Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Preventing IT Heat Disasters
Caricato da
mio2010Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Preventing IT Heat Disasters
Caricato da
mio2010Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Preventing IT Heat Disasters
Backup Air Conditioners for Small to Mid-Size
Server Rooms and Network Closets
A Guide for IT Managers
IT managers with small to mid-size server rooms and network
closets know their equipment is especially vulnerable to
overheating during air-conditioning outages, yet frequently they
do not have a backup cooling system in place.
Such equipment rooms are often located in leased space
within general-use office buildings, whose temperature is
controlled by the building’s central air conditioning system.
Here, most lease agreements prevent installation of a
permanent backup system, which usually requires cutting an
opening in an outer wall or the roof and, in many cases, interior
walls.
At the same time, continuing to operate with no backup
system at all, or relying on out-of-date solutions such as electric
fans, risks heat-caused equipment failure and possible damage,
as well as system downtime.
Fortunately, a class of commercial portable air conditioners,
also called portable spot coolers, can solve this problem by
providing IT managers with backup air conditioning that does
not require lease-prohibited construction. This paper will
examine the advantages of using such portable air conditioners
as backup systems.
Air-Conditioning Outages Likely to Increase
If current predictions hold true, rising average temperatures
and more frequent periods of severe hot weather, as well as
Copyright © 2008 MovinCool 1
Preventing Heat Disasters
growing IT equipment-room heat densities, will likely put
greater stress on air-conditioning systems, resulting in an
increased number of outages.
In addition, as businesses become more and more dependent
on IT equipment for critical everyday operations such as
Internet transactions, internal and external e-mail, IP
telephones, etc., they are less able to bear the cost of even short
periods of downtime, including those caused by scheduled
maintenance outages.
The Challenges of Not Having a Backup Air Conditioner
Without a backup air conditioner, it is almost impossible to
avoid having a certain amount of downtime. Although
air-conditioning outages can occur any time, they often occur
during the hottest weather, when systems are most stressed.
During these periods of severe heat, in the absence of air
conditioning, IT equipment can heat up very fast, leaving only a
short window of time in which to act.
Servers contain a company’s valuable data, but when they
are overheated they will usually shut down before any serious
harm is done to them or data is lost. The most sensitive pieces
of equipment, however, are the network routers. These handle
internal and external data transmissions, including e-mail and
IP telephones. If they heat up too much, they may become
permanently damaged and need to be replaced entirely, often at
considerable cost.
In a heat emergency, one tempting solution is to use portable
evaporative coolers, also called swamp coolers. Since these work
by evaporation, however, they add significant amounts of
humidity to the air and are therefore not generally suitable for
use in IT equipment rooms.
Another solution, often resorted to in the past but still not
unheard of today, is to open doors and use electric fans to bring
in outside air. This assumes, however, that cross-ventilating
doors are available, and that leaving such doors open will not
create a security problem. It also assumes that the air outside is
cooler than it is inside and relatively low in humidity, neither of
which is necessarily the case during heat waves, when outages
are most likely to occur.
Moreover, especially with the higher heat densities of today’s
IT equipment, fans can provide only partial, temporary relief at
best. They can often keep the temperature from rising as
quickly as it would otherwise, but they usually can’t prevent the
inevitable. When the temperature inside the server room
Copyright © 2008 MovinCool 2
Preventing Heat Disasters
reaches a critical level, the only real solution is to shut all the
equipment down and wait for the air conditioning to be
repaired. This of course may take hours or, in the worst cases, a
day or longer. In the meantime, business activities that depend
on the IT equipment are brought to a halt.
Air-Conditioning Backups: A Historical Perspective
In the early days of IBM mainframes, which put out very large
amounts of heat, the vendor provided both an air conditioning
system and a redundant backup system as part of a total
package.
With the transition to server technology and the development
of large data centers containing dozens of server racks,
dedicated air conditioners and N+1 or N+2 redundant backup
systems became the rule, as they still are.
On the other hand, many companies with a relatively small
number of servers and whose air conditioning was supplied by
the building's central cooling system, did not at first feel the
need for a dedicated backup system. As long as downtime was
not excessive, the lack of a backup was not a problem.
Yet as IT and telecom applications have continued to
proliferate in the general business world, not only has the
number of servers and routers used by a typical company
grown, but the heat density of that equipment has also grown.
Accordingly, air conditioning and air-conditioning backups have
today become critical factors for even smaller server and
telecom rooms.
The Solution: Portable Air Conditioners as Backup Systems
The introduction of a relatively new class of commercial
portable air conditioners, also called portable spot coolers, has
given IT managers of smaller server and telecom rooms a
convenient way of solving their air-conditioning backup
problems.
