Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Vlplus 252 Influences Hattie Ranking Dec 2017
Caricato da
api-483011066Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Vlplus 252 Influences Hattie Ranking Dec 2017
Caricato da
api-483011066Copyright:
Formati disponibili
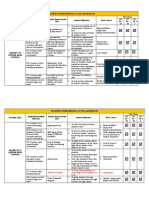
Visible Learningplus 250+ Influences on Student Achievement
STUDENT ES CURRICULA ES HOME ES SCHOOL ES
Prior knowledge and background Reading, writing and the arts Family structure Leadership
✓ The Visible Learning
students ← Field independence 0.68 Comprehensive instructional 0.72 Adopted vs non-adopted care 0.25 Collective teacher efficacy 1.57
research synthesises
reseajh@svoi.et.ie:[
programs for teachers
Non-standard dialect use -0.29 Engaged vs disengaged fathers 0.20 Principals/school leaders 0.32
Piagetian programs 1.28
Comprehension programs 0.47
Intact (two-parent) families 0.23 School climate 0.32
findings from 1,400
Prior ability 0.94
Drama/arts programs 0.38
Other family structure 0.16 School resourcing meta-analyses of 80,000
Prior achievement 0.55
Exposure to reading 0.43
Home environment External accountability systems 0.31 studies involving 300
Music programs 0.37
Relating creativity to achievement 0.40 Corporal punishment in the home -0.33 Finances 0.21 million students, into what
producing ← Phonics instruction 0.70
issues
finip%¥ised works best in education.
Relations of high school to 0.60 Early years’ interventions 0.44 Types of school
university achievement
→ real,ewa? Repeated reading programs 0.75
work 4 Home visiting 0.29 Charter schools 0.09
Relations of high school achievement to 0.38 Second/third chance programs 0.53
Moving between schools -0.34 Religious schools 0.24
career performance
&¥Im¥emE%
Sentence combining programs 0.15
Parental autonomy support 0.15 Single-sex schools 0.08
Self-reported grades 1.33
Spelling programs 0.58
Parental involvement 0.50 Summer school 0.23
Working memory strength 0.57
Visual-perception programs 0.55 Key for rating
Parental military deployment -0.16 Summer vacation effect -0.02
Beliefs, attitudes and dispositions
Vocabulary programs 0.62
Positive family/home dynamics 0.52 School compositional effects Potential to considerably
Attitude to content domains 0.35
Whole language 0.06
Television -0.18 College halls of residence 0.05 accelerate student achievement
Concentration/persistence/ engagement 0.56
0.45
q .s n #e g as Ii s on &
Family resources Desegregation 0.28
Grit/incremental vs. entity thinking 0.25 Potential to accelerate
Math and sciences
Family on welfare/state aid -0.12 Diverse student body 0.10
Mindfulness 0.29 student achievement
Manipulative materials on math 0.30
Non-immigrant background 0.01 Middle schools’ interventions 0.08
Morning vs. evening → important 0
0.12
Mathematics programs 0.59 Likely to have positive impact
Parental employment 0.03 Out-of-school curricula experiences 0.26
\
I
and skills Perceived task value 0.46
.
Science programs 0.48 on student achievement
Socio-economic status 0.52 School choice programs 0.12
Positive ethnic self-identity 0.12
Use of calculators 0.27
School size (600-900 students at 0.43 Likely to have small positive
Positive self-concept 0.41
Self-efficacy 0.92
Other curricula programs
i. secondary) impact on student achievement
Bilingual programs 0.36 Other school factors
Stereotype threat 0.33
unanswered 1 unknown .
Likely to have a negative impact
Career interventions 0.38 with students
Counseling effects 0.35
Student personality 0.26 more time on student achievement
Chess instruction 0.34 spending lives Generalized school effects 0.48
Motivational approach, orientation to understand their personal
Conceptual change programs 0.99 Modifying school calendars/ 0.09 ES Effect size calculated using
Achieving motivation and approach 0.44 timetables Cohen’s d
Creativity programs 0.62
Boredom •-0.49 Pre-school programs 0.28
Diversity courses 0.09
Deep motivation and approach 0.69 Suspension/expelling students -0.20
Extra-curricula programs 0.20
Depression -0.36
Integrated curricula programs 0.47
all factors led I
d.gg!dependency
Lack of stress 0.17
:#
in
present to present Juvenile delinquent programs 0.12
motioned into
µ
Mastery goals 0.06
poison Motivation 0.42
Motivation/character programs
Outdoor/adventure programs
0.34
0.43
beaten Performance goals g-0.01
ledge .
