Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Güç Elektroniği Vize Soru Ve Çözüm
Caricato da
Aslax İTUCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Güç Elektroniği Vize Soru Ve Çözüm
Caricato da
Aslax İTUCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1. Some concepts which are related with DC-DC power converters are given.
Briefly explain;
a) “duty cycle”, “switching frequency”, “output voltage ripple” and “inductor volt-second balance”.
b) “continuous (CCM)”, “boundary (BCM)” and “discontinuous (DCM)” conduction modes. What are the
characteristic properties of these modes? Sketch three identical current waveforms for every mode. How do load
resistor (R), inductor (L) and switching frequency (fs) values affect the operation modes?
2. What is a magnetically coupled DC-DC power converter? What are the main advantages and disadvantages of using
transformers in power converters? Sketch the circuit schema of the “flyback” and “forward” converters. Explain the
main differences between these two converters?
3. Propose a suitable power converter for given applications and explain why.
a) 12V to 24V battery charger with isolation.
b) Low ripple input current MPPT converter for PV modules.
c) 200V to 5V LED driver with constant output current.
d) 12V to -5V converter for analog IC power supplies.
e) Power Factor Correction converter with continuous input current.
4. A CCM buck converter is suitable for “constant output current” battery charger applications. Design a 36V to 24V
battery charger with constant 9A output current. Battery voltage varies 20V to 28V between empty and charged states.
Inductor and switching frequency values are given L = 200µH and fs = 100kHz.
a) Calculate output power (Po), average input current (Id) and duty cycle (D) for empty and charged conditions.
b) Calculate peak-to-peak inductor current ripple (ΔiL) for empty and charged conditions.
c) Plot the input current waveforms for empty and charged conditions.
d) For the worst case, plot the capacitor current and calculate the required capacitor value to obtain Δvo = 0.25V.
5. An electronic device with 15V / 7A ratings is supplied by a 12V battery through a DCM buck-boost converter.
Switching frequency of the converter is given as 20kHz.
a) Calculate the critical inductor value (Lcrit) for this converter?
b) Select L = 0.75*Lcrit and calculate D, Δ1 and Δ2 values.
c) Plot the inductor current and inductor voltage waveforms, calculate maximum inductor current value.
d) Plot the capacitor current and calculate the required capacitor value to obtain Δvo/Vo = 1%.
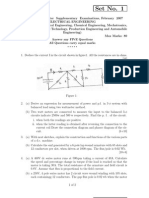
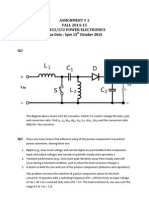
6. A different DC-DC power converter is given at the figure. Assume CCM;
DTs : main switch ON – diode OFF
D’Ts : main switch OFF – diode ON
a) Sketch two sub-circuits for DTs and D’Ts time intervals and find inductor
voltage values for these sub-circuits.
b) Apply inductor volt-second balance and calculate the voltage conversion
ratio of the converter. Which type of a converter is this?