There are two types of portable air conditioners: air-cooled
and water-cooled. Water-cooled portable air conditioners are
more efficient than air-cooled ones, but they use high-pressure
water lines that can leak. Therefore, like portable evaporative
coolers, they are usually considered unsuitable for use with IT
equipment. For the purposes of this paper, the terms “portable
air conditioners” or “portable spot coolers” refer only to
air-cooled systems.
Copyright © 2008 MovinCool 3
Preventing Heat Disasters
Portable air conditioners are self-contained units, containing
both a compressor and evaporator coil. Cold refrigerant flows
from the compressor into to the evaporator coil. A fan blows
over the coil, pushing cold air out. A second fan pushes exhaust
hot air out through the system’s built-in flexible ducting,
usually to the empty space above a drop ceiling. Excess
moisture removed from the air collects in a small condensation
tank, which can be emptied manually or, with most models,
automatically via a pump.
Benefits of Portable Air Conditioners
The most important benefit of portable air conditioners is that
they allow quick and easy installation that does not violate
most lease agreements and does not normally require prior
approval of the building owner. Installation usually consists of
no more than rolling a unit in, removing a drop-ceiling panel
and positioning the exhaust duct in the space where the panel
was.
Another outstanding benefit of portable air conditioners is
their flexibility. Whenever necessary, they can be quickly and
easily moved to a different location in the server room and their
airflow redirected. This is particularly helpful if any new hot
spots develop when equipment is added or racks are
reconfigured.
Renting vs. Buying
Because installation is so fast and simple, portable air
conditioners are popular as rental units for emergency use. In
many cases this may be a completely satisfactory solution.
However, the popularity of portable air conditioners extends to
many more applications than just IT equipment rooms.
This means that if an outage occurs during a heat wave,
when the demand for rentals is usually running high, there
may be a significant delay before the dealer can arrive. It is also
possible that dealers in a particular area will run out of units
with the required cooling capacity and voltage. In addition, not
all dealers have 24/7 service, which can be a problem if the
outage occurs at night, on a weekend or on a holiday.
For companies who can’t afford to gamble on a delay, having
their own backup portable air conditioner may be a better
solution. That way, when an outage occurs, the unit only has to
be rolled in and hooked up. Such a procedure usually takes only
Copyright © 2008 MovinCool 4
Preventing Heat Disasters
minutes to accomplish, but even so, if the outage occurs during
off-hours, there is still some risk that equipment may shut
down or suffer damage before company personnel can arrive.
For companies who can’t tolerate any amount of downtime,
on the other hand, the best solution is to install a portable air
conditioner as a permanent backup, with the thermostat
adjusted a few degrees above the maximum temperature
allowed by the main air-conditioning system. With this kind of
setup, if there is an air conditioning outage or other
malfunction, the backup unit takes over automatically.
Direct benefits include:
• Eliminating the risk of equipment damage and system
downtime
• Removing the stress and difficulty of having to deal with
an emergency situation
• Eliminating emergency calls to IT personnel during
off-hours
• Assuring peace of mind
4 Things to Look for in a Portable Air Conditioner
When choosing a portable air conditioner as a backup
air-conditioning system, here are four important things to look
for:
Quality of manufacturing: Above all, a backup air
conditioner must be reliable. Look for equipment that is built to
the highest quality standards.
Specifically, check to see if the fan motors are fully enclosed
in protective housings to prevent dust from building up. Dust
that accumulates on the motors can absorb moisture, leading to
corrosion or electrical shorts.
Also, examine the casters for their durability. Are they
securely attached to the frame by a mounting plate and
heavy-duty bolts, or only by the caster stem? The stem is a
weak point that can bend and cause a caster to malfunction if it
goes over a rough or uneven surface.
Next, look at the sheet-metal panels to see if they have
stress-relief notches at the bends. Also, are the panels attached
to the frame at load-bearing points by machine screws and weld
nuts, or by lighter-duty sheet-metal screws? Is the weight of the
fan housing supported by a sturdy, interior frame panel, or only
by a lighter cover panel?
Another important area to pay attention to is the
refrigeration unit itself. Is it hermetically sealed, or does it have
Copyright © 2008 MovinCool 5
Preventing Heat Disasters
service valves, which are prone to leaks? Also, are the
refrigerant pipes connected by reducers and expanders, or by
pinching and brazing?
Pinching and brazing restricts the flow of the refrigerant,
reducing cooling efficiency and long-term performance. In
addition, the connections created using this method are weaker
and more subject to vibration-caused stress cracks and
subsequent leakage.
Finally, check the drain pan to see if it is fully insulated, not
just powder-coated. This ensures that moisture will not come
into contact with the metal surface of the pan, protecting it from
corrosion and possible leaks.
