Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
General Biology Lecture Notes
Caricato da
Lovely Joy Magayon0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
32 visualizzazioni5 pagineIts all about biology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoIts all about biology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
32 visualizzazioni5 pagineGeneral Biology Lecture Notes
Caricato da
Lovely Joy MagayonIts all about biology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 5
GENERAL BIOLOGY LECTURE NOTES RNA (RIBONUCLEIC ACID) - can travel
throughout the cell to where it is
TOPIC: CHEMICAL BASIS OF LIFE
needed.
4 TYPES OF ORGANIC MOLECULES
TOPIC: LIFE PROCESSES
CARBOHYDRATES- organic compounds
ENERGY- ability to do work.
composed of carbon, hydrogen, and
oxygen in a ratio of two hydrogen atoms METABOLISM- process in which different types
to one oxygen atom. of chemical reactions happen inside your body.
LIPIDS (FATS)- group of hydrophobic
CLASSIFICATION OF METABOLISM:
biomolecules, long term energy storage
PROTEINS- organic compounds formed CATABOLISM- energy is released.
mainly of hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, and ANABOLISM- energy is stored.
nitrogen.
REPRODUCTION- process of producing new
NUCLEIC ACID- make proteins that are
present in almost every structure. organism.
2 TYPES OF REPRODUCTION:
3 TYPES OF CARBOHYDRATES
MONOSACCHARIDE- contains carbon, SEXUAL REPRODUCTION- two parent
hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of one to ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION- one parent
two to one; simplest carbohydrate GROWTH- humans are made of millions of cells
DISACCHARIDE- double sugar formed and this has a number of benefits; cells can be
from two monosaccharide linked specialized to do particular tasks; groups of cells
together in a condensation reaction. can function as organs making a more efficient
POLYSACCHARIDE- complex molecule but complex organism.
composed of three or more
monosaccharide linked together in a REPAIR- formation of cells growing.
condensation reaction. COMMUNICATION and RESPONSE- transfer of
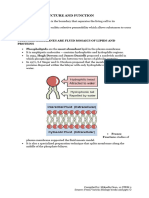
4 BASIC GROUPS OF LIPIDS information from one part of the organism to
another using both chemical and electrical
TRIGLYCERIDES- include fats and oils signals as a response of stimuli.
PHOSPHOLIPID- contains glycerol and 2
TOPIC: CELLS AND THEIR ENVIRONMENT
fatty acids
STEROIDS- 4 fused rings of carbon to PASSIVE TRANSPORT- substances are
which different functional groups are transported across the membrane without any
attached. energy input from the cell.
WAXES- non polar; found in the ears of
animals and protective coating of leaves. DIFFUSION- process by which molecules and ions
can tend to scatter themselves through the
2 TYPES OF NUCLEIC ACID available space.
DNA (DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID)- SIMPLE DIFFUSION- the unassisted diffusion of
typically remains within the center, or solutes to plasma membrane.
nucleus of a cell.
OSMOSIS- diffusion of water to a selectively 2 STEPS IN PHOTOSYNTHESIS:
permeable membrane.
LIGHT- DEPENDENT REACTION- requires
FACILITATED DIFFUSION- provides passage for light; occur in thylakoid.
certain needed substances that are both lipid LIGHT- INDEPENDENT REACTION or
insoluble and too large to pass through the CALVIN CYCLE- occur in stroma; doesn’t
membrane. need light to function.
FILTRATION- process in which water and solutes CHLOROPLASTS- food producers of the cell;
are forced to a membrane (capillary wall) by fluid found in plants; converts sun’s light energy into
or hydrostatic pressure. sugars.
PRESSURE GRADIENT- a gradient that actually STROMA- liquid that sorrounds the thylakoids;
pushes solute containing fluid from a higher fills the interior of the chloroplast.
pressure to the lower pressure area.