c) What is the average value of inductor current? Find an expression for
peak-to-peak inductor current ripple, maximum and minimum values of
inductor current.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Learn to Design a High-Frequency Power Transformer Using Forward TopologyDocumento3 pagineLearn to Design a High-Frequency Power Transformer Using Forward TopologyNiranjan kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Line Commutated Converters ExplainedDocumento10 pagineLine Commutated Converters ExplainedJay Romar PabianiaNessuna valutazione finora
- DADocumento40 pagineDAkrishneel sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Power System PPT On CORONADocumento13 paginePower System PPT On CORONAg4ubhNessuna valutazione finora
- Device Coordination PDFDocumento89 pagineDevice Coordination PDFMothafukin MorrisseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Neutral Point ShiftDocumento24 pagineNeutral Point Shiftscrib_111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Elektri̇k Maki̇nalari Ders Notlari (Z.öztürk)Documento41 pagineElektri̇k Maki̇nalari Ders Notlari (Z.öztürk)llbilgekaganll83% (6)
- Microconverter 12-Bit Adcs and Dacs With Embedded High Speed 62-Kb Flash Mcu Aduc841/Aduc842/Aduc843Documento88 pagineMicroconverter 12-Bit Adcs and Dacs With Embedded High Speed 62-Kb Flash Mcu Aduc841/Aduc842/Aduc843qhan90100% (1)
- Biopotential AmplifiersDocumento15 pagineBiopotential AmplifiersJesus PeñaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Lecture On Autotransformers For Power Engineering StudentsDocumento6 pagineA Lecture On Autotransformers For Power Engineering StudentsBojanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 InvertersDocumento86 pagineUnit 4 InvertersHaritha RkNessuna valutazione finora
- Intermolecular Forces: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Chemistry 2 Quarter 3 - Module 1 - AY 2021 - 2022Documento6 pagineIntermolecular Forces: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Chemistry 2 Quarter 3 - Module 1 - AY 2021 - 2022almafebe caselNessuna valutazione finora
- Solutions Manual For: Arm Assembly LanguageDocumento129 pagineSolutions Manual For: Arm Assembly Languagemohammed IrheemNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Line Communication TechniqueDocumento6 paginePower Line Communication TechniqueVikas AsodariyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 08 Power System Transients (KP)Documento68 pagine08 Power System Transients (KP)Prabu KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Otomatik Kontrol - Benjamin C.Kuo Ders Notları PDFDocumento960 pagineOtomatik Kontrol - Benjamin C.Kuo Ders Notları PDFEEM Ders Notları100% (5)
- Power Electronics: DR - Arkan A.Hussein Power Electronics Fourth ClassDocumento13 paginePower Electronics: DR - Arkan A.Hussein Power Electronics Fourth Classmohammed aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Parameters of OpampDocumento15 pagineParameters of OpampcutesandNessuna valutazione finora
- Serway PSE Quick ch27Documento15 pagineSerway PSE Quick ch27Julio S. RendónNessuna valutazione finora
- Rr210303-Electrical-Engineering Feb 2007Documento8 pagineRr210303-Electrical-Engineering Feb 2007devineni100% (1)
- SCR and Thyristor Triggering Methods and Commutation TechniquesDocumento14 pagineSCR and Thyristor Triggering Methods and Commutation TechniquesmalathynarayaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Double Frequency Buck ConverterDocumento36 pagineDouble Frequency Buck ConverterSanthosh Guduru100% (1)
- Voltage Regulation of 3-Phase Alternator by ZPF and ASA MethodsDocumento6 pagineVoltage Regulation of 3-Phase Alternator by ZPF and ASA Methods61EEPrabhat PalNessuna valutazione finora
- EE 201 - HW 1 Solutions W2007Documento11 pagineEE 201 - HW 1 Solutions W2007mrm3zaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Drives and Control for AutomationDocumento2 pagineElectrical Drives and Control for AutomationMathews P RejiNessuna valutazione finora
- A Bridgeless Totem-Pole Interleaved PFC Converter For Plug-In Electric Vehicles PDFDocumento4 pagineA Bridgeless Totem-Pole Interleaved PFC Converter For Plug-In Electric Vehicles PDFLeMeniz InfotechNessuna valutazione finora
- Bridgeless PFC TopologiesDocumento8 pagineBridgeless PFC Topologiessolid690Nessuna valutazione finora
