Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Major changes to India's wage laws
Caricato da
anon_7865192730 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
136 visualizzazioni3 pagineThe Code on Wages, 2019 consolidates three existing laws - The Minimum Wages Act, 1948, The Payment of Wages Act, 1936, and The Payment of Bonus Act, 1965. Some key changes introduced include expanding coverage to all employments and establishments, introducing a floor wage set by the central government, and increasing penalties for non-compliance. It also introduces provisions for compounding certain offences and establishes inspector-cum-facilitators to help employers comply with the law in addition to inspections.
Descrizione originale:
The Key changes made by the introduction of Code on Wages, 2019.
Titolo originale
Code on Wages, 2019
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThe Code on Wages, 2019 consolidates three existing laws - The Minimum Wages Act, 1948, The Payment of Wages Act, 1936, and The Payment of Bonus Act, 1965. Some key changes introduced include expanding coverage to all employments and establishments, introducing a floor wage set by the central government, and increasing penalties for non-compliance. It also introduces provisions for compounding certain offences and establishes inspector-cum-facilitators to help employers comply with the law in addition to inspections.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
136 visualizzazioni3 pagineMajor changes to India's wage laws
Caricato da
anon_786519273The Code on Wages, 2019 consolidates three existing laws - The Minimum Wages Act, 1948, The Payment of Wages Act, 1936, and The Payment of Bonus Act, 1965. Some key changes introduced include expanding coverage to all employments and establishments, introducing a floor wage set by the central government, and increasing penalties for non-compliance. It also introduces provisions for compounding certain offences and establishes inspector-cum-facilitators to help employers comply with the law in addition to inspections.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 3
Major Changes introduced by the Code on Wages, 2019
The Code on Wages, 2019 consists of IX chapters. While the applicability, coverage, definitions an
provisions for equal remuneration are listed in Chapter I, provisions relating to minimum wages are
listed in Chapter II, Chapter III contains provisions relating to payment of wages, Chapter IV deals with
payment of bonus, Chapter V contains provisions relating to constitution of Advisory Board, Chapter
VI deals with the manner of raising claims on wages, provisions relating to appointment of an
Inspector-cum-Facilitator are set out in Chapter VII, Chapter VIII lists out the offences and penalties
and lastly Chapter IX deals with miscellaneous provisions.
S.No Old Statutes Code on Wages
1. The Equal Remuneration Act, 1976 recognised The Wage Code (“WC”) allowed a third
only male and female employees in respect of category of gender, i.e. Transgenders to also
which discrimination was prohibited. be protected from discrimination in matters
of payment of remuneration for carrying out
same or similar work.
2. Minimum Wages Act, 1948 (“MWA”) was only The WC extends its coverage to all
applicable to the scheduled employments set employments, irrespective of whether they
out therein. are in the organized or the unorganized
sector.
3. Payment of Wages Act, 1936 (“PWA”) was The WC covers all employees irrespective of
applicable to employees earning not more than their monthly salary.
INR 24,000 (Indian Rupees Twenty-Four
Thousand only) per month.
4. PWA was only applicable to 'industrial or other WC uses the term 'establishment' which
establishments'. The statute defined 'industrial means 'any place where any industry, trade,
or other establishment' to mean business, manufacture or occupation is
establishments relating to motor transport or carried on', thus extending the application
air transport services, dock, wharf, jetty, inland of the chapter on payment of wages to
vessel, mine, quarry, oilfield, plantation, commercial establishments as well.
production or manufacture of articles for their
use / transport / sale, construction /
development / maintenance of buildings etc.,
and any other establishment which the
appropriate government may, having regard to
the nature thereof and other relevant
circumstances, specify. This means that for the
PWA to be applicable to shops and
establishments, the appropriate government
must issue a notification to that effect.
5. Payment of Bonus Act, 1965 was only Under the WC, it is up to the discretion of
applicable to workers earning wages up to INR the appropriate government to prescribe
21,000 (Indian Rupees Twenty-One Thousand the wage ceiling for eligibility of payment of
only) per month. bonus.