Perceptual-motor programs 0.08
ISurface motivation and approach
Reducing anxiety 0.42
Play programs 0.50
•-0.11
Social skills programs 0.39
Physical influences
Tactile stimulation programs 0.58
ADHD -0.90
students ADHD – treatment with drugs 0.32
↳
many curricula not
also
present Breastfeeding 0.04 addressed .
these Deafness -0.61
with LOOK INTO PROGRAMS
issues
)
.
Exercise/relaxation 0.26 IN FU1-0RE
Gender on achievement 0.08
also
rioted
and Lack of illness 0.26
to
drug wedge Lack of sleep -0.05
alcohol
Full compared to pre-term/low birth weight 0.57
Relative age within a class 0.45
The Visible Learningplus program materials are licensed from the Visible Learning Limited Partnership and Cognition Education Group
PAGE 1 of 2 | November 2017
were
all highlightedaddressed
and
present
Visible Learning plus
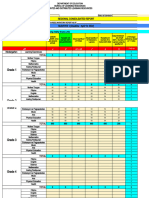
250+ Influences on Student Achievement
CLASSROOM ES TEACHER ES TEACHING: Focus ES TEACHING: Focus on ES TEACHING: Focus on ES
Classroom composition effects Teacher attributes on student learning teaching/instructional implementation
Detracking 0.09 Average teacher effects 0.32 strategies strategies method
Mainstreaming/inclusion 0.27 Teacher clarity 0.75 Strategies emphasizing student meta-cognitive/ Strategies emphasizing learning intentions Implementations using technologies
self-regulated learning
s¥EEr
•
§
Multi-grade/age classes 0.04 Teacher credibility →
0.90 Appropriately challenging goals 0.59 Clickers 0.22
Elaboration and organization 0.75
Open vs. traditional classrooms 0.01 Teacher estimates of achievement 1.29 Behavioral organizers 0.42 Gaming/simulations 0.35
Elaborative interrogation 0.42
Reducing class size 0.21 Teacher expectations 0.43 Clear goal intentions 0.48 Information communications 0.47
Evaluation and reflection 0.75 technology (ICT)
Retention (holding students back) -0.32 Teacher personality attributes 0.23 Cognitive task analysis 1.29
Meta-cognitive strategies 0.60 Intelligent tutoring systems 0.48
Small group learning 0.47 Teacher performance pay 0.05 Concept mapping 0.64
=
Help seeking 0.72 Interactive video methods 0.54
Tracking/streaming 0.12 Teacher verbal ability 0.22 Goal commitment 0.40
Self-regulation strategies 0.52 Mobile phones 0.37
Within class grouping 0.18 Teacher-student interactions Learning goals vs. no goals 0.68
Self-verbalization and 0.55 One-on-one laptops 0.16
School curricula for gifted students Student rating of quality of teaching 0.50 Learning hierarchies-based 0.19
self-questioning
approach Online and digital tools 0.29
Ability grouping for gifted students 0.30 Teachers not labeling students 0.61 Strategy monitoring 0.58
Planning and prediction 0.76 Programmed instruction 0.23
Acceleration programs 0.68 Teacher-student relationships 0.52 Transfer strategies 0.86
Setting standards for self-judgement 0.62 Technology in distance education 0.01
Enrichment programs 0.53 Teacher education Student-focused interventions
Strategies emphasizing success criteria Technology in mathematics 0.33
Classroom influences Initial teacher training programs 0.12 Aptitude/treatment interactions 0.19
Mastery learning 0.57 Technology in other subjects 0.55
Background music 0.10 Micro-teaching/video review 0.88 Individualized instruction 0.23
•
of lessons Worked examples 0.37 Technology in reading/literacy 0.29
Behavioral intervention programs 0.62 Matching style of learning 0.31
Professional development 0.41 Strategies emphasizing feedback Technology in science 0.23
Classroom management 0.35 Student-centered teaching 0.36
programs Classroom discussion 0.82 Technology in small groups 0.21
Cognitive behavioral programs 0.29 Student control over learning 0.02
Teacher subject matter knowledge 0.11 Different types of testing 0.12 Technology in writing 0.42
