Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
DS Omeprazole
Caricato da
steffaguilar010 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
185 visualizzazioni2 pagineOmeprazole inhibits activity of acid (proton) pump, and binds to hydrogen-potassium adenosine triphosphatase, located at secretory surface of the gastric parietal cells. Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug or its components.
Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
DS-omeprazole
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoOmeprazole inhibits activity of acid (proton) pump, and binds to hydrogen-potassium adenosine triphosphatase, located at secretory surface of the gastric parietal cells. Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug or its components.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
185 visualizzazioni2 pagineDS Omeprazole
Caricato da
steffaguilar01Omeprazole inhibits activity of acid (proton) pump, and binds to hydrogen-potassium adenosine triphosphatase, located at secretory surface of the gastric parietal cells. Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug or its components.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
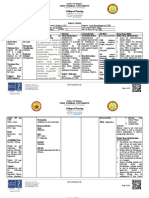
Cebu Normal University
College of Nursing
Osmenia Blvd. Cebu City 6000
NAS III – Pharmacology, Therapeutics and Diagnostics
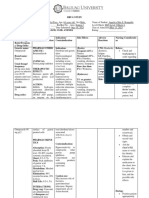
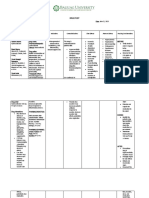
DRUG STUDY
Name of Patient Age Height
Diagnosis Sex Weight
Doctor Date of Admission Body Build
Drug Data Classification Mechanism of Action Indication
Generic Name Pharmacologic Class Inhibits activity of acid (proton) pump, and binds to General Indications
omeprazole proton pump inhibitors hydrogen-potassium adenosine triphosphatase, Symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux disease
located at secretory surface of the gastric parietal (GERD) without esophageal lesions
Trade Name Therapeutic Class cells, to block formation of gastric acid. Erosive esophagitis and accompanying
Losec, Prilosec Antiulcer agents symptoms caused by GERD
Pharmacokinetics Maintenance of healing erosive esophagitis
Patient’s Dose Pregnancy Risk Category Pathologic hypersecretory conditions (such as
C Onset Zollinger-Ellison syndrome)
Duodenal ulcer (short-term treatment)
Minimum Dose Peak
Helicobacter pylori infection and duodenal ulcer
disease, to eradicate H. pylori with
Duration
clarithromycin (dual therapy)
Maximum Dose
H. pylori infection and duodenal ulcer disease,
Drug Half Life
to eradicate H. pylori with clarithromycin and
amoxicillin (triple therapy)
Contents
Short-term treatment of active benign gastric
Availability ulcer
Capsules (delayed-release):
10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg Patient’s Actual Indication
Routes of administration
PO
Source: Source: Source: Source:
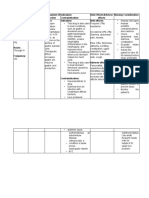
Contraindications Adverse Reactions Nursing Responsibilities
Contraindicated in: CNS: headache, dizziness, asthenia Before
Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to Assess patient’s history: Hypersensitivity to omeprazole or
drug or its components. GI: diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, any of its components; pregnancy, lactation
constipation, flatulence
Precaution
Conduct physical assessment: Skin lesions; T; reflexes,
affect; urinary output, abdominal exam; respiratory
Use cautiously with pregnancy, lactation Musculoskeletal: back pain
auscultation
Drug interaction Respiratory: cough, upper respiratory tract infection Dosage adjustments aren't needed for patients with renal
Drug-drug. or hepatic impairment.
Ampicillin esters, iron derivatives, Skin: rash Omeprazole increases its own bioavailability with repeated
ketoconazole: may exhibit poor bioavailability dosages. Drug is labile in gastric acid; less drug is lost to
in patients taking omeprazole because hydrolysis because drug increases gastric pH.
optimal absorption of these drugs needs a Don't confuse Prilosec with Prozac, Prilocaine, or Prinivil.
low gastric pH. Avoid using together. During
Diazepam, phenytoin, warfarin: decreases Tell patient to swallow capsules whole and not to open,
hepatic clearance, possibly leading to crush, or chew them.
increased serum levels. Monitor closely. Administer drug 30 minutes before meals.
