Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Exercise Metabolism
Caricato da
Lew MingCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Exercise Metabolism
Caricato da
Lew MingCopyright:
Formati disponibili
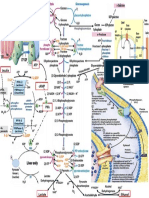
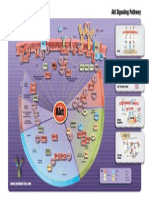
SnapShot: Exercise Metabolism
SnapShot: XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Brendan Egan,1 John A. Hawley,2 and Juleen R. Zierath3
1
School of Health and Human Performance, Dublin City University, Glasnevin, Dublin 9, Ireland
AUTHOR
2
Mary XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
MacKillop Institute for Health Research, Centre for Exercise and Nutrition,
AFFILIATION
AustralianXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Catholic University, Melbourne, VIC 3000, Australia
3
Department of Molecular Medicine and Surgery and Department of Physiology and Pharmacology,
Section of Integrative Physiology, Karolinska Institutet, 17177 Stockholm, Sweden
Sources of energy provision in skeletal muscle Inter-organ communication
ATP hydrolysis ATP + H 2O ADP + P i + H + + energy
Secreted factors: IL-6, IL-15, myostatin,
ATP resynthesis Muscle BAIBA, lactate, exosomes, and others
Anaerobic pathways:
Phosphocreatine degradation ADP + PCr + H + ATP + Cr
Adenylate kinase reaction 2ADP ATP + AMP Adipocytes Bone
Anaerobic glycolysis Glycogen + 3 ADP 2 lactate + 2 H + + 3 ATP
Aerobic pathways:
Carbohydrate oxidation Glucose + 6 O 2 + 38 ADP + 38 P i 6CO 2 + 6H 2O + 38 ATP
Lipid oxidation Palmitate + 23 O 2 + 130 ADP + 130 P i 16 CO 2 + 146 H 2O + 130 ATP Liver Brain
Contraction-induced modulators of gene expression in skeletal muscle
Stimulus Sensor Downstream effector
P iO 2 PHDs HIF-1α
NAD +:NADH SIRTs PGC-1α, FOXO1, p53
AMP:ATP AMPK HDAC, PGC-1α, CREB, SIRT1, HIF-1α
Mechanical stress MAPKs PGC-1α, CREB, ATF2
[Ca 2+ ] i CaMKs HDAC, CREB, SRF
Mechanosensation FAK mTOR, p70 S6K
Sarcolemmal disruption PA Akt, mTOR, FOXO1
Exosomes CAPILLARY
Glucose FFA
GLUT4 CD36
Autocrine/paracrine
signaling
ATP-PCr
ATP Glucose Glycogen IMTG
FFA
ADP HK PHOS GS FABP Lipolysis
FFA
PA FAK p38, ERK1/2, JNK CaMKII AMPK SIRTs PHDs LDH G-6-P G-1-P
LAC Glycolysis FA-CoA
Akt NAD + NADH
P ATP CPT1
HDAC HDAC RIP140 PYR
ADP
mTOR FOXOs
MurF PGC-1α PGC-1α
TORC1 TORC2 ATP PDH
MAFbx MEF2 CREB GEF ERRα FOXO1 PPARs
V H+
Atrogenes Glucose metabolism Lipid metabolism
IV H + Electron Ac-CoA β-oxidation
transport
MRFs PGC-1α HIF-1β PRC III H + chain
PGC-1β
p70 S6K
4E-BP1 ATP
MyoD MyoG ERRα HIF-1α PGC-1α
II NADH, FADH 2,
Protein MEF2 VEGF ERRα
PPARs NRF-1/2 ATP, CO 2
translation H+ TCA
initiation
Myogenesis Angiogenesis
I cycle
Transcriptional regulators NAD +, FAD,
and mitochondrial genes ADP+P i
mtDNA
miR-1, -133a, -133b, -181a, miR-9, -23a, -23b, -31 NUCLEUS
Tfam
Autophagy MITOCHONDRION
SARCOPLASM
Adaptive Changes in mRNA expression and protein content Hypertrophy
responses:
Change mRNA
from
baseline Protein content, enzyme function Mitochondrial biogenesis
Improved exercise performance
and whole-body metabolism
Acute exercise Hours Days Weeks Months Chronic exercise training
Expanding and differentiating skeletal EXPAND DIFFERENTIATE
muscle progenitor cells (myoblasts) are The MyoCult™ Expansion Kit (Catalog The MyoCult™ Differentiation Kit
common practices during the study of #05960) is formulated for the expansion and (Catalog #05965) is formulated to
