Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Amp Baca
Caricato da
Arif KusumaCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Amp Baca
Caricato da
Arif KusumaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Amplifier
Definition
Amplifiers are electronic components in use to strengthen power. In use, the amplifier will
amplify the sound signal that amplify the signal current I and voltage V of the electrical input.
Meanwhile, the output will be the electric current and voltage is greater.
1. Power Amplifier Class A
Class A is the most linear amplifiers among all classes of amplifiers.
The amplifier transistor includes hot because of its work continuously at full power.
Amplifier Class A is the most inefficient amplifiers. Its efficiency value of about 20.
2. Power Amplifier Class B
Positive and negative portions of the signal is handled by a different part of the circuit.
Class B amplifiers operate cooler than class A
3. Power Amplifier Class AB
Comparison of class A and B. The quality is comparable to Class A with a lower level of
output level Efficiency Amplifier similar to Class B. Amplifier efficiency is about 50
4. Class D Power Amplifier
While this is indeed some Class D Amplifier run in digital mode. More suitable when the
so-called "switching" amplifier Theoretically Class D Amplifier 100% efficient, but in
practice, the efficiency ranges between 80-90%.
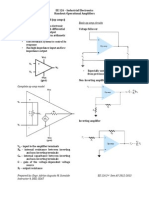
1. Inverting Amplifier
Inverting amplifier circuit is electronics circuit which serve to strengthen and reverse the
polarity of the input signal. So, there is a minus sign in the formula of gains.
2. Non-inverting Amplifier
The amplifier is called a non-inverting amplifier because the input of the amplifier is
non-inverting input of Op Amp. the opposite of the inverting amplifier, whose inputs
included in the non-inverting input so that the polarity of the output will be the same as
the polarity of the input.
This amplifier has an input is made through a non-inverting input. Thus the output
voltage will be a single phase with the input voltage. Amplifier circuit inverting and
non-inverting typically use IC Op-Amp 741.
3. Differential Amplifier
The amplifier is called the difference amplifier because the output is based on the
difference between the voltage on the feet (3 +) and foot (2-). There is Rf as feedback.
Function
1. The sensor amplifier output current 4. Summers
2. The sensor amplifier whose output 5. Integrators
voltage 6. Differentiators
3. The sensor amplifier output resistance
Materials
We can find the Amplifier in Op-amp IC , like on IC 741 , IC 3140 , now the IC is made from
semiconductor. The inside of the ic there are transistor, resistor , capacitor that made from
semikonductor wafer. Semiconductor is made from silikon and germanium materialsals
Characteristic
1. Offset Voltage Output
Offset voltage output (output offset voltage) VOO is the price of the Op Amp output
voltage to the ground (ground) on the input voltage condition Vid = 0. Ideally, the
price VOO = 0 V
2. Barriers Feedback
Barriers inputs (input resistance) Ri of the Op Amp is a huge barrier between the two
inputs Op Amp. Ideally barriers Op Amp input is infinite.
3. Barriers Output
Barriers output (output resistance) of Op Amp RO is the resistance in that arise during
Op Amp working as a signal generator. Ideally the price barrier RO Op Amp output is
equal to 0.
4. Response Time
The response time (response time) of the Op Amp is the time required by the output to
be changed after the input changed. Ideally price Op Amp response time is = 0
seconds
5. Characteristics Of Temperature
As it is known, a semiconductor material that changes its characteristics when the
temperature changes significantly. In an ideal Op Amp, the characteristic does not
change with changes in temperature
6. Input Terminal
Op-Amp has two input terminals, namely:
• Non-inverting (+)
• Inverting (-)
Aplication
LM35 TEMPERATURE RANGE SENSOR + LED
Temperature Sensor Networks Is Simple Using LM35 With Red And Green as LED
indication.
This circuit can detect a desired temperature or undesirable.
1. A voltage of 5V will raise LM35 temperature sensor, the sensor will detect the
ambient temperature.
2. After the sensor will channel temperature information it receives with the principle (1
degree = 10mV). So if the sensor detects the ambient temperature 32 degrees, then it
will distribute (32 degree x 10mV) is equal 320mv to the line output.
3. 320mv voltage is small, and therefore the IC Op-Amp LM741 (1)works as an
amplifier of 10x, the reinforcement will be = (Rf / Ri) +1.
The voltage that it came into 320mv 320mv x 10 = 3200mv / 3,2v
4. The output voltage from pin 6 IC Op-Amp LM741 (1) and into the pin 3 (non
inverting) IC Op-Amp LM741 (2). LM741 Op-Amp IC (2) work as a comparison /
comparator. Where the comparison is Vinput IC LM741 Op-Amp (1) with Vout of the
potentiometer.
5. Here Potentiometer as Vref (Voltage Reference / Reference)
If you rotate the pot until 3Volt (measured with AVO / Multimeter on pin 2 and 3 pot)
then if the incoming voltage of IC Op-Amp LM741 (1) is greater than 3Volt then
Vout would be worth +10 (+ Saturation), and if the incoming voltage is below 3Volt
then Vout would be worth -10 (-Saturasi).