THYLAKOID- disk like shape
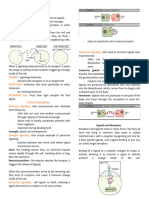
ACTIVE TRANSPORT PROCESS- whenever a cell
uses its ATP supply to move the substances GRANUM/ GRANA- set of thylakoids.
across the membrane. CHLOROPHYLL- green pigment; absorbs the suns
SODIUM POTASSIUM PUMP- simultaneously light energy.
carry sodium ions out of and potassium ions into ATP or ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE- carries
the cell. energy within the cell; main energy currency of
EXOCYTOSIS- moves substances out of the cell. the cell; a high energy molecule within cells that
stores and transports the chemical energy on
ENDOCYTOSIS- moves substances into the cell. organism needs for metabolism.
PHAGOCYTOSIS- cell eating; certain white blood TOPIC: CELLULAR RESPIRATION
cells that act as scavenger cells that protects the
body by ingesting bacteria and other foreign CELLULAR RESPIRATION- is a metabolic process
debris; takes in larger substances (bacteria). involving many different reactions taking place.
PINOCYTOSIS- plasma membrane invaginates to 2 TYPES OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION;
form a tiny pit and then its edges fused around AEROBIC RESPIRATION- process of
the droplet of extracellular fluid containing producing cellular energy involving
dissolve proteins or fats; takes in fluids and oxygen.
solute. ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION- a type of
TOPIC: PHOTOSYNTHESIS respiration using used electron
acceptors other than oxygen molecule;
PHOTOSYNTHESIS- process of making food. does not involve oxygen.
FORMULA OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS: 3 STEPS OF AEROBIC RESPIRATION:
6CO2 + 6H2O + energy (sunlight) GLYCOLYSIS
C6H12O6 + 6O2 KREBS CYCLE
CHEMICAL ENERGY- refers to the energy stored ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN
in the chemical bonds between atoms in
molecules.
2 STEPS OF ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION: original amount of genetic information; a type of
cell division that is seen during the formation of
GLYCOLYSIS
gametes (sex cells).
FERMENTATION
STAGES OF MEIOSIS 1:
TOPIC: AUTOTROPHS AND HETEROTROPHS
PROPHASE 1- the homologous pairs of
AUTOTROPHS- can manufacture their own
chromosomes come to lie next to one
foods; producer
another, each chromosomes consist of
HETEROTROPHS- cannot manufacture their own two chromatids attached by a
food; consumer centromere.
METAPHASE 1- the spindle fibers
2 TYPES OF AUTOTROPHS: arranged the homologous chromosome
PHOTOAUTOTROPHS- are organisms pairs in the middle of the cell.
who get the energy to make organic ANAPHASE 1- the spindle fiber separate
materials from sunlight; all plants, green the homologous pairs and pull them to
algae, and bacteria. opposite poles of the cell.
CHEMOAUTOTROPHS- are organisms TELOPHASE 1- the chromosome gather
that obtain energy from inorganic into nuclei, and the original cell divides;
chemical processes. then cytokinesis takes place resulting in
two haploid cells. Each chromosomes in
2 TYPES OF HETEROTROPHS: the haploid cells consist of two sister
CONSUMERS chromatids; daughter cells are not
identical.
DECOMPOSERS
STAGES OF MEIOSIS 2:
TYPES OF CONSUMERS:
PROPHASE 2- spindle fibers form again,
HERBIVORES- are animals that eat
and chromosomes condense once
plants.
more.
CARNIVORES- is an animal that gets food
METAPHASE 2- spindle fibers align
from killing and eating other animals.
chromosomes along the center of the
OMNIVORES- an animal or person that
cell.
eats food of both plants and animals.
ANAPHASE 2- sister chromatids are
TYPES OF DECOMPOSERS: separated and pulled to opposite poles
of the cell.
DETRITIVORES- an organism that feeds
TELOPHASE 2- new nuclei are formed;
on and breaks down dead plants or
then cytokinesis follows resulting into
animal matter.
four haploid cells.
SAPROPHYTES- a plant, fungus, or
microorganism that lives on dead or TOPIC: PRINCIPLES OF INHERITANCE
decaying organic matter.