Drug-herb. Administer antacids with omeprazole, if needed.
Male fern: male fern is inactivated in alkaline
environments. Patient should separate
After
administration.
Pennyroyal: may change rate of formation of Caution patient not to perform hazardous activities if
toxic metabolites of pennyroyal. Avoid using dizziness occurs
together. Arrange for further evaluation of patient after 8 wks of
therapy for gastroreflux disorders; not intended for
maintenance therapy.
Instruct patient to have regular medical follow-up visits.
Inform patient of the possible side effects of drug and
advise to consult with your health care provider if
uncomfortable
Advise patient to report severe headache, worsening of
symptoms, fever, and chills.
Source: Source: Source:
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Thyroid PathologyDocumento9 pagineThyroid PathologyNada MuchNessuna valutazione finora
- VertigoDocumento3 pagineVertigoGirishNessuna valutazione finora
- Laban - Sub Kamal Salman Mahmoud Jaber Mustafa: Done byDocumento40 pagineLaban - Sub Kamal Salman Mahmoud Jaber Mustafa: Done byKool Kaish100% (1)
- Angina PectorisDocumento17 pagineAngina PectorisRakesh Reddy100% (1)
- Nac Osce Comprehensive ReviewDocumento177 pagineNac Osce Comprehensive ReviewAisha SyedNessuna valutazione finora
- Myasthenia GravisDocumento3 pagineMyasthenia Gravisapi-3822433100% (2)
- OMEPRAZOLEDocumento1 paginaOMEPRAZOLERheza0% (1)
- Science Investigatory ProjectDocumento14 pagineScience Investigatory ProjectTrixie Rose Cortez100% (1)
- Cholecystitis NCPDocumento4 pagineCholecystitis NCPdark-canales33% (3)
- DRUG-STUDY OmeprazoleIV AngelicaRonquilloDocumento4 pagineDRUG-STUDY OmeprazoleIV AngelicaRonquillokarl eiron delos santosNessuna valutazione finora
- Newborn Physical ExaminationDocumento4 pagineNewborn Physical ExaminationastrikusumadewiNessuna valutazione finora
- Copd Drug StudyDocumento9 pagineCopd Drug StudyJoegie Ario100% (1)
- Acetylcysteine Drug Study - FranciscoDocumento4 pagineAcetylcysteine Drug Study - FranciscoFaye Andrea Francisco100% (1)
- NCP For LeukemiaDocumento2 pagineNCP For Leukemiaخالد الغامديNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study (Covid Case)Documento5 pagineDrug Study (Covid Case)YessaminNessuna valutazione finora
- Clarithromycin (Biaxin)Documento1 paginaClarithromycin (Biaxin)Jocelyn Rivera100% (1)
- CEFUROXIMEDocumento3 pagineCEFUROXIMEGwyn RosalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitesDocumento3 pagineDrug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitesGino B. BulanaNessuna valutazione finora
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocumento6 pagineCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityChelsea WuNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento7 pagineDrug StudyKaren AtilanoNessuna valutazione finora
- OmeprazoleDocumento2 pagineOmeprazoleIvan Matthew SuperioNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study: Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDocumento2 pagineDrug Study: Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityJoshua DavantesNessuna valutazione finora
- Ce Fur OximeDocumento2 pagineCe Fur OximeDan Dan ManaoisNessuna valutazione finora
- Cefuroxime, Celecoxib, ChloridineDocumento2 pagineCefuroxime, Celecoxib, ChloridinekrizzywhizzyNessuna valutazione finora
- Name of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento4 pagineName of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesNemo Del RosarioNessuna valutazione finora
- DRUG STUDY Durano Aireen E.Documento4 pagineDRUG STUDY Durano Aireen E.Doneva Lyn MedinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dacanay Jungco Omeprazole DsDocumento2 pagineDacanay Jungco Omeprazole DsTRISHA JUNGCONessuna valutazione finora
- Peptic Ulcer Disease in Chil Den: Gastroenterology Department Mingfang Sun 2020.7.7Documento23 paginePeptic Ulcer Disease in Chil Den: Gastroenterology Department Mingfang Sun 2020.7.7Clifford MartinNessuna valutazione finora
