Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
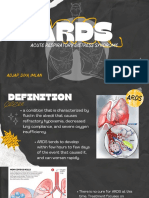
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) Pathophysiology
Caricato da
エド パジャロンTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) Pathophysiology
Caricato da
エド パジャロンCopyright:
Formati disponibili
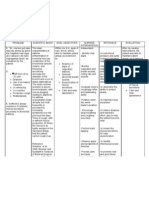
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
Pathophysiology
Modifiable Risk Factors: Non-modifiable Risk
Factors:
Smoking
Obesity Older age
Alcohol abuse
Low protein in the blood
Oxygen use for a pre-existing lung
condition
Recent high-risk surgery
Disease process:
The cause of ARDS is fluid leaked from the
smallest blood vessels in the lungs into the tiny air
sacs where blood is oxygenated. Normally, a
protective membrane keeps this fluid in the
vessels. Severe illness or injury, however, can
cause damage to the membrane, leading to the
fluid leakage of ARDS.
Sign and symptoms: Sign and symptoms:
severe shortness of breath Blood test
Cough Pulse oximetry test
Confusion Chest X-ray
Drowsiness CT scan
Fatigue Echocardiogram
Hypotension
Bluish lips and nails
Fever
Nursing Diagnosis:
Ineffective breathing pattern.
Impaired gas exchange related to increased
alveolar-capillary permeability, interstitial edema
and decreased lung compliance
Activity intolerance
Independent: Dependent:
Collaborative:
Suction via endotracheal Administer analgesics
tube as needed to and/or sedatives as Monitor oxygen
maintain clear airways ordered saturation and ETCO2
levels every 30 to 60
Allow periods of Obtain ABGs as ordered
or indicated; monitor and minutes initially after
uninterrupted rest.
instituting mechanical
Assess skin color, report results
ventilation; report
capillary refill, and the
changes to the physician
presence of edema every
4 hours.
Monitor urine output
hourly; report output of
less than 30 mL per hour.
Assess lung sounds and
chest excursion every 1
to 2 hours.
Complications:
Infections.
(Pneumonia)
Pneumothorax
Lung Scarring
Blood Clots
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- ARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome) : EarlyDocumento1 paginaARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome) : EarlyDora Elena HurtadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - NursingDocumento14 pagineAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - NursingyellowbyunsNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Nursing Management and Interventions - NurseslabsDocumento2 pagineAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Nursing Management and Interventions - NurseslabsSachin SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory EmergenciesDocumento21 pagineRespiratory EmergenciesMohamed Anas SayedNessuna valutazione finora
- EDIT Respiratory Failure Assessment and Problem SolvingDocumento66 pagineEDIT Respiratory Failure Assessment and Problem Solvingmursidstone.mursidNessuna valutazione finora
- ASTHMA DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT GUIDEDocumento4 pagineASTHMA DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT GUIDEeverydayisagift9999Nessuna valutazione finora
- Update in Airway Obstuction DiseaseDocumento42 pagineUpdate in Airway Obstuction DiseaseTiyaTyraSidoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Dyspnea - DR AllenDocumento50 pagineDyspnea - DR AllenalmiraerickaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Bronchial AsthmaDocumento45 pagineBronchial Asthmamuluken mulatieNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocumento29 pagineAcute Respiratory Distress SyndromeRucelyn CampitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocumento29 pagineAcute Respiratory Distress SyndromeRucelyn CampitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Supplementary Material 1b Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocumento7 pagineSupplementary Material 1b Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeJanela Chriselle B. TICARNessuna valutazione finora
- Shortness of Breath: ER Perspective Shaesta TabassumDocumento46 pagineShortness of Breath: ER Perspective Shaesta TabassumAjay DherwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Asthma DX Article 1Documento16 pagineAsthma DX Article 1Pat Caz SarNessuna valutazione finora
- Therapy Basics AsthmaDocumento82 pagineTherapy Basics AsthmaShrestha BhowmickNessuna valutazione finora