GREGOR MENDEL- Father of Modern Genetics
TOPIC: MEIOSIS
MENDELS LAW OF HEREDITY:
MEIOSIS- process where a single cell divides
LAW OF SEGREGATION- Each inherited
twice to produce four cells containing half the
trait is defined by a gene pair. Parental
genes are randomly separated to the sex INHERITANCE- caused by a combination
cells so that sex cells contain only one of environmental factors and mutations
gene of the pair. Offspring therefore in multiple genes.
inherit one genetic allele from each CHROMOSOME ABNORMALITIES-
parent when sex cells unite in typically occur due to a problem with cell
fertilization. division; caused by an excess or
LAW OF INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT- deficiency of the genes that are located
Genes for different traits are sorted in the chromosomes or by structural
separately from one another so that the changes within chromosomes.
inheritance of one trait is not dependent MITOCHONDRIAL GENETIC
on the inheritance of another. INHERITANCE- caused by mutations in
LAW OF DOMINANCE- An organism with the non- nuclear DNA of mitochondria.
alternate forms of a gene will express
MONOGENETIC INHERITANCE examples:
the form that is dominant.
CYSTIC FIBROSIS- affects mostly the
MONOHYBRID CROSS- is a breeding experiment
lungs, but also the pancreas, liver,
between P generation (parental generation)
kidneys and intestines.
organisms that differ in a single trait.
SICKLE CELL ANEMIA- abnormality in the
DIHYBRID CROSS- is a breeding experiment oxygen- carrying protein haemoglobin
between P generation (parental generation) found in red blood cells.
organisms that differ in two traits. HUNTINGTON’S DISEASE- death of brain
cells.
TEST CROSS- are used to test an individual’s
genotype by crossing it with an individual of a MULTIFACTORIAL GENETIC INHERITANCE
known genotype. example:
PUNNETT SQUARE- is a square diagram that is HEART DISEASE
used to predict the genotypes of a particular HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE
cross or breeding experiment. OBESITY
GENETIC TRAITS- are characteristics that are CHROMOSOME ABNORMALITIES example:
enclosed in DNA.
DOWN SYNDROME- occurs when a
GENETIC DISORDER- is a diseased caused in person has three copies of chromosome
whole or in part by a change in the DNA 21.
sequence away from a normal sequence; caused TURNER SYNDROME- short and webbed
by an abnormality in an individual’s genome. neck, low-set ears, low hair line at the
TYPES OF GENETIC INHERITANCE: back of the neck, short stature and
swollen hands and feet seen at birth.
SINGLE GENE GENETIC INHERITANCE or KLINEFELTER SYNDROME- sterility and
MONOGENETIC INHERITANCE- caused small testicles.
by changes or mutations that occur in
the DNA sequence of a single gene;
disorders of a single gene.
MULTIFACTORIAL GENETIC
INHERITANCE or POLYGENIC
MITOCHONDRIAL GENETIC INHERITANCE ALLELES- an alternative form of a gene
example: that occurs at the same locus on
homologous chromosomes.
LEBER’S HEREDITARY OPTIC ATROPHY
DOMINANT ALLELE- an allele that is
(eye disease)
always expressed when present,
CHANGES IN CHROMOSOMES: regardless of whether the organism is
homozygous or heterozygous for that
DELETION- a mutation in which a part of gene.
a chromosome or a sequence of DNA is
RECESSIVE ALLELE- genes are recessive if
lost during DNA replication. the phenotype that they code for is only
DUPLICATION- it refers to the expressed when the genes are
occurrence of a segment twice in the homozygous.
same chromosome. It results in addition
PARENT GENERATION- generation that
of one or more genes to a chromosome.
supplies gametes to the filial generation.
TRANSLOCATION- caused by
FILIAL GENERATION- generation that
rearrangement of parts between non-
receives gametes from the parental
homologous chromosomes. generation.
INVERSION- a chromosome
HYBRID- an offspring resulting from the
rearrangement in which a segment of a
mating between individuals of two
chromosome is reversed end to end.
different genetic constitutions.
GENETIC TERMINOLOGIES:
HAPLOID- condition of having only one
set of chromosomes per cell.
DIPLOID- condition of having two sets of
chromosomes per cell.
CHROMOSOMES- structures within the
nucleus of eukaryotic cells composed of
chromatin and visible at cell division.
HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES-
chromosome that are similar in
morphology (shape and form) and
genetic constitution.
RECOMBINATION- exchange of genetic
material between chromosomes.
GENOTYPE- the genetic make- up of an
individual.
PHENOTYPE- the physical or chemical
expression of an organism’s gene.
GENE- a discrete unit of hereditary
information that usually specifies a
protein.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Biology Principles Review11-20-14Documento19 pagineBiology Principles Review11-20-14Afidah CamarNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Principles ReviewDocumento18 pagineBiology Principles ReviewCharles GuillermoNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Principles Review11!20!14!1!11Documento18 pagineBiology Principles Review11!20!14!1!11shashaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Quiz Bee Reviewer - High School LevelDocumento6 pagineScience Quiz Bee Reviewer - High School LevelFamella GalmakNessuna valutazione finora
- Cholesterol Proteins Glycocalyx/carbohydrates: Phospholipid BilayerDocumento11 pagineCholesterol Proteins Glycocalyx/carbohydrates: Phospholipid BilayerGreenard Imperial GualbertoNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology NotesDocumento5 pagineBiology NotesFaith SNNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell EnergyDocumento29 pagineCell EnergyKimberly Anne T. RinNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochem IntroDocumento6 pagineBiochem IntroAlliah CasingNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Reviewer (1) - CompressedDocumento61 pagineBiology Reviewer (1) - CompressedkevinNessuna valutazione finora
- ELS HardDocumento3 pagineELS HardmppsregistrarNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 2nd GradingDocumento27 pagineBiology 2nd GradingMara MayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry - Reviewer (Carbohydrates)Documento8 pagineBiochemistry - Reviewer (Carbohydrates)hi hoNessuna valutazione finora
- Condensed Biology Georgia Eoct Study GuideDocumento13 pagineCondensed Biology Georgia Eoct Study GuideTiffany Gallina100% (1)
- Doing Bio Study NotesDocumento12 pagineDoing Bio Study Notesmenondhanvin108Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Long NoteDocumento12 pagineBio Long Notejacob guerreroNessuna valutazione finora
- NS EMBRYOLOGY - LECTURE (BS PSYCHOLOGY 4A) Activity 2Documento6 pagineNS EMBRYOLOGY - LECTURE (BS PSYCHOLOGY 4A) Activity 2sugarxglossNessuna valutazione finora
- Gened. Science and TechnologyDocumento11 pagineGened. Science and TechnologyRachael De Guzman RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideDa EverandBiology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (2)
- REVIEWER-Gen Bio-Q4Documento8 pagineREVIEWER-Gen Bio-Q4Pauline Jean Cueto BundaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio ReviewerDocumento16 pagineBio ReviewerQueenie SyNessuna valutazione finora
- General Biology NotesDocumento2 pagineGeneral Biology NotesjeayNessuna valutazione finora
- NCHEM Lecture Notes:: BiochemistryDocumento8 pagineNCHEM Lecture Notes:: BiochemistryJoymae Olivares TamayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Macromolecules - Are Large Molecules Composed of Thousands of Covalently Connected AtomsDocumento6 pagineMacromolecules - Are Large Molecules Composed of Thousands of Covalently Connected AtomsBon Joey BernestoNessuna valutazione finora
- MITOCHONDRIONDocumento6 pagineMITOCHONDRIONCheradee AnimNessuna valutazione finora
