Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
1 - First Take Home Exercise: Various Experts View On Reading
Caricato da
Annalie Jeane ManaloDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1 - First Take Home Exercise: Various Experts View On Reading
Caricato da
Annalie Jeane ManaloCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Name: Annalie Jeane B.
Manalo
First Take Home Exercise: Various experts view on Reading
1. Partnership for Reading, National Reading Panel, Reading First Law (2002) - reading is
"a complex system of deriving meaning from print" that requires:
a) an understanding of how speech sounds are related to print- viewed
that Phonemic Awareness Instructions and Phonics Instructions are
significantly better on the forms of training in helping the reader acquire
phonemic awareness because this skill enables to apply in reading to
manipulate speech sounds in words and spelling.
b) decoding (word identification) skills,
c) fluency - found a better, and more extensive, body of research on guided
oral reading procedures. Generally, the Panel found that these
procedures tended to improve word recognition, fluency (speed and
accuracy of oral reading), and comprehension with most groups.
d) vocabulary and background knowledge,
e) active comprehension strategies, and - found a variety of methods by
which readers acquire vocabulary through explicit instruction and
improve their comprehension of what they read. The Panel also found
that although there has been considerable success in teaching a variety
of effective text comprehension strategies that lead to improved text
comprehension, the most promising lines of research within the reading
comprehension strategies area focused on teacher preparation to teach
comprehension and enhance vocabulary.
f) a motivation to read.
These key elements define the content of reading instruction, and research provides
guidelines for building many of the important skills.
2. Nell Duke and P. David Pearson (2002) - Effective Practices for Developing Reading
Comprehension. They viewed that reading should be in place in addition to
comprehension strategy instruction—such as reading real texts for real purposes,
reading a range of text genres, and writing texts for others to understand. They highlight
the importance of routine for improving comprehension and how teachers can support
learners in building strategic thinking, which is likely to be more important that gaining
mastery of specific strategies.
3. Robert Ruddell, Martha Rapp Ruddell, Harry Singer (1994) – A reading model is a
graphic attempt, to depict how an individual perceives a word, processes a clause and
comprehend a text.
1 | First Take Home Exercise: Various Experts view on Reading
4. Diane Henry Leipzig (2001) –
a. Reading is a multifaceted process involving:
i. Word Recognition - Identify the words in print
ii. Comprehension - Construct an understanding from them
iii. Fluency - Coordinate identifying words and making meaning so that
reading is automatic and accurate
iv. and motivation.
b. Reading in its fullest sense involves weaving together word recognition and
comprehension in a fluent manner.
5. Christine Cziko, Cynthia Greenleaf, Lori Hurwitz, Ruth Schoenbach (2000)
a. Reading is not just a basic skill - students' reading ability goes to primary grade
teachers, and upper elementary and secondary school teachers at each grade
level need teach only new vocabulary and concepts relevant to new content.
Seen this way, reading is a simple process: readers decode (figure out how to
pronounce) each word in a text and then automatically comprehend the
meaning of the words, as they do with their everyday spoken language. This is
not our understanding of reading.
b. Reading is a complex process - The text evoked voices, memories, knowledge,
and experiences from other times and places—some long dormant, some more
immediate. If you were reading complex text about complex ideas or an
unfamiliar type of text, you were working to understand it, your reading most
likely characterized by many false starts and much backtracking. You were
probably trying to relate it to your existing knowledge and understanding.
c. Reading is problem solving - complex process of problem solving in which the
reader works to make sense of a text not just from the words and sentences on
the page but also from the ideas, memories, and knowledge evoked by those
words and sentences.
d. Fluent reading is not the same as decoding - Skillful reading does require
readers to carry out certain tasks in a fairly automatic manner. Decoding skills—
quick word recognition and ready knowledge of relevant vocabulary, for
example—are essential to successful reading. However, they are by no means
sufficient, especially when texts are complex or otherwise challenging.
e. Reading is situationally bounded - A person who understands one type of text is
not necessarily pro-ficient at reading all types. Reading is influenced by
situational factors, among them the experiences readers have had with
particular kinds of texts and reading for particular purposes.