- COPD: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease ExplainedDocumento15 pagineCOPD: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease ExplainedMary Grace AgataNessuna valutazione finora
- ARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome)Documento38 pagineARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome)Zahrine HananiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Ards: Guide - DR - Shiv.S.Sharma - Dr.Y. JamraDocumento40 pagineCute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Ards: Guide - DR - Shiv.S.Sharma - Dr.Y. JamraandenaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCM 112 LEC Topic 9 Respiratory Distress Syndrome RDSDocumento4 pagineNCM 112 LEC Topic 9 Respiratory Distress Syndrome RDSViviene Faye FombuenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pneumonias (PNAs) CAP HAP VAPDocumento37 paginePneumonias (PNAs) CAP HAP VAPaniqahmed6565Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Foundations II: Caring for Clients with Oxygenation ProblemsDocumento4 pagineNursing Foundations II: Caring for Clients with Oxygenation ProblemsAlec Xavier MirandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Resource ViewDocumento54 pagineResource ViewHamza AdeelNessuna valutazione finora
- Ards PDFDocumento31 pagineArds PDFJohanisa SultanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Documento16 pagineChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Kimberly Abella CabreraNessuna valutazione finora
- Case 2Documento41 pagineCase 2JUVIELY PREMACIONessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome....Documento55 pagineAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome....sangi vinayagamNessuna valutazione finora
- Block Q IM Orals ReviewerDocumento107 pagineBlock Q IM Orals ReviewerCarl Vin PasionNessuna valutazione finora
- Ajol File Journals - 355 - Articles - 50270 - Submission - Proof - 50270 4237 72298 1 10 20100129Documento4 pagineAjol File Journals - 355 - Articles - 50270 - Submission - Proof - 50270 4237 72298 1 10 20100129Nessy Nicholle SatruionNessuna valutazione finora
- The System: RespiDocumento219 pagineThe System: Respilalaine22dale100% (1)
- ACUTE Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)Documento16 pagineACUTE Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)prayitno mulyaniNessuna valutazione finora
- By S F Hashmi Guided by DR D G Mhaisekar Sir 22TH FEB 2011Documento57 pagineBy S F Hashmi Guided by DR D G Mhaisekar Sir 22TH FEB 2011Fazlullah Hashmi100% (1)
- Chronic Cough EvaluationDocumento43 pagineChronic Cough EvaluationJoshua HendersonNessuna valutazione finora
- DD Nyeri Dada & Sesak NapasDocumento15 pagineDD Nyeri Dada & Sesak Napassafinatun najahNessuna valutazione finora
- Pulmonary ConditionsDocumento42 paginePulmonary ConditionsMinetteNessuna valutazione finora
- Kardiorespirasi 5Documento83 pagineKardiorespirasi 5Naufal MubarakNessuna valutazione finora
- Managing Dyspnea: Understanding Causes and TreatmentsDocumento17 pagineManaging Dyspnea: Understanding Causes and TreatmentsChingHuaNessuna valutazione finora
- This Young Man Has Long History of Productive Cough and Wheezing. He Is Afebrile and Chest Auscultation Reveals Coarse Crackles at Right Lower ChestDocumento57 pagineThis Young Man Has Long History of Productive Cough and Wheezing. He Is Afebrile and Chest Auscultation Reveals Coarse Crackles at Right Lower ChestdrstraoNessuna valutazione finora
- Upper Airway InfectionsDocumento5 pagineUpper Airway InfectionsTreesa LouiseNessuna valutazione finora
- Resp 180214084710Documento72 pagineResp 180214084710Karla Geraldine Carhuas VeliNessuna valutazione finora
- PBL 2nd Sem Scenario 1Documento164 paginePBL 2nd Sem Scenario 1stephaniecaronan15Nessuna valutazione finora
- Asuhan Keperawatan: Karsinoma ParuDocumento42 pagineAsuhan Keperawatan: Karsinoma ParuYohanes DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnostic Tests: Community-Acquired PneumoniaDocumento23 pagineDiagnostic Tests: Community-Acquired PneumoniaJim Christian EllaserNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute RFDocumento7 pagineAcute RFLoren SangalangNessuna valutazione finora
- Askep ARDSDocumento23 pagineAskep ARDSnovitanurkamilahNessuna valutazione finora
- COPD and Lung CancerDocumento42 pagineCOPD and Lung CancerENKELI VALDECANTOSNessuna valutazione finora
- Pulmonary Edema: Topic OutlineDocumento2 paginePulmonary Edema: Topic OutlineKdamnz100% (1)
