Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
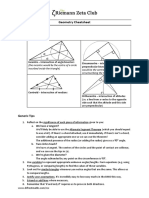
Theorem 80
Caricato da
Kim LaguardiaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Theorem 80
Caricato da
Kim LaguardiaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
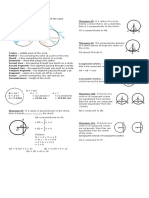
Theorem 74 Theorem 81
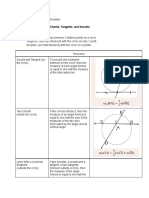
If a radius is perpendicular to a chord, then it If two central angles of a circle (or of congruent
bisects the chord. circles) are congruent, then the corresponding
chords are congruent.
Theorem 75
Theorem 82
If a radius of a circle bisects a chord that is not a
diameter, then it is perpendicular to that chord. If two chords of a circle (or of congruent circles)
are congruent, then the corresponding central
angles are congruent.
Theorem 76
The perpendicular bisector of a chord passes
Theorem 83
through the center of the circle.
If two arcs of a circle (or of congruent circles)
are congruent, then the corresponding chords
Theorem 77 are congruent.
If two chords of a circle are equidistant from the
center, then they are congruent. Theorem 84
If two chords of a circle (or of congruent circles)
Theorem 78 are congruent, then the corresponding arcs are
congruent.
If two chords of a circle are congruent, then
they are equidistant from the center of the
circle. Theorem 85
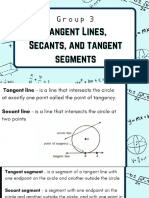
If two tangent segments are drawn to a circle
Theorem 79 from an external point, then those segments
are congruent. (Two-Tangent Theorem)
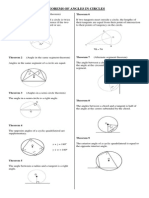
If two central angles of a circle (or of congruent
circles) are congruent, then their intercepted
arcs are congruent. Theorem 86
Theorem 80 The measure of an inscribed angle or a tangent-
If two arcs of a circle (or of congruent circles) chord angle (vertex on a circle) is one-half the
are congruent, then the corresponding central measure of its intercepted arc.
angles are congruent.
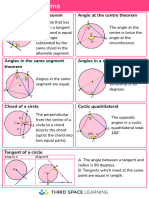
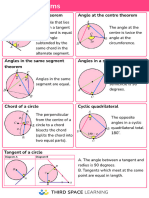
Theorem 87 Theorem 93
The measure of a chord-chord angle is one-half If a quadrilateral is inscribed in a circle, its
the sum of the measures of the arcs intercepted opposite angles are supplementary.
by the chord-chord angle and its vertical angle.
Theorem 94
Theorem 88
If a parallelogram is inscribed a circle, it must be
The measure of a secant-secant angle, a secant- a rectangle.
tangent angle, or a tangent-tangent angle
(vertex outside a circle) is one-half the
difference of the measures of the intercepted Theorem 95
arcs.
If two chords of a circle intersect inside the
circle, then the product of the measures of one
chord is equal to the product of the measures
Theorem 89
of the segments of the other chord. (Chord-
If two inscribed or tangent-chord angles Chord Power Theorem)
intercept the same arc, then they are
congruent.
Theorem 96
If a tangent segment and a secant segment are
Theorem 90
drawn from an external point to a circle, then
If two inscribed or tangent-chord angles the square of the measure of the tangent
intercept congruent arcs, then they are segment is equal to the product of the
congruent. measures of the entire secant segment and its
external part. (Tangent-Secant Power Theorem)
Theorem 97
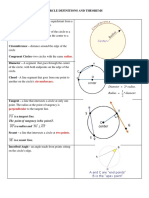
Theorem 91
If two secant segments are drawn from an
An angle inscribed in a semicircle is a right external point to a circle, then the product of
angle. the measures of one secant segment and its
external part is equal to the product of the
measures of the other secant segment and its
Theorem 92 external part. (Secant-Secant Power Theorem)
The sum of the measures of a tangent-tangent Theorem 98
angle and its minor arc is 180.