- Name of Drugs Mode of Action Indications Side Effects Nursing ManagementDocumento3 pagineName of Drugs Mode of Action Indications Side Effects Nursing ManagementJane Arian BerzabalNessuna valutazione finora
- Borres Drugstudy-M2w7Documento3 pagineBorres Drugstudy-M2w7gnmalisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Viii. Pharmacologic Intervention (Drug Study)Documento10 pagineViii. Pharmacologic Intervention (Drug Study)Cyril Jane Caanyagan AcutNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Presentation Peptic Ulcer: Ma. Christina T. Alvarez Wup - Bs Nursing Iii-2Documento18 pagineCase Presentation Peptic Ulcer: Ma. Christina T. Alvarez Wup - Bs Nursing Iii-2Shane Aileen AngelesNessuna valutazione finora
- Phinma - University of Iloilo College of Allied Health Sciences Drug StudyDocumento3 paginePhinma - University of Iloilo College of Allied Health Sciences Drug Studylhie cabanlitNessuna valutazione finora
- Omeprazole Drug StudyDocumento4 pagineOmeprazole Drug StudyjoanneNessuna valutazione finora
- DS Clarithromycin GI ARLEDDocumento5 pagineDS Clarithromycin GI ARLEDvivi's eyebrowsNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento22 pagineDrug StudySierraSiwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento22 pagineDrug StudySierraSiwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dick PharmaDocumento10 pagineDick PharmaMaverick LimNessuna valutazione finora
- DRUG StudyDocumento3 pagineDRUG StudyArturo Jr Garces RNNessuna valutazione finora
- DRUG STUDE - CEFA (Echanique)Documento1 paginaDRUG STUDE - CEFA (Echanique)Echanique, James F.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cefuroxime Drug Study ChanDocumento5 pagineCefuroxime Drug Study Chanczeremar chanNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study Zofran11Documento2 pagineDrug Study Zofran11Claire Alyssa Madriaga GidoNessuna valutazione finora
- Patient Name: Garcia, Himelia C. Medical Diagnosis: Acute CVD InfarctDocumento5 paginePatient Name: Garcia, Himelia C. Medical Diagnosis: Acute CVD InfarctRaidis PangilinanNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrocortisone DSDocumento3 pagineHydrocortisone DSArone Sebastian100% (1)
- JM Drug Study CaseDocumento4 pagineJM Drug Study CaseMilky Lescano LargozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study (Med Ward Duty)Documento6 pagineDrug Study (Med Ward Duty)Kimberly Abellar LatoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cefuroxime 1Documento3 pagineCefuroxime 1Gwyn RosalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Pre Drug StudyDocumento22 pagineCase Pre Drug StudyBenjie DimayacyacNessuna valutazione finora
- ESOMEPRAZOLEDocumento6 pagineESOMEPRAZOLEGwyn RosalesNessuna valutazione finora
- DRUG TAB OmeprazoleDocumento1 paginaDRUG TAB Omeprazoleaiera angelique LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug-Tabulation (2) For CHN IndiDocumento5 pagineDrug-Tabulation (2) For CHN IndiKANT JAMES D. MAHANNessuna valutazione finora
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocumento7 pagineCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityGwyn RosalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Patient ProfileDocumento9 pagineNursing Patient ProfileDy SantiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Ana Surgery WardDocumento11 pagineDrug Ana Surgery WardJames QuilingNessuna valutazione finora
- CEFOTAXIMEDocumento3 pagineCEFOTAXIMEChoox PriiNessuna valutazione finora
- Evangelista Drug-StudyDocumento15 pagineEvangelista Drug-Studydinglasanerica57Nessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study RyDocumento30 pagineDrug Study RyRyrey Abraham PacamanaNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento2 pagineUntitledKimNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study Pedia WardDocumento2 pagineDrug Study Pedia WardCayanne ChuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugn Study 2 0Documento15 pagineDrugn Study 2 0Ken ChavezNessuna valutazione finora