Decreasing disruptive behavior 0.34 Strategies emphasizing student perspectives
Feedback 0.70 Technology with college students 0.42
Mentoring 0.12 influences were present in learning
all highlighted teaching Peer tutoring 0.53
Providing formative evaluation 0.48 Technology with 0.44
Positive peer influences 0.53 the course of elementary students
during Questioning 0.48
Strong classroom cohesion 0.44 FURTHER Volunteer tutors 0.26
Technology with high 0.30
RESARCH Response to intervention 1.29
Students feeling disliked -0.19
- Learning strategies
Teaching/instructional strategies
school students
Deliberate practice 0.79 Technology with learning 0.57
Adjunct aids 0.32 needs students
Effort 0.77
Collaborative learning 0.34 Use of PowerPoint 0.26
=
Imagery 0.45
Key for rating
The Visible Learning Interleaved practice 0.21
Competitive vs. 0.24 Visual/audio-visual methods 0.22
individualistic learning
Potential to considerably research synthesises Mnemonics 0.76
Cooperative learning 0.40
Web-based learning 0.18
Implementations using out-of-school learning
accelerate student achievement findings from 1,400 Note taking 0.50
Cooperative vs. competitive learning 0.53
After-school programs 0.40
Potential to accelerate meta-analyses of 80,000 Outlining and transforming 0.66
Cooperative vs. 0.55
- Distance education 0.13
Practice testing 0.54 individualistic learning
student achievement studies involving 300
⑥
Home-school programs 0.16
Record keeping 0.52 Direct instruction 0.60
Likely to have positive impact million students, into what Homework 0.29
Rehearsal and memorization 0.73 Discovery-based teaching 0.21
on student achievement works best in education. Spaced vs. mass practice 0.60 Explicit teaching strategies 0.57
Service learning 0.58
Likely to have small positive Implementations that emphasize school-wide
Strategy to integrate with prior 0.93 Humor 0.04
teaching strategies
impact on student achievement knowledge
Inductive teaching 0.44
⑨
-
Co- or team teaching 0.19
Study skills 0.46
Inquiry-based teaching 0.40
Likely to have a negative impact Interventions for students with 0.77
Summarization 0.79
on student achievement Jigsaw method 1.20 learning needs
Teaching test taking and coaching 0.30
Philosophy in schools 0.43 Student support programs – 0.21
ES Effect size calculated using Time on task 0.49
Problem-based learning 0.26 college
Cohen’s d -
Underlining and highlighting 0.50
Problem-solving teaching 0.68 Teaching creative thinking 0.34
Reciprocal teaching 0.74 Whole-school improvement 0.28
programs
Scaffolding 0.82
be
all ci must
addressed future
Teaching communication skills 0.43 In
and strategies
The Visible Learningplus program materials are licensed from the Visible Learning Limited Partnership and Cognition Education Group
PAGE 2 of 2 | November 2017
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- WISC IV Handout PDFDocumento121 pagineWISC IV Handout PDFvaluat100% (1)
- Reflective AssignmentDocumento5 pagineReflective AssignmentVictor Murambiwa100% (3)
- Bowlby Attachment TheoryDocumento10 pagineBowlby Attachment Theoryfatimapanda100% (1)
- Vcal Poetry Lesson Plan SequenceDocumento6 pagineVcal Poetry Lesson Plan Sequenceapi-483011066Nessuna valutazione finora
- Root - Cause AnalysisDocumento2 pagineRoot - Cause AnalysisAnne Dinopol-MalinginNessuna valutazione finora
- DLL CparDocumento3 pagineDLL CparVenus EstacioNessuna valutazione finora
- 250 Influences Final - Javier Touron - INED21Documento2 pagine250 Influences Final - Javier Touron - INED21pacoperez2008Nessuna valutazione finora
- Written Report in Foundations of Special and Inclusive Education TOPIC: Process of Inclusion-Philippine ModelDocumento6 pagineWritten Report in Foundations of Special and Inclusive Education TOPIC: Process of Inclusion-Philippine ModelMariee Begonia Macaraeg100% (1)