- Dyspnoea 2Documento1 paginaDyspnoea 2Shubham TarapureNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory Emergencies: Dispnu ?Documento35 pagineRespiratory Emergencies: Dispnu ?Mentari Indah SariNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromDocumento19 pagineAcute Respiratory Distress SyndromTaqdees ManzoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Caring For The Mechanically Ventilated PatientDocumento2 pagineCaring For The Mechanically Ventilated PatientKat AlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer for NCMB312 Skills Lab FINALSDocumento12 pagineReviewer for NCMB312 Skills Lab FINALSchrisver008Nessuna valutazione finora
- Shortness of BreathDocumento17 pagineShortness of BreathChingHuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abc Lec NotesDocumento5 pagineAbc Lec NoteshanhananicasNessuna valutazione finora
- RespiratoryDocumento161 pagineRespiratoryDanity_Anne_Ba_1326100% (1)
- Armando Hasudungan: AuthorsDocumento1 paginaArmando Hasudungan: AuthorsShubham TarapureNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory System DiseasesDocumento31 pagineRespiratory System Diseasesglenn johnstonNessuna valutazione finora
- Pulmonology MCQsDocumento49 paginePulmonology MCQsaliakbar178100% (1)
- Case Discussion - CopdDocumento63 pagineCase Discussion - CopdrajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesDa EverandMedical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesNessuna valutazione finora
- Health and IllnessDocumento16 pagineHealth and Illnessエド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- Low Birth Weight Babies Respiratory DistressDocumento22 pagineLow Birth Weight Babies Respiratory Distressエド パジャロン100% (3)
- Heal The World by Michael JacksonDocumento2 pagineHeal The World by Michael Jacksonエド パジャロン50% (2)
- OlanzapineDocumento2 pagineOlanzapineエド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysio of LaborDocumento2 paginePathophysio of Laborエド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocumento4 pagineBenign Prostatic Hyperplasiaエド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- GN causes blood and protein in urineDocumento14 pagineGN causes blood and protein in urineエド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- A Mixed Hearing Loss Is A Combination of ADocumento3 pagineA Mixed Hearing Loss Is A Combination of Aエド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- Myasthenia GravisDocumento7 pagineMyasthenia Gravisエド パジャロン100% (1)
- Healthcare 06 00063Documento12 pagineHealthcare 06 00063エド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- FDAR Format PDFDocumento1 paginaFDAR Format PDFエド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- Abruptio Placentae (Autosaved)Documento13 pagineAbruptio Placentae (Autosaved)エド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- Sterile Field RationaleDocumento16 pagineSterile Field Rationaleエド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- E. Coli Is The Most Commonly Isolated OrganismDocumento2 pagineE. Coli Is The Most Commonly Isolated Organismエド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- Prioritization and Lists of Identified Nursing DiagnosisDocumento1 paginaPrioritization and Lists of Identified Nursing Diagnosisエド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Cystic FibrosisDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of Cystic Fibrosisエド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- Ears and Nose 2Documento8 pagineEars and Nose 2エド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- B. The Absence of Disease.: C. EmergencyDocumento7 pagineB. The Absence of Disease.: C. Emergencyエド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- Kohlberg's Theory On Moral DevelopmentDocumento16 pagineKohlberg's Theory On Moral Developmentエド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- MNCHNDocumento7 pagineMNCHNエド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP FearDocumento3 pagineNCP Fearエド パジャロン100% (1)
- HygieneDocumento6 pagineHygieneエド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- Hygiene Skin and FootDocumento45 pagineHygiene Skin and Footエド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- Mesopotamian CultureDocumento3 pagineMesopotamian Cultureエド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- Steps in PPEDocumento3 pagineSteps in PPEエド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- Hygiene Skin and FootDocumento45 pagineHygiene Skin and Footエド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Herbal Medicines Approved by DOHDocumento2 pagine10 Herbal Medicines Approved by DOHエド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding the PRECEDE-PROCEED ModelDocumento14 pagineUnderstanding the PRECEDE-PROCEED Modelエド パジャロン100% (1)