6. Under the MWA, the respective state As per the WC, the Central Government shall
governments were responsible for fixing and fix a 'floor wage' taking account the
notifying the basic rate of wages for the minimum living standards of a worker.
workers employed in the scheduled However, the Central Government may
establishments. prescribe different floor wages for different
geographical areas. The respective state
governments may fix a different minimum
wage for areas falling under their
jurisdiction, provided such wage should at
least match the Floor Wage.
7. The criteria for fixing the minimum wage rate is WC has provided certain guidelines to the
not elaborated under the MWA. appropriate governments for the purpose of
fixing / revising the minimum wage rate,
which include the skill required, the
arduousness of the work assigned to the
worker, the cost of living of the worker, and
the geographical location of the place of
work.
8. The former labour laws authorized labour The WC introduces the concept of
‘inspectors’ to carry out inquiry and ‘inspector-cum-facilitator’ who shall not
investigation into alleged contraventions of the only carry out inspections, but also provide
stipulated provisions. employers and workers with information on
how to improve their compliance with the
law. While the inspector-cum-facilitator
retains the labour inspector’s power to
examine the workplace, search and seize
copies of relevant documents, the WC, also
states that before initiation of prosecution
for any non-compliance, the inspector-cum-
facilitator would provide an opportunity to
the employer to comply with the provisions
of the WC.
9. In the former laws there was no provision for The WC has introduced a provision for
compounding of offences. compounding of offences which states that,
any offence punishable under the Code, not
being an offence punishable with
imprisonment only, or with imprisonment
and also with fine, may, on an application of
the accused person, either before or after
the institution of any prosecution, be
compounded by a Gazetted Officer, as the
appropriate Government may, by
notification, specify, for a sum of 50 (fifty)
per cent. of the maximum fine provided for
such offence, in the manner as may be
prescribed.
However, such an opportunity is unavailable
to an employer for the second time or
thereafter within a period of 5 (five) years
from the date of either:
(i) commission of a similar offence which
was earlier compounded; or (ii) commission
of a similar offence for which such person
was earlier convicted.
10 Under the former laws, the maximum fine The WC states that for any failure to pay the
imposed by the labour authorities for the sums due to the employee, the employer
contravention of the relevant provisions was shall be punishable with fine which may
from INR 500 (Indian Rupees Five Hundred extend to INR 50,000 (Indian Rupees Fifty
only) to INR 20,000 (Indian Rupees Twenty Thousand only), while for any failure to
Thousand only). comply with other provisions of the WC, the
employer shall be punishable with fine
which may extend to INR 20,000 (Indian
Rupees Twenty Thousand only).
11. Under the former labour laws the limitation The WC increased the period of limitation to
period for filing of claims in relation to payment 3 (three) years.
of any sums due was between 6 (six) months to
2 (two) years.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Code On Wage 2019Documento27 pagineCode On Wage 2019Kumaar utsav100% (1)
- Analysis - Code of Wages, 2019Documento8 pagineAnalysis - Code of Wages, 2019Nikhil JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Code On Wages, 2019Documento8 pagineCode On Wages, 2019CHANDA SINGHNessuna valutazione finora
- Code On Wages 2019Documento52 pagineCode On Wages 2019PramodNessuna valutazione finora
- India's Wage Code Consolidates Labour LawsDocumento50 pagineIndia's Wage Code Consolidates Labour LawsTanu Priya100% (1)
- Brief Notes On New Labour Codes 2020: by Advocate Anees S. Kazi, MumbaiDocumento16 pagineBrief Notes On New Labour Codes 2020: by Advocate Anees S. Kazi, MumbaiVinay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- The Code on Wages, 2019: Key HighlightsDocumento19 pagineThe Code on Wages, 2019: Key HighlightsRafunsel PresentationNessuna valutazione finora