- Classroom and Group M B Results ReportDocumento1 paginaClassroom and Group M B Results Reportapi-512159926Nessuna valutazione finora
- Perceptions and Opinion of Happiness Among University Students in A Malaysian University. Asean Journal of PsychiatryDocumento8 paginePerceptions and Opinion of Happiness Among University Students in A Malaysian University. Asean Journal of PsychiatryKarim Al-JashamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Strategies in Handling Students With Intellectual DisabilityDocumento19 pagineTeaching Strategies in Handling Students With Intellectual DisabilityNedgee HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Literature Review On Scientific CreativityDocumento7 pagineLiterature Review On Scientific CreativityJoseph ClementsNessuna valutazione finora
- The Teacher and The Community, School Culture and Organizational LeadershipDocumento3 pagineThe Teacher and The Community, School Culture and Organizational LeadershipPhft87% (23)
- Teachers' M&E ReportDocumento8 pagineTeachers' M&E Reportmelody lazagaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 Values of Art in EducationDocumento14 pagine1.1 Values of Art in EducationHomer Punzalan0% (3)
- Action Plan Brigada EskwelaDocumento2 pagineAction Plan Brigada EskwelaMarjorie Delrosario Pilon96% (102)
- Homeroom Guidance Grade 9 Quarter 2 - Module 9:: Unique Experiences Make Me StrongDocumento7 pagineHomeroom Guidance Grade 9 Quarter 2 - Module 9:: Unique Experiences Make Me StrongMarites Prado67% (3)
- Vlplus 252 Influences Hattie Ranking Dec 2017Documento2 pagineVlplus 252 Influences Hattie Ranking Dec 2017api-483011066Nessuna valutazione finora
- Corwin 250 Influences 10.1.2018Documento2 pagineCorwin 250 Influences 10.1.2018zvonimir bosnjakNessuna valutazione finora
- 250+ Influences On Student Achievement: Visible LearningDocumento2 pagine250+ Influences On Student Achievement: Visible LearningcandyNessuna valutazione finora
- Individual Faculty and TA Annual Evaluation Score (From 2021) - 20220225-132150-CSTDocumento2 pagineIndividual Faculty and TA Annual Evaluation Score (From 2021) - 20220225-132150-CSTAmal ElgamalNessuna valutazione finora
- Teacher's Evaluation 2023-2024 Semester 1 - TDocumento2 pagineTeacher's Evaluation 2023-2024 Semester 1 - TgekyurisNessuna valutazione finora
- 2018 2019 Measures of Teacher PracticeDocumento1 pagina2018 2019 Measures of Teacher Practiceapi-545192512Nessuna valutazione finora
- Etica SocialDocumento10 pagineEtica SocialOliveira De Atija AntonioNessuna valutazione finora
- Ranstadlerr Classroom Management PlanDocumento21 pagineRanstadlerr Classroom Management Planapi-449409521Nessuna valutazione finora
- 20 21 Eggleston Teacher Observation Record - Sheet1Documento2 pagine20 21 Eggleston Teacher Observation Record - Sheet1api-399051557Nessuna valutazione finora
- Accomplishment Report: Department of EducationDocumento6 pagineAccomplishment Report: Department of EducationJaneth Torrente BantayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mancera Turtal Bessingga BautistaDocumento3 pagineMancera Turtal Bessingga BautistaMechelle PacapatNessuna valutazione finora
- 2nd SEM 2020-SAC SHS FIDP Final - BIOLOGY 2Documento12 pagine2nd SEM 2020-SAC SHS FIDP Final - BIOLOGY 2Zerille Anne Inson AgregadoNessuna valutazione finora
- 2017 2018 Measures of Teacher PracticeDocumento1 pagina2017 2018 Measures of Teacher Practiceapi-545192512Nessuna valutazione finora
- Best Practices Guide To Intervention: Teaching Students With Severe Emotional and Behavioral DisordersDocumento101 pagineBest Practices Guide To Intervention: Teaching Students With Severe Emotional and Behavioral DisordersenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Marksheet Arushi PalDocumento1 paginaMarksheet Arushi PalMekill PatidarNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 2 - SSM Term ProjectDocumento10 pagineGroup 2 - SSM Term ProjectKaleb BerhanuNessuna valutazione finora
