Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
History of Genetics Timeline: Jo Ann Lane
Caricato da
Chairmane Burce0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
96 visualizzazioni3 pagineIt shows how genetics discover from different people.
Titolo originale
Timeline of Genetics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoIt shows how genetics discover from different people.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
96 visualizzazioni3 pagineHistory of Genetics Timeline: Jo Ann Lane
Caricato da
Chairmane BurceIt shows how genetics discover from different people.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 3
Lane, Jo Ann.
Access Excellence @ the national health museum , 1994,
www.accessexcellence.org/AE/AEPC/WWC/1994/geneticstln.html .
History of Genetics Timeline
Jo Ann Lane
1994 Woodrow Wilson Collection
As scientists sought to understand more about the nature of inheritance of traits, hereditary
processes were explained in ever increasing detail beginning at the populational level and
going toward the molecular level. Keeping this fact in mind will help in understanding the
timeline which follows.
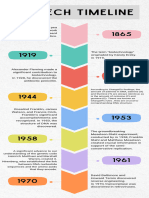
Year Scientist(s) Discovery
Charles Darwin Joint announcement of the theory of natural selection-that
1858 Alfred Russel members of a population who are better adapted to the
Wallace environment survive and pass on their traits.
1859 Charles Darwin Published The Origin of Species.
Published the results of his investigations of the inheritance
1866 Gregor Mendel
of "factors" in pea plants.
Carl Correns Hugo
Mendel's principles were independently discovered and
1900 de Vries Erich von
verified, marking the beginning of modern genetics.
Tschermak
Pointed out the interrelationships between cytology and
1902 Walter Sutton Mendelism, closing the gap between cell morphology and
heredity.
Nettie Stevens Independently described the behavior of sex chromosomes-
1905
Edmund Wilson XX determines female; XY determines male.
Proposed that some human diseases are due to "inborn errors
1908 Archibald Garrod
of metabolism" that result from the lack of a specific enzyme.
Proposed a theory of sex-linked inheritance for the first
Thomas Hunt mutation discovered in the fruit fly, Drosophila, white eye.
1910
Morgan This was followed by the gene theory, including the principle
of linkage.
1927 Hermann J. Muller Used x-rays to cause artificial gene mutations in Drosophila.
Proposed that some unknown "principle" had transformed the
1928 Fred Griffith
harmless R strain of Diplococcus to the virulent S strain.
Harriet B.
Demonstrated the cytological proof for crossing-over in
1931 Creighton
maize.
Barbara McClintock
George Beadle Irradiated the red bread mold, Neurospora, and proved that
1941
Edward Tatum the gene produces its effect by regulating particular enzymes.
Oswald Avery
Reported that they had purified the transforming principle in
1944 Colin MacLeod
Griffith's experiment and that it was DNA.
Maclyn McCarty
Organized a phage course at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory
which was taught for 26 consecutive years. This course was
1945 Max Delbruck
the training ground of the first two generations of molecular
biologists
late Developed the hypothesis of transposable elements to explain
Barbara McClintock
1940s color variations in corn.
Discovered a one-to-one ratio of adenine to thymine and
1950 Erwin Chargaff guanine to cytosine in DNA samples from a variety of
organisms.
1951 Rosalind Franklin Obtained sharp X-ray diffraction photographs of DNA.
Used phages in which the protein was labeled with 35S and
Martha Chase
1952 the DNA with 32P for the final proof that DNA is the
Alfred Hershey
molecule of heredity.
Francis Crick
1953 Solved the three-dimensional structure of the DNA molecule.
James Watson
Matthew Meselson Used isotopes of nitrogen to prove the semiconservative
1958
Frank Stahl replication of DNA.
Purified DNA polymerase I from E. coli, the first enzyme
1958 Arthur Kornberg
that made DNA in a test tube.
Marshall Nirenberg Led teams that cracked the genetic code- that triplet mRNA
1966
H. Gobind Khorana codons specify each of the twenty amino acids.
Hamilton Smith Isolated the first restriction enzyme, HindII, that could cut
1970
Kent Wilcox DNA molecules within specific recognition sites.
Paul Berg
1972 Produced the first recombinant DNA molecules.
Herb Boyer
Led the team at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory that refined
1973 Joseph Sambrook DNA electrophoresis by using agarose gel and staining with
ethidium bromide.
Annie Chang Showed that a recombinant DNA molecule can be maintained
1973
Stanley Cohen and replicated in E. coli.
International meeting at Asilomar, California urged the
1975 adoption of guidelines regulating recombinant DNA
experimentation.