- Three New Labour Codes: Country: IndiaDocumento17 pagineThree New Labour Codes: Country: IndiaChanakya NitiNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit - 5 Employee's Compensation Act, 1923Documento28 pagineUnit - 5 Employee's Compensation Act, 1923armsarivu100% (1)
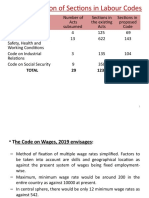
- Rationalization of Sections in Labour Codes: Total 29 1232 480Documento49 pagineRationalization of Sections in Labour Codes: Total 29 1232 480AadhityaNessuna valutazione finora
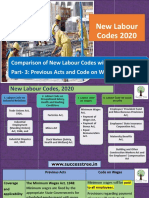
- 4 Comparing Previous Act With New Labour Codes (Part - 3)Documento13 pagine4 Comparing Previous Act With New Labour Codes (Part - 3)abdul gani khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation on Industrial Disputes Act, 1947: Key Provisions and ConceptsDocumento35 paginePresentation on Industrial Disputes Act, 1947: Key Provisions and ConceptsRajendra Meena100% (1)
- Equal Remuneration Act, 1976Documento30 pagineEqual Remuneration Act, 1976Nidhi Shukla0% (1)
- Summary of Employees Compensation ActDocumento17 pagineSummary of Employees Compensation ActParul Prasad50% (2)
- Highlights On Labour CodesDocumento68 pagineHighlights On Labour CodesGhanashyam Dey100% (1)
- Industrial Disputes Act 1947Documento49 pagineIndustrial Disputes Act 1947Aman MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- The Industrial Disputes Act, 1947 Later PartDocumento24 pagineThe Industrial Disputes Act, 1947 Later Partalifiya100% (7)
- The Payment of Wages ActDocumento13 pagineThe Payment of Wages ActShubham GuravNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture-4 Labour Laws and Indian Constitution: Class Notes - Industrial RelationsDocumento9 pagineLecture-4 Labour Laws and Indian Constitution: Class Notes - Industrial RelationsPrashant Singh SuryavanshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Labour CodeDocumento25 pagineLabour CodeMaksood AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparative Analysis of The Code On Wages, 2019 With Previous Legislations in ForceDocumento14 pagineComparative Analysis of The Code On Wages, 2019 With Previous Legislations in ForcebabuliNessuna valutazione finora
- ISO 9001:2015 Certified Labour Law UpdatesDocumento28 pagineISO 9001:2015 Certified Labour Law UpdatesShiva SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- EDB-All Labour CodesDocumento140 pagineEDB-All Labour Codesgprakasammsw100% (2)
- Mcqs On Minimum Wages Act 1948Documento3 pagineMcqs On Minimum Wages Act 1948Suresh BoiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Labour Laws - G4Documento22 pagineLabour Laws - G4Arfa FatimaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Comparing Previous Act With New Labour CodesDocumento12 pagine1 Comparing Previous Act With New Labour Codesabdul gani khan100% (1)
- Payment Wages Act 1936Documento15 paginePayment Wages Act 1936vipin jaiswalNessuna valutazione finora
- PF Fund PPT NewDocumento25 paginePF Fund PPT NewTaniya ThakkarNessuna valutazione finora
- ILO Impct IndiaDocumento28 pagineILO Impct IndiaMahesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 300+ TOP Minimum Wages Act 1948 MCQs and Answers 2021Documento20 pagine300+ TOP Minimum Wages Act 1948 MCQs and Answers 2021Rupali Gupta100% (1)
- Payment of Bonus Act 1965 Key ProvisionsDocumento9 paginePayment of Bonus Act 1965 Key Provisionsshanky631Nessuna valutazione finora
- Labour Laws1 MCQDocumento65 pagineLabour Laws1 MCQjitintoteja50% (2)
- Minimum Wages Act 1948Documento33 pagineMinimum Wages Act 1948Jaison S RozarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Code on Occupational Safety Threshold IncreasedDocumento14 pagineCode on Occupational Safety Threshold IncreasedAbdul HudaifNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Disputes Act, 1947Documento42 pagineIndustrial Disputes Act, 1947samrulezzz100% (3)
- Economy Labour Laws and Industrial Relations in India - Quick Revision NoteDocumento7 pagineEconomy Labour Laws and Industrial Relations in India - Quick Revision Notedilipkkr50% (2)
- Employees Compensation ActDocumento25 pagineEmployees Compensation Actsairishikesh999Nessuna valutazione finora
- Labour Laws KPTCL NotesDocumento9 pagineLabour Laws KPTCL NotesSanthosh RMNessuna valutazione finora