- 2023 Q4 School MEA Dashboard - FinalDocumento31 pagine2023 Q4 School MEA Dashboard - FinalCleofe PavoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ascent Academies of Utah - Teacher Observation Record Teacher: Eggleston Grade(s) : 7,8,9 Subject(s) : ELA and Theatre School Year: 2021-22Documento3 pagineAscent Academies of Utah - Teacher Observation Record Teacher: Eggleston Grade(s) : 7,8,9 Subject(s) : ELA and Theatre School Year: 2021-22api-399051557Nessuna valutazione finora
- Template For Annual Improvement PlanDocumento5 pagineTemplate For Annual Improvement PlanChan Chanielou JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Plan (Linear)Documento6 pagineLearning Plan (Linear)Joseph ManaligodNessuna valutazione finora
- Age of Learning - Flyer - My Math Academy - ENDocumento2 pagineAge of Learning - Flyer - My Math Academy - ENvillasenor.annelNessuna valutazione finora
- Gad Action Plan - Sy 2022 - 2023Documento1 paginaGad Action Plan - Sy 2022 - 2023Christine Joy PerionNessuna valutazione finora
- Del Monte, Buug, Zamboanga Sibugay Annual Implementation Plan/ Work and Financial Plan FY 2021Documento5 pagineDel Monte, Buug, Zamboanga Sibugay Annual Implementation Plan/ Work and Financial Plan FY 2021ShirleyNessuna valutazione finora
- AuntieDocumento1 paginaAuntieROSE MENDEZNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment DetailsDocumento7 pagineAssessment Detailsapi-596436208Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ac Remedial 1Documento2 pagineAc Remedial 1jack macabatalNessuna valutazione finora
- Planning WorksheetDocumento3 paginePlanning Worksheetlaurice alteaNessuna valutazione finora
- School Solutions: Trust of 10000+ Top SchoolsDocumento11 pagineSchool Solutions: Trust of 10000+ Top SchoolsNamrat DhillonNessuna valutazione finora
- University of Caloocan City Graduate SchoolDocumento2 pagineUniversity of Caloocan City Graduate SchoolRosanna Jose CuevasNessuna valutazione finora
- Revised Smea Template: Baybay City DivisionDocumento13 pagineRevised Smea Template: Baybay City DivisionRosalie NopalNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Module For Mathematics 8 - : Mindanao Mission AcademyDocumento20 pagineLearning Module For Mathematics 8 - : Mindanao Mission AcademyCJ SarsalejoNessuna valutazione finora
- Brigada-Eskwela-Taechers Action Plan IndividualDocumento4 pagineBrigada-Eskwela-Taechers Action Plan IndividualAlmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Region VII Q1Q2 LR Inventory DORO Consolidated Forms LAS CLRDocumento777 pagineRegion VII Q1Q2 LR Inventory DORO Consolidated Forms LAS CLRzshaninajeorahNessuna valutazione finora
- 106551-SJES-Science-Intervention-Plan-grade 3Documento4 pagine106551-SJES-Science-Intervention-Plan-grade 3Jaime DailegNessuna valutazione finora
- Curriculum Implementation: School: DLMNHSDocumento2 pagineCurriculum Implementation: School: DLMNHSRick RanteNessuna valutazione finora
- School Improvement Project TitleDocumento3 pagineSchool Improvement Project TitleMilagrosBautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cocubes TemplateDocumento21 pagineCocubes TemplateShdjdjNessuna valutazione finora
- It Nas Survey 2018Documento12 pagineIt Nas Survey 2018pragatistartsmartNessuna valutazione finora
- Republic of The PhilippinesDocumento2 pagineRepublic of The PhilippinesDabe Genesis Ligalig100% (1)
- Online Progress Card Academic Session: 2021-2022: Maxfort School Dwarka New DelhiDocumento1 paginaOnline Progress Card Academic Session: 2021-2022: Maxfort School Dwarka New Delhiyuvrajkalra22Nessuna valutazione finora
- V.annual Implementation PlanDocumento13 pagineV.annual Implementation Planeugem galapateNessuna valutazione finora
