Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Oxygen Usually Has A Name Ending in - Ate. (E.g. Copper (II) Sulfate: Contains Oxygen
Caricato da
amandaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Oxygen Usually Has A Name Ending in - Ate. (E.g. Copper (II) Sulfate: Contains Oxygen
Caricato da
amandaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Compounds
-- Very different properties from the elements that form it
-- Pure substance that contains two or more elements chemically combined in a fixed
ratio.
For example, water (H2O) is a compound made only by joining together two atoms of
hydrogen to one atom of oxygen. Hence, the ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms
in water is always 2:1.
-- Fixed composition by mass.
-- The smallest particle of a compound that can exist independently is a molecule.
Clarification: Common Error
Correct: Compounds are not the only ones that exist as molecules. Even elements exist
as molecules too. For example, hydrogen and oxygen exist as H2 and O2 molecules
respectively.
Textbook, pg 33: Hydrogen reacts with iodine to form the compound, hydrogen iodide. If
the reaction is not yet completed, it would contain three types of particles: hydrogen
iodide, hydrogen and iodine.
Naming Compounds
1. A compound made up of two elements has a name that ends in –ide. (Exceptions
for compounds ending in –ide with more that two elements.)
2. A compound that contains hydroxide ions is named a hydroxide. (E.g. potassium
hydroxide)
3. A compound that contains a negatively charged polyatomic ion containing
oxygen usually has a name ending in –ate. (E.g. Copper (II) sulfate: contains oxygen
atoms in the sulfate ion. Exceptions)
Decomposition of Compounds:
-- Heat can be used to form compounds. Similarly, heat can also be used to break
down compounds into elements or simpler compounds. Such a chemical reaction is
called thermal decomposition. Besides using heat, compounds can also be broken
down into simpler substances by using electricity.
Mixtures
-- Formed when two or more substances are added together without chemical bonds
being formed.
-- The components of a mixture are not fixed. They can present in any ratio. Each
component retains its chemical and physical properties.
A mixture can be made up of:
Two elements
Two compounds
One element and one compound.
A mixture of A mixture of A mixture of one
two elements two compounds element and one compound
It can also be a:
Solution (Looks the same throughout, unlike oil and water: Consists of solute
[substance dissolved] and solvent [substance that dissolves the solute] E.g. salt
and water: water is the solvent and salt is the solute)
Suspension (Consists of a solid and a liquid, where the solid cannot fully
dissolve or cannot dissolve at all in the liquid e.g. soil and water)
Emulsion (Consists of two immiscible liquids (Cannot mix with each other,
as they are not soluble in each other e.g. oil and water)
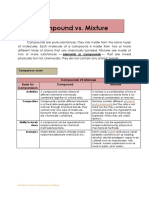
Difference between mixture and compound (SPEC)
Mixture Compound
Separation The components of a mixture The elements in a compound can
can be separated into its only be separated by chemical
constituents that make up the reactions or by using electricity.
mixture by physical methods, (Cannot be split into constituent
such as filtration, distillation or
elements by physical methods of
chromatography separation)
Properties The chemical properties of a The physical and chemical
mixture are the same as those of properties of a compound are
its components. different from those of the
elements in the compound.
Energy No chemical reaction takes place A chemical reaction takes place
Change when a mixture is formed – when a compound is formed –
usually there is little or no usually there is an energy
energy change. change, e.g. the reactants get
hot.
Composition The components of a mixture The elements in a compound are
can be mixed in any always combined in a fixed
proportion. proportion.
Melting & Vary according to the Fixed melting and boiling
Boiling composition. Melt and boil points.
