Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Anaphase I Begins When The Two Chromosomes of Each
Caricato da
matDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Anaphase I Begins When The Two Chromosomes of Each
Caricato da
matCopyright:
Formati disponibili
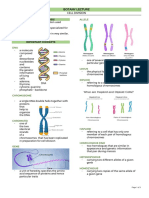
MEIOSIS- cell division intended for sex cells Anaphase I
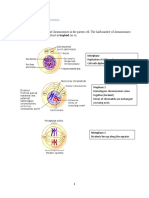
Meiosis I – Reductional Division Anaphase I begins when the two chromosomes of each
Meosis II- Equational Division bivalent (tetrad) separate and start moving toward
opposite poles of the cell as a result of the action of the
REDUCTIONAL DIVISION spindle. Notice that in anaphase I the sister chromatids
remain attached at their centromeres and move together
Prophase I toward the poles.
the chromosomes have already duplicated.
Telophase I
During prophase I, they coil and become shorter and
thicker At each pole, during this stage, there is a complete
LEPTOTENE haploid set of chromosomes (but each chromosome still
-Chromosomes are long thin thread has two sister chromatids). A cleavage furrow appears,
-This is the stage after G2 and by the end of this stage the parent cell has divided
into two daughter cells. This separation of the cytoplasm
ZYGOTENE
is called cytokinesis.
-Chromosomes are paired (Homologous
chromosome) =2 Daughter Cell
PACHYTENE P II
-Chromosomes are tightly paired
M II
-This is the stage where crossing over takes
place A II
-There is Synaptonemal Complex
T II
Protein that will facilitate the actual
crossing over or the sharing of the Relevance of having 2 genetically unidentical
genetic material. chromosome?
For Variation. There will be uniqueness in
*Crossing over- sharing of the genetic material offspring because the sperm and egg cell that
DIPLOTENE has been utilized are not the same.
How Mitosis differ from Meiosis I?
Tetrad/ Bivalent chromosomes MITOSIS
-There is same number of the chromosome
*Synapsis- pairing of the homologous -Cells involved in this process are body cells
chromosome -There are no sharing of genetic material
*Bivalent Chromosomes- Chromosomes that -Chromosomes align in a single line when it is on
has the same homologous but this is already metaphase stage
double stranded or the sister chromatid of the -There is splitting of centromere
chromosome MEIOSIS
*Chiasma- actual point where crossing over -There is a reduction in the number of
takes place chromosomes
DIAKINESIS -Sex cells are involved
-Chromosomes will just be moving at the -There is sharing of genetic material
equatorial plate so that there will be movement -Chromosomes are align in equatorial plate in pairs
towards the opposite pole of cell -There is no splitting of centromere.
The chromosomes simply move towards the
Metaphase I opposite pole without splitting of centromere
The pairs of chromosomes (bivalents) become that is happening randomly
arranged on the metaphase plate and are attached to
the now fully formed meiotic spindle
Difference of Mitosis from Meiosis II MEIOSIS – This will ensure that the organism resulting
from fertilization will always be a diploid number
MEIOSIS II
*prior to Gametogenesis happen what is being done is
-There are 4 unidentical cells produced
Meiosis I and Meiosis II
-Cell has a haploid number of chromosome
How is meiosis related to Mendelian laws of
MITOSIS inheritance?
-There are 2 identical cell produced -Law of segregation
-Cell has a diploid number of chromosomes Same with anaphase where in there is
movement of chromosome/ separating
MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS -Law of Independent Assortment
-Chromosome align in equatorial plate in a single Same thing happen in anaphase I and anaphase
line II. There is independent assortment of the
Relationship of Meiosis and Fertilization chromosome.
Meiosis is the one that prepares the cell to undergo
fertilization. If there is no Meiosis, there will be no It is meiosis that will ensure that the cell has
egg cell and sperm cell that is being utilized in unidentical genetic component. Meiosis will ensure
fertilization. Meiosis is involved in the process of that the chromosome that is separating/
Gametogenisis segregating have already sharing genetic material
-Spermatogenesis during the prior stage of meiosis. So that the
-Oogenesis resulting daughter cell will be unidentical to each
other
Fertilization- mating of egg and sperm cell in
order to form zygote that has a diploid number
If cell division during gametogenesis is non-meiotic,
what is the consequence in the future generation of
the diploid organism?