- Tos - Table of SpecificationDocumento2 pagineTos - Table of SpecificationCharlyn CaraballaNessuna valutazione finora
- How Are Dominance, Codominance and Incomplete Dominance Patterns of Inheritance Different From Each Other - Sarthaks EConnectDocumento1 paginaHow Are Dominance, Codominance and Incomplete Dominance Patterns of Inheritance Different From Each Other - Sarthaks EConnectPaarth GoyalNessuna valutazione finora
- ENHANCED MEA Template MAHAYAGDocumento6 pagineENHANCED MEA Template MAHAYAGHermis Rivera CequiñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Del Monte, Buug, Zamboanga Sibugay Annual Implementation Plan/ Work and Financial Plan FY 2021Documento11 pagineDel Monte, Buug, Zamboanga Sibugay Annual Implementation Plan/ Work and Financial Plan FY 2021ShirleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Sotto, Juliana, OliverosDocumento1 paginaSotto, Juliana, OliverosYana SottoNessuna valutazione finora
- LEARNING THEORIES - COGNITIVE LEARNING THEORIES L CHAPTER 5 CHAPTER LEARNING OUTCOMES - Mona Kumari - Academia - Edu PDFDocumento1 paginaLEARNING THEORIES - COGNITIVE LEARNING THEORIES L CHAPTER 5 CHAPTER LEARNING OUTCOMES - Mona Kumari - Academia - Edu PDFMasline MakucheteNessuna valutazione finora
- SOP QualityDocumento18 pagineSOP QualityChristina Manguiob EscasinasNessuna valutazione finora
- Planning Grid Junior Cert 1st Year Wood TechnologyDocumento6 paginePlanning Grid Junior Cert 1st Year Wood Technologyapi-543529812Nessuna valutazione finora
- Humss1 Tos Answerkey Q2 Summative-TestDocumento2 pagineHumss1 Tos Answerkey Q2 Summative-TestHanz Albrech AbellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Action Plan: A. Bonifacio Integrated SchoolDocumento2 pagineMathematics Action Plan: A. Bonifacio Integrated SchoolJaylord LosabiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Education: School: School Head: The Learning Delivery Modality Implementation PlanDocumento9 pagineDepartment of Education: School: School Head: The Learning Delivery Modality Implementation PlanvinderNessuna valutazione finora
- INTERVENTION OR REMEDIATION PLAN FOR THE IDENTIFIED LEARNING GAPS IN Grade 10Documento5 pagineINTERVENTION OR REMEDIATION PLAN FOR THE IDENTIFIED LEARNING GAPS IN Grade 10Mylyn MinaNessuna valutazione finora
- MS1 Seq 4 Me & My School PDFDocumento8 pagineMS1 Seq 4 Me & My School PDFSamir Bounab100% (8)
- Teacher Performance in Bihar, India: Implications for EducationDa EverandTeacher Performance in Bihar, India: Implications for EducationNessuna valutazione finora
- MeetinsDocumento2 pagineMeetinsapi-483011066Nessuna valutazione finora
- BBBBDocumento1 paginaBBBBapi-483011066Nessuna valutazione finora
- VCAL Senior Literacy: Time Capsule ICT Ethical ConsiderationsDocumento1 paginaVCAL Senior Literacy: Time Capsule ICT Ethical Considerationsapi-483011066Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vce English - Student ObservationsDocumento2 pagineVce English - Student Observationsapi-483011066Nessuna valutazione finora
- How To A Teachers GuideDocumento3 pagineHow To A Teachers Guideapi-483011066Nessuna valutazione finora
- Managing Challenging Behaviours 2019.: Listed Below Are Prevention and Intervention Methods That I UsedDocumento1 paginaManaging Challenging Behaviours 2019.: Listed Below Are Prevention and Intervention Methods That I Usedapi-483011066Nessuna valutazione finora
- English Comparative Sac Moderation Marking TipsDocumento3 pagineEnglish Comparative Sac Moderation Marking Tipsapi-483011066Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vcal Senior Literacy: Time Capsule: School Week Lesson Title Lesson Content Resources Assessment Learning OutcomeDocumento1 paginaVcal Senior Literacy: Time Capsule: School Week Lesson Title Lesson Content Resources Assessment Learning Outcomeapi-483011066Nessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled 2Documento1 paginaUntitled 2api-483011066Nessuna valutazione finora