Points over a range of temperatures.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Combining Chemicals - Fun Chemistry Book for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksDa EverandCombining Chemicals - Fun Chemistry Book for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksNessuna valutazione finora
- Sophisticated ChemistryDocumento9 pagineSophisticated ChemistryKingsleyNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Ib Chemistry (SL+HL) - S1.1 Introduction To The Particulate Nature of MatterDocumento58 pagine01 Ib Chemistry (SL+HL) - S1.1 Introduction To The Particulate Nature of MatterricardochavezrNessuna valutazione finora
- GED Chemistry Note2 (Compounds and Solutions)Documento4 pagineGED Chemistry Note2 (Compounds and Solutions)Shahadat Hussain Parvez100% (1)
- CLASSIFICATION - OF - MATTER-week 2-pptshwDocumento31 pagineCLASSIFICATION - OF - MATTER-week 2-pptshwAlyssa Crizel CalotesNessuna valutazione finora
- Elements, Compounds and MixturesDocumento9 pagineElements, Compounds and MixturesOmkar DeshpandeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-2 - Matter-and-EnergyDocumento26 pagineChapter-2 - Matter-and-EnergyJam BermejoNessuna valutazione finora
- Compounds Are Pure Substances in BahasaDocumento2 pagineCompounds Are Pure Substances in BahasaAde Butet RoetadyNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes On Elements Compounds MixturesDocumento6 pagineNotes On Elements Compounds Mixturesvihaan.kharbandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pure SubstanceDocumento3 paginePure Substanceaubrey caresusaNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 1 Stoichiometric RelationshipsDocumento49 pagineTopic 1 Stoichiometric RelationshipsMohammad Andrew GhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 The Components of MatterDocumento33 pagine1.1 The Components of MatterwisyahazmanNessuna valutazione finora
- HTTPSBMC - unideb.hupublicdocuments2022!09!132BMCI Lecture Week2 Compounds Mixtures PDFDocumento82 pagineHTTPSBMC - unideb.hupublicdocuments2022!09!132BMCI Lecture Week2 Compounds Mixtures PDFayoubNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Reviewer A. Phase Change in MatterDocumento6 pagineScience Reviewer A. Phase Change in MatterNicole VictorinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 - Elements, Compounds and MixturesDocumento2 pagineChapter 4 - Elements, Compounds and MixturesMahad AsimNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Classifying MatterDocumento14 pagineChapter 2 Classifying Matteranneth renteriaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 Intro To MatterDocumento33 pagine1.1 Intro To MatterHoang Dung LAMNessuna valutazione finora
- General Chemistry 1 - Week 1: Mr. Daryl Vince D. Romerosa - SST1Documento41 pagineGeneral Chemistry 1 - Week 1: Mr. Daryl Vince D. Romerosa - SST1Abcd Reyes100% (1)
- Tutorial 2 (Eng Science)Documento1 paginaTutorial 2 (Eng Science)Azaa anuarNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of The 5 Branches of ChemistryDocumento18 pagineOverview of The 5 Branches of ChemistryMohammad khalidNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 Basic Concepts in ScienceDocumento51 pagineModule 3 Basic Concepts in Sciencehs4fptm82gNessuna valutazione finora
- 2,.pure Substance. Mixtures. Solutions-1Documento18 pagine2,.pure Substance. Mixtures. Solutions-1mohit s sNessuna valutazione finora
- Elements Compounds MixturesDocumento18 pagineElements Compounds MixturesDONABEL ESPANONessuna valutazione finora
- Substances: Copper CoinDocumento4 pagineSubstances: Copper CoinDane BosevNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEM1003 Lecture 1 & 2Documento5 pagineCHEM1003 Lecture 1 & 2Eli FalzunNessuna valutazione finora
- Is Matter Around Us PureDocumento11 pagineIs Matter Around Us Purelohitha chary100% (1)
- Compound and MixtureDocumento14 pagineCompound and MixtureJUNAID KHANNessuna valutazione finora
- The Two Classification of MatterDocumento3 pagineThe Two Classification of MatterDenise CalzadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ros Unit 2 Matter and EnergyDocumento18 pagineRos Unit 2 Matter and EnergyNina GanapaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Aim1 T What Is MatterDocumento1 paginaAim1 T What Is Matterapi-299809358Nessuna valutazione finora