- Workmen's Compensation ActDocumento25 pagineWorkmen's Compensation Actanandita28100% (1)
- Labour Notes (Self Made)Documento43 pagineLabour Notes (Self Made)ZxyerithNessuna valutazione finora
- The Payment of Gratuity Act 1972Documento13 pagineThe Payment of Gratuity Act 1972Dev Thakkar100% (2)
- Labour LawDocumento40 pagineLabour Lawshivender77786% (14)
- Labour Laws in India NotesDocumento198 pagineLabour Laws in India NotesKedar BhasmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Labour Laws & Scheme PDFDocumento39 pagineLabour Laws & Scheme PDFVikas SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Decoding India's New Labour CodesDocumento59 pagineDecoding India's New Labour CodesRizwan PathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Social Security in IndiaDocumento49 pagineSocial Security in IndiaKaran Gupta100% (1)
- Maternity Benefits Act 1961Documento3 pagineMaternity Benefits Act 1961Divyansh BhargavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Minimum Wages Act - 1948Documento8 pagineMinimum Wages Act - 1948Shaji Mullookkaaran100% (3)
- Constitutional Law Perspective in Labour LawDocumento76 pagineConstitutional Law Perspective in Labour LawchaitanyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Minimum Wages Act, 1948 PDFDocumento18 pagineMinimum Wages Act, 1948 PDFPankaj BhanwraNessuna valutazione finora
- New Labour Code Bill 2020 For EPFODocumento25 pagineNew Labour Code Bill 2020 For EPFOAbdul HudaifNessuna valutazione finora
- Social Security Code, 2020: Key Changes for Unorganised WorkersDocumento11 pagineSocial Security Code, 2020: Key Changes for Unorganised WorkersAbdul Hudaif100% (1)
- Maternity Benefit ActDocumento29 pagineMaternity Benefit ActShivone DiasNessuna valutazione finora
- The Industrial Relations Code, 2020Documento27 pagineThe Industrial Relations Code, 2020Hardik ShettyNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison of key provisions in previous labour laws and new Labour Code on Social SecurityDocumento12 pagineComparison of key provisions in previous labour laws and new Labour Code on Social Securityabdul gani khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Useful Tips On Labour Laws: Composed BYDocumento17 pagineUseful Tips On Labour Laws: Composed BYJimmy David100% (1)
- Dr. Meeta JoshiDocumento33 pagineDr. Meeta JoshiKarunya RamasamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Bombay Industrial Relations Act, 1946 SummaryDocumento29 pagineBombay Industrial Relations Act, 1946 SummaryJay Kothari100% (1)
- Labour Laws GuideDocumento14 pagineLabour Laws Guidesohel alamNessuna valutazione finora
- Wage Code BillDocumento12 pagineWage Code Billsrinivas rajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Bombay Tenancy and Agricultural Lands Act 1948Documento4 pagineBombay Tenancy and Agricultural Lands Act 1948Keith10w0% (1)
- Sandoval V HretDocumento5 pagineSandoval V HretSarah Jane UsopNessuna valutazione finora
- United States v. Hosea Hampton, 4th Cir. (2011)Documento2 pagineUnited States v. Hosea Hampton, 4th Cir. (2011)Scribd Government DocsNessuna valutazione finora
- Recase T - THBT ASEAN Should Suspend The Membership of Myanmar Until The Tatmadaw Cedes Power To The Democratically Elected GovernmentDocumento3 pagineRecase T - THBT ASEAN Should Suspend The Membership of Myanmar Until The Tatmadaw Cedes Power To The Democratically Elected GovernmentTania Regina PingkanNessuna valutazione finora
- Slump Sale AgreementDocumento35 pagineSlump Sale AgreementSagar Teli100% (1)
- Amended Articles of IncorporationDocumento5 pagineAmended Articles of IncorporationAileen Castro RigorNessuna valutazione finora
- 106) People vs. Cayat (68 Phil 12, 18 (1939) )Documento10 pagine106) People vs. Cayat (68 Phil 12, 18 (1939) )Carmel Grace KiwasNessuna valutazione finora
- Injustice and Bias in Canadian Family CourtroomsDocumento50 pagineInjustice and Bias in Canadian Family CourtroomsMohamed Fidjel100% (1)
- Chapter 18 Section 3Documento8 pagineChapter 18 Section 3api-206809924Nessuna valutazione finora
- The ICC and Confronting Myths in AfricaDocumento24 pagineThe ICC and Confronting Myths in AfricaWendel DamascenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Audit Document - Opsa Audit Report - SPD Complaint Case Audit Improper Search and Seizure 2023Documento34 pagineFinal Audit Document - Opsa Audit Report - SPD Complaint Case Audit Improper Search and Seizure 2023CBS13Nessuna valutazione finora