2 | First Take Home Exercise: Various Experts view on Reading
6. Kenneth Goodman (1998), Kenneth Goodman (1981) - presents a conception of reading
as a guessing game. These misreadings are not called errors; they are "miscues. Goal of
reading is constructing meaning in response to text. It requires interactive use of
graphophonics, syntactic and semantic cues to construct meaning.
7. Adams (1990) – viewed the need not remain trapped in the phonics versus teaching-for-
meaning dilemma. She proposes that phonics can work together with the whole
language approach to teaching reading and provides an integrated treatment of the
knowledge and process involved in skillful reading, the issues surrounding their
acquisition, and the implications for reading instruction. Thinking and Learning About
Print.
8. Barr, Sadow, Blachowicz (1990) – viewed that drawing on both the 'bottom-up' and
'top-down' approaches is the interactive model, which presents reading as a process in
which the reader uses the lexical and syntactic information in a text, not necessarily
linearly, to construct meaning while utilizing his own knowledge, expectations and
assumptions. It is this integrative model which is applied in the comprehension of
academic content.
9. Dechant (1991)
a. Top-down reading models suggest that processing of text begins in the mind of
the readers with:
i. Meaning-driven processes
ii. An assumption about the meaning of a text.
b. Readers identify letters and words only to confirm their assumptions about
meaning of the text.
c. A bottom-up reading model emphasizes a single-direction, part-to-whole
processing of text.
i. Emphasizes the written or printed text
ii. Says reading is driven by a process that results in meaning
iii. Influences reader’s world knowledge.
10. Flesch (1995) – viewed with Reading Ease Formula that tells how easy or difficult a text
is to read. It also tells us how difficult it is to understand.
11. Klein, Peterson, Simington (1991) – reading is a process, strategic, interactive and
reading instruction requires orchestration. He viewed that reading means getting
meaning from certain combinations of letters. Teach the child what each letter stands
for and he/she can read.
3 | First Take Home Exercise: Various Experts view on Reading
Online References:
Partnership for Reading, National Reading Panel, Reading First Law (2002)
https://www.nichd.nih.gov/sites/default/files/publications/pubs/nrp/Documents/report.pd
f
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/National_Reading_Panel
https://lincs.ed.gov/publications/html/mcshane/chapter2.html
Nell Duke and P. David Pearson (2002)
https://lincs.ed.gov/professional-development/resource-collections/profile-348
https://www.learner.org/workshops/teachreading35/pdf/Dev_Reading_Comprehension.pdf
Robert Ruddell, Martha Rapp Ruddell, Harry Singer (1994)
https://www.slideshare.net/AbbieLaudato/reading-models-and-schema-theory
Diane Henry Leipzig (2001)
http://www.adlit.org/article/352/
Christine Cziko, Cynthia Greenleaf, Lori Hurwitz, Ruth Schoenbach (2000)
https://www.nwp.org/cs/public/print/resource/787
Kenneth Goodman (1998), Kenneth Goodman (1981)
http://people.uncw.edu/kozloffm/goodman.html
https://www.slideshare.net/AbbieLaudato/reading-models-and-schema-theory
Adams (1990)
https://www.readingrockets.org/articles/researchbytopic/4831
Barr, Sadow, Blachowicz (1990)
cms.education.gov.il/NR/rdonlyres/...EC63.../TheoreticalBasisforthisCurriculum.doc
Dechant (1991)
https://www.slideshare.net/AbbieLaudato/reading-models-and-schema-theory
Flesch (1995)
https://www.google.com/search?rlz=1C1GCEU_enPH854PH854&biw=1366&bih=657&q=Kle
in,+Peterson,+Simington+(1991)&tbm=isch&source=univ&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjwmdX-
3_TjAhVFUN4KHSvMCjkQsAR6BAgJEAE#imgrc=GoIKc_5Si8BkYM:
Klein, Peterson, Simington (1991)
https://www.google.com/search?rlz=1C1GCEU_enPH854PH854&biw=1366&bih=657&q=Kle
in,+Peterson,+Simington+(1991)&tbm=isch&source=univ&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjwmdX-
3_TjAhVFUN4KHSvMCjkQsAR6BAgJEAE#imgrc=GoIKc_5Si8BkYM:
4 | First Take Home Exercise: Various Experts view on Reading