2 Cell ???, ??MONTH??
myogenesis, disease modeling, ??DATE??,
and 200? ©200?
maintenance Elsevier
of human Inc.
myoblasts. DOI XXXXXXXXX
The MyoCult™ differentiate human myoblasts into See online version for ???
co-culture systems. MyoCult™ media are expansion medium provided in this kit myotubes. This kit also includes a cell
specifically formulated to expand, suppresses the expression of key myogenic attachment substrate to support optimal
maintain, and differentiate primary human differentiation genes while maintaining the adherence to culture vessels and maintain
myoblasts. These specialized media are expression of myogenic progenitor markers. myotube morphology for downstream To learn more about MyoCult™ products available
Myoblasts expanded in MyoCult™ expansion assays. Myotubes generated from the for myogenic research, visit www.myocult.com.
designed to provide researchers with
standardized workflows and culture medium are fully compatible with the MyoCult™ MyoCult™ Differentiation Kit can serve as a
systems to minimize cell culture variability Differentiation Kit (Catalog #05965). robust two-dimensional in vitro myofiber
and increase experimental reproducibility. model for myogenic studies.
DOCUMENT #27054| VERSION 1.0.0
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Biochem SuperTableDocumento2 pagineBiochem SuperTablePrincess MarielleNessuna valutazione finora
- MetabolismDocumento1 paginaMetabolismClaudius AlexiusNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOCHEMISTRY - Summary of PathwaysDocumento8 pagineBIOCHEMISTRY - Summary of PathwaysWendy Mae100% (9)
- Brookewean STGDocumento37 pagineBrookewean STGapi-308068901Nessuna valutazione finora
- David Shier - Ricki Lewis - Jackie Butler - Hole's Human Anatomy & Physiology-Mcgraw Hill Education (2019)Documento1.025 pagineDavid Shier - Ricki Lewis - Jackie Butler - Hole's Human Anatomy & Physiology-Mcgraw Hill Education (2019)stephcruz0726Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biochem SuperTable PDFDocumento2 pagineBiochem SuperTable PDFPrincess MarielleNessuna valutazione finora
- Chicken Wing DissectionDocumento13 pagineChicken Wing DissectionJaga_Sahsiny_1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksDa EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- 11 - Carbohydrate MetabolismDocumento68 pagine11 - Carbohydrate MetabolismcheckmateNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription and TranslationDocumento9 pagineTranscription and TranslationlinhNessuna valutazione finora
- Guide To Better GuardingDocumento20 pagineGuide To Better GuardingLew MingNessuna valutazione finora
- HHMI - The p53 Gene and CancerDocumento4 pagineHHMI - The p53 Gene and CancerThe vegetal saiyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis in Grasshopper TestisDocumento7 pagineMeiosis in Grasshopper TestisRonisa100% (3)
- Somatic Embryogenesis Book PDFDocumento503 pagineSomatic Embryogenesis Book PDFveeroo ahmad100% (1)
- AMPKDocumento2 pagineAMPKDavid Robin100% (1)
- Clonal SelectionDocumento12 pagineClonal SelectionUmang PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Fungi Are Not Plants - Biology Book Grade 4 | Children's Biology BooksDa EverandFungi Are Not Plants - Biology Book Grade 4 | Children's Biology BooksNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Edexcel Unit 2 Model AnswersDocumento2 pagineBiology Edexcel Unit 2 Model Answers--------82% (22)
- Guide Near Miss Reporting Public ConsultDocumento11 pagineGuide Near Miss Reporting Public ConsultLew MingNessuna valutazione finora
