Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
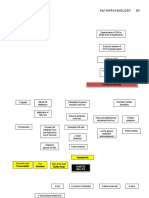
Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart Disease
Caricato da
jonel lorenzoTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart Disease
Caricato da
jonel lorenzoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart Disease
Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors:
Etiology
Family history of RHD Environmental factors
Group A Beta-
Age (5-15 years old) Low Socioeconomic Status
Hemolytic
Past history of Rheumatic Geographical Location
Streptococcus
Fever
Bacteria invades the upper
respiratory tract (tonsils and
pharynx)
Inflammation of affected tissues
Macrophages attack bacteria, and then Production of Cytokines, TNF,
present its antigen to the immune system Endogenous Pyrogens (IL 1 and IL 6)
Production of antibodies (IgG & IgM) Release of Prostaglandin Stimulation of liver to produce
E2 acute phase proteins
Activation of complement system, opsonic
Increased thermostat point
phagocytosis, production of NK cells to Increased C Increased
in the hypothalamus
combat pathogens Reactive Fibrinogen
Protein
Increased thermostat point
Immune system cross-reacts and causes in the hypothalamus RBCs stick
tissue injury to normal body cells due to together
Molecular Mimicry (rouleaux)
Increased body
temperature
Multi-systemic effects Increased
Hyperthermia Erythrocyte
Sedimentation
A Rate (ESR)
A
Immune system cross- Immune system Immune system Immune system Immune system
reacts with Basal Ganglia cross-reacts with cross-reacts with Skin cross-reacts with cross-reacts with
Synovial membrane subcutaneous tissue myocardial tissue
Disruption in Presence of ring-like
motor signals Leakage of plasma lesions (Erythema Presence of
proteins and fluid Marginatum) subcutaneous
nodules
Involuntary muscle
contractions Swelling of the joint
(Sydenham’s Chorea)
Compression of
nerve endings Endocarditis Pericarditis Myocarditis
Pain and tenderness Mechanical injury Increased Myocardium loses
of the joint caused by permeability of its contractility
inflammation and capillaries
tachycardia
Arthritis migrates Decreased Cardiac E
upward to different Shifting of plasma Output
joints Erosion of mitral and fibrinogen to
valve leaflets pericardial sac
Decreased Perfusion
Migratory
Polyarthritis Aggregation of Swelling of
platelets and fibrin pericardium Sympathetic
along the valve Response: Increased
Heart Rate, Increased
C Contractility,
Vasoconstriction
Fomation of vegetations along
the edges of the leaflets
D
B
B C D
Vegetations heal Increased Residual Volume of LV
with fibrosis and Pericardial Increased
calcifications layers rub pressure on
Increased Pressure in LV
each other parietal
Permanent pericardium
Dilatation/Hypertrophy of LV
distortions of the
Pericardial
leaflets of the valve
friction rub on Compression
auscultation Increased Volume in LA
of nerves
Mitral Stenosis Mitral Regurgitation
Increased Volume in Pulmonary Vein
Sharp, stabbing
F
localized pain
Increased Pressure in
Pulmonary
E Pulmonary capillary bed
Decreased CO despite edema, dyspnea
compensatory mechanisms
Pulmonary
Hypertension
Decreased Heart Rate
Cardiogenic shock Increased Pressures in the RV and RA
Hypoperfusion Dilatation/Hypertrophy of RV
Hypoxia Cor Pulmonale
Multi-organ failure
F
DEATH
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Essentials of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2nd Ed. - W. Frontera, Et. Al., (Saunders, 2008) WW PDFDocumento847 pagineEssentials of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2nd Ed. - W. Frontera, Et. Al., (Saunders, 2008) WW PDFRecuperare100% (9)
- Clinical MedicineDocumento18 pagineClinical MedicineRishikesh AsthanaNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Kombucha Tea?Documento12 pagineWhat Is Kombucha Tea?starprideNessuna valutazione finora