Developed the chain termination (dideoxy) method for
1977 Fred Sanger
sequencing DNA.
The first genetic engineering company (Genentech) is
1977 founded, using recombinant DNA methods to make
medically important drugs.
Somatostatin became the first human hormone produced
1978
using recombinant DNA technology.
Three independent research teams announced the discovery
1981
of human oncogenes (cancer genes).
Used blood samples collected by Nancy Wexler and her co-
1983 James Gusella workers to demonstrate that the Huntington's disease gene is
on chromosome 4.
Published a paper describing the polymerase chain reaction
1985 Kary B. Mullis
(PCR), the most sensitive assay for DNA yet devised.
The Human Genome Project began with the goal of
1988 determining the entire sequence of DNA composing human
chromosomes.
Coined the term DNA fingerprinting and was the first to use
1989 Alec Jeffreys DNA polymorphisms in paternity, immigration, and murder
cases.
Identified the gene coding for the cystic fibrosis
Francis Collins
1989 transmembrane conductance regulator protein (CFTR) on
Lap-Chee Tsui
chromosome 7 that, when mutant, causes cystic fibrosis.
First gene replacement therapy-T cells of a four-year old girl
were exposed outside of her body to retroviruses containing
1990
an RNA copy of a normal ADA gene. This allowed her
immune system to begin functioning.
FlavrSavr tomatoes, genetically engineered for longer shelf
1993
life, were marketed.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- History of GeneticsDocumento1 paginaHistory of GeneticsSofia Rose EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- TimelineDocumento2 pagineTimelineapi-282582740Nessuna valutazione finora
- Origin and Importance of GeneticsDocumento12 pagineOrigin and Importance of Geneticshuyenthanh1807100% (1)
- Genetic Time LineDocumento13 pagineGenetic Time LineMark WilliamsNessuna valutazione finora
- Year Researcher Contribution/DiscoveryDocumento4 pagineYear Researcher Contribution/DiscoveryJenny SecangNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1.1Documento70 pagineChapter 1.1AS2012B2 FATIN NUR AQILAH BINTI DAZALINessuna valutazione finora
- Biotech-Genetic Sci. TimelineDocumento4 pagineBiotech-Genetic Sci. TimelinedreyyNessuna valutazione finora
- Pangenesis: Using Synthesized Aniline Dyes To Identify Chromosomes, The Structures of The Cell NucleusDocumento3 paginePangenesis: Using Synthesized Aniline Dyes To Identify Chromosomes, The Structures of The Cell NucleusRei HarredNessuna valutazione finora
- Cytogen ReviewerDocumento4 pagineCytogen ReviewerSophia Mae ClavecillaNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA TimelineDocumento2 pagineDNA TimelineMinaMilićNessuna valutazione finora
- Recent Breakthroughs in GeneticsDocumento3 pagineRecent Breakthroughs in GeneticsnmaarsNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Genetics Timeline: by Waleed CheemaDocumento7 pagineHistory of Genetics Timeline: by Waleed CheemaWC - 12MA 669502 Central Peel SSNessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular Biology and Microbial GeneticsDocumento30 pagineMolecular Biology and Microbial GeneticsManideepVendraNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics History TimelineDocumento13 pagineGenetics History Timelinerengachen100% (1)
- جزيئيةDocumento3 pagineجزيئيةغروري في صمتيNessuna valutazione finora
- Mapping, Sequencing, and Analysis of Genomes. Genomics Looks at TheDocumento3 pagineMapping, Sequencing, and Analysis of Genomes. Genomics Looks at TheJ Patrick LorenzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sr. No. Name Nationality Profession Book Discovery Speciality 1 2 3 4 5 6 Unit 6Documento3 pagineSr. No. Name Nationality Profession Book Discovery Speciality 1 2 3 4 5 6 Unit 6Dashrath KarkiNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics HistoryDocumento3 pagineGenetics HistoryErille GomezNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetic Code - Wikipedia DiscoveryDocumento2 pagineGenetic Code - Wikipedia Discoveryapi-243852896Nessuna valutazione finora
- Proyecto Quimica ArticuloDocumento20 pagineProyecto Quimica ArticuloIsabel MerchanNessuna valutazione finora
- History of GeneticsDocumento2 pagineHistory of GeneticsDianne JoyNessuna valutazione finora
- References:: 1-Essen4al of Molecular Biology by George M. Malacinski 4 Edi4on 2Documento19 pagineReferences:: 1-Essen4al of Molecular Biology by George M. Malacinski 4 Edi4on 2Ibrahim QariNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1Documento47 pagineUnit 1Ansh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Structure and DiscoveryDocumento65 pagineDNA Structure and DiscoveryMyldred ClaravallNessuna valutazione finora
