Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Sample Lesson For Pronouns Objective Pronouns
Caricato da
KrischelleTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Sample Lesson For Pronouns Objective Pronouns
Caricato da
KrischelleCopyright:
Formati disponibili
SAMPLE LESSON FOR PRONOUNS
OBJECTIVE PRONOUNS
Quick Explanation:
Pronouns stand in the place of the noun or nouns. This reduces the number of times the noun is repeated.
There are many forms of pronouns. Among them are:
o Subjective (he, I, it, she, they, we, and you)
o Objective (her, him, it, me, them, us, and you)
o Possessive (hers, his, its, mine, ours, theirs, yours)
o Reflexive (herself, himself, itself, myself, ourselves, themselves, and your selves)
o Indefinite (anybody, anyone, anything, everybody, everyone, everything, nobody, no one, none, nothing,
somebody, someone, something)
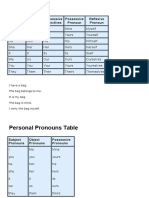
PERSPECTIVE SUBJECTIVE POSSESSIVE OBJECTIVE NUMBER
CASE CASE CASE
First Person I my, mine me Singular
we our, ours us Singular
Second Person you your, yours you Singular/
Plural
Third Person he, she, it his, her, hers, its him, her, it Singular
we, they our, ours, their them Plural
who, whoever whose whom, whomever Singular/
Plural
Examples of Objective Pronouns
Unlike the subjective pronoun that does the action, the objective pronoun receives the action of the verb.
The objective pronoun may be a direct or indirect object.
o The direct object completes the meaning of the verb
Mom walks me.
Mom walks me. (me-direct object completes the meaning of the verb walk)
o The indirect object tells to or for whom (or what) the action is taking place.
Mom walks me to school. (indirect object)
Mom walks me to school. (me-indirect object) (Where does Mom walk? to school)
Objective pronouns can also be the object in a prepositional phrase.
o Mom walks with me.
with is the preposition; me is the object of the preposition with; with me is the prepositional phrase)
Guided Objective Pronoun Practice:
Use the Pronoun Case Chart to select and use the correct possessive pronoun:
Lava covers it.
o What does lava cover? it (direct object)
Woodsman wrestles it to the ground!
o How does the woodsman wrestle? to the ground (prepositional phrase)
o What does the woodsman wrestle? it (indirect object)
My family gives me praise.
o (What does the family give? To whom?) praise (direct object); me (indirect object) to (preposition)
I like him. (Who do I like?)
o him (direct object)
Independent Objective Pronoun Practice
Use the Pronoun Case Chart to select and use the correct possessive pronoun:
o My brother gave me a noogie.
What did my brother give? a noogie
SAMPLE LESSON FOR PRONOUNS
To whom does he give the noogie? me-indirect object
o Gerald’s friend asked him for it.
Gerald’s friend asked who? him-indirect object
What did Gerald ask for? it -object of the preposition, for –preposition
o The teacher gave us a surprise.
What did the teacher give? a surprise
To whom did the teacher give it? us-indirect object
o Our teacher surprises us.
What does the teacher do? surprise
Who does the teacher surprise? us-direct object
Sample Lesson for
Objective Pronouns
PRONOUNS
O Pronouns stand in the place of the noun or nouns.
This reduces the number of times the noun is
repeated.
O There are many forms of pronouns. Among them
are:
O Subjective (he, I, it, she, they, we, and you)
O Objective (her, him, it, me, them, us, and you)
O Possessive (hers, his, its, mine, ours, theirs, yours)
O Reflexive (herself, himself, itself, myself, ourselves,
themselves, and your selves)
O Indefinite (anybody, anyone, anything, everybody,
everyone, everything, nobody, no one, none, nothing,
somebody, someone, something)
PRONOUN CASE CHART
PERSPECTIVE SUBJECTIVE POSSESSIVE OBJECTIVE NUMBER
CASE CASE CASE
First Person I my, mine me Singular
we our, ours us Singular
Second you your, yours you Singular/
Person Plural
Third Person he, she, it his, her, hers, him, her, it Singular
its
we, they our, ours, them Plural
their
who, whoever whose whom, Singular/
whomever Plural
OBJECTIVE PRONOUNS
O Unlike the subjective pronoun that does the action, the objective
pronoun receives the action of the verb.
O The objective pronoun may be a direct or indirect object.
O The direct object completes the meaning of the verb
O Mom walks me. (direct object)
O The indirect object tells to or for whom (or what) the action is
taking place.