- Cultural, Social, Political Change and Responses To Change: Carl Justin Bailon Cidny Calimag Kate CastilloDocumento18 pagineCultural, Social, Political Change and Responses To Change: Carl Justin Bailon Cidny Calimag Kate Castillojonel lorenzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology-Threatened MiscarriageDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology-Threatened MiscarriageMoses Gabriel ValledorNessuna valutazione finora
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Psycho-Oncology - The 6 Phases of Cancer EbookDocumento101 paginePsycho-Oncology - The 6 Phases of Cancer EbookAndré Amorim100% (2)
- FNCP FinaaaalDocumento5 pagineFNCP FinaaaalSoniaMarieBalanay0% (1)
- Tetanus PathoDocumento3 pagineTetanus PathoElisha Gine AndalesNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 ElementDocumento4 pagine5 ElementkayrodeNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology-AppendicitisDocumento3 pagineAnatomy and Physiology-AppendicitisMaria Socorro Sismundo DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Practice Test/Exam About Communicable Diseases (NLE 1-20)Documento4 pagineNursing Practice Test/Exam About Communicable Diseases (NLE 1-20)jay5ar5jamorabon5torNessuna valutazione finora
- CKD - For Concept MappingDocumento7 pagineCKD - For Concept MappingKennette Lim0% (1)
- CHN EvaluationDocumento6 pagineCHN EvaluationDarlyn DocogNessuna valutazione finora
- RHD PathophysiologyDocumento3 pagineRHD PathophysiologyRichmond LacadenNessuna valutazione finora
- ABRUPTIO PLACENTAE PathophysiologyDocumento3 pagineABRUPTIO PLACENTAE PathophysiologyBarda GulanNessuna valutazione finora
- H MoleDocumento2 pagineH MoleJoanna Marie Datahan EstomoNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Rheumatic Fever PathophysiologyDocumento1 paginaAcute Rheumatic Fever PathophysiologyMoonyeen Jann Casera BalicNessuna valutazione finora
- Inp Eval ExamDocumento3 pagineInp Eval Examd1choosenNessuna valutazione finora
- Adult HealthDocumento28 pagineAdult HealthL1NEDS DNessuna valutazione finora
- Dela Rosa 2A MCN-Module 05Documento2 pagineDela Rosa 2A MCN-Module 05Atsu MiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are The Functions of Informed ConsentDocumento2 pagineWhat Are The Functions of Informed ConsentKyla Angeli InfantadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture NCM 109Documento11 pagineLecture NCM 109Evangeline Anne MacanasNessuna valutazione finora
- Schistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Documento10 pagineSchistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Tiger Knee100% (1)
- Pneumonia PathoDocumento2 paginePneumonia PathoDerick Nyl PascualNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz LeukemiaDocumento4 pagineQuiz LeukemiaHanna La MadridNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: AnatomyDocumento76 pagineThe Cardiovascular System: The Heart: AnatomyDeepuNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Pressure Measurement Is An Important Part of The Patient's Data Base. It Is Considered To BeDocumento1 paginaBlood Pressure Measurement Is An Important Part of The Patient's Data Base. It Is Considered To BeMir MirNessuna valutazione finora
- FINALS ReviewerDocumento14 pagineFINALS ReviewerJustine Simeon lagunzadNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Scenario - NebulizationDocumento2 pagineCase Scenario - NebulizationHilario. Hayascent.Reign.M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care in MR.X With Urinary Retention: Disusun OlehDocumento4 pagineNursing Care in MR.X With Urinary Retention: Disusun OlehHafin WardanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 35 Communication in Children - PilliteriDocumento20 pagineChapter 35 Communication in Children - PilliteriPhillip ChingNessuna valutazione finora
- FNCPDocumento14 pagineFNCPhelloaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology Cushing S SyndromeDocumento4 paginePathophysiology Cushing S SyndromeMaria Luisa VillalunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic PyelonephritisDocumento5 pagineChronic PyelonephritisIsak ShatikaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Nursing Diagnosis Body Image Disturbance Is Most Likely To Be Written For Which of The Following PersonsDocumento3 pagineThe Nursing Diagnosis Body Image Disturbance Is Most Likely To Be Written For Which of The Following PersonsenzoNessuna valutazione finora