- People Vs de Los SantosDocumento8 paginePeople Vs de Los Santostaktak69Nessuna valutazione finora
- Territorial JurisdictionDocumento264 pagineTerritorial JurisdictionshraddhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Format of Application: For Official Use Only SL - No. of Application Year Course Whether ApprovedDocumento8 pagineFormat of Application: For Official Use Only SL - No. of Application Year Course Whether Approvedabhishek123hitNessuna valutazione finora
- International Criminal Law Professor Scharf's Module on Nuremberg TrialsDocumento245 pagineInternational Criminal Law Professor Scharf's Module on Nuremberg TrialsAlba P. Romero100% (1)
- Library Rules and RegulationsDocumento10 pagineLibrary Rules and RegulationsDiane ManuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Rivera Family Property Dispute ResolvedDocumento1 paginaRivera Family Property Dispute ResolvedMalen Crisostomo Arquillo-SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- A. Nature and Characteristics of VATDocumento4 pagineA. Nature and Characteristics of VATKIAN AGEASNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Social Rights in The CharterDocumento43 pagine01 Social Rights in The CharterLich_king2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Demand of NoticeDocumento6 pagineDemand of NoticeBhuvneshwari RathoreNessuna valutazione finora
- EPacific Vs CabansayDocumento2 pagineEPacific Vs CabansayStephanie Valentine100% (1)
- Basic Structure Doctrine Established in Landmark Keshvananda Bharati CaseDocumento6 pagineBasic Structure Doctrine Established in Landmark Keshvananda Bharati CaseNandita AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Consitutional and Statutory Basis of TaxationDocumento50 pagineConsitutional and Statutory Basis of TaxationSakshi AnandNessuna valutazione finora
- Written Task 1 - Child Pornography in CartoonsDocumento4 pagineWritten Task 1 - Child Pornography in CartoonsMauri CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Joseph Muller Corporation Zurich v. Societe Anonyme de Gerance Et D'armement, and Petromar Societe Anonyme, 451 F.2d 727, 2d Cir. (1971)Documento4 pagineJoseph Muller Corporation Zurich v. Societe Anonyme de Gerance Et D'armement, and Petromar Societe Anonyme, 451 F.2d 727, 2d Cir. (1971)Scribd Government DocsNessuna valutazione finora
- Letter From ElectedsDocumento2 pagineLetter From ElectedsJon RalstonNessuna valutazione finora
- Ernie Allen - NCMEC - Criminal Trial - Doc 2Documento7 pagineErnie Allen - NCMEC - Criminal Trial - Doc 2BrivahoNessuna valutazione finora
- Appelant Final Memorial WWWDocumento25 pagineAppelant Final Memorial WWWSrivathsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Supreme Court Appeal on Murder ConvictionDocumento43 pagineSupreme Court Appeal on Murder ConvictionVinita Ritwik100% (1)
- University of London La2024 ZADocumento3 pagineUniversity of London La2024 ZASaydul ImranNessuna valutazione finora
- Hell Put to Shame: The 1921 Murder Farm Massacre and the Horror of America's Second SlaveryDa EverandHell Put to Shame: The 1921 Murder Farm Massacre and the Horror of America's Second SlaveryValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Double Lives: True Tales of the Criminals Next DoorDa EverandDouble Lives: True Tales of the Criminals Next DoorValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (34)
- Nicole Brown Simpson: The Private Diary of a Life InterruptedDa EverandNicole Brown Simpson: The Private Diary of a Life InterruptedValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (16)
- If You Tell: A True Story of Murder, Family Secrets, and the Unbreakable Bond of SisterhoodDa EverandIf You Tell: A True Story of Murder, Family Secrets, and the Unbreakable Bond of SisterhoodValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (1788)
- Hearts of Darkness: Serial Killers, The Behavioral Science Unit, and My Life as a Woman in the FBIDa EverandHearts of Darkness: Serial Killers, The Behavioral Science Unit, and My Life as a Woman in the FBIValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (19)