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Listening in the Classroom: Teaching Students How to ListenDa EverandListening in the Classroom: Teaching Students How to ListenNessuna valutazione finora
- Conversation Strategies: Pair and Group Activities for Develping Communicative CompetenceDa EverandConversation Strategies: Pair and Group Activities for Develping Communicative CompetenceValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Teaching Reading Comprehension by Using Intensive Reading Technique at Grade VDocumento9 pagineTeaching Reading Comprehension by Using Intensive Reading Technique at Grade Vde faNessuna valutazione finora
- Bab 2 SkripsiDocumento21 pagineBab 2 Skripsiarsyil dwi anugrahNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter IiDocumento20 pagineChapter IiMhmmd AkbarNNessuna valutazione finora
- A. Background of The ResearchDocumento26 pagineA. Background of The Researchhajrin hi abdurrahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- DPE - Developmental Reading PDFDocumento130 pagineDPE - Developmental Reading PDFJaenelyn AlquizarNessuna valutazione finora
- Materi CMD Presentasi 2Documento4 pagineMateri CMD Presentasi 2Rima HermawatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading Comprehension and Vocabulary DevelopmentDocumento44 pagineReading Comprehension and Vocabulary DevelopmentKenneth Joe Jose LuqueyNessuna valutazione finora
- 3615 7074 1 SMDocumento20 pagine3615 7074 1 SMspeedotNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.teaching Reading and WritingDocumento10 pagine4.teaching Reading and WritingPio MelAncolico Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter IIDocumento9 pagineChapter IIfitriNessuna valutazione finora
- National Seminar Proceeding - 576Documento9 pagineNational Seminar Proceeding - 576Chika Rizky AmaliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Ii 2003Documento33 pagineChapter Ii 2003Ari RenaldiNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER II Full RapDocumento20 pagineCHAPTER II Full RapKougryston71Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bella Septian Almunda Pratama - CHAPTER IIDocumento22 pagineBella Septian Almunda Pratama - CHAPTER IIFeya NuevoNessuna valutazione finora
- Devt - L Reading Lecture Handout NEWDocumento10 pagineDevt - L Reading Lecture Handout NEWIan EnoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sub-Skills Approach and Extensive Approach To Reading in TeflDocumento9 pagineSub-Skills Approach and Extensive Approach To Reading in Teflmudianto midenNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Reading and WritingDocumento14 pagineTeaching Reading and WritingEd-Jay RoperoNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching of Speaking, Listening and Reading Reviewer MajorshipDocumento21 pagineTeaching of Speaking, Listening and Reading Reviewer MajorshipalexaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter II AnecdoteDocumento12 pagineChapter II AnecdoteApriel YaediNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento31 pagineChapter 2KristinemaywamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Reading and WritingDocumento4 pagineTeaching Reading and WritingDherick RaleighNessuna valutazione finora
- Grades 6 8Documento103 pagineGrades 6 8riddle_oneNessuna valutazione finora
- Theories of Reading ComprehensionDocumento19 pagineTheories of Reading ComprehensionMetchell ManlimosNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter IIDocumento17 pagineChapter IIAbdul R. SidikNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Receptive Skills - RDocumento4 pagineTeaching Receptive Skills - RGheorghita Dobre100% (1)
- Input 2 and 3 Task 4Documento4 pagineInput 2 and 3 Task 4Reynaldo V Tanglao Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Teachers Know Comprehension PDFDocumento9 pagineTeachers Know Comprehension PDFemysamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Teachers Know Comprehension PDFDocumento9 pagineTeachers Know Comprehension PDFemysamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Amam Musfiroh - CHAPTER II PDFDocumento16 pagineAmam Musfiroh - CHAPTER II PDFnikmah khairaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter I1Documento25 pagineChapter I1umiNessuna valutazione finora