6. The output of IC Op-Amp LM741 (2) is decisive or Red LED: Green LED is
illuminated.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Transmotec: 770 Series Ø45 MM 21-114 WDocumento1 paginaTransmotec: 770 Series Ø45 MM 21-114 WzyozkdNessuna valutazione finora
- Miniature Basic Switch That Offers High Reliability and SecurityDocumento7 pagineMiniature Basic Switch That Offers High Reliability and SecurityArif KusumaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ni Myrio-1950: User Guide and SpecificationsDocumento20 pagineNi Myrio-1950: User Guide and SpecificationsBa Bi100% (1)
- BST Bno055Documento118 pagineBST Bno055Arif KusumaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ni Myrio-1950: User Guide and SpecificationsDocumento20 pagineNi Myrio-1950: User Guide and SpecificationsBa Bi100% (1)
- BuzzerDocumento3 pagineBuzzerArif KusumaNessuna valutazione finora
- E6b2-C Ds e 6 1 csm491 PDFDocumento5 pagineE6b2-C Ds e 6 1 csm491 PDFculi0101Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bno055 DS000 12Documento105 pagineBno055 DS000 12Sampa DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Bts 7960Documento28 pagineBts 7960Nairo FilhoNessuna valutazione finora
- AmplifierDocumento7 pagineAmplifierArif KusumaNessuna valutazione finora
- Handson Technology: 775 Ball Bearing DC MotorDocumento13 pagineHandson Technology: 775 Ball Bearing DC MotorArif KusumaNessuna valutazione finora
- 74LS04Documento5 pagine74LS04marioromo100% (1)
- Transistor EnglishDocumento5 pagineTransistor EnglishArif KusumaNessuna valutazione finora
- Transistor EnglishDocumento5 pagineTransistor EnglishArif KusumaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dialog Bahasa InggrisDocumento6 pagineDialog Bahasa InggrisArif KusumaNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet CaptionDocumento5 pagineWorksheet CaptionArif KusumaNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Dual Operational Amplifiers Hwd4558Documento8 pagineDual Operational Amplifiers Hwd4558MARIPANessuna valutazione finora
- Scope ArtDocumento5 pagineScope ArtYuber AlejandroNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 ELX 225.3 Electronics Circuits (3-1-2)Documento3 pagine3 ELX 225.3 Electronics Circuits (3-1-2)Bikal AdhikariNessuna valutazione finora
- PROJECT BIDIRECTIONAL VISITOR COUNTER ConfirmDocumento14 paginePROJECT BIDIRECTIONAL VISITOR COUNTER Confirmsaikat Sarkar100% (1)
- Features Descriptio: LT1097 Low Cost, Low Power Precision Op AmpDocumento12 pagineFeatures Descriptio: LT1097 Low Cost, Low Power Precision Op Amphamid_violinNessuna valutazione finora
- Bootstrapping Your Op Amp Yields Wide Voltage Swings: DesignfeatureDocumento8 pagineBootstrapping Your Op Amp Yields Wide Voltage Swings: DesignfeatureNishant_s123Nessuna valutazione finora
- AD5933Documento12 pagineAD5933Abubakar SidikNessuna valutazione finora
- VCO Basics and OperationDocumento8 pagineVCO Basics and OperationHasnat HamimNessuna valutazione finora
- Multipliers ApplicationsDocumento16 pagineMultipliers ApplicationsVictorSNessuna valutazione finora
- Wien S Bridge Oscillator Using Op Amp PDFDocumento19 pagineWien S Bridge Oscillator Using Op Amp PDFTarun BarthwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Scmitt Trigger by Using Ic-741 AIM: To Study The Operation of Schmitt Trigger Using Op-Amp Using IC-741. Apparatus Required: SNO Apparatus Range QTYDocumento35 pagineScmitt Trigger by Using Ic-741 AIM: To Study The Operation of Schmitt Trigger Using Op-Amp Using IC-741. Apparatus Required: SNO Apparatus Range QTYKarthik KolliparaNessuna valutazione finora
- LIC NOtesDocumento125 pagineLIC NOtesDina GaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics Experiment 9Documento3 pagineElectronics Experiment 9Dulce DeNessuna valutazione finora
- Rms2dc Ltc1968 Demo Circuit-Dc427b A B CDocumento4 pagineRms2dc Ltc1968 Demo Circuit-Dc427b A B CsastrakusumawijayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear IC Lab GuideDocumento50 pagineLinear IC Lab Guide2K20EC132 NikhilNessuna valutazione finora
- BiPAP Synchrony 2 Service Manual PDFDocumento155 pagineBiPAP Synchrony 2 Service Manual PDFBryan GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Voca Vol 1 PDFDocumento253 pagineVoca Vol 1 PDFmakhdum shaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Low Power Nine-Bit Sigma-Delta ADC Design Using TSMC 0.18micron TechnologyDocumento5 pagineLow Power Nine-Bit Sigma-Delta ADC Design Using TSMC 0.18micron Technologyeditor_ijtel100% (1)
- Syllabus For Applied ElectronicsDocumento28 pagineSyllabus For Applied ElectronicsvinayakbondNessuna valutazione finora
- Aircraft Autostabilization SystemDocumento21 pagineAircraft Autostabilization SystemPushkala RaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Sensor Signal ConditoningDocumento203 pagineSensor Signal ConditoningHanny BerchmansNessuna valutazione finora
- AM5766Documento10 pagineAM5766Kanthan Kanth0% (1)
- Operational Amplifiers and LinearDocumento558 pagineOperational Amplifiers and Linearasmonov100% (4)
- Op-Amp Circuits ExplainedDocumento6 pagineOp-Amp Circuits Explainedkyope17Nessuna valutazione finora
- Manual Ece 1201 OkDocumento64 pagineManual Ece 1201 OkAbraham AlemNessuna valutazione finora
- Classical Mechanics Exam QuestionsDocumento26 pagineClassical Mechanics Exam QuestionsRITESH KUMAR SINGHNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.cs Lab Manual Original (1,2,4,5,9,10,11,12)Documento113 pagine1.cs Lab Manual Original (1,2,4,5,9,10,11,12)I AM A PROGRAMMERNessuna valutazione finora
- LIC Unit 1Documento20 pagineLIC Unit 1sietgunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Datasheet LM358Documento25 pagineDatasheet LM358Erlina YanuariniNessuna valutazione finora
- P 103Documento7 pagineP 103An HoaNessuna valutazione finora