There will be chromosomal abnormality that will
cause death for organism. Because the meiosis is
the one that will bring the chromosomes into
haploid that when fertilization happen, the two
haploid bring together to come up with diploid
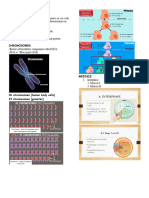
CHROMOSOMES
Somatic/ Sex cell Total
Autosome Diploid
HUMANS 44 xy 44 xx 46
DROSOPHILA 6 xy 6xx 8
ALLIUM 18 xy 18 xx 20
CEPA
Phaseolous sp. DEVELOPING MICROSPORE
-scientific name of bean POLLEN GRAIN
STIGMA, STYLE, OVARY 2 Cell:
-Part of the flower that is involved in the reproductive -Generative Cell- cell that will generate
cell.
-Tube cell- developed in pollen tube
-Part of pistil or stamen
(2N) MEGASPORE MOTHER CELL
-End product of mitosis POLLEN TUBE will develop sperm nuclei with egg nuclei
to form ZYGOTE
-will undergo meiosis
And other Sperm Nuclei will meet the polar nuclei in
(4) MEGASPORE order to form endosperm
-3 generates, 1 will continue EMBRYO
DEVELOPING MEGASPORE -developing zygote that will later give rise to epicotyl,
hypocotyl then later on will give rise to a new plant.
-Continuously develop and will result to meiosis II
EMBRYO SAC DROSOPHILA
-Megaspore became embryo 1. SPERMATOGONIA
-Immature egg cell
-Will undergo the process of mitosis -There are 8 chromosomes
*End of mitosis, there will be 8 cell that you can see in 2. PRIMARY SPERMATOCYTE
the embryo sac*
-There are 8 chromosomes
(3) ANTIPODAL CELL -No mitotic division happened just simply
-result of mitotic division enlargement of cell.
-g2 state
(2) POLAR NUCLEI CELL 3. SECONDARY SPERMATOCYTE
(2) SYNERGIDS CELL - 2 Secondary spermatocyte because cytokinesis
happened
(1) EGG CELL -4 Chromosomes each
ANTHER -Process: Meiosis I will give rise on secondary
spermatocyte having half of the number of
-Part of stamen
chromosome
FILAMENT 4. SPERMATIDS
-Holds the anther -4 cell
-undergo mitotic division -result of meiosis II
-There are 4 chromosomes (haploid number)
(2N) 5. SPERMATOZOA or MATURED SPERM CELL
-mitotic division -matured cell is result of spermiogenesis
MICROSPORE MOTHER CELL
*SPERMIOGENESIS- development of flagella of
-undergo meiotic division sperm cell
HAPLOID MICROSPORE *SPERMATOGENESIS- formation of sperm cell
OOGONIUM
-Immature egg cell resulting from oogenesis
-there are 8 chromosomes
PRIMARY OOCYTE
*Meiosis I
Because of spherical shape, there will be uneven
division of cytoplasm during cytokinesis
-there are 8 chromosomes
SECONDARY OOCYTE
-4 chromosomes
-big cell
FIRST POLAR BODY
-Small cell
FIRST POLAR BODY
OVUM or OOTID
SECOND POLAR BODIES
-degenerate during the process of fertilization
OVUM
-Continuous in the process of fertilization
ZYGOTE
EGG
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Meiosis 2Documento6 pagineMeiosis 2Areefa MohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Biosc 150 Exam 4 Study Guide: Chapter 13: MeiosisDocumento23 pagineBiosc 150 Exam 4 Study Guide: Chapter 13: MeiosisKhusbu PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Cycle - Sequence ofDocumento5 pagineCell Cycle - Sequence ofkami gourgaemNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproduction 2Documento36 pagineReproduction 2Emanuel John BangoNessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis: Cell DivisionDocumento21 pagineMeiosis: Cell DivisionAthena AretaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaphy and Phisiology Midterm NotesDocumento19 pagineAnaphy and Phisiology Midterm NotesLucy AlmonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocumento4 pagineMitosis and MeiosisMicah Porcal ArelladoNessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis: Chromatids (The Two Halves of A Duplicated Chromosome), As inDocumento29 pagineMeiosis: Chromatids (The Two Halves of A Duplicated Chromosome), As inyamamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis and Meiosis InfographDocumento1 paginaMitosis and Meiosis InfographPatricia BonganayNessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis ReviewerDocumento2 pagineMeiosis ReviewerGlenn GalvezNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell DivisionDocumento3 pagineCell DivisionChristina DaligconNessuna valutazione finora
- 2nd MT Biology ReviewerDocumento4 pagine2nd MT Biology ReviewerAliah HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Chromosomes: Karyotype of A Male HumanDocumento7 pagineChromosomes: Karyotype of A Male HumanKEITHLYN EIZEL RAMITERRENessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis - Clay ModellingDocumento4 pagineMeiosis - Clay ModellingAlexandra M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis WorksheetDocumento4 pagineMeiosis WorksheetIZ - 12JR 1013186 Lincoln Alexander SSNessuna valutazione finora