O Mom walks me to school. (indirect object)
O Objective pronouns can also be the object in a prepositional
phrase.
O Mom walks with me. (with is the preposition; me is the object of
the preposition)
OBJECTIVE PRONOUN PRACTICE
O Lava covers it. (What does lava
cover?)
O Woodsman wrestles it to the ground!
(How does the woodsman wrestle?)
O My family gives me praise. (What
does the family give? To whom?)
O I like him. (Who do I like?)
INDEPENDENT OBJECTIVE PRONOUN
PRACTICE
O My brother gave me a noogie.
O What did my brother give?
O To whom does he give the noogie?
O Gerald’s friend asked him for it.
O Gerald’s friend asked who?
O What did Gerald ask for?
O The teacher gave us a surprise.
O What did the teacher give?
O To whom did the teacher give it to?
O Our teacher surprises us.
O What does the teacher do?
O Who does the teacher surprise?
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- English for Execs: And Everyone Who Desires to Use Good English and Speak English Well!Da EverandEnglish for Execs: And Everyone Who Desires to Use Good English and Speak English Well!Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Lesson For Pronouns Relative PronounsDocumento8 pagineSample Lesson For Pronouns Relative PronounsJuniza Jahaya100% (1)
- PronounDocumento29 paginePronounAlfa RizkiNessuna valutazione finora
- PronounDocumento38 paginePronounAlfa RizkiNessuna valutazione finora
- Material of Pronoun and ExercisesDocumento10 pagineMaterial of Pronoun and ExercisesWahyu WulandariNessuna valutazione finora
- Kumpulan Materi (S1 Keperawatan)Documento24 pagineKumpulan Materi (S1 Keperawatan)Yesi RosianiNessuna valutazione finora
- PronounsDocumento3 paginePronounsFatouNessuna valutazione finora
- Good Morning!Documento21 pagineGood Morning!Mike Edrian BantingNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Lesson For Pronouns Idefinite Pronouns Quick ExplanationDocumento7 pagineSample Lesson For Pronouns Idefinite Pronouns Quick ExplanationCarl Voughn Jeric CatalbasNessuna valutazione finora
- Pronoun Bhs InggrisDocumento45 paginePronoun Bhs InggrisCut Raudahtul FitriNessuna valutazione finora
- PRONOUNSDocumento3 paginePRONOUNSdiakitebocar10Nessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding PronounsDocumento27 pagineUnderstanding Pronounsannisa nurul apNessuna valutazione finora
- PRONOUNSDocumento3 paginePRONOUNSleydi merinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pronouns Its TypesDocumento6 paginePronouns Its TypesMuhammad AdilNessuna valutazione finora
- John Got A New Job Children Should: PronounsDocumento3 pagineJohn Got A New Job Children Should: PronounsIoana IvanNessuna valutazione finora
- CONTENTDocumento44 pagineCONTENTkamawisNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit ThreeDocumento9 pagineUnit ThreefaizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Everything about pronounsDocumento43 pagineEverything about pronounsanneNessuna valutazione finora
- Pronouns - Basic NotesDocumento4 paginePronouns - Basic NotesFrancis Guerrero TimbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Subject Pronoun: (Subjective Case)Documento5 pagineSubject Pronoun: (Subjective Case)Arun KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Pronoun Usage Grammar HandoutDocumento4 paginePronoun Usage Grammar HandoutCazembe WilliamsNessuna valutazione finora
- Understand Pronouns - The 8 Categories ExplainedDocumento41 pagineUnderstand Pronouns - The 8 Categories ExplainedJohn Harvey Magos0% (1)
- Unit Three 3 PronounsDocumento9 pagineUnit Three 3 Pronounskatia oussNessuna valutazione finora
- Les Pronoms PersonnelsDocumento10 pagineLes Pronoms PersonnelsarunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Choosing The Correct Pronoun and Noun Cases, TipsDocumento5 pagineChoosing The Correct Pronoun and Noun Cases, Tipsolen marpaungNessuna valutazione finora
- Grammatical Usage of PronounsDocumento60 pagineGrammatical Usage of PronounsMuffin DyNessuna valutazione finora
- Serbian Personal PronounsDocumento4 pagineSerbian Personal PronounsElaNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Pronouns - Grammar Reference Sheet: (A Pronoun Is A Word That Is Used To Take The Place of A Noun.)Documento1 paginaTypes of Pronouns - Grammar Reference Sheet: (A Pronoun Is A Word That Is Used To Take The Place of A Noun.)Zeina M. HarfoushNessuna valutazione finora