The length of an arc is equal to the
circumference of its circle times the fractional
part of the circle determined by the arc.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 01e0d1i 0Documento3 pagine01e0d1i 0Niño Enrique ManalastasNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics: Distance From The CenterDocumento7 pagineMathematics: Distance From The CenterSchool PurposeNessuna valutazione finora
- Math10 Q2 W5 6Documento2 pagineMath10 Q2 W5 66 9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Circle TheoremsDocumento2 pagineCircle TheoremsRi-ann VinculadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Theorem ListDocumento10 pagineTheorem ListsNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics 10 ReivewerDocumento7 pagineMathematics 10 Reivewerning ningNessuna valutazione finora
- ChromeDocumento1 paginaChromeJohn DoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics ReviewerDocumento2 pagineMathematics Revieweremerlayn21Nessuna valutazione finora
- Circles TheoryDocumento4 pagineCircles TheoryJamal AliyevNessuna valutazione finora
- 4a MathDocumento1 pagina4a MathRhian Nicole S. JuanitezNessuna valutazione finora
- CircleGeoInv-Jonathan JiangDocumento11 pagineCircleGeoInv-Jonathan JiangJonathan JiangNessuna valutazione finora
- Schoolisfun's Math Level 2 Subject Test Guide and FormulasDocumento40 pagineSchoolisfun's Math Level 2 Subject Test Guide and Formulassudhakaralla1100% (2)
- I. Chords, Arcs, Central Angles, and Inscribed AnglesDocumento7 pagineI. Chords, Arcs, Central Angles, and Inscribed AnglesF RUAMAR, ADRIENNE MAE M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Circle Theorems: Add Up To 180º (Supplementary Angles)Documento1 paginaCircle Theorems: Add Up To 180º (Supplementary Angles)liberto21Nessuna valutazione finora
- Circle Theorems PDFDocumento1 paginaCircle Theorems PDFJoseph MusabukaNessuna valutazione finora
- Circle Theorems PDFDocumento1 paginaCircle Theorems PDFJoseph MusabukaNessuna valutazione finora
- Theorems and Postulates On Math Q2 Q3Documento3 pagineTheorems and Postulates On Math Q2 Q3glaiveashNessuna valutazione finora
- Arithmetic MeansDocumento8 pagineArithmetic MeansMargie Ballesteros ManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tangent Chord Theorem The Measurement of An Angle Formed by A Chord and A Tangent Intersecting at The Point of Tangency Is Half The Measure of The Intercepted Arc. 20231217 184512 0000Documento36 pagineTangent Chord Theorem The Measurement of An Angle Formed by A Chord and A Tangent Intersecting at The Point of Tangency Is Half The Measure of The Intercepted Arc. 20231217 184512 0000Chesther KimNessuna valutazione finora
- The Central Angle-Intercepted Arc Postulate, The Inscribed Angle TheoremDocumento4 pagineThe Central Angle-Intercepted Arc Postulate, The Inscribed Angle TheoremCedrick Nicolas ValeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Circle Theorems PosterDocumento1 paginaCircle Theorems PosterPatrick Chukwunonso A.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Circle Theorems PosterDocumento1 paginaCircle Theorems PosterDare JamesNessuna valutazione finora
- Circle and TheoremsDocumento1 paginaCircle and TheoremsDare JamesNessuna valutazione finora
- Circle Theorems Year 10 DrillingDocumento10 pagineCircle Theorems Year 10 DrillingPugarnes GopalanNessuna valutazione finora
- 19.3 - Symetry Properties of CirclesDocumento3 pagine19.3 - Symetry Properties of CirclesRaffaella LaxaldeNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer For 3RD Quarter Grd10mathDocumento2 pagineReviewer For 3RD Quarter Grd10mathNokrayNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter IIDocumento19 pagineChapter IIMark Jason DuganNessuna valutazione finora
- Math GR10T3 LA2 & AU3 ReviewerDocumento5 pagineMath GR10T3 LA2 & AU3 ReviewerGab AquinoNessuna valutazione finora
- AsdsadaddwsdasdsddwDocumento35 pagineAsdsadaddwsdasdsddwredlegend606Nessuna valutazione finora
- Relationships Among Chords, Arcs, Central AnglesDocumento45 pagineRelationships Among Chords, Arcs, Central Anglesjoshuaomnos9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chords, Arcs, and Central AnglesDocumento37 pagineChords, Arcs, and Central Anglesbb nnNessuna valutazione finora
- Circle Theorems: DR J Frost (Jfrost@tiffin - Kingston.sch - Uk)Documento30 pagineCircle Theorems: DR J Frost (Jfrost@tiffin - Kingston.sch - Uk)Jump SkillNessuna valutazione finora