- DC-DC Converter: Understanding Buck-Boost Topology and Its LimitationsDocumento13 pagineDC-DC Converter: Understanding Buck-Boost Topology and Its LimitationsnasiruddinNessuna valutazione finora
- EE308 Electric DrivesDocumento2 pagineEE308 Electric DriveselecenggNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 Lecture 1 - 4Documento17 pagineModule 1 Lecture 1 - 4ukassyahNessuna valutazione finora
- On AC Voltage ControllersDocumento25 pagineOn AC Voltage ControllersSahil ChoudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Push Pull ConvertersDocumento44 paginePush Pull ConvertersRaminNessuna valutazione finora
- 9a02308 Electrical Mechines IDocumento4 pagine9a02308 Electrical Mechines IsivabharathamurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Waveguides Written ReportDocumento10 pagineWaveguides Written Reporttareq omarNessuna valutazione finora
- Boost DesignDocumento4 pagineBoost DesignmuthukumartharaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Emailing 300 TOP Operational Amplifiers Questions and Answers OP-AMP - PDF Version 1Documento15 pagineEmailing 300 TOP Operational Amplifiers Questions and Answers OP-AMP - PDF Version 1Jesan tonikNessuna valutazione finora
- Using PIC Microcontrollers to Control Triacs PhaseDocumento22 pagineUsing PIC Microcontrollers to Control Triacs PhaseMarko Lukic100% (1)
- Haberleşme Sistemleri - Kocaeli Üniversitesi Sarp Ertürk Ders NotlarıDocumento197 pagineHaberleşme Sistemleri - Kocaeli Üniversitesi Sarp Ertürk Ders NotlarıEEM Ders Notları20% (5)
- Wide Swing Cascode Current MirrorDocumento4 pagineWide Swing Cascode Current MirrorSunil M. PaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Electro-technical and Marine Electrical Work Questions - Part 2Documento10 pagineElectro-technical and Marine Electrical Work Questions - Part 2serkan1234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hopkinson'S Test: Technical Manual FORDocumento6 pagineHopkinson'S Test: Technical Manual FORNitish BhardwajNessuna valutazione finora
- PUT Experiment EditedDocumento9 paginePUT Experiment EditedReineirDuranNessuna valutazione finora
- Boost ConveterDocumento27 pagineBoost ConveterMohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- DC - Ac Inv.Documento82 pagineDC - Ac Inv.Jegadeeswari GNessuna valutazione finora
- Signals and Amplifiers ExplainedDocumento71 pagineSignals and Amplifiers ExplainedJaveria ZaidiNessuna valutazione finora
- EE328 Final Exam ProblemsDocumento4 pagineEE328 Final Exam ProblemsFawzi Radwan100% (1)
- Unsymmetrical Fault AnalysisDocumento49 pagineUnsymmetrical Fault AnalysisabdulbabulNessuna valutazione finora
- Special Electrical Machines SyllabusDocumento2 pagineSpecial Electrical Machines SyllabusSubhadra Devi. PNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Paper - Load BlinderDocumento9 pagine5 Paper - Load BlindermubarakkirkoNessuna valutazione finora
- Control Relay with ArduinoDocumento5 pagineControl Relay with ArduinoMallikarjun RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.to Find Voltage Regulation of Single Phase TransformerDocumento7 pagine1.to Find Voltage Regulation of Single Phase Transformershahabrandhawa50% (2)
- Ge2151 Beee NotesDocumento143 pagineGe2151 Beee NotesNanda Subramanian100% (1)
- Zener DiodeDocumento6 pagineZener DiodeKumar shantanu BasakNessuna valutazione finora
- Double Frequency Buck ConverterDocumento68 pagineDouble Frequency Buck ConverterSanthosh GuduruNessuna valutazione finora
- AE LAB - Experiment No.2-1Documento4 pagineAE LAB - Experiment No.2-1Prajwal PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- 08 BJT ModelDocumento10 pagine08 BJT ModelMeenakshi VenkataramanNessuna valutazione finora
- DC to DC Converter FundamentalsDocumento40 pagineDC to DC Converter FundamentalsJamir CalNessuna valutazione finora
- Switch Gear Functions and ComponentsDocumento6 pagineSwitch Gear Functions and ComponentsAdeel Mustafa100% (1)
- Assignment 2Documento2 pagineAssignment 2Anonymous m8duka3qUNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment2 NewdocxDocumento3 pagineAssignment2 NewdocxAstinSohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Paper 1 IITD Power ElectronicsDocumento1 paginaSample Paper 1 IITD Power ElectronicsSambeet PanigrahiNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 04 Power ElectronicsDocumento3 pagineAssignment 04 Power ElectronicsTayyab Hussain0% (1)