- History of GeneticsDocumento4 pagineHistory of GeneticsJanine FandaganiNessuna valutazione finora
- 1038751-Mol Bio Kecture 1Documento26 pagine1038751-Mol Bio Kecture 1rohith sai enNessuna valutazione finora
- Nucleotides, nucleic acids and the genetic material explainedDocumento41 pagineNucleotides, nucleic acids and the genetic material explainedMario Mallare AbesamisNessuna valutazione finora
- Biotechnology: Quar TerDocumento5 pagineBiotechnology: Quar TerShanaia Kaye Bais PamintuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Biotechnology TimelineDocumento1 paginaBiotechnology Timelinesophtzu9Nessuna valutazione finora
- KLP 4 Modern BioteknoDocumento7 pagineKLP 4 Modern BioteknoSakina Ayu PutriNessuna valutazione finora
- Biotechnology Years Micah MemorizationDocumento2 pagineBiotechnology Years Micah MemorizationMNJJ.LNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Genetics-1Documento10 pagineHistory of Genetics-1Jacqueline Rose Alipo-onNessuna valutazione finora
- BIO302 PPT SlidesDocumento287 pagineBIO302 PPT SlidesTayyaba ArbabNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics: The Science of Heredity and VariationDocumento8 pagineGenetics: The Science of Heredity and VariationMikeNessuna valutazione finora
- History of GeneticsDocumento53 pagineHistory of GeneticsJaycel SamanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Molecular Biology StoryDocumento9 pagineThe Molecular Biology StoryVideo ProjectsNessuna valutazione finora
- Inbound 3939766930476133732Documento59 pagineInbound 3939766930476133732Hana MarieNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Molecular BiologyDocumento18 pagineHistory of Molecular Biologysubhash nayak100% (1)
- Bio 8. Timelines in History of GeneticsDocumento4 pagineBio 8. Timelines in History of GeneticsDiasanta, Dylan Y.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Module+1+ +Introduction+to+CytogeneticsDocumento3 pagineModule+1+ +Introduction+to+CytogeneticsAngelica Camille B. AbaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cytogenetics: Genetics Seek To UnderstandDocumento12 pagineCytogenetics: Genetics Seek To UnderstandMyukee ConcepcionNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To GeneticsDocumento38 pagineIntroduction To GeneticsCaptain WolfNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Dna - ScientistsDocumento21 pagineHistory of Dna - Scientistsapi-244168124Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dna Structure and Classic Experiment EarlDocumento2 pagineDna Structure and Classic Experiment EarlEarl TrinidadNessuna valutazione finora
- SCIENTISTS Biology 11 and 12Documento3 pagineSCIENTISTS Biology 11 and 12MARSHMALLOW GAMINGNessuna valutazione finora
- The Existence of GenesDocumento2 pagineThe Existence of GenesMrMarkitosNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer 7 ScienceDocumento7 pagineReviewer 7 ScienceJhanna Gil BuctolanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Human Genetic Code The Human Genome Codeand Beyond FS24Documento6 pagineThe Human Genetic Code The Human Genome Codeand Beyond FS24Marie Serena McConnellNessuna valutazione finora
- Important Scientists and Their ContributionsDocumento3 pagineImportant Scientists and Their Contributionschannel of dhyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Timeline of The Discovery of DNA: Cell-NucleiDocumento4 pagineTimeline of The Discovery of DNA: Cell-NucleiElton John TubaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 2intro HistoryDocumento12 pagine1 2intro HistoryAlfina Victoria Fumera CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Biotechnology TimelineDocumento4 pagineBiotechnology TimelineGaybrielle Asha BombalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec2 Genetic TimelineDocumento28 pagineLec2 Genetic TimelineSITI BAZILAH BINTI BILAK KPM-GuruNessuna valutazione finora