- Language Analysis RevisionDocumento3 pagineLanguage Analysis Revisionapi-483011066Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vcal Senior Literacy Student ObservationsDocumento2 pagineVcal Senior Literacy Student Observationsapi-483011066Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plans 1-5Documento15 pagineLesson Plans 1-5api-483011066Nessuna valutazione finora
- VCE Assessment Tasks Outcomes Record Book.: Keeping Reliable RecordsDocumento1 paginaVCE Assessment Tasks Outcomes Record Book.: Keeping Reliable Recordsapi-483011066Nessuna valutazione finora
- School ProfileDocumento1 paginaSchool Profileapi-483011066Nessuna valutazione finora
- All ObservationsDocumento12 pagineAll Observationsapi-483011066Nessuna valutazione finora
- Marking Poetry UnitDocumento2 pagineMarking Poetry Unitapi-483011066Nessuna valutazione finora
- Marking Time Capsule UnitDocumento2 pagineMarking Time Capsule Unitapi-483011066Nessuna valutazione finora
- MeetinsDocumento2 pagineMeetinsapi-483011066Nessuna valutazione finora
- 6805 Manuscript 39739 1 10 20210512Documento6 pagine6805 Manuscript 39739 1 10 20210512Carla Jubells GilNessuna valutazione finora
- Jenis Kanak-Kanak Keperluan Khas Yang Guru Kerap Mengendalikan (Pilih Hanya 1 Orang)Documento2 pagineJenis Kanak-Kanak Keperluan Khas Yang Guru Kerap Mengendalikan (Pilih Hanya 1 Orang)yelobellNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Attitude Formation and Change: Consumer Behavior, Eighth EditionDocumento35 pagineConsumer Attitude Formation and Change: Consumer Behavior, Eighth Editionjugnu4selfNessuna valutazione finora
- Inside Listening and Speaking Level 3Documento136 pagineInside Listening and Speaking Level 3lolyoshi86% (7)
- Daily Learning Plan (DLP) Name Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterDocumento4 pagineDaily Learning Plan (DLP) Name Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterRoselyn DawongNessuna valutazione finora
- Mindy Womack: ObjectiveDocumento2 pagineMindy Womack: Objectiveapi-448492086Nessuna valutazione finora
- Student Motivation ScaleDocumento26 pagineStudent Motivation ScaleScholar WinterflameNessuna valutazione finora
- Pr1 ProposalDocumento6 paginePr1 ProposalZenyll Deserei AquinoNessuna valutazione finora
- 5e Lesson Plan Template2Documento7 pagine5e Lesson Plan Template2api-456159937Nessuna valutazione finora
- Global Citizen Essay: Martinez, Gabriela 3/2/17 Global Seminar Ms - MontesDocumento4 pagineGlobal Citizen Essay: Martinez, Gabriela 3/2/17 Global Seminar Ms - Montesapi-319343009Nessuna valutazione finora
- Course Outline - HRMA 345Documento3 pagineCourse Outline - HRMA 345DrKomal KhalidNessuna valutazione finora
- Prof. Robert NeimeyerDocumento2 pagineProf. Robert Neimeyercell_tNessuna valutazione finora
- Field Study 104Documento56 pagineField Study 104Tiff Miranda86% (7)
- Lesson 8 The Roles of Technology in Delivering The CurriculumDocumento1 paginaLesson 8 The Roles of Technology in Delivering The CurriculumJunebern ManpatilanNessuna valutazione finora
- Title-The Effect of Parental Employment On Child's Emotional IntelligenceDocumento4 pagineTitle-The Effect of Parental Employment On Child's Emotional IntelligenceSamanwita LalaNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 PictureDocumento1 pagina5 PictureETC100% (1)
- Abraham Maslow: Self ActualizationDocumento11 pagineAbraham Maslow: Self ActualizationshellyNessuna valutazione finora
- Donna Mestdagh Colleague ReferenceDocumento2 pagineDonna Mestdagh Colleague Referenceapi-104924860Nessuna valutazione finora
- Yoga Upasana - Rajesh Panicker (Profile)Documento13 pagineYoga Upasana - Rajesh Panicker (Profile)Yoga UpasanaNessuna valutazione finora