08Documento34 pagineDaft 7e - PPT - Ch08asdfaNessuna valutazione finora
- Educ 606 Module 2 Early Childhood DevelopmentDocumento5 pagineEduc 606 Module 2 Early Childhood DevelopmentLennex Marie Sario100% (1)
- Oral History PDFDocumento2 pagineOral History PDFOguzhan DonmezNessuna valutazione finora
- Attitude Similarity Linked to Interpersonal AttractionDocumento3 pagineAttitude Similarity Linked to Interpersonal AttractionDred ZerozNessuna valutazione finora
- Pyramid Principle Consulting MethodologyDocumento5 paginePyramid Principle Consulting MethodologyajaisbNessuna valutazione finora
- Conceptualization and Description of HRD in GhanaDocumento12 pagineConceptualization and Description of HRD in GhanarmyawsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Clean Approaches For Coaches PDFDocumento26 pagineClean Approaches For Coaches PDFEmili Giralt GuarroNessuna valutazione finora
- Why "Everything Is FairDocumento2 pagineWhy "Everything Is Fairmtr_dintuNessuna valutazione finora
- Van Richten's Guide To The Vistani PDFDocumento97 pagineVan Richten's Guide To The Vistani PDFFlavio Dupim Pires100% (5)
- Daftar Pustaka Aphasia References ListDocumento4 pagineDaftar Pustaka Aphasia References ListDamar Gilang UtamaNessuna valutazione finora