- West Visayas State University 3Documento3 pagineWest Visayas State University 3pircanoNessuna valutazione finora
- BurnsDocumento9 pagineBurnsVincentus BinNessuna valutazione finora
- Professional Adjustments For Student MidwivesDocumento52 pagineProfessional Adjustments For Student MidwivesRyan Michael OducadoNessuna valutazione finora
- ConsultsDocumento16 pagineConsultsRaq KhoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology Cholelithiasis 2Documento2 paginePathophysiology Cholelithiasis 2Jamie HaravataNessuna valutazione finora
- St. Paul University Philippines: Scenario 1Documento2 pagineSt. Paul University Philippines: Scenario 1Miguel LigasNessuna valutazione finora
- Kawasaki DiseaseDocumento7 pagineKawasaki DiseaseRitamariaNessuna valutazione finora
- PATHOPHYSIO (Megaloblastic Anemia)Documento3 paginePATHOPHYSIO (Megaloblastic Anemia)Giselle EstoquiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Doctor'S Order and Progress Notes Sheet: University of Northern PhilippinesDocumento3 pagineDoctor'S Order and Progress Notes Sheet: University of Northern PhilippinesPrincess QuirinaNessuna valutazione finora
- West Visayas State UniversityDocumento3 pagineWest Visayas State UniversitypircanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Buddy WorksDocumento3 pagineBuddy WorksJamaica Leslie NovenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of TetanusDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of TetanusAnitha SuprionoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP IcuDocumento2 pagineNCP IcuDiana MuañaNessuna valutazione finora
- Family Nursing Care Plan: Group A3 - ObDocumento4 pagineFamily Nursing Care Plan: Group A3 - ObErika CadawanNessuna valutazione finora
- NCM 122 Ratio FinalsDocumento2 pagineNCM 122 Ratio FinalsLorenz Jude CańeteNessuna valutazione finora
- LRDR ProceduresDocumento67 pagineLRDR ProceduresJustJ ThingsNessuna valutazione finora
- TOF (Pathophysiology)Documento4 pagineTOF (Pathophysiology)Doreen Claire M. WallangNessuna valutazione finora
- Action Plan - Inadequate IncomeDocumento2 pagineAction Plan - Inadequate IncomeBenedict James BermasNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Spinal Cord Injury 1Documento1 paginaPathophysiology of Spinal Cord Injury 1Kristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isNessuna valutazione finora
- ReflectionDocumento42 pagineReflectionRaidis PangilinanNessuna valutazione finora
- BioethicsCasesEEI 316232215 PDFDocumento38 pagineBioethicsCasesEEI 316232215 PDFAman UllahNessuna valutazione finora
- SEMINAR On New FilariaDocumento50 pagineSEMINAR On New FilariaArun JvNessuna valutazione finora
- Jerson Jeck AlcidoDocumento5 pagineJerson Jeck AlcidoJerson Jeck Salumanda AlcidoNessuna valutazione finora
- Potassium ChlorideDocumento2 paginePotassium ChlorideSetiram Zenitram50% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The GallbladderDocumento1 paginaAnatomy and Physiology of The GallbladderRojanisa Baculi RomathoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing AssessmentDocumento4 pagineNursing AssessmentFlor SabaysabayNessuna valutazione finora
- Case 4Documento14 pagineCase 4bekbekk cabahugNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart Disease: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors: EtiologyDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart Disease: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors: EtiologyGenette Sy SolisNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Output For The Patho of RHDDocumento2 pagineFinal Output For The Patho of RHDJustine Dinice MunozNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaphy CardioDocumento10 pagineAnaphy Cardiojonel lorenzoNessuna valutazione finora
- PHARMACOLOGYDocumento3 paginePHARMACOLOGYjonel lorenzoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCCCCCPDocumento10 pagineNCCCCCPjonel lorenzoNessuna valutazione finora