- DocumentDocumento5 pagineDocumentPRECIOUS LOVE LAGRIMASNessuna valutazione finora
- St. Mary'S College Drug StudyDocumento4 pagineSt. Mary'S College Drug StudyCHRISTIAN CALAMBANessuna valutazione finora
- Uep - Edu.ph: Generic NameDocumento13 pagineUep - Edu.ph: Generic NameKenneth JazminNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study FinalDocumento10 pagineDrug Study FinalJashine DajayNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study TudayanDocumento2 pagineDrug Study TudayanPatrick ArellanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cefuroxime and Ketorolac Drug StudyDocumento5 pagineCefuroxime and Ketorolac Drug StudyDeva HiyasNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study DoxycyclineDocumento1 paginaDrug Study DoxycyclineCruzado April Kyl DC.BSN - 2BNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug TabulationDocumento6 pagineDrug TabulationKANT JAMES D. MAHANNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study: Therapeutic Class: Antilipemics Pharmacologic Class: Hmg-CoaDocumento8 pagineDrug Study: Therapeutic Class: Antilipemics Pharmacologic Class: Hmg-CoaKristine YoungNessuna valutazione finora
- Mental Changes in AgingDocumento4 pagineMental Changes in AgingPRINTDESK by DanNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading and WritingDocumento9 pagineReading and WritingDECEDERIO CANDOLENessuna valutazione finora
- DynaMed Plus - Pulmonary Embolism (PE)Documento85 pagineDynaMed Plus - Pulmonary Embolism (PE)Gamer MadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Early Onset SchizophreniaDocumento3 pagineEarly Onset SchizophreniaDoc Prince CaballeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Compensated Dengue Shock Syndrome (A97.2) and Obesity (E.661)Documento3 pagineCompensated Dengue Shock Syndrome (A97.2) and Obesity (E.661)NyomanGinaHennyKristiantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Nclex Questions For Fundamentals of NursDocumento32 pagineNclex Questions For Fundamentals of NursJrBong SemaneroNessuna valutazione finora
- Integrated Management On Childhood Imci ReportDocumento29 pagineIntegrated Management On Childhood Imci ReportvernaNessuna valutazione finora
- HistoryDocumento15 pagineHistoryDanica Mae PepitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Musculoskeletal DrugsDocumento29 pagineMusculoskeletal DrugsjanulNessuna valutazione finora
- What Causes EpilepsyDocumento2 pagineWhat Causes EpilepsyJames CollinsNessuna valutazione finora
- Medicinal Plant Diversity and Their Therapeutic Uses in Selected Village Common Forests in Chittagong Hill Tracts Bangladesh PDFDocumento25 pagineMedicinal Plant Diversity and Their Therapeutic Uses in Selected Village Common Forests in Chittagong Hill Tracts Bangladesh PDFHarold CaragNessuna valutazione finora
- Case StudyDocumento12 pagineCase Studyapi-291857811Nessuna valutazione finora
- Intern ReportDocumento7 pagineIntern ReportDLNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs Affecting The Central Nervous SystemDocumento22 pagineDrugs Affecting The Central Nervous Systemአብይ በላይነሽ ጥላሁንNessuna valutazione finora
- Mayer Gross Textbook 3e Review Bjp1990Documento2 pagineMayer Gross Textbook 3e Review Bjp1990Amàr AqmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Identification of Staphylococcus in Samples From Patients With Periodontitis by NGSDocumento3 pagineIdentification of Staphylococcus in Samples From Patients With Periodontitis by NGSLuis Enrique BizantNessuna valutazione finora
- Cholinergic AntagonistDocumento17 pagineCholinergic AntagonistShahid HameedNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Management of PatientDocumento30 pagineNursing Management of PatientShreyas WalvekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Oxidized LDL (Blog Post)Documento10 pagineOxidized LDL (Blog Post)simasNessuna valutazione finora
- Gut Probe in A PillDocumento12 pagineGut Probe in A PillLaya LastNessuna valutazione finora