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocumento45 pagineMatter and Its PropertiesLu NaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry PDFDocumento74 pagineChemistry PDFVed JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Stoichiometric Relationships Chapter 1Documento9 pagineStoichiometric Relationships Chapter 1api-392847673Nessuna valutazione finora
- Element Compound Mixtures NotesDocumento18 pagineElement Compound Mixtures NotesSumit ParicharakNessuna valutazione finora
- Pure Substance, Mixtures, SolutionsDocumento15 paginePure Substance, Mixtures, Solutionsclocke80% (5)
- Chapter 2.7Documento1 paginaChapter 2.7Mohamed AmrNessuna valutazione finora
- MATTERDocumento3 pagineMATTERkatherine regioNessuna valutazione finora
- Ust Shape ReviewerDocumento28 pagineUst Shape ReviewerkNessuna valutazione finora
- Elements Compounds MixturesDocumento33 pagineElements Compounds MixturesKunwar DaniyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Atoms and Bohr Model of AtomsDocumento31 pagineAtoms and Bohr Model of Atomsogedengbed28Nessuna valutazione finora
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocumento32 pagineMatter and Its Propertiesahmad batataNessuna valutazione finora
- Elements, Compounds & Mixtures (Notes)Documento1 paginaElements, Compounds & Mixtures (Notes)mohammed mahdyNessuna valutazione finora
- Olevel ChemistryDocumento2 pagineOlevel ChemistryMuhammad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes of Is Matter Around Us Pure - Class 9Documento13 pagineNotes of Is Matter Around Us Pure - Class 9Atharva VarshneyNessuna valutazione finora
- General Chemistry Reviewer-ZaraDocumento7 pagineGeneral Chemistry Reviewer-ZaraMara LaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Substance A Substance Is Matter Which Has A Specific Composition and Specific PropertiesDocumento8 pagineSubstance A Substance Is Matter Which Has A Specific Composition and Specific Propertiesaishajutt041Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Matter in Our SurroundingsDocumento15 pagineChapter 2 Matter in Our SurroundingsShivani YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Faculty of Science and TechnologyDocumento4 pagineFaculty of Science and TechnologyMARLY DAYANARA CASADO CABRALNessuna valutazione finora
- Qca 1bDocumento48 pagineQca 1bAlfredo Salamanca :Nessuna valutazione finora
- General ChemistryDocumento10 pagineGeneral Chemistryhehe xdNessuna valutazione finora
- General Chemistry 1Documento56 pagineGeneral Chemistry 1Liezel Brillantes100% (1)
- Classification of MatterDocumento41 pagineClassification of MatterRicardo Jr. Uy100% (1)
- Chemistry IGCSE Rev PackDocumento39 pagineChemistry IGCSE Rev Packرهام کاظمیNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEM (No Formula)Documento4 pagineCHEM (No Formula)palacioaya28Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pure Substances and Impure MaterialsDocumento2 paginePure Substances and Impure MaterialsEnock SemweziNessuna valutazione finora
- Self-Instructed Module in Science 6Documento21 pagineSelf-Instructed Module in Science 6NikkiBoy Reyes BernabeNessuna valutazione finora
- Classifications of MatterDocumento3 pagineClassifications of MatterLOSOCON, MARYJOY C.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Lesson 1Documento8 pagineChemistry Lesson 1Vinod Varadan SNessuna valutazione finora
- Brgy. Alang-Alang, Capitol Site, Borongan City 6800: Division of Eastern SamarDocumento4 pagineBrgy. Alang-Alang, Capitol Site, Borongan City 6800: Division of Eastern SamarRaquelNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Basic ChemistryDocumento25 pagineChapter 2 Basic ChemistryBAYA, ZSEANNEL RAIVEN V.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrozirconation - Final 0Documento11 pagineHydrozirconation - Final 0David Tritono Di BallastrossNessuna valutazione finora
- Rosemarie ManlapazDocumento3 pagineRosemarie ManlapazRonald ManlapazNessuna valutazione finora
- Simplified Cost Accounting Part Ii: Solutions ManualDocumento58 pagineSimplified Cost Accounting Part Ii: Solutions ManualAnthony Koko CarlobosNessuna valutazione finora