- Grammar Guide To Spanish PronounsDocumento7 pagineGrammar Guide To Spanish PronounsAlaa OmarNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A PronounDocumento9 pagineWhat Is A PronounJOSE MANUEL EspirituNessuna valutazione finora
- PronounsDocumento10 paginePronounstrongbmse183686Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pronouns KIPS Academy (Free Download)Documento16 paginePronouns KIPS Academy (Free Download)AyshahNessuna valutazione finora
- SEMI-final Exam. Eng2.Documento3 pagineSEMI-final Exam. Eng2.Allan Arancel MagsipocNessuna valutazione finora
- Personal Pronouns Personal Pronouns Are Used To Refer To Oneself, The People One Is Talking To, or The People or Things One Is Talking AboutDocumento2 paginePersonal Pronouns Personal Pronouns Are Used To Refer To Oneself, The People One Is Talking To, or The People or Things One Is Talking AboutTALVIN LEENessuna valutazione finora
- CS English Review Oct 2015 Pronouns PDFDocumento25 pagineCS English Review Oct 2015 Pronouns PDFMark Anthony CasupangNessuna valutazione finora
- FFFF 84 Ffffffee 4 DDocumento2 pagineFFFF 84 Ffffffee 4 DLexi gallinedemNessuna valutazione finora
- English Word Order RulesDocumento4 pagineEnglish Word Order RulesSkruzdelyte MielaNessuna valutazione finora
- PronounDocumento17 paginePronounRIZA BULACANNessuna valutazione finora
- PronounsDocumento8 paginePronounseulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Comprometidos con tu ingreso a la universidadDocumento3 pagineComprometidos con tu ingreso a la universidadTATIANA HERRERA VILLAMILNessuna valutazione finora
- Hers, It, Its, They, Them, Their, Theirs.: Table of Personal PronounsDocumento5 pagineHers, It, Its, They, Them, Their, Theirs.: Table of Personal PronounsWolfo ChicoNessuna valutazione finora
- Refrescamos pronounsDocumento43 pagineRefrescamos pronounscristtianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pronouns of English Grammar Guides - 95690Documento2 paginePronouns of English Grammar Guides - 95690GemaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pronouns: Refuerzo, Reyes, Santos, UyDocumento26 paginePronouns: Refuerzo, Reyes, Santos, UydeniseNessuna valutazione finora
- OBJECT PRONOUNS EXPLAINEDDocumento6 pagineOBJECT PRONOUNS EXPLAINEDLupitha HernándezNessuna valutazione finora
- PRONOUN GUIDEDocumento9 paginePRONOUN GUIDEStevenCullenNessuna valutazione finora
- Pronouns: The First Group By: Annisa Firly N Anna Fitryana Neng Allisha BellaDocumento11 paginePronouns: The First Group By: Annisa Firly N Anna Fitryana Neng Allisha BellaAnna FitriyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- PronounDocumento4 paginePronounmohammadadan424Nessuna valutazione finora
- PronounsDocumento7 paginePronounsMagalí StylesNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4Documento52 pagineModule 4Iris CarranzaNessuna valutazione finora
- John's Basic English Reviewer (Notes)Documento40 pagineJohn's Basic English Reviewer (Notes)Mary Bianca ZipaganNessuna valutazione finora
- Pronouns and Its CasesDocumento29 paginePronouns and Its CasesDWYGHT QORBAN INFANTENessuna valutazione finora
- The Pronoun: Nominative CaseDocumento17 pagineThe Pronoun: Nominative CasePadhy ParthosarathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Parts of Speech: By: Tiyas Saputri, S.S., M.PDDocumento42 pagineParts of Speech: By: Tiyas Saputri, S.S., M.PDFirda JinanNessuna valutazione finora
- PronounsDocumento26 paginePronounsSteven DaviesNessuna valutazione finora
- Pronouns:, Have Three FormsDocumento6 paginePronouns:, Have Three FormsRomnick Manaog-PastoralNessuna valutazione finora
- Pronouns Types FunctionsDocumento16 paginePronouns Types FunctionskakakarlNessuna valutazione finora
- FundamentalsDocumento4 pagineFundamentalsAshley OlbinarNessuna valutazione finora
- PronounDocumento31 paginePronounJoyce Ann CascayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Shimano Brakes ManualDocumento36 pagineShimano Brakes ManualKon Arva100% (1)