Such quality-oriented details are telling indicators of
high-quality equipment that is designed and manufactured with
long-term reliability in mind.
Verified performance: When comparing performance
specifications, check to see if the equipment carries a
performance-verification mark such as ETL Verified or UL
Verified.
Unlike the ETL Listed or UL Listed marks, which are safety
certifications, the ETL Verified and UL Verified marks are
performance certifications.
ETL Verified or UL Verified means that the equipment has
been independently tested and found to perform at the levels
the manufacturer says it will, using actual performance data,
not calculated data.
This type of performance-verification mark is another
indicator of high quality.
Industry-standard measurements: Cooling capacity,
measured in Btu/hr or tons (12,000 Btu/hr = 1 ton), is the most
basic measure of an air conditioner’s ability to cool a given
space.
When choosing a portable air conditioner, be sure that the
manufacturer’s claimed cooling capacity has been arrived at
following an industry-accepted standard from the American
Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning
Engineers (ASHRAE), and not just an arbitrary one. Otherwise,
the unit may provide inadequate cooling.
For portable spot air conditioners, the relevant ASHRAE
Standard 128-1989 specifies ambient conditions of 95 ºF at
60% RH. Unless this standard is used, the cooling capacity of
the equipment in question may be much lower than what is
claimed.
Copyright © 2008 MovinCool 6
Preventing Heat Disasters
Manufacturers of quality equipment, however, will adhere to
this standard and clearly state that they have used these
conditions when measuring cooling capacity.
Established manufacturer: Look for a company that
stands out in the industry and has established itself for many
years as a leading manufacturer of air-conditioning equipment.
This is a good sign that the company will be around to support
their equipment well into the future.
Also look for a company with a broad distribution base and a
large number of dealers who will support and service their
equipment throughout North America and globally.
MovinCool Portable Air Conditioners
MovinCool, the world’s largest manufacturer of commercial
portable air conditioners, offers a complete line of models used
in a variety of applications, including server and telecom rooms,
network closets and other IT equipment rooms. Models are
available with cooling capacities as high as 60,000 Btu/h
(5 tons) and in all voltage ranges.
Within the air-conditioning industry, MovinCool enjoys a
reputation for highest quality and reliability. Dealers who
specialize in renting portable air conditioners, and who stand to
lose significant profit if they have to replace a unit once it is
delivered, consistently say they prefer MovinCool models for
their rental fleets because they know they can always count on
them to deliver the high levels of performance their customers
demand.
MovinCool is a brand of DENSO, one of the world’s largest
manufacturer of automotive parts. As the principal supplier of
advanced automotive technology, systems and components,
including air conditioning to all the of the world’s major car
manufacturers, DENSO’s commitment to quality is paramount.
In the 1980s, DENSO pioneered the concept of workspace
spot cooling to meet its own factory needs in Japan. Since then,
MovinCool has developed a wide range of portable and
ceiling-mount air conditioning systems for many different
applications. For more information, visit MovinCool at
http://www.movincool.com.
Note: No product can eliminate all risks and guarantee protection 100 percent of the time.
Copyright © 2008 MovinCool 7
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Union Delivery Menu-1Documento9 pagineUnion Delivery Menu-1mio2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Char Lie ChaplinDocumento12 pagineBio Char Lie ChaplinsvsaravananNessuna valutazione finora
- SAP 4.6 Basic Skills Self-StudyDocumento153 pagineSAP 4.6 Basic Skills Self-Studyapi-3758541100% (2)
- Metronidazole Injection GradeDocumento3 pagineMetronidazole Injection Grademio2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2715Documento6 pagine2715leandrojjNessuna valutazione finora
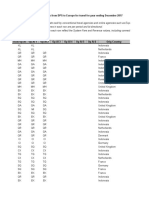
- 2018 Schengen Visa Statistics PDFDocumento1 pagina2018 Schengen Visa Statistics PDFmio2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- Preventing IT Heat DisastersDocumento7 paginePreventing IT Heat Disastersmio2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- 07 Heike Online HowToStudyIDP NovemberDocumento6 pagine07 Heike Online HowToStudyIDP NovemberBhagat PratikNessuna valutazione finora
- Oracle XE Install GuideDocumento7 pagineOracle XE Install Guidechotoiyeu272Nessuna valutazione finora