- Quarternary AssessmentDocumento9 pagineQuarternary AssessmentSebastian Luise BillonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Group G: Lysosome and MitochondriaDocumento2 pagineGroup G: Lysosome and MitochondriaFaith Perl NiloNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Cells Microscopy 1Documento14 pagineBiology Cells Microscopy 1Andrea Trish NicolasNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Components of The Cell MembraneDocumento2 pagineStructural Components of The Cell MembraneYumiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Mol Finals ReviewerDocumento11 pagineCell Mol Finals Reviewerswifthomeworks100Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bot 1Documento16 pagineBot 1Lawrence SarmientoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson1 2Documento4 pagineLesson1 2Cheradee AnimNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Ib Topic 1 SummaryDocumento10 pagineBiology Ib Topic 1 SummaryMagdalena CzajaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecturer: Yuyun Wirasasmita, M.Farm., Apt at Stikes Ist ButonDocumento13 pagineLecturer: Yuyun Wirasasmita, M.Farm., Apt at Stikes Ist Butonsifa al rishalNessuna valutazione finora
- BioNOTES Midterm Study GuideDocumento14 pagineBioNOTES Midterm Study Guidebro jo lolNessuna valutazione finora
- Botany ReviewerDocumento10 pagineBotany ReviewerJARISSA DIZON GALLAZANessuna valutazione finora
- Energy TransformationDocumento14 pagineEnergy TransformationJoaquine ArateaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Introduction Chapter One NotesDocumento15 pagineBiology Introduction Chapter One NotesemmelineNessuna valutazione finora
- Biological Molecules/Biomolecules: O CarbohydrateDocumento6 pagineBiological Molecules/Biomolecules: O CarbohydrateRamona BaculinaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Study Guide (Wheaton) Complete)Documento7 pagineBiology Study Guide (Wheaton) Complete)Jireh HuangNessuna valutazione finora
- BAB 2 Principle of Cellular LifeDocumento49 pagineBAB 2 Principle of Cellular LifeMuhammad Dalili Al FarisNessuna valutazione finora
- Cells, Tissues, Glands and Membranes HODocumento116 pagineCells, Tissues, Glands and Membranes HOᜀᜎ᜔ᜎᜒᜈ᜔ ᜃᜓᜇᜒᜀᜋᜆ᜔Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physiology02 Cell PhysiologyDocumento63 paginePhysiology02 Cell PhysiologysmpoojasubashNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Revision 2017Documento62 pagineBiology Revision 2017Katherine O'Neill-RobinsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept of Cell Structures and FunctionsDocumento3 pagineConcept of Cell Structures and FunctionsTyron ChuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Prelecture Questions 2Documento7 paginePrelecture Questions 2kaslana kianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochem FinalsDocumento5 pagineBiochem Finalsjnssmylpz16Nessuna valutazione finora
- Review Notes2Documento31 pagineReview Notes2Diether Añonuevo DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Anatomy and Physiology: Topic: The CellsDocumento121 pagineHuman Anatomy and Physiology: Topic: The CellsJoan Ano CaneteNessuna valutazione finora
- Transes Chap 1 MicrobioDocumento4 pagineTranses Chap 1 MicrobioFReyes KarylleNessuna valutazione finora
- CellDocumento4 pagineCellshiela marieNessuna valutazione finora
- !!!cell Biology SciOly Notes 1pager RegionalDocumento3 pagine!!!cell Biology SciOly Notes 1pager RegionalJes He100% (1)
- No Test Problem From - Bring Pencil WednesdayDocumento7 pagineNo Test Problem From - Bring Pencil WednesdayTene JohnsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochem LectureDocumento100 pagineBiochem Lectureana.tacbadNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Anatomy and Physiology AnswersDocumento80 pagineHuman Anatomy and Physiology Answersdocabol100% (1)
- Biology MCAS Standards For Cell MaterialDocumento9 pagineBiology MCAS Standards For Cell MaterialRachel FrankenfieldNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture No. 1 Instructor Dr. Saima Hanif Course Biochemistry-IDocumento36 pagineLecture No. 1 Instructor Dr. Saima Hanif Course Biochemistry-Ikhadija tariqNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 2 - Introduction To BiochemistryDocumento34 pagineWeek 2 - Introduction To BiochemistryPaula LouiseNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio EnergeticsDocumento36 pagineBio EnergeticsKimberly Jean EstoqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio ReviewerDocumento4 pagineBio ReviewerElla ReeveNessuna valutazione finora