- MEIOSIS and MITOSISDocumento4 pagineMEIOSIS and MITOSISHannaj May De GuzmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 1 - Meiosis NotesDocumento3 pagineBio 1 - Meiosis NotesJayson RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- MeiosisDocumento2 pagineMeiosisMerann NepaNessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis PDFDocumento22 pagineMeiosis PDFEbook DownloadNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell DivisionDocumento5 pagineCell DivisionJohanna GultianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis II - Group 2Documento15 pagineMeiosis II - Group 2Yoongi MinNessuna valutazione finora
- MEIOSISDocumento8 pagineMEIOSISAmelie BalibagonNessuna valutazione finora
- Handout MeiosisDocumento4 pagineHandout MeiosisMoira Regina Lugo QuiogueNessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction SlidesDocumento29 pagineMeiosis and Sexual Reproduction Slidesmysticgalaxy2823Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cueva - Assignment Mitosis and MeiosisDocumento11 pagineCueva - Assignment Mitosis and MeiosisCristine Jane CuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 ScanDocumento5 pagine3 ScanAsadNessuna valutazione finora
- MeiosisDocumento32 pagineMeiosisJadcel OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis 1Documento37 pagineMeiosis 1Afaq AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis and The Sexual Life Cycle Reviewer NotesDocumento23 pagineMeiosis and The Sexual Life Cycle Reviewer NotesJestoni BigaelNessuna valutazione finora
- MeiosisDocumento9 pagineMeiosisRudzi UdziNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell-Cycle and Cell DivisionDocumento3 pagineCell-Cycle and Cell DivisionToby TrollyNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 4Documento4 pagineExercise 4BARRIENTOS, MARIE NICOLENessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis Meiosis Halves The Number of Chromosomes in The Parent Cell. The Half Number of ChromosomesDocumento4 pagineMeiosis Meiosis Halves The Number of Chromosomes in The Parent Cell. The Half Number of ChromosomesTracia WalcottNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocumento8 pagineMitosis and MeiosisShiela BelandresNessuna valutazione finora
- 5a - Topic 4b Cell Cycle - Meiosis & Stem CellsDocumento77 pagine5a - Topic 4b Cell Cycle - Meiosis & Stem CellsAlis SyamimiNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocumento21 pagine2 Mitosis Vs MeiosisKinjNessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis Lab 211Documento8 pagineMeiosis Lab 211Tracy LykaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Cycle&MitosisDocumento43 pagineCell Cycle&MitosisPrecy Ann ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Biol Activity 5 Word2003Documento16 pagineBiol Activity 5 Word2003Faith Jessica ParanNessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis and Mitosis DifferenceDocumento27 pagineMeiosis and Mitosis DifferenceZarmae A. NarcisoNessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis (Reduction Division)Documento20 pagineMeiosis (Reduction Division)kim joshua galoloNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocumento21 pagineMitosis and MeiosisJuLie Ann DeGuzman GeslaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Cytogenetics Mitosis & Meiosis and Their DiferrencesDocumento11 pagineCytogenetics Mitosis & Meiosis and Their DiferrencesGeemilReyNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis MeiosisDocumento8 pagineMitosis MeiosisSyndy Mae Wasing DosogNessuna valutazione finora
- Differences Between Mitosis and MeiosisDocumento2 pagineDifferences Between Mitosis and MeiosisJeannifer ManjaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical 5: Cell Divisions: Mitosis & Meiosis: Name: Vo Minh Hanh ID: BTBTIU16064Documento3 paginePractical 5: Cell Divisions: Mitosis & Meiosis: Name: Vo Minh Hanh ID: BTBTIU16064Keiko InoueNessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis and MitosisDocumento22 pagineMeiosis and Mitosisyaqoob008Nessuna valutazione finora
- MeiosisDocumento34 pagineMeiosisJared CoyagboNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell DivisionDocumento3 pagineCell DivisionmunozayshiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocumento7 pagineMitosis Vs MeiosisJD DX100% (1)
- 4th Module 2 Cel ReproductionDocumento57 pagine4th Module 2 Cel ReproductionLocal ClownNessuna valutazione finora