- Web User MagsDocumento76 pagineWeb User Magsmio2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- The International Office - : Martin-Luther-University Halle-WittenbergDocumento2 pagineThe International Office - : Martin-Luther-University Halle-Wittenbergmio2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- Epson Manual ReferenceDocumento23 pagineEpson Manual Referencemio2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- Turisztikai Kiadvany en PDFDocumento11 pagineTurisztikai Kiadvany en PDFmio2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2715Documento6 pagine2715leandrojjNessuna valutazione finora
- Turisztikai Kiadvany en PDFDocumento11 pagineTurisztikai Kiadvany en PDFmio2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tuition Fees Study Programmes Taught in EnglishDocumento2 pagineTuition Fees Study Programmes Taught in Englishmio2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pul Sysadmin Ebook v2Documento10 paginePul Sysadmin Ebook v2mio2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tips On Mountain FlyingDocumento18 pagineTips On Mountain Flyingtomallor101Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2715Documento6 pagine2715leandrojjNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Pilot GuideDocumento24 pagineStudent Pilot GuideShakil KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Turisztikai Kiadvany en PDFDocumento11 pagineTurisztikai Kiadvany en PDFmio2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Case Study GB Mkting 1.Documento13 pagineCase Study GB Mkting 1.Raj PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Walkthrough On Javascript Coding Standards and Best PracticesDocumento39 pagineWalkthrough On Javascript Coding Standards and Best PracticesKapa AnuradhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Graphics 2marksDocumento12 pagineComputer Graphics 2marksArul Prakash50% (2)
- CSS 11 Supplemental Learning Materials - Week 2 - No Performance ActivityDocumento21 pagineCSS 11 Supplemental Learning Materials - Week 2 - No Performance Activityyolanda renosNessuna valutazione finora
- Core2 HP PatchDocumento102 pagineCore2 HP PatchMabu DbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Self Encryption Project: FeaturesDocumento2 pagineMobile Self Encryption Project: Featuressyed ihtishamNessuna valutazione finora
- MeowDocumento1 paginaMeowkzypt57247Nessuna valutazione finora
- Use Case: Proactively Managing End-To-End 2G/3G/4G RAN HealthDocumento2 pagineUse Case: Proactively Managing End-To-End 2G/3G/4G RAN HealthUlysseNessuna valutazione finora
- The Influence of Social Networking Sites On Student S Academic Performance in MalaysiaDocumento8 pagineThe Influence of Social Networking Sites On Student S Academic Performance in MalaysiaKhei Laqui SNNessuna valutazione finora
- Cena Activity 1Documento3 pagineCena Activity 1api-535082025Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ipv6 Addressing & Routing Protocols: Isp/Ixp WorkshopsDocumento42 pagineIpv6 Addressing & Routing Protocols: Isp/Ixp WorkshopsAnup Kumar RajakNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Trends in Hospital DesignDocumento3 pagineModern Trends in Hospital DesignAkshat SinghalNessuna valutazione finora
- Ujian Wi NDT Rad Intep Modul 1 BambangDocumento26 pagineUjian Wi NDT Rad Intep Modul 1 BambangBambang FirdiansyahNessuna valutazione finora
- DOPDocumento54 pagineDOPprasalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Infoblox Installation Guide 805 Series AppliancesDocumento20 pagineInfoblox Installation Guide 805 Series AppliancesrinsonjohnpNessuna valutazione finora
- B&M Trading - Style GuideDocumento8 pagineB&M Trading - Style GuideKatie MarshallNessuna valutazione finora
- B700 Error CodesDocumento3 pagineB700 Error Codescastlelvania23Nessuna valutazione finora
- Env 2Documento32 pagineEnv 2Deeksha HRNessuna valutazione finora
- Recorder DuetsDocumento11 pagineRecorder DuetsPedro Daniel Macalupú Cumpén92% (13)
- Web Hancer Removal InstructionsDocumento2 pagineWeb Hancer Removal Instructionstommyp100Nessuna valutazione finora
- Erop 17Documento600 pagineErop 17Ari cNessuna valutazione finora
- Report Project PaperDocumento22 pagineReport Project PaperAsraihan Raihan100% (1)
- Monitoring and Reporting Using The CMORE PlatformDocumento8 pagineMonitoring and Reporting Using The CMORE PlatformInternational Relief and DevelopmentNessuna valutazione finora
- EX-0118 Virtual Assessment Guidance For Candidates - 2Documento12 pagineEX-0118 Virtual Assessment Guidance For Candidates - 2harsha alapatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Darbuka Operation Manual ENGDocumento84 pagineDarbuka Operation Manual ENGEmrah ErtemNessuna valutazione finora
- CN Unit-IDocumento167 pagineCN Unit-I18W91A0C0Nessuna valutazione finora
- How2r1 DatasheetDocumento3 pagineHow2r1 DatasheetMike PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Power of Love PP PresentationDocumento27 paginePower of Love PP Presentationademasi1Nessuna valutazione finora
- RedBus TicketDocumento2 pagineRedBus TicketrohanNessuna valutazione finora
- (WEEK 1) PPC Class GuidelinesDocumento22 pagine(WEEK 1) PPC Class Guidelinesdave lucasNessuna valutazione finora