- CSEC Mathematics - Circle TheoremsDocumento30 pagineCSEC Mathematics - Circle TheoremsCarl Agape DavisNessuna valutazione finora
- 2lessons Circle TheoremsDocumento29 pagine2lessons Circle TheoremsFATMA HINDI / F MOHAMMED HUSSEIN HINDI -Nessuna valutazione finora
- Circile TheoremsDocumento1 paginaCircile Theoremssuryanshkothari14Nessuna valutazione finora
- Glossary Terms: R Is The Radius of The Circle and L Is The Arc LengthDocumento4 pagineGlossary Terms: R Is The Radius of The Circle and L Is The Arc LengthBonbert LascoNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit CircleDocumento29 pagineUnit CircleAnghel ManjaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Circle Geometry Revision Booklet-1Documento33 pagineCircle Geometry Revision Booklet-1lulamangwenya67Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2.6 CIRCLES and Related Segments and AnglesDocumento50 pagine2.6 CIRCLES and Related Segments and AnglesJamill BalajadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Good Afternoon Class!: HELLO, I Am Teacher AnnDocumento36 pagineGood Afternoon Class!: HELLO, I Am Teacher AnnAnn Claudeth MaboloNessuna valutazione finora
- 100 Concepts in MathDocumento7 pagine100 Concepts in MathKierr KawasakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Q2 - WK 4 - Circle and Other Related Terms - TheoremsDocumento28 pagineQ2 - WK 4 - Circle and Other Related Terms - TheoremsJENNALYN RESARENessuna valutazione finora
- Review - Mathematics, Surveying and Transportation EngineeringDocumento11 pagineReview - Mathematics, Surveying and Transportation EngineeringPaulyne TuganoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6.1 - 6.4 Chapter 6.1 Chord Properties: Homework P. 310-311 (1-10, 16)Documento2 pagineChapter 6.1 - 6.4 Chapter 6.1 Chord Properties: Homework P. 310-311 (1-10, 16)Xin Yuan ZhuNessuna valutazione finora
- PreCalc Questions With ObjectivesDocumento2 paginePreCalc Questions With ObjectivesShayla LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Quadratic: ST NDDocumento8 pagineQuadratic: ST NDtheturfkitchenNessuna valutazione finora
- Circle: Tycho Crater, One of Many Examples of Circles That Arise in NatureDocumento14 pagineCircle: Tycho Crater, One of Many Examples of Circles That Arise in NatureZulaika ZulkifliNessuna valutazione finora
- Algebra 12 AnglesDocumento44 pagineAlgebra 12 AnglesTrixie Agustin100% (1)
- Chord C Angle and ArcDocumento46 pagineChord C Angle and ArcAngolluan ErickaNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry Postulates TheoremsDocumento4 pagineGeometry Postulates TheoremsCresencio Genobiagon JrNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled DocumentDocumento3 pagineUntitled DocumentArmono GenioNessuna valutazione finora
- Circle PropertiesDocumento1 paginaCircle PropertiesIrenettaNessuna valutazione finora
- MathanginaDocumento4 pagineMathanginaKittea KitteaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer in MathDocumento2 pagineReviewer in MathJosh Deinille ManarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Circle Definitions and TheoremsDocumento8 pagineCircle Definitions and TheoremsGani Almeron100% (1)
- Definitions and Theorems For Circle GeometryDocumento8 pagineDefinitions and Theorems For Circle GeometryPaula FanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry Cheatsheet: DefinitionsDocumento2 pagineGeometry Cheatsheet: DefinitionskdsaflNessuna valutazione finora
- 2223-2-Mx10-W3-5-Postulates On CirclesDocumento50 pagine2223-2-Mx10-W3-5-Postulates On CirclesSamantha Xillzen MENDOZANessuna valutazione finora
- Aviation Maths Links-06march23Documento2 pagineAviation Maths Links-06march23DIPNessuna valutazione finora
- Spherical CoordinatesDocumento7 pagineSpherical CoordinatesEdvardo PagvaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Shortcuts On Straight Line and ParabolaDocumento10 pagineShortcuts On Straight Line and ParabolaArnab Dutta100% (1)
- Tiruvannamalai District Graph: 10 STD Mathematics-Algebra Ex 3.16Documento14 pagineTiruvannamalai District Graph: 10 STD Mathematics-Algebra Ex 3.16PoomalaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Programare CNCDocumento42 pagineProgramare CNCFrone Cosmin100% (1)
- Parametrized Surfaces: Vector Calculus (MATH-243) Instructor: Dr. Naila AmirDocumento12 pagineParametrized Surfaces: Vector Calculus (MATH-243) Instructor: Dr. Naila AmirRakhmeen GulNessuna valutazione finora