- Edward William Lane's Lexicon - Volume 7 - Page 186 To 277Documento92 pagineEdward William Lane's Lexicon - Volume 7 - Page 186 To 277Serge BièvreNessuna valutazione finora
- IOSH Managing Safely Leaflet For Training ProvidersDocumento6 pagineIOSH Managing Safely Leaflet For Training ProvidersShakil Ahmad AligNessuna valutazione finora
- MGMT 400-Strategic Business Management-Adnan ZahidDocumento5 pagineMGMT 400-Strategic Business Management-Adnan ZahidWaleed AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Consolidated PCU Labor Law Review 1st Batch Atty Jeff SantosDocumento36 pagineConsolidated PCU Labor Law Review 1st Batch Atty Jeff SantosJannah Mae de OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Surgical Nursing Nclex Questions 5Documento18 pagineMedical Surgical Nursing Nclex Questions 5dee_day_8Nessuna valutazione finora
- SWOT ANALYSIS - TitleDocumento9 pagineSWOT ANALYSIS - TitleAlexis John Altona BetitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Extraction of Non-Timber Forest Products in The PDFDocumento18 pagineExtraction of Non-Timber Forest Products in The PDFRohit Kumar YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Bahasa Inggris XIIDocumento1 paginaBahasa Inggris XIIclaudiaomega.pNessuna valutazione finora
- BurnsDocumento80 pagineBurnsAlina IlovanNessuna valutazione finora
- Exposicion Verbos y AdverbiosDocumento37 pagineExposicion Verbos y AdverbiosmonicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Recall and SkepticismDocumento4 pagineTotal Recall and Skepticismdweiss99Nessuna valutazione finora
- Project Report On Amazon vs. FlipkartDocumento86 pagineProject Report On Amazon vs. FlipkartDimple100% (3)
- Early Pregnancy and Its Effect On The Mental Health of Students in Victoria Laguna"Documento14 pagineEarly Pregnancy and Its Effect On The Mental Health of Students in Victoria Laguna"Gina HerraduraNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz 3 Indigenous People in The PhilippinesDocumento6 pagineQuiz 3 Indigenous People in The PhilippinesMa Mae NagaNessuna valutazione finora
- 20 Great American Short Stories: Favorite Short Story Collections The Short Story LibraryDocumento10 pagine20 Great American Short Stories: Favorite Short Story Collections The Short Story Librarywileyh100% (1)
- Paper 2Documento8 paginePaper 2Antony BrownNessuna valutazione finora
- (Applied Logic Series 15) Didier Dubois, Henri Prade, Erich Peter Klement (Auth.), Didier Dubois, Henri Prade, Erich Peter Klement (Eds.) - Fuzzy Sets, Logics and Reasoning About Knowledge-Springer NeDocumento420 pagine(Applied Logic Series 15) Didier Dubois, Henri Prade, Erich Peter Klement (Auth.), Didier Dubois, Henri Prade, Erich Peter Klement (Eds.) - Fuzzy Sets, Logics and Reasoning About Knowledge-Springer NeAdrian HagiuNessuna valutazione finora
- NAT FOR GRADE 12 (MOCK TEST) Language and CommunicationDocumento6 pagineNAT FOR GRADE 12 (MOCK TEST) Language and CommunicationMonica CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- Autobiography of A 2nd Generation Filipino-AmericanDocumento4 pagineAutobiography of A 2nd Generation Filipino-AmericanAio Min100% (1)
- Cloze Tests 2Documento8 pagineCloze Tests 2Tatjana StijepovicNessuna valutazione finora
- Music Education (Kodaly Method)Documento4 pagineMusic Education (Kodaly Method)Nadine van Dyk100% (2)
- The Impact of Video Gaming To The Academic Performance of The Psychology Students in San Beda UniversityDocumento5 pagineThe Impact of Video Gaming To The Academic Performance of The Psychology Students in San Beda UniversityMarky Laury GameplaysNessuna valutazione finora
- Womack - Labor History, Industrial Work, Economics, Sociology and Strategic Position PDFDocumento237 pagineWomack - Labor History, Industrial Work, Economics, Sociology and Strategic Position PDFhmaravilloNessuna valutazione finora
- The Distracted Mind - ExcerptDocumento15 pagineThe Distracted Mind - Excerptwamu885Nessuna valutazione finora
- Percy JacksonDocumento13 paginePercy JacksonDawn Marco0% (2)
- Singular & Plural Nouns: Regular PluralsDocumento4 pagineSingular & Plural Nouns: Regular PluralsМарина ВетерNessuna valutazione finora
- Software Quality Metrics MethodologyDocumento17 pagineSoftware Quality Metrics MethodologySumit RajputNessuna valutazione finora