- Ee270 HW2Documento7 pagineEe270 HW2saiedali2005Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assignmnet 02 RevisedDocumento3 pagineAssignmnet 02 RevisedBilal Ayub100% (1)
- Product Data Sheet: Acti 9 Idpna Vigi - Rcbo - 1P+N - 16A - C Curve - 4500A - 30ma - Type AcDocumento3 pagineProduct Data Sheet: Acti 9 Idpna Vigi - Rcbo - 1P+N - 16A - C Curve - 4500A - 30ma - Type AcFede MysynaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Weight Volume Relationships For StudentsDocumento35 pagineChapter 3 Weight Volume Relationships For StudentsHahahahahahahahahaNessuna valutazione finora
- anualCMOSMixed SignalCircuitDesign2ndEdJacobBaker PDFDocumento374 pagineanualCMOSMixed SignalCircuitDesign2ndEdJacobBaker PDFMonideepika SNessuna valutazione finora
- Gate Chemical 2008Documento12 pagineGate Chemical 2008Adil RiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Non-Standard Models and The Sociology of Cosmology (Lopez Corredoira)Documento41 pagineNon-Standard Models and The Sociology of Cosmology (Lopez Corredoira)Dr Abhas MitraNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Atomization Quality On Lean Blow Out Limits and Acoustic Oscillations in A Swirl Stabilized BurnerDocumento26 pagineEffect of Atomization Quality On Lean Blow Out Limits and Acoustic Oscillations in A Swirl Stabilized Burnermechmuthu1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Modelling A Linear and Limited Travel SolenoidDocumento6 pagineModelling A Linear and Limited Travel SolenoidsayproNessuna valutazione finora
- Units and Dimensions: Introduction To Chemical Engineering CalculationsDocumento24 pagineUnits and Dimensions: Introduction To Chemical Engineering Calculationsrazanmk961214Nessuna valutazione finora
- Holip 201207110500417645Documento105 pagineHolip 201207110500417645Jose Sanchez Palma100% (2)
- Vibration Switches Modelo 365 e 366Documento1 paginaVibration Switches Modelo 365 e 366cleitonmoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Led 3 MM - DatasheetDocumento6 pagineLed 3 MM - DatasheetKroscop San Martin de LunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Catalogo Hedland - FlussometriDocumento84 pagineCatalogo Hedland - Flussometrisixin93551Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reaffirmed 2019Documento8 pagineReaffirmed 2019Ashish DubeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Differences Between Salient Pole and Non-Salient Pole Synchronous MachinesDocumento25 pagineDesign Differences Between Salient Pole and Non-Salient Pole Synchronous MachinesHiren KapadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Super X/Xi Series VRF: Variable Refrigerant Flow SystemsDocumento104 pagineSuper X/Xi Series VRF: Variable Refrigerant Flow SystemsIván CovarrubiasNessuna valutazione finora
- Lagrangian method introductionDocumento8 pagineLagrangian method introductionAhmed Saad SabitNessuna valutazione finora
- Moroccan Ministry of EnergyDocumento2 pagineMoroccan Ministry of EnergySiyuan SunNessuna valutazione finora
- Differences Between Vcs and Vas Based On Diff ParametersDocumento2 pagineDifferences Between Vcs and Vas Based On Diff Parametersdhanashree chavanNessuna valutazione finora
- ES.1803 Topic 25 Notes: Jeremy OrloffDocumento17 pagineES.1803 Topic 25 Notes: Jeremy OrloffPeper12345Nessuna valutazione finora
- Volume 3 of 3 - Package-2Documento56 pagineVolume 3 of 3 - Package-2Pranoy BaruaNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermon HPTDocumento2 pagineThermon HPTParag B HatwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal properties of solids: Debye's modelDocumento22 pagineThermal properties of solids: Debye's modelVishu DespoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anomalous Skin Effect (Apr 27, 2022)Documento2 pagineAnomalous Skin Effect (Apr 27, 2022)Jay BhattacharyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Laws & TheoremsDocumento14 pagineNetwork Laws & Theoremstroy guillNessuna valutazione finora
- LTspice - IV PresentationDocumento263 pagineLTspice - IV PresentationrobertNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnetic Forces, Materials, and DevicesDocumento18 pagineMagnetic Forces, Materials, and DevicesJefry Pasaribu GoratNessuna valutazione finora