- Broken: The most shocking childhood story ever told. An inspirational author who survived it.Da EverandBroken: The most shocking childhood story ever told. An inspirational author who survived it.Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (43)
- Selling the Dream: The Billion-Dollar Industry Bankrupting AmericansDa EverandSelling the Dream: The Billion-Dollar Industry Bankrupting AmericansValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (17)
- The Girls Are Gone: The True Story of Two Sisters Who Vanished, the Father Who Kept Searching, and the Adults Who Conspired to Keep the Truth HiddenDa EverandThe Girls Are Gone: The True Story of Two Sisters Who Vanished, the Father Who Kept Searching, and the Adults Who Conspired to Keep the Truth HiddenValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (36)
- Perfect Murder, Perfect Town: The Uncensored Story of the JonBenet Murder and the Grand Jury's Search for the TruthDa EverandPerfect Murder, Perfect Town: The Uncensored Story of the JonBenet Murder and the Grand Jury's Search for the TruthValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (68)
- The Bigamist: The True Story of a Husband's Ultimate BetrayalDa EverandThe Bigamist: The True Story of a Husband's Ultimate BetrayalValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (103)
- The Franklin Scandal: A Story of Powerbrokers, Child Abuse & BetrayalDa EverandThe Franklin Scandal: A Story of Powerbrokers, Child Abuse & BetrayalValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (45)
- The Gardner Heist: The True Story of the World's Largest Unsolved Art TheftDa EverandThe Gardner Heist: The True Story of the World's Largest Unsolved Art TheftNessuna valutazione finora
- Cold-Blooded: A True Story of Love, Lies, Greed, and MurderDa EverandCold-Blooded: A True Story of Love, Lies, Greed, and MurderValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (53)
- Gotti's Rules: The Story of John Alite, Junior Gotti, and the Demise of the American MafiaDa EverandGotti's Rules: The Story of John Alite, Junior Gotti, and the Demise of the American MafiaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Rescue Artist: A True Story of Art, Thieves, and the Hunt for a Missing MasterpieceDa EverandThe Rescue Artist: A True Story of Art, Thieves, and the Hunt for a Missing MasterpieceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- The Last Outlaws: The Desperate Final Days of the Dalton GangDa EverandThe Last Outlaws: The Desperate Final Days of the Dalton GangValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- Diamond Doris: The True Story of the World's Most Notorious Jewel ThiefDa EverandDiamond Doris: The True Story of the World's Most Notorious Jewel ThiefValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (18)
- To the Bridge: A True Story of Motherhood and MurderDa EverandTo the Bridge: A True Story of Motherhood and MurderValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- A Deadly Game: The Untold Story of the Scott Peterson InvestigationDa EverandA Deadly Game: The Untold Story of the Scott Peterson InvestigationValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (48)
- The Truth About Aaron: My Journey to Understand My BrotherDa EverandThe Truth About Aaron: My Journey to Understand My BrotherNessuna valutazione finora
- Reasonable Doubts: The O.J. Simpson Case and the Criminal Justice SystemDa EverandReasonable Doubts: The O.J. Simpson Case and the Criminal Justice SystemValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (25)
- Bloodlines: The True Story of a Drug Cartel, the FBI, and the Battle for a Horse-Racing DynastyDa EverandBloodlines: The True Story of a Drug Cartel, the FBI, and the Battle for a Horse-Racing DynastyValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (8)
- Unanswered Cries: A True Story of Friends, Neighbors, and Murder in a Small TownDa EverandUnanswered Cries: A True Story of Friends, Neighbors, and Murder in a Small TownValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (178)
- To Kill and Kill Again: The Terrifying True Story of Montana's Baby-Faced Serial Sex MurdererDa EverandTo Kill and Kill Again: The Terrifying True Story of Montana's Baby-Faced Serial Sex MurdererValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (157)