Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Ce8612 Environmental and Irrigation Drawing
Caricato da
siva laxmiTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Ce8612 Environmental and Irrigation Drawing
Caricato da
siva laxmiCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CE8612 ENVIRONMENTAL AND IRRIGATION DRAWING
PART A: IRRIGATION ENGINEERING
1. TANK COMPONENTS
Fundamentals of design
Tank surplus weir
Tank sluice with tower head
Drawings showing foundation details, plan and elevation
2. IMPOUNDING STRUCTURES
Design principles
Earth dam
Profile of Gravity Dam
3. CROSS DRAINAGE WORKS
General design principles
Aqueducts
Syphon aqueduct (Type III)
Canal drop (Notch Type)
Drawing showing plan, elevation and foundation details.
4. CANAL REGULATION STRUCTURES
General Principles
Direct Sluice
Canal regulator
Drawing showing detailed plan, elevation and foundation details.
PART B: ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING
1. WATER SUPPLY AND TREATMENT
Design and Drawing of flash mixer, flocculator, clarifier
Rapid sand filter
Service reservoirs
Pumping station
House service connection for water supply and drainage.
2. SEWAGE TREATMENT & DISPOSAL
Design and Drawing of screen chamber
Grit channel
Primary clarifier
Activated sludge process
Aeration tank
Trickling filter
Sludge digester
Sludge drying beds
Septic tanks and disposal arrangements
TEXTBOOKS
1. Satya Narayana Murthy Challa, “Water Resources Engineering: Principles
and Practice”, New Age International Publishers, New Delhi, 2002.
2. Garg, S.K., “Irrigation Engineering and Design of Structures”, New Age
International
Publishers, New Delhi, 1997.
3. Manual on Water Supply and Treatment, CPHEEO, Government of India, New
Delhi, 1999.
4. Manual on “Sewerage and Sewage Treatment Systems- Part A, B and C”
CPHEEO,
Ministry of Urban Development, Government of India, New Delhi, 2013.
REFERENCES
1. Mohanakrishnan. A, “A few Novel and Interesting Innovative Irrigation Structures:
Conceived, Designed and Executed in the Plan Projects in Tamil Nadu”, Publ.
No. 44 and Water Resources Development & Management Publ.No.43, IMTI
Thuvakudy, Trichy, 2011.
2. Raghunath, H.M. “Irrigation Engineering”, Wiley India Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, 2011.
3. Sharma R.K.,“Irrigation Engineering and Hydraulic Structures”, Oxford and IBH
Publishing Co., New Delhi, 2002.
4. Peary, H.S., ROWE, D.R., Tchobanoglous, G., “Environmental Engineering”,
McGrawHillBook Co., New Delhi, 1995.
5. Metcalf and Eddy, “Wastewater Engineering, Treatment and Reuse”, Tata
McGrawHill,New Delhi, 2010.
6. Qasim,S.R., Motley, E.M and Zhu.G. “Water works Engineering – Planning,
Design and
Operation”, Prentice Hall, New Delhi, 2009.
7. Qasim, S. R. “Wastewater Treatment Plants, Planning, Design & Operation”,
CRC
Press,New York, 2010
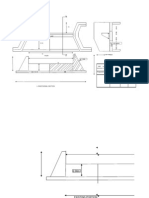
TANK SURPLUS WEIR
INTRODUCTION
Surplus weirs are used to dispose of the surplus water from tank to downstream channels,
downstream or surplus courses, or drainage channels. It disposes the water from upstream
catchments to downstream catchments or downstream tanks. These interlinked tanks in a
certain area are called a “Cascade”. Tanks in a cascade all have a common supply channel.
DESIGN ELEMENTS
1) Estimation of flood discharge.
2) Length of surplus weir.
3) Crest width.
4) Base width.