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDa EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Chloroplast IsolationDocumento6 pagineChloroplast IsolationWilson GomargaNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis Quiz MR ADocumento4 paginePhotosynthesis Quiz MR Aapi-353447897100% (1)
- 2nd Grading Earth and Life Science 2016-2017Documento3 pagine2nd Grading Earth and Life Science 2016-2017Mariel VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell MCQ Collection Biology Grade XiDocumento22 pagineCell MCQ Collection Biology Grade XiRam P. SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology HSC Answers ARC 2006Documento31 pagineBiology HSC Answers ARC 2006timeflies23Nessuna valutazione finora
- Screenshot 2022-11-27 at 10.26.50 AMDocumento21 pagineScreenshot 2022-11-27 at 10.26.50 AMburrinithin97Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1st Quarter ExamDocumento3 pagine1st Quarter ExamMARY ROSE D. BORINAGANessuna valutazione finora
- 15 PhotosynthesisDocumento10 pagine15 PhotosynthesisEarl Adam LambacoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 6th Ed Booksmedicos - Org (1) (0730-0800)Documento71 pagineLehninger Principles of Biochemistry 6th Ed Booksmedicos - Org (1) (0730-0800)Ricky HerreraNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Organelles - Structure and Functions of Cell OrganellesDocumento18 pagineCell Organelles - Structure and Functions of Cell OrganellesUnza WaqarNessuna valutazione finora
- Toaz - Info Notes Biology A Level PRDocumento30 pagineToaz - Info Notes Biology A Level PRThoon Nadi NaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mindmap - Cell Structure - AS LevelDocumento1 paginaMindmap - Cell Structure - AS LevelDr Selvakumari100% (2)
- What Are Cell OrganellesDocumento19 pagineWhat Are Cell OrganellesMaraon CharitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Energy 2013 NotesDocumento90 pagineCell Energy 2013 Notesapi-26963416Nessuna valutazione finora
- The First Comparative Examination 2021-22: Class X (ICSE) Biology SCIENCE Paper - 3 Time: Two Hours Maximum Marks: 80Documento7 pagineThe First Comparative Examination 2021-22: Class X (ICSE) Biology SCIENCE Paper - 3 Time: Two Hours Maximum Marks: 80Sarthac JainNessuna valutazione finora
- A LEVEL Crop Science Mcqs 6049-1Documento90 pagineA LEVEL Crop Science Mcqs 6049-1tapiwa nzvatu100% (3)
- Biology Essay 1 - How Energy Is Transferred Within and Between OrganismsDocumento3 pagineBiology Essay 1 - How Energy Is Transferred Within and Between OrganismsEva Dewsbury100% (3)
- As Level Chapter 1 Cell StructureDocumento52 pagineAs Level Chapter 1 Cell StructureNajma Previa Jati100% (1)
- Photosynthesis Interactive NotebookDocumento26 paginePhotosynthesis Interactive NotebookAshley Farnham67% (3)
- AP Biology Study Guide PDFDocumento80 pagineAP Biology Study Guide PDFnax nittleman100% (3)
- Chapter 10. Photosynthesis AnswersDocumento3 pagineChapter 10. Photosynthesis Answerskarlitarmz100% (2)
- Organic CompondsDocumento55 pagineOrganic CompondsHappy Monamaladi Sibahle MoepyaNessuna valutazione finora
- (WWW - Jeeneetadda.in) NT - 13Documento17 pagine(WWW - Jeeneetadda.in) NT - 13Nanjundeswaran shanmugasundaramNessuna valutazione finora
- Jan 2004 U1Documento4 pagineJan 2004 U1api-3726022Nessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Cell Presentation PawitchayaDocumento23 paginePlant Cell Presentation PawitchayaPawitchayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell: The Unit of Life: SolutionsDocumento12 pagineCell: The Unit of Life: SolutionsIhtisham Ul HaqNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of ChlorophyllDocumento94 pagineStructure of ChlorophyllSunil Kumar SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Growth Processes: Transpiration, Photosynthesis, and RespirationDocumento12 paginePlant Growth Processes: Transpiration, Photosynthesis, and RespirationAbhilash ShawNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 8 - Revision NotesDocumento10 pagineClass 11 Biology Chapter 8 - Revision NotesHARKIRIT KAUR100% (1)
- Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocumento16 paginePhotosynthesis in Higher PlantsMohammed ArifuddinNessuna valutazione finora