- Improving Students' Reading Skill Through Communicative Language Teaching Method Chapter IIDocumento16 pagineImproving Students' Reading Skill Through Communicative Language Teaching Method Chapter IIdwiNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 8 - Teaching ReadingDocumento33 pagineGroup 8 - Teaching Readingsyafa tiaraNessuna valutazione finora
- American University of BeirutDocumento60 pagineAmerican University of BeirutDaniel Leonard SinagaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.teaching Reading and WritingDocumento9 pagine4.teaching Reading and WritingRinna NLNessuna valutazione finora
- Finals Module Teaching English in The ElemDocumento55 pagineFinals Module Teaching English in The ElemHaifa dulayNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 - 06202244061Documento31 pagineChapter 2 - 06202244061ChaNessuna valutazione finora
- ApqhsnsiDocumento11 pagineApqhsnsiRozak HakikiNessuna valutazione finora
- 307-Article Text-557-1-10-20230303Documento11 pagine307-Article Text-557-1-10-20230303etikelavaishnavi09Nessuna valutazione finora
- Majorship Area: English Focus: Teaching Reading and Writing LET CompetenciesDocumento32 pagineMajorship Area: English Focus: Teaching Reading and Writing LET CompetenciesEd-Jay RoperoNessuna valutazione finora
- How We Can Improve Our Reading, Thinking and Comprehension: SupervisedDocumento4 pagineHow We Can Improve Our Reading, Thinking and Comprehension: Supervisedعلي توفيق مشهدNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter IiDocumento15 pagineChapter IiNonny WiondyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Two Review of The LiteratureDocumento14 pagineChapter Two Review of The LiteraturemifNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Two Review of The LiteratureDocumento15 pagineChapter Two Review of The LiteraturemifNessuna valutazione finora
- Review of Literature: A. Theoretical FrameworkDocumento21 pagineReview of Literature: A. Theoretical FrameworkSuWeny GuloNessuna valutazione finora
- Hill, Tomlinson (2003) - Coursebook Listening ActivitiesDocumento11 pagineHill, Tomlinson (2003) - Coursebook Listening ActivitiesMelina San Miguel GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hard Copy ETMDocumento5 pagineHard Copy ETManis thahirahNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter IIDocumento15 pagineChapter IIGustari AulyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Review of Related LiteratureDocumento7 pagineReview of Related LiteratureJMSUYODNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading Comprehension MALT 107Documento21 pagineReading Comprehension MALT 107Diana ArcangelNessuna valutazione finora
- 86-File Utama Naskah-254-1-10-20210601Documento9 pagine86-File Utama Naskah-254-1-10-20210601Colm SuppleNessuna valutazione finora
- English - Language Arts - Theories in Reading InstructionDocumento4 pagineEnglish - Language Arts - Theories in Reading InstructionClem Vincent100% (1)
- Bab IiDocumento20 pagineBab IiAmr GamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Tefl (Reading) - Linda Mariani GuloDocumento14 pagineTefl (Reading) - Linda Mariani GuloLinda Mariani GuloNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading and WritingDocumento15 pagineReading and WritingShalom Boker TovNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading at A Glance: Bottom-Up Model (Phillip Gough, 1972)Documento2 pagineReading at A Glance: Bottom-Up Model (Phillip Gough, 1972)Kristine AbreoNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER II (English)Documento14 pagineCHAPTER II (English)Andi AldiNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning To Read and Reading To Learn in English: - Parbati Kumari PokharelDocumento7 pagineLearning To Read and Reading To Learn in English: - Parbati Kumari Pokharelkhanh linhNessuna valutazione finora
- Interacting with Informational Text for Close and Critical ReadingDa EverandInteracting with Informational Text for Close and Critical ReadingNessuna valutazione finora