- Nursing Informatics at The Pacific Rim: Presented byDocumento28 pagineNursing Informatics at The Pacific Rim: Presented byエド パジャロンNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Management: The Respiratory SystemDocumento80 pagineNursing Care Management: The Respiratory Systemcute_gurljhoanNessuna valutazione finora
- DR. RekhaDocumento3 pagineDR. RekhaHR Medico PlacementsNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk For AspirationDocumento2 pagineRisk For AspirationGly Mtg100% (6)
- Acute Bronchitis Symptoms Causes TreatmentDocumento5 pagineAcute Bronchitis Symptoms Causes TreatmentDianne LegionNessuna valutazione finora
- Croup: Dr. Shveta Sethi Narula A.P. MicrobiologyDocumento14 pagineCroup: Dr. Shveta Sethi Narula A.P. Microbiology12. Akshit AtwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Bronchitis: Presented By:-Himanshi B. B. Sc. (N) 3 Year Gcon (Tehri)Documento29 pagineBronchitis: Presented By:-Himanshi B. B. Sc. (N) 3 Year Gcon (Tehri)HimanshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Respiratory FailureDocumento17 pagineAcute Respiratory FailurejulianajosNessuna valutazione finora
- Diskusi Topik 2 (PPOK) - Nafisa Zulpa Elhapidi - 406202067Documento59 pagineDiskusi Topik 2 (PPOK) - Nafisa Zulpa Elhapidi - 406202067nafisa zulfaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory MCQsDocumento80 pagineRespiratory MCQsteenup9182% (11)
- Lab08 SpirometryDocumento2 pagineLab08 Spirometryulgeny0% (1)
- Lung Volumes & Capacities ExplainedDocumento1 paginaLung Volumes & Capacities ExplainedGeorge ZachariahNessuna valutazione finora
- Neet PG Round 3Documento302 pagineNeet PG Round 3saravananNessuna valutazione finora
- Plethysmograph yDocumento1 paginaPlethysmograph ymilananandNessuna valutazione finora
- BronchiectasisDocumento25 pagineBronchiectasisDewi PermatasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento1 paginaIneffective Airway ClearancejomerdalonaNessuna valutazione finora
- Oxygen Therapy Systems: NCM 107.1 Evangeline B. MananquilDocumento48 pagineOxygen Therapy Systems: NCM 107.1 Evangeline B. Mananquilacademic purposesNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory Failure (Aan) PDFDocumento19 pagineRespiratory Failure (Aan) PDFYudionoNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Cares Provider List - Sept 2016Documento966 pagineCommunity Cares Provider List - Sept 2016ArizonaBennieNessuna valutazione finora
- Aneesha Pal PPT On AsthmaDocumento9 pagineAneesha Pal PPT On AsthmaSuneel Kumar Prajapati78% (9)
- 8649-Article Text-39271-1-10-20210315Documento8 pagine8649-Article Text-39271-1-10-20210315DoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Physiotherapy For Respiratory Conditions.: September 2018Documento9 paginePhysiotherapy For Respiratory Conditions.: September 2018ioabvNessuna valutazione finora
- Astrand CalculterDocumento1 paginaAstrand CalculterHarinder BrarNessuna valutazione finora
- RespirationDocumento10 pagineRespirationADWAIT LALUNessuna valutazione finora
- NIV ProformaDocumento10 pagineNIV ProformaWael N Sh GadallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Texas Children's Center For Telehealth Nursing and Allied Health Professionals Distance Education and CNE/CEU OfferingDocumento35 pagineTexas Children's Center For Telehealth Nursing and Allied Health Professionals Distance Education and CNE/CEU Offeringabdo_hegaze100% (1)
- Asthma Control Test ACT SurveyDocumento3 pagineAsthma Control Test ACT SurveyDian Sidiq WibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chest Tube Drainage of The Pleural SpaceDocumento10 pagineChest Tube Drainage of The Pleural SpaceFernandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Acute Respiratory Failure PDFDocumento7 pagineManagement of Acute Respiratory Failure PDFJulian LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- 2019 (Wright Et Al.) - Physical Therapies in Pediatric Respiratory Disease PDFDocumento20 pagine2019 (Wright Et Al.) - Physical Therapies in Pediatric Respiratory Disease PDFNicolas ParejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Modes of Mechanical Ventilation For The Operating Room BestPracResAnest 2015 PDFDocumento15 pagineModes of Mechanical Ventilation For The Operating Room BestPracResAnest 2015 PDFRicardoNessuna valutazione finora