- Cyto 3Documento2 pagineCyto 3Zharlene DoloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Heredity and Variation: 1. Cell DivisionDocumento24 pagineChapter 3 Heredity and Variation: 1. Cell DivisionnamikNessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis and MitosisDocumento6 pagineMeiosis and MitosisSummer LoveNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOLS102-UOB-Chapter 10Documento8 pagineBIOLS102-UOB-Chapter 10Noor JanahiNessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis: Dr. Shayma'a J. Ahmed Prof. Genetic Engineerin& BiotechnologyDocumento31 pagineMeiosis: Dr. Shayma'a J. Ahmed Prof. Genetic Engineerin& BiotechnologyMariam QaisNessuna valutazione finora
- Genbio Reviwer FinalsDocumento5 pagineGenbio Reviwer FinalsChesley CarolinoNessuna valutazione finora
- MeiosisDocumento17 pagineMeiosisSanaa SamkoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Division (Edited)Documento12 pagineCell Division (Edited)Ian Karlo NuñezNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Division Study NotesDocumento9 pagineCell Division Study NotesShaira Galban GamponNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Year - BS Medical Technology - 2 Sem - 1 BlockDocumento20 pagine2 Year - BS Medical Technology - 2 Sem - 1 BlockBelle Lat100% (1)
- Genetics: An Introduction: Peter J. RussellDocumento72 pagineGenetics: An Introduction: Peter J. RussellAli SeenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Division Mitosis MeiosisDocumento49 pagineCell Division Mitosis MeiosisAli Namialus100% (1)
- 5.lab - Time For Mitosis-1Documento3 pagine5.lab - Time For Mitosis-1Eskil LarsenNessuna valutazione finora
- Elmer J Sabalilag Stem 1: Mitosis MeiosisDocumento1 paginaElmer J Sabalilag Stem 1: Mitosis MeiosisAria NichiNessuna valutazione finora
- A Level Biology Notes 2023Documento423 pagineA Level Biology Notes 2023Melogina ManoNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Biology: Meiosis and Sexual Life CyclesDocumento13 pagineBiology Biology: Meiosis and Sexual Life CyclesRosemond FabienNessuna valutazione finora
- Botany NCERT Cell CycleDocumento11 pagineBotany NCERT Cell CycleVishal SorteyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cueva - Assignment Mitosis and MeiosisDocumento11 pagineCueva - Assignment Mitosis and MeiosisCristine Jane CuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Today and Tomorrow With Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions Manual 1Documento36 pagineBiology Today and Tomorrow With Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions Manual 1janesilvapwoikcfjgbNessuna valutazione finora
- Crossing Over: Cc5 AssignmentDocumento18 pagineCrossing Over: Cc5 AssignmentAnjishnu Mukhopadhyay BIOTECH SXCBNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 3.4-3.6 Meiosis Gizmo - StudentDocumento11 pagineCH 3.4-3.6 Meiosis Gizmo - StudentKaylia SimmondsNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 - Gen Bio 1 - MidtermDocumento7 pagineModule 3 - Gen Bio 1 - MidtermAngel Cuacko GacmatanNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Test Revision Sheet T1 Y10 23Documento4 pagineBiology Test Revision Sheet T1 Y10 23Chloe WNessuna valutazione finora
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 3Documento7 pagineGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 3karyo eseymNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 CytogeneticsDocumento23 pagineModule 3 CytogeneticsFrances Riane SimoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis: J. Richard McintoshDocumento17 pagineMitosis: J. Richard McintoshAlejandro CastañedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2 Week 2Documento9 pagineModule 2 Week 2Mycel Ann AcuzarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - Cell Cycle and MitosisDocumento22 pagineChapter 3 - Cell Cycle and MitosisMae Angela MorenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Division and Inheritance PatternDocumento22 pagineCell Division and Inheritance PatternSheraz ChaudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice TestDocumento5 paginePractice Testcarmen sandiegoNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 8 - Q4 - Week 2Documento19 pagineScience 8 - Q4 - Week 2AlfielAquino100% (3)
- 12th Biology Practicals 2022-23Documento10 pagine12th Biology Practicals 2022-23dig vijayNessuna valutazione finora
- Amoeba Sisters - MeiosisDocumento2 pagineAmoeba Sisters - MeiosisCourtlynn RodgersNessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis Foldable Activity: ProceduresDocumento2 pagineMeiosis Foldable Activity: ProceduresJeff SanfordNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Cell DivisionDocumento43 pagine4 Cell DivisionPrem ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- MeiosisDocumento8 pagineMeiosisRohit MaldeNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 6 Lab ActivitiesDocumento5 pagineUnit 6 Lab ActivitiesNabeel NastechNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis Meiosis NOTESDocumento11 pagineMitosis Meiosis NOTESCaden DiazNessuna valutazione finora