- David: PeterDocumento1 paginaDavid: Peterjonel lorenzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)Documento13 pagineObsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)jonel lorenzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Avian Influenza: "Bird Flu"Documento10 pagineAvian Influenza: "Bird Flu"jonel lorenzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Characteristics and Aspects of Society and CultureDocumento13 pagineCharacteristics and Aspects of Society and Culturejonel lorenzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cam4 6 1861Documento10 pagineCam4 6 1861Ćatke TkećaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rational Use of The Drug (Rud) : Rovina Ruslami, DR., SPPD, PHDDocumento31 pagineRational Use of The Drug (Rud) : Rovina Ruslami, DR., SPPD, PHDamaliaramadhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Application For The Post of Assistant Professor in DentistryDocumento5 pagineApplication For The Post of Assistant Professor in DentistryVenkata Ramana Murthy VasupilliNessuna valutazione finora
- FACTSHEET YouthSuicideRevisedSpring2010Documento10 pagineFACTSHEET YouthSuicideRevisedSpring2010Riyan SudrajadNessuna valutazione finora
- 05 2019 Pediatric Infectious Diseases LAYOUT R3Documento58 pagine05 2019 Pediatric Infectious Diseases LAYOUT R3khalid alharbiNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Surgical Logbook For Orthopedic Residents AcceptanceDocumento7 pagineElectronic Surgical Logbook For Orthopedic Residents AcceptanceKhalil ur RehmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Discharge Plan FhayeDocumento4 pagineDischarge Plan FhayeTin-Tin RutaquioNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.scope of Diagnostic RadiologyDocumento28 pagine2.scope of Diagnostic RadiologyphilipNessuna valutazione finora
- Acetaminophen PoisoningDocumento19 pagineAcetaminophen PoisoningMARIA TELLEZNessuna valutazione finora
- Characterization of Acne Associated With UpadacitiDocumento8 pagineCharacterization of Acne Associated With UpadacitiDo u know BTS?Nessuna valutazione finora
- Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria: Section 13Documento2 pagineParoxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria: Section 13MANGNessuna valutazione finora
- Sadhana Intensive CourseDocumento16 pagineSadhana Intensive Courseapi-241382210Nessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar Obat Alkes Trolley EmergencyDocumento15 pagineDaftar Obat Alkes Trolley EmergencydevitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Digestive SystemDocumento28 pagineDigestive Systemtessacruz1186Nessuna valutazione finora
- KalanchoeDocumento1 paginaKalanchoeAnonymous iOYpj92Nessuna valutazione finora
- Screening Questionnaire: Dha Eligibility LetterDocumento2 pagineScreening Questionnaire: Dha Eligibility LetterDr. Emad Elbadawy د عماد البدويNessuna valutazione finora
- LMC ICD-10 PowerPointDocumento77 pagineLMC ICD-10 PowerPointNicholas HenryNessuna valutazione finora
- Acceptance SamplingDocumento52 pagineAcceptance SamplingA MNessuna valutazione finora
- DLR - Tips and Tricks PDFDocumento9 pagineDLR - Tips and Tricks PDFSelda CoktasarNessuna valutazione finora
- A Day in The Life of A Clinical Research AssociateDocumento4 pagineA Day in The Life of A Clinical Research AssociatenishitpataniNessuna valutazione finora
- Surving Sepsis Campaign ResultDocumento8 pagineSurving Sepsis Campaign Resultmaria arenas de itaNessuna valutazione finora
- Central Diabetes InsipidusDocumento8 pagineCentral Diabetes InsipidusasdwasdNessuna valutazione finora
- U.p.diary 2020 (English) PDFDocumento431 pagineU.p.diary 2020 (English) PDFAbhayNessuna valutazione finora
- Mwalya Wambua Final ProjectDocumento49 pagineMwalya Wambua Final ProjectWILSON MACHARIANessuna valutazione finora
- Iraq Biotechnology Conference May 7 - 9 Agenda ENGLISHDocumento6 pagineIraq Biotechnology Conference May 7 - 9 Agenda ENGLISHGavin Macgregor-SkinnerNessuna valutazione finora