- 5th Take Home ActivityDocumento39 pagine5th Take Home ActivityAnnalie Jeane ManaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Task 7: Matching Type: Name: Annalie Jeane ManaloDocumento1 paginaTask 7: Matching Type: Name: Annalie Jeane ManaloAnnalie Jeane ManaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Planning: 1 - Task 2: Game PlanDocumento1 paginaPlanning: 1 - Task 2: Game PlanAnnalie Jeane Manalo50% (4)
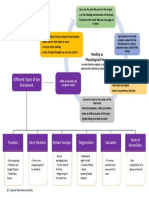
- Different Types of Eye Movement: Reading As Physiological ProcessDocumento1 paginaDifferent Types of Eye Movement: Reading As Physiological ProcessAnnalie Jeane ManaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Dnyanadeep's IAS: UPSC Essay Series - 7Documento2 pagineDnyanadeep's IAS: UPSC Essay Series - 7Rahul SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- RBG - CRM BRD - Marketing - v4.1Documento68 pagineRBG - CRM BRD - Marketing - v4.1Manvi Pareek100% (2)
- SATB All Glory Laud and HonorDocumento1 paginaSATB All Glory Laud and HonorGeorge Orillo BaclayNessuna valutazione finora
- Docshare - Tips Upstream Advanced c1 Test BookletDocumento3 pagineDocshare - Tips Upstream Advanced c1 Test BookletCosmin OaieNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering ConsultancyDocumento30 pagineEngineering Consultancynaconnet100% (2)
- CA IPCC Accounting Guideline Answers May 2015Documento24 pagineCA IPCC Accounting Guideline Answers May 2015Prashant PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Democracy in SomalilandDocumento118 pagineDemocracy in SomalilandAbdirahman IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Muzakarah Jawatankuasa Fatwa Majlis Kebangsaan Bagi Hal Ehwal Ugama Islam Malaysia Kali KeDocumento7 pagineMuzakarah Jawatankuasa Fatwa Majlis Kebangsaan Bagi Hal Ehwal Ugama Islam Malaysia Kali KeSiti Zubaidah ZulkhairieNessuna valutazione finora
- SSPC - Guia 12Documento6 pagineSSPC - Guia 12José Alvaro Herrera Ramos50% (2)
- ESSAYDocumento1 paginaESSAYJunalie GregoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Food Safety Plan of Catalonia: GuidelinesDocumento38 pagineFood Safety Plan of Catalonia: GuidelinesralapubsNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit5 v1.0022101210Documento52 pagineUnit5 v1.0022101210Lily KkNessuna valutazione finora
- Academic 8 2.week Exercise Solutions PDFDocumento8 pagineAcademic 8 2.week Exercise Solutions PDFAhmet KasabalıNessuna valutazione finora
- SDS SheetDocumento8 pagineSDS SheetΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNessuna valutazione finora
- 9702 s02 QP 1Documento20 pagine9702 s02 QP 1Yani AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Section D Textual QuestionsDocumento52 pagineSection D Textual Questionsxander ganderNessuna valutazione finora
- High-Frequency Injection-Based SensorlessDocumento12 pagineHigh-Frequency Injection-Based SensorlessRiad BOUZIDINessuna valutazione finora
- Project BBADocumento77 pagineProject BBAShivamNessuna valutazione finora
- CarozziDocumento20 pagineCarozziNicholas Matthew WelshNessuna valutazione finora
- Στέργος Νεκτάριος-Μικκιος-CVDocumento4 pagineΣτέργος Νεκτάριος-Μικκιος-CVNektarios MikkiosNessuna valutazione finora
- Ebook Fulfilling Destiny As Demanded by GodDocumento94 pagineEbook Fulfilling Destiny As Demanded by GodIfeanyi OmeiheakuNessuna valutazione finora
- The Divine Liturgy Syro Malankara ChurchDocumento4 pagineThe Divine Liturgy Syro Malankara ChurchGian Marco TallutoNessuna valutazione finora
- Redemption and The Relief Work RevisedDocumento234 pagineRedemption and The Relief Work RevisedYewo Humphrey MhangoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdf-To-Word EditedDocumento48 paginePdf-To-Word EditedJames Genesis Ignacio LolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Boado Notes On Criminal LawDocumento55 pagineBoado Notes On Criminal LawJoy100% (3)
- Maintenance ManagerDocumento4 pagineMaintenance Managerapi-121382389Nessuna valutazione finora
- HistogramDocumento7 pagineHistogramTesfaye MinaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Demonstration MethodDocumento16 pagineDemonstration Methodfrankie aguirreNessuna valutazione finora
- LIFT OFF ModuleDocumento28 pagineLIFT OFF ModulericardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sand Casting Lit ReDocumento77 pagineSand Casting Lit ReIxora MyNessuna valutazione finora