5) Aprons of the weir
6) Upstream aprons
7) Downstream aprons
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Pipeline Design for Water EngineersDa EverandPipeline Design for Water EngineersValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Sjbit CIVIL-VI-HYDRAULIC-STRUCTURES-AND-IRRIGATION-DESIGN-DRAWIN-10CV65-NOTES PDFDocumento93 pagineSjbit CIVIL-VI-HYDRAULIC-STRUCTURES-AND-IRRIGATION-DESIGN-DRAWIN-10CV65-NOTES PDFprasadnn2001100% (2)
- Irrigation Drawing ManualDocumento46 pagineIrrigation Drawing Manualkalai vaani100% (2)
- Soil Mechanics Lab Viva QuestionsDocumento2 pagineSoil Mechanics Lab Viva QuestionsRamaswamy Koodalloor Parasuraman73% (11)
- Tank Surplus WeirDocumento2 pagineTank Surplus Weirrameshbabu_197967% (9)
- Highway Engineering Lab ManualDocumento11 pagineHighway Engineering Lab Manualsaranya0% (1)
- Visit Report 1 (Gangapur Dam)Documento9 pagineVisit Report 1 (Gangapur Dam)Pmokal960% (5)
- B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAM CE-2355 ENVIRONMENTAL AND IRRIGATION DRAWING LABDocumento3 pagineB.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAM CE-2355 ENVIRONMENTAL AND IRRIGATION DRAWING LABjohnalbinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Santosh Kumar Septic Tank For 10 UssersDocumento68 pagineSantosh Kumar Septic Tank For 10 UssersAnonymous Rb7BxQdZ100% (2)
- Structural Design and Drawing Reinforced ConcreteDocumento3 pagineStructural Design and Drawing Reinforced Concretesidhareddy manigandan100% (1)
- V Semester Environment and Agriculture Question BankDocumento9 pagineV Semester Environment and Agriculture Question BankMohamed Raees100% (1)
- Question Paper Code: X10249: Reg. No.Documento4 pagineQuestion Paper Code: X10249: Reg. No.Srikrishnan Dhanaji0% (1)
- CE8701 Estimation, Costing and Valuation Engineering Notes 2Documento32 pagineCE8701 Estimation, Costing and Valuation Engineering Notes 2Raja Siddu100% (1)
- ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING-II SYLLABUSDocumento212 pagineENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING-II SYLLABUSRaj Bakhtani100% (4)
- New TankDocumento47 pagineNew TankGTS100% (9)
- A Mini Project ReportDocumento37 pagineA Mini Project ReportChintuu Sai100% (2)
- 1 - Old TankDocumento49 pagine1 - Old Tanknaveen75% (4)
- Experiment - 1 AIM: To Determine The Reduced Level of An Object When Base Is Instruments Used: Theodolite, Tape, Leveling Staff, Ranging RodDocumento12 pagineExperiment - 1 AIM: To Determine The Reduced Level of An Object When Base Is Instruments Used: Theodolite, Tape, Leveling Staff, Ranging RodSakthi Murugan100% (1)
- Software Application Lab ManualDocumento87 pagineSoftware Application Lab ManualKiran M S100% (1)
- 01 Design of Surplus Weir With Stepped Apron PDFDocumento9 pagine01 Design of Surplus Weir With Stepped Apron PDFSrinivas Reddy100% (2)
- Drawing Model SurplusweirDocumento4 pagineDrawing Model SurplusweirVenkatarathnam Pulipati100% (1)
- Design of Sub Structures NotesDocumento40 pagineDesign of Sub Structures NotesIlakkiya Dharmalingam100% (1)
- New Tank ProjectDocumento6 pagineNew Tank Projectlaxmanrokz100% (7)
- (Environmental Engineering Vol. 1) Dr. B.C. Punmia - Water Supply Engineering 1 (Standard Book House) - Libgen - LiDocumento255 pagine(Environmental Engineering Vol. 1) Dr. B.C. Punmia - Water Supply Engineering 1 (Standard Book House) - Libgen - LiPoojan Pasawala100% (1)
- Hydrology & Irrigation Engineering Jan 2014Documento2 pagineHydrology & Irrigation Engineering Jan 2014Prasad C MNessuna valutazione finora
- Two Marks OAI551 - Environment and Agriculture ALDocumento34 pagineTwo Marks OAI551 - Environment and Agriculture ALSuganthiVasan75% (4)
- Estimation of construction projectDocumento7 pagineEstimation of construction projectIrfan KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 10 Canal OutletsDocumento65 pagineChapter 10 Canal OutletsUMAR FAROOQ67% (3)
- Extensive Survey ProjectDocumento2 pagineExtensive Survey ProjectShaik Jhoir45% (11)
- Highway Engineering: by RangwalaDocumento3 pagineHighway Engineering: by RangwalaJATINKUMAR CHAUDHARINessuna valutazione finora
- Geotechnical Lab Assignment AnalysisDocumento4 pagineGeotechnical Lab Assignment AnalysisVageesha Shantha Veerabhadra Swamy50% (2)
- Water Supply and Sanitary Engineering GuidebookDocumento5 pagineWater Supply and Sanitary Engineering GuidebookVinod Kumar31% (16)