- ChemistryDocumento35 pagineChemistryMaruti GoudaNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of Nuclear Genetic Material - Dna, Rna and Gene: CourseDocumento65 pagineStructure of Nuclear Genetic Material - Dna, Rna and Gene: Coursebharath margamNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Important DiscoveriesDocumento9 pagine3 Important Discoveriesomar.villanueva.b21Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dna TimelineDocumento4 pagineDna Timeline228500Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Genomics Age (Review and Analysis of Smith's Book)Da EverandThe Genomics Age (Review and Analysis of Smith's Book)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Eucaryotic Gene RegulationDa EverandEucaryotic Gene RegulationRichard AxelNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review of Detection Methods For The Plant VirusesDocumento9 pagineA Review of Detection Methods For The Plant VirusesMayra GameroNessuna valutazione finora
- NSSBIO3E HKDSE Analysis 2021 Ts eDocumento13 pagineNSSBIO3E HKDSE Analysis 2021 Ts ekatie yuNessuna valutazione finora
- Acanthamoeba Strains Isolated From Organs of Freshwater FishesDocumento8 pagineAcanthamoeba Strains Isolated From Organs of Freshwater FishestishaNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Biology - Principles of Inheritance and Variations - Notes (Part I)Documento13 pagine12 Biology - Principles of Inheritance and Variations - Notes (Part I)Jayadevi ShanmugamNessuna valutazione finora
- 6nucleic Acids PDFDocumento52 pagine6nucleic Acids PDFNica Lyca MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- ElectrophoresisDocumento32 pagineElectrophoresismadhaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Reflection On Biorisk ManagementDocumento2 pagineReflection On Biorisk ManagementqueenNessuna valutazione finora
- First Draft Phage TherapyDocumento16 pagineFirst Draft Phage Therapyapi-324155293Nessuna valutazione finora
- VAIBHAVDocumento1 paginaVAIBHAVUpadhayayAnkurNessuna valutazione finora
- A KaryotypeDocumento2 pagineA KaryotypeHOLA AHORANessuna valutazione finora
- Actina 1Documento2 pagineActina 1Anonymous yeHhCYNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal Tentang Nipah VirusDocumento6 pagineJurnal Tentang Nipah VirusSosial EkonomiNessuna valutazione finora
- Video Recap of Codon Chart Video Companion by Amoeba SistersDocumento2 pagineVideo Recap of Codon Chart Video Companion by Amoeba SistersJack From State Farm67% (3)
- CTD 05-2008 en PDFDocumento303 pagineCTD 05-2008 en PDFMarija MarinkovićNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics1 MbbsDocumento32 pagineGenetics1 MbbsSubham YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOC15 Summer Genetics Course Syllabus Dr. Clare HasenkampfDocumento5 pagineBIOC15 Summer Genetics Course Syllabus Dr. Clare HasenkampfforbioNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet16 Transcription To TranslationDocumento3 pagineWorksheet16 Transcription To Translationliterally deadNessuna valutazione finora
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of DNA PDFDocumento5 pagineAgarose Gel Electrophoresis of DNA PDFBiologistAhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Xii Biology Marking Scheme Pre Board Examination Term - 2Documento8 pagineXii Biology Marking Scheme Pre Board Examination Term - 2N GirishmaNessuna valutazione finora
- HERU SETIAWAN-Week-4 Assigment Gene InteractionDocumento2 pagineHERU SETIAWAN-Week-4 Assigment Gene InteractionHeru SetiawanNessuna valutazione finora
- GDR - Poc Update (01.07.21)Documento2 pagineGDR - Poc Update (01.07.21)Dr ThietNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz 10 - Modern TechniquesDocumento2 pagineQuiz 10 - Modern Techniqueswilly wonka0% (1)
- European Journal of Pharmacology: Yeuan Ting Lee, Yi Jer Tan, Chern Ein Oon TDocumento9 pagineEuropean Journal of Pharmacology: Yeuan Ting Lee, Yi Jer Tan, Chern Ein Oon TVishal BondeNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 Protein TroubleshootingDocumento3 pagine8 Protein Troubleshootingசுப விஜய் ப்ரீத்திNessuna valutazione finora
- Current State of Alzheimer'S Disease Research and TherapeuticsDocumento382 pagineCurrent State of Alzheimer'S Disease Research and TherapeuticsyusufNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategy For Solving Restriction Digestion ProblemsDocumento2 pagineStrategy For Solving Restriction Digestion ProblemsPranav tembe100% (4)
- (PRINTING) Science 7 Summative Test 3Documento2 pagine(PRINTING) Science 7 Summative Test 3JoelmarMondonedoNessuna valutazione finora
- Vaccines For COVID-19 - The Current State of Play PDFDocumento8 pagineVaccines For COVID-19 - The Current State of Play PDFdiana.alyNessuna valutazione finora
- CellDocumento5 pagineCellsumitkguptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Test - IB Biology 10.1 - QuizletDocumento4 pagineTest - IB Biology 10.1 - QuizletSumi VjNessuna valutazione finora