- ANNEX D NUS Safety SOP On Management of HazeDocumento7 pagineANNEX D NUS Safety SOP On Management of HazeLew MingNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To CERT (2015!10!15)Documento68 pagineIntroduction To CERT (2015!10!15)Lew MingNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Sixteen Cell SignalingDocumento96 pagineChapter Sixteen Cell SignalingRu LiliNessuna valutazione finora
- BS en Iso 11688-1-2009 (2010)Documento44 pagineBS en Iso 11688-1-2009 (2010)Lew MingNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab ReportDocumento8 pagineLab ReportLatoya JonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecological Aspects of EnvironmentDocumento23 pagineEcological Aspects of EnvironmentAARSHNessuna valutazione finora
- Metabolismo Del EjercicioDocumento2 pagineMetabolismo Del EjercicioJuan Ramón Guerrero LópezNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 2Documento29 pagineClass 2Roy Anderson Oropeza ClavoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 16 10-25-22Documento19 pagineLecture 16 10-25-22Caleb HeNessuna valutazione finora
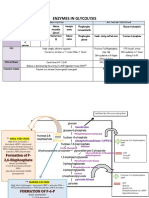
- BMM LEC 10 SN Enzymes in GlycolysisDocumento5 pagineBMM LEC 10 SN Enzymes in GlycolysisSARAH SAFIAH TAJUL ARIFFINNessuna valutazione finora
- Alcohol Metabolism: Oh My! Now What?Documento5 pagineAlcohol Metabolism: Oh My! Now What?pranjlNessuna valutazione finora
- A 59-Year-Old Man With A History of Diabetes and Alcohol Abuse Is Brought To The Emergency Room in A Semiconscious and Minimally Responsive StateDocumento43 pagineA 59-Year-Old Man With A History of Diabetes and Alcohol Abuse Is Brought To The Emergency Room in A Semiconscious and Minimally Responsive StateAnonymous eDD0YqzPMNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 GluconeogenesisDocumento18 pagine10 GluconeogenesiskulturewearzmNessuna valutazione finora
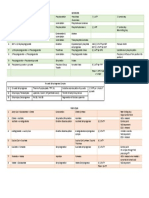
- Metabolic Enzyme Regulation: GlycolysisDocumento4 pagineMetabolic Enzyme Regulation: GlycolysisBigBoostingNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 17 10-27-22Documento14 pagineLecture 17 10-27-22Caleb HeNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Chemical Functions OF EicosanoidsDocumento25 pagineBio Chemical Functions OF EicosanoidsOyanan MahendrarajahNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio - CO 6Documento2 pagineBio - CO 6Jae Bert UbisoftNessuna valutazione finora
- Regulation of LipidsDocumento13 pagineRegulation of LipidsNeha SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- LMR - Biochemistry: CarbohydratesDocumento6 pagineLMR - Biochemistry: CarbohydratesYuku BabyNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 3390@biom10071068Documento18 pagine10 3390@biom10071068Hillary OziokoNessuna valutazione finora
- Insulin Secretion - Newer PerspectiveDocumento6 pagineInsulin Secretion - Newer PerspectivehhhNessuna valutazione finora
- L20 Signal Transduction and Mechanism of Hormone ActionDocumento51 pagineL20 Signal Transduction and Mechanism of Hormone Actionyebadem228Nessuna valutazione finora
- Carbo ChemDocumento123 pagineCarbo ChemHan MichelNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9 - Energy Metabolism and Membrane Physiology of The ErythrocyteDocumento5 pagineChapter 9 - Energy Metabolism and Membrane Physiology of The ErythrocyteAira UsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mhs - DNM - Met. KH - 22Documento25 pagineMhs - DNM - Met. KH - 22punthadewaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol-2012-Hemmings-A011189Documento4 pagineCold Spring Harb Perspect Biol-2012-Hemmings-A011189tadilakshmikiranNessuna valutazione finora