- CT Lab Viva QuestionsDocumento7 pagineCT Lab Viva Questionsmahesh75% (8)
- A Study On Water AbsorbingDocumento2 pagineA Study On Water AbsorbingInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- Quantity of Water (Water Supply Engineering)Documento7 pagineQuantity of Water (Water Supply Engineering)Shuvanjan Dahal100% (7)
- Download Water Supply Engineering PDFDocumento2 pagineDownload Water Supply Engineering PDFRao Lokendra Singh20% (5)
- Extensive Survey Project Fieldwork and Data CollectionDocumento38 pagineExtensive Survey Project Fieldwork and Data CollectionRizwan Arshad Abhimanigala BalagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Underwater ConstructionDocumento11 pagineUnderwater ConstructionSwaraj Gaikwad100% (1)
- Thesis M.TechDocumento109 pagineThesis M.TechSonu Dhangar100% (10)
- Design and Drawing of Irrigation StructuresDocumento6 pagineDesign and Drawing of Irrigation StructuresRam Krishna Arikatla100% (3)
- Water Supply and Sanitary Engineering PDFDocumento3 pagineWater Supply and Sanitary Engineering PDFVinod Kumar56% (16)
- Design of Sewerage System ReportDocumento22 pagineDesign of Sewerage System Reportsyed muneeb haider100% (4)
- Unit 4 Irrigation CanalsDocumento25 pagineUnit 4 Irrigation CanalsAmal ZakirNessuna valutazione finora
- Compression Memeber NumericalDocumento6 pagineCompression Memeber NumericalDeepak SahNessuna valutazione finora
- Viva Answers PDFDocumento9 pagineViva Answers PDFbishry ahamed100% (5)
- Jack WellDocumento2 pagineJack Welldpk60% (5)
- Major Project ReportDocumento49 pagineMajor Project ReportMohini BhartiNessuna valutazione finora
- Causes of Failure of Weirs On Permeable Soils and Their RemediesDocumento18 pagineCauses of Failure of Weirs On Permeable Soils and Their RemediesMr. Y. RajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Principles For Sarda Type and Straight Glacis FallDocumento12 pagineDesign Principles For Sarda Type and Straight Glacis Fallshweta0% (1)
- Irrigation Water Resources and Water Power Engineering (SI Units) 10th Edition 2019 - Auth - Dr. P.N. MODIRDocumento1.233 pagineIrrigation Water Resources and Water Power Engineering (SI Units) 10th Edition 2019 - Auth - Dr. P.N. MODIRBasoz Arif Ahmad85% (13)
- CE 8512 W&WW Analysis LabDocumento74 pagineCE 8512 W&WW Analysis LabSuria Prakash50% (2)
- Design of Check DamDocumento5 pagineDesign of Check DamNaveen Yadav90% (10)
- Gabion Stractures: Department of Civil EngineeringDocumento31 pagineGabion Stractures: Department of Civil EngineeringSagar Rathod83% (12)
- Civil-Vii-Air Pollution and Control (10cv765) - NotesDocumento134 pagineCivil-Vii-Air Pollution and Control (10cv765) - NotesEshwar Prasad50% (4)
- Irrigation Engineering Course OverviewDocumento2 pagineIrrigation Engineering Course Overview017Harshit gargNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1Documento22 pagineLecture 1Issa DrdrNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydraulic Structures LN9Documento69 pagineHydraulic Structures LN9Nijaz Lukovac100% (5)
- Title of The Paper: Water Supply Engineering Subject Code: 11CBCI54Documento1 paginaTitle of The Paper: Water Supply Engineering Subject Code: 11CBCI54Sharmilaa Suresh KannanNessuna valutazione finora
- SyllabusDocumento3 pagineSyllabusVinothNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Engineering Course OverviewDocumento3 pagineEnvironmental Engineering Course OverviewPartha PratimNessuna valutazione finora
- CFD 5Documento30 pagineCFD 5siva laxmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Plate14 DrawingDocumento2 paginePlate14 Drawingsiva laxmi0% (1)
- CFD 2Documento10 pagineCFD 2siva laxmiNessuna valutazione finora
- CFD Methods for Modelling Air Pollution ProblemsDocumento2 pagineCFD Methods for Modelling Air Pollution Problemssiva laxmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaerobic Processes (Chapter 10) : AdvantagesDocumento13 pagineAnaerobic Processes (Chapter 10) : AdvantagesΔημητρηςΣαρακυρουNessuna valutazione finora
- Plate 1Documento4 paginePlate 1siva laxmiNessuna valutazione finora
- July 15 Single Roomed Building With VerandahDocumento5 pagineJuly 15 Single Roomed Building With Verandahsiva laxmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Plate 13 DiagramDocumento2 paginePlate 13 Diagramsiva laxmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of A Good ReportDocumento2 paginePrinciples of A Good Reportsiva laxmiNessuna valutazione finora