- Nature and Scope of Marketing Marketing ManagementDocumento51 pagineNature and Scope of Marketing Marketing ManagementFeker H. MariamNessuna valutazione finora
- The Bloodless GospelDocumento7 pagineThe Bloodless GospelKJVNessuna valutazione finora
- Galvanometer: Project Prepared By:-Name - Pragati Singh Class - Xii A AcknowledgementDocumento11 pagineGalvanometer: Project Prepared By:-Name - Pragati Singh Class - Xii A AcknowledgementANURAG SINGHNessuna valutazione finora
- Critique On A Film Director's Approach To Managing CreativityDocumento2 pagineCritique On A Film Director's Approach To Managing CreativityDax GaffudNessuna valutazione finora
- Conserve O Gram: Understanding Histograms For Digital PhotographyDocumento4 pagineConserve O Gram: Understanding Histograms For Digital PhotographyErden SizgekNessuna valutazione finora
- Write 10 Lines On My Favourite Subject EnglishDocumento1 paginaWrite 10 Lines On My Favourite Subject EnglishIrene ThebestNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Calculus: Performance TaskDocumento6 pagineBasic Calculus: Performance TasksammyNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Steel Grating Catalogue 2010 - SERIES 1 PDFDocumento6 pagine3 Steel Grating Catalogue 2010 - SERIES 1 PDFPablo MatrakaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomechanics of Advanced Tennis: January 2003Documento7 pagineBiomechanics of Advanced Tennis: January 2003Katrien BalNessuna valutazione finora
- Obsolescence 2. Book Value 3. Depreciation 4. Depletion EtcDocumento9 pagineObsolescence 2. Book Value 3. Depreciation 4. Depletion EtcKHAN AQSANessuna valutazione finora
- Agricultural Sciences P1 Nov 2015 Memo EngDocumento9 pagineAgricultural Sciences P1 Nov 2015 Memo EngAbubakr IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Quality CircleDocumento33 pagineQuality CircleSudeesh SudevanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mesopotamia CivilizationDocumento56 pagineMesopotamia CivilizationYashika TharwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Masonry Brickwork 230 MMDocumento1 paginaMasonry Brickwork 230 MMrohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Reaction rate determination and simulation of hydrogenation processDocumento3 pagineReaction rate determination and simulation of hydrogenation processToMemNessuna valutazione finora
- AIATS 2021 (OYMCF) Test 01 Offline - Code A - SolutionsDocumento34 pagineAIATS 2021 (OYMCF) Test 01 Offline - Code A - Solutionsbhavyakavya mehta100% (1)
- Euro4 vehicle diesel engines 199 - 397 kW (270 - 540 hpDocumento6 pagineEuro4 vehicle diesel engines 199 - 397 kW (270 - 540 hpBranislava Savic63% (16)
- Homo Sapiens ActivityDocumento8 pagineHomo Sapiens ActivityJhon Leamarch BaliguatNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 5 CMADocumento10 pagineLesson 5 CMAAssma SabriNessuna valutazione finora
- Ireland in Pre Celtic TimesDocumento398 pagineIreland in Pre Celtic TimesGrant MacDonald100% (5)
- Estwani ISO CodesDocumento9 pagineEstwani ISO Codesनिपुण कुमारNessuna valutazione finora
- 40 Multiple Choice Questions in Basic StatisticsDocumento8 pagine40 Multiple Choice Questions in Basic StatisticsLevi CorralNessuna valutazione finora
- A Systematic Scoping Review of Sustainable Tourism Indicators in Relation To The Sustainable Development GoalsDocumento22 pagineA Systematic Scoping Review of Sustainable Tourism Indicators in Relation To The Sustainable Development GoalsNathy Slq AstudilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 10 - Mock Test - English - Feb - 2023Documento12 pagineGrade 10 - Mock Test - English - Feb - 2023rohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bitcoin MambaDocumento17 pagineBitcoin MambaJean MilenixNessuna valutazione finora
- STEM Spring 2023 SyllabusDocumento5 pagineSTEM Spring 2023 SyllabusRollins MAKUWANessuna valutazione finora
- Class 9th Chemistry Unit#4 Structure of MoleculesDocumento8 pagineClass 9th Chemistry Unit#4 Structure of MoleculesIrfanullahNessuna valutazione finora
- OROLO & W. D. GannDocumento56 pagineOROLO & W. D. GannGaurav Garg100% (1)
- Voltaire's Candide and the Role of Free WillDocumento3 pagineVoltaire's Candide and the Role of Free WillAngy ShoogzNessuna valutazione finora