- 2021 CHO Metabolism 1Documento48 pagine2021 CHO Metabolism 1xb2k9gzkc9Nessuna valutazione finora
- F6P PFK-2 Fr. 2,6 BP FBP-2: Insulin Glucagon GlycolysisDocumento4 pagineF6P PFK-2 Fr. 2,6 BP FBP-2: Insulin Glucagon GlycolysisKate TaylorNessuna valutazione finora
- BiochimieDocumento3 pagineBiochimieCDM achiffaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rate Limiting StepsDocumento2 pagineRate Limiting StepsvictoreffiomNessuna valutazione finora
- GluconeogenesisDocumento21 pagineGluconeogenesisNoor Al Huda MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- תרשיםDocumento1 paginaתרשיםliaorNessuna valutazione finora
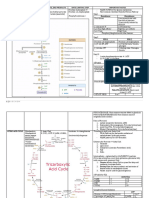
- ' Biochemistry ' Biochemistry-Metabolism Section Ii: Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative PhosphorylationDocumento10 pagine' Biochemistry ' Biochemistry-Metabolism Section Ii: Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylationgksah711Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction BCHN 222 2022Documento39 pagineIntroduction BCHN 222 2022Francisca ManyisaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4A. Cellular RespirationDocumento5 pagine4A. Cellular RespirationIrish Mae LunaNessuna valutazione finora
- PI3 Kinase Akt Signaling: mTORC2Documento0 paginePI3 Kinase Akt Signaling: mTORC2alexandru_mg3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Substrates&EnzymesDocumento15 pagineSubstrates&EnzymesTanyaTouchéNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycolysis ASAS 4104Documento8 pagineGlycolysis ASAS 4104AlbanMugotiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cho MetabDocumento1 paginaCho MetabKarla Faye UcangNessuna valutazione finora
- Aspergillus Oryzae Laea Regulates Kojic Acid Synthesis Genes PDFDocumento4 pagineAspergillus Oryzae Laea Regulates Kojic Acid Synthesis Genes PDFBich Phuong NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOCHEMDocumento15 pagineBIOCHEMKrizzia OñateNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 GluconeogenesisDocumento31 pagine1 Gluconeogenesisemery100% (1)
- Lab Metting On Friday 2011.03.11Documento17 pagineLab Metting On Friday 2011.03.11Alamgir HossainNessuna valutazione finora
- Beverages: Saccharomyces Species in The Production of BeerDocumento18 pagineBeverages: Saccharomyces Species in The Production of BeerRoberta RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Beverages 02 00034 v2Documento18 pagineBeverages 02 00034 v2maria choque callisayaNessuna valutazione finora
- ZBM0031 01LIP2RBLipolysisKit08 08Documento9 pagineZBM0031 01LIP2RBLipolysisKit08 08evanconstantine77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Musculoskeletal System 2006 WebsiteDocumento4 pagineMusculoskeletal System 2006 WebsiteMasniahNessuna valutazione finora
- Akt Signaling Pathway: RTK GPCR NFGBDocumento1 paginaAkt Signaling Pathway: RTK GPCR NFGBSalazar ÁngelNessuna valutazione finora
- PATHWAYS SummaryDocumento5 paginePATHWAYS Summaryslu.veniegasmb.1144Nessuna valutazione finora
- MOM Inspection Requirements Lifting EquipmentDocumento1 paginaMOM Inspection Requirements Lifting EquipmentLew MingNessuna valutazione finora
- 79 313 1 SMDocumento33 pagine79 313 1 SMLew MingNessuna valutazione finora
- BennettDocumento271 pagineBennettLew MingNessuna valutazione finora
- 1000 MCQ in ENTDocumento104 pagine1000 MCQ in ENTLew Ming100% (1)
- CombinepdfDocumento39 pagineCombinepdfLew MingNessuna valutazione finora