- PECI 405 ECPP 7th Sem CivilDocumento96 paginePECI 405 ECPP 7th Sem CivilYasaswi AkkirajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Tender RulesDocumento24 pagineTender RulesNiranjanNessuna valutazione finora
- History of PlumbingDocumento2 pagineHistory of PlumbingPaola Marie JuanilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Minimum Plumbing FacilitiesDocumento6 pagineMinimum Plumbing Facilitiesjeckson magbooNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care of The Client With High-Risk Labor and DeliveryDocumento23 pagineNursing Care of The Client With High-Risk Labor and DeliveryMarie Ashley CasiaNessuna valutazione finora
- WASH in Schools: 2016 Jakarta ReportDocumento29 pagineWASH in Schools: 2016 Jakarta ReportNoel Abantao100% (1)
- The Incidence of COVID-19 Along The ThaiCambodian Border Using Geographic Information System (GIS), Sa Kaeo Province, Thailand PDFDocumento5 pagineThe Incidence of COVID-19 Along The ThaiCambodian Border Using Geographic Information System (GIS), Sa Kaeo Province, Thailand PDFInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- OSHA CHAPTER 4 Emergency Preparedness, Reponeses (EPR) and Fire SafetyDocumento9 pagineOSHA CHAPTER 4 Emergency Preparedness, Reponeses (EPR) and Fire Safetyseri100% (4)
- Assessment of The Awareness, Perception, Attitudes, and Preparedness of Health-Care Professionals Potentially Exposed To COVID-19 in The United Arab EmiratesDocumento12 pagineAssessment of The Awareness, Perception, Attitudes, and Preparedness of Health-Care Professionals Potentially Exposed To COVID-19 in The United Arab EmiratesSarah SanadNessuna valutazione finora
- Traveller GreeceDocumento2 pagineTraveller GreeceElefteriosNessuna valutazione finora
- Spib SEDocumento6 pagineSpib SErosieNessuna valutazione finora
- Philippine Clean Water Act of 2004Documento7 paginePhilippine Clean Water Act of 2004Joyce Lapuz100% (4)
- Global Burden of Disease Study 2017Documento27 pagineGlobal Burden of Disease Study 2017albgomezNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study: Possible Measles Outbreak Facilitator Version: ObjectivesDocumento14 pagineCase Study: Possible Measles Outbreak Facilitator Version: ObjectivesIndonesia TodayNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Report: Intestinal Obstruction in A Child With Massive AscariasisDocumento4 pagineCase Report: Intestinal Obstruction in A Child With Massive AscariasisWella Vista EdwardNessuna valutazione finora
- Certificate of Physical FitnessDocumento2 pagineCertificate of Physical FitnessHarsh SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- GE Water & Process Technologies. Protecting Public Health With ZeeWeed MembranesDocumento77 pagineGE Water & Process Technologies. Protecting Public Health With ZeeWeed MembranesTiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Teratogenic Pregnancy RisksDocumento40 pagineTeratogenic Pregnancy RisksVonny RiskaNessuna valutazione finora
- Guder Quarterly Report 2022Documento7 pagineGuder Quarterly Report 2022mohammedamin oumerNessuna valutazione finora
- Improving Nation'S Welfare: Infectious Disease As A Problem in SocietyDocumento3 pagineImproving Nation'S Welfare: Infectious Disease As A Problem in SocietyGiselleNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading 5 - Health RequirementsDocumento8 pagineReading 5 - Health RequirementsHani MasriNessuna valutazione finora
- HBM Slides (SEMINAR)Documento60 pagineHBM Slides (SEMINAR)Simran Josan100% (1)
- Pathfit 1Documento2 paginePathfit 1Brian AnggotNessuna valutazione finora
- Amoud University Postgraduate TimetablesDocumento7 pagineAmoud University Postgraduate TimetablesPPM Class-2021Nessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetic Prevention ProjectDocumento6 pagineDiabetic Prevention ProjectStephen NdireNessuna valutazione finora
- 2009 Red Book 7th EdDocumento96 pagine2009 Red Book 7th EdRashid AlahmerNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Paraphernalia Laws Undermine Harm ReductionDocumento24 pagineDrug Paraphernalia Laws Undermine Harm ReductionCato InstituteNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Analysis For Boys P1Documento34 pagineData Analysis For Boys P1Nonit HathilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bringing Events Back: Austin-Travis County Covid-19 Safety Guide For Venues & Special EventsDocumento13 pagineBringing Events Back: Austin-Travis County Covid-19 Safety Guide For Venues & Special EventsAnonymous Pb39klJNessuna valutazione finora