- Sector Areas and Arc Lengths QP Edexcel GcseDocumento8 pagineSector Areas and Arc Lengths QP Edexcel GcseLOVE WITH MATHEMATICSNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide 1.1 - Coordinates and LinesDocumento9 pagineStudy Guide 1.1 - Coordinates and LinesAlaysa Dida-AgunNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 2nd Year TestDocumento2 pagineChapter 3 2nd Year TestDanish KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 (Guided Notes) - Module 3-Inscribed AnglesDocumento10 pagineUnit 4 (Guided Notes) - Module 3-Inscribed AnglesYosief AdaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths ProjectDocumento7 pagineMaths ProjectDevansh BajoriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Spherical CoordinatesDocumento3 pagineSpherical CoordinatesHIẾU NGUYỄN HÀ TRỌNGNessuna valutazione finora
- 024eec5a83031-MOCK TEST (MATHS) - 08 (07.04.2020)Documento8 pagine024eec5a83031-MOCK TEST (MATHS) - 08 (07.04.2020)Aman GoelNessuna valutazione finora
- New Century Maths Year 10 5.2 Teaching ProgramDocumento31 pagineNew Century Maths Year 10 5.2 Teaching ProgramEileenNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 The Midpoint FormulaDocumento5 pagine3 The Midpoint FormulaJohn Ramer Lazarte InocencioNessuna valutazione finora
- Stereographic ProjectionDocumento14 pagineStereographic ProjectionAdrian Salcedo ChiticaNessuna valutazione finora
- Your Company Name: 123 Main Street Suite #321 City, State 01234Documento20 pagineYour Company Name: 123 Main Street Suite #321 City, State 01234ramuNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus TB AnswersDocumento19 pagineCalculus TB AnswersMatthewNessuna valutazione finora
- PST EuclDocumento52 paginePST Euclo0obavuongo0oNessuna valutazione finora
- CEET416 - Reverse CurvesDocumento3 pagineCEET416 - Reverse Curvespipeds100% (7)
- Math14 Lesson 6 CIRCLEDocumento19 pagineMath14 Lesson 6 CIRCLERoy Vinzon Martin Arceo100% (1)
- MA 105 Calculus: Lecture 40: U. K. Anandavardhanan IIT BombayDocumento113 pagineMA 105 Calculus: Lecture 40: U. K. Anandavardhanan IIT Bombaynp_nikhilNessuna valutazione finora
- MATH10-QUARTER2-MODULE3-The Relations Among Chords, Arcs, Central Angles, and Inscribed AnglesDocumento26 pagineMATH10-QUARTER2-MODULE3-The Relations Among Chords, Arcs, Central Angles, and Inscribed AnglesDreyzen GanotisiNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometric Design of Highways 3-Vertical AlignmentDocumento11 pagineGeometric Design of Highways 3-Vertical Alignmentrodge macaraegNessuna valutazione finora
- GeometryDocumento607 pagineGeometryjeffconnors100% (1)
- 23 - Triple Integrals in Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinates SolutionsDocumento2 pagine23 - Triple Integrals in Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinates SolutionsKhoi NNessuna valutazione finora
- Precalculus11 q1 Mod4 Hyperbolas v1Documento38 paginePrecalculus11 q1 Mod4 Hyperbolas v1Daine GamiaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Theorems On Tangent and SecantDocumento37 pagineTheorems On Tangent and SecantxannieNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Derivative AllenDocumento38 pagineApplication of Derivative AllenAditi KharatNessuna valutazione finora
- Summative Test AllDocumento141 pagineSummative Test AllLairepmi EmjaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)Da EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsDa EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersDa EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (6)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Da EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Math Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeDa EverandMath Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeDa EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- Calculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusDa EverandCalculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Interactive Math Notebook Resource Book, Grade 6Da EverandInteractive Math Notebook Resource Book, Grade 6Nessuna valutazione finora
- Geometric Patterns from Patchwork Quilts: And how to draw themDa EverandGeometric Patterns from Patchwork Quilts: And how to draw themValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormDa EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)