- Edoc - Pub As 4084 2012 Steel Storage RackingDocumento2 pagineEdoc - Pub As 4084 2012 Steel Storage RackingLew MingNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology (Mitosis Cell Division)Documento3 pagineBiology (Mitosis Cell Division)Harry ParconNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy & Physiology of CellDocumento14 pagineAnatomy & Physiology of CellBrianna ValerioNessuna valutazione finora
- Extra Nuclear InheritanceDocumento13 pagineExtra Nuclear InheritanceTony BernardNessuna valutazione finora
- S 2 Unit 5 Course Book, Work Book Ques and KeysDocumento12 pagineS 2 Unit 5 Course Book, Work Book Ques and KeysHein Aung ZinNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3-Cell Cycle and CheckpointsDocumento53 pagineLesson 3-Cell Cycle and CheckpointsHonleth Jheney MamarilNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 11Documento38 pagineChapter 11Joysshi LadaNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Bio Unit 3 Study GuideDocumento4 pagineAP Bio Unit 3 Study GuideKaycia HenryNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Activity 2 (Meiosis)Documento4 pagineLaboratory Activity 2 (Meiosis)Jean V. GetizoNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Genetics Concepts and Applications 11th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions ManualDocumento12 pagineHuman Genetics Concepts and Applications 11th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions Manualantheagian4p4y4100% (32)
- Production of Reproductive Hormones: NCM 107 NotesDocumento5 pagineProduction of Reproductive Hormones: NCM 107 NotesJohn Lawrence YbanezNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth and Life Science Q2 LP 3Documento7 pagineEarth and Life Science Q2 LP 3Jhoana OrenseNessuna valutazione finora
- Name - Odango, Clint Xavier F. BSN 1B Score - MCC 1 Seatwork The Cells Date 02/04/2021 A. Draw The Animal Cell and Label The Following PartsDocumento3 pagineName - Odango, Clint Xavier F. BSN 1B Score - MCC 1 Seatwork The Cells Date 02/04/2021 A. Draw The Animal Cell and Label The Following Partsclint xavier odangoNessuna valutazione finora
- 5th Sem Syllabus BotanyDocumento3 pagine5th Sem Syllabus BotanyAdnan BandayNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocumento58 pagineChapter 3 - Cell Structures and Their FunctionsAldrin BlasNessuna valutazione finora
- Cancer Cell and Cell CycleDocumento10 pagineCancer Cell and Cell CycleRouie AzucenaNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Frqs - KeysDocumento39 pagineAP Frqs - Keysanson3225877976Nessuna valutazione finora
- DLP - Menstrual CycleDocumento5 pagineDLP - Menstrual CycleRigel Del CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- SpirogyraDocumento3 pagineSpirogyraAbrar AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Tn12th135 - 12th Bio-Zoology Chapter 1 Full Guide (English Medium) - Way To Success - Techie TamilanDocumento20 pagineTn12th135 - 12th Bio-Zoology Chapter 1 Full Guide (English Medium) - Way To Success - Techie TamilanCOMMON MANNessuna valutazione finora
- Artificial Hybridisation MCQDocumento6 pagineArtificial Hybridisation MCQKartik Gaming 2.0Nessuna valutazione finora
- G8 Biology Lesson 2 Heredity Inheritance and Variation of TraitsDocumento2 pagineG8 Biology Lesson 2 Heredity Inheritance and Variation of TraitsCindy CrahayNessuna valutazione finora
- Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes: @usbfirdausDocumento25 pagineGene Regulation in Eukaryotes: @usbfirdausnur maliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 Psm1041Documento16 pagineChapter 6 Psm1041Roxanne PastranaNessuna valutazione finora
- CELL CYCLE PresentationDocumento22 pagineCELL CYCLE PresentationCalvin YusopNessuna valutazione finora