- Janitorial Safety Training Guide: Ership, ActDocumento32 pagineJanitorial Safety Training Guide: Ership, Act757rustam100% (2)
- Basic Measures of EpidemiologyDocumento51 pagineBasic Measures of EpidemiologyHafiz SabghatullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Tuberculosis - The Most Common Symptoms of TB Disease Are Cough With PhlegmDocumento6 pagineTuberculosis - The Most Common Symptoms of TB Disease Are Cough With PhlegmMargareta PratiwiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Rights of Nature: A Legal Revolution That Could Save the WorldDa EverandThe Rights of Nature: A Legal Revolution That Could Save the WorldValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionDa EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (542)
- High Performance Loudspeakers: Optimising High Fidelity Loudspeaker SystemsDa EverandHigh Performance Loudspeakers: Optimising High Fidelity Loudspeaker SystemsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- The Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesDa EverandThe Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionDa EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cyanide Canary: A True Story of InjusticeDa EverandThe Cyanide Canary: A True Story of InjusticeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (51)
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionDa EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (331)
- Understanding Automotive Electronics: An Engineering PerspectiveDa EverandUnderstanding Automotive Electronics: An Engineering PerspectiveValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (16)
- Lithium-Ion Battery: The Power of Electric Vehicles with Basics, Design, Charging technology & Battery Management SystemsDa EverandLithium-Ion Battery: The Power of Electric Vehicles with Basics, Design, Charging technology & Battery Management SystemsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Off-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemDa EverandOff-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemNessuna valutazione finora
- 8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionDa Everand8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (6)
- C++ Programming Language: Simple, Short, and Straightforward Way of Learning C++ ProgrammingDa EverandC++ Programming Language: Simple, Short, and Straightforward Way of Learning C++ ProgrammingValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- The Rare Metals War: the dark side of clean energy and digital technologiesDa EverandThe Rare Metals War: the dark side of clean energy and digital technologiesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Build Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionDa EverandBuild Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeDa EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (8)
- Ramblings of a Mad Scientist: 100 Ideas for a Stranger TomorrowDa EverandRamblings of a Mad Scientist: 100 Ideas for a Stranger TomorrowNessuna valutazione finora
- The Fast Track to Your Technician Class Ham Radio License: For Exams July 1, 2022 - June 30, 2026Da EverandThe Fast Track to Your Technician Class Ham Radio License: For Exams July 1, 2022 - June 30, 2026Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Current Interruption Transients CalculationDa EverandCurrent Interruption Transients CalculationValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Art of Commenting: How to Influence Environmental Decisionmaking With Effective Comments, The, 2d EditionDa EverandArt of Commenting: How to Influence Environmental Decisionmaking With Effective Comments, The, 2d EditionValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- The Graphene Revolution: The Weird Science of the Ultra-thinDa EverandThe Graphene Revolution: The Weird Science of the Ultra-thinValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (4)
- Operational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignDa EverandOperational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)