Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Ninja - Anemias PDF
Caricato da
Erica Hyeyeon Lee0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
66 visualizzazioni1 paginaTitolo originale
11. Ninja - Anemias.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
66 visualizzazioni1 paginaNinja - Anemias PDF
Caricato da
Erica Hyeyeon LeeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 1
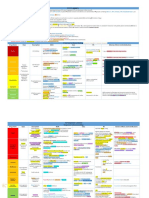
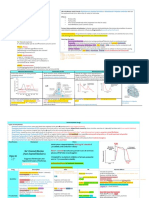
Anemias
→ Anemia: ↓ number of RBCs or ↓ Hb concentration
→ Macrocytic RBCs!vitamin B12 or folate deficiency
→ Microcytic RBCs! iron deficiency anemia: results from acute/chronic blood loss, insufficient intake or in heavily menstruating/pregnant women
→ Normocytic RBCs! acute blood loss & hemolysis
→ Iron is stored as ferritin in intestinal mucosal cells
→ Phlebotomy → for chronic iron overload without anemia
→ Vitamin B12!cofactor for many rxns; deficiency!microcytic megaloblastic anemia and neurologic abnormalities
o Ultimate source: microbial synthesis!not synthesized by plants or animals (found in meat, eggs and dairy)
o stored in the liver; would take about 5 years to develop the anemia from depleting stores requires R Factor & Intrinsic Factor
review o absorbed only after its formed a complex w/ intrinsic factor in the distal ileum via receptor-mediated transport system
notes o deficiency results from malabsorption d/t lack of IF (pernicious anemia) or defective transporter or d/t nutritional deficiency as seen in strict vegetarians, partial or total gastrectomy and any condition that affects the distal ileum
o deficiency prevents synthesis of purines required for DNA synthesis & chronic pancreatitis: cannot cleave RF-B12 complex
o deficiency causes accumulation of homocysteine and methylmalonyl-CoA
o SXS include neurologic syndrome!paresthesia in peripheral nerves, weakness and progresses to spasticity, ataxia and other CNS dysfxn
o admin of folic acid will NOT prevent neurologic SXS even though it will correct the anemia
→ Folic acid! cofactor for many rxns; deficiency!microcytic megaloblastic anemia
o Deficiency can develop within 1-6mon after intake has stopped :fast depletion of stores
o deficiency prevents synthesis of purines required for DNA synthesis dUMP --> dTMP
o deficiency causes accumulation of homocysteine
o deficiency is often caused by inadequate dietary intake (alcoholics and liver disease), increased demand (pregnant women, pts with hemolytic anemia), malabsorption syndromes affecting the jejunum, or certain drugs (methotrexate,
trimethoprim and pyrimethamine or long term therapy with phenytoin) ** phenytoin does not cause megaloblastic changes
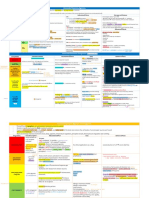
Drug Name Class Description Uses Pharmacodynamics Adverse effects
/Contraindications
Nausea
Ferrous Sulfate Iron deficiency anemia!hypochromic microcytic anemia Epigastric discomfort
Ferrous gluconate Oral iron therapy Abdominal cramps
Ferrous iron is most
Ferrous fumarate TXT should continue 3-6mon after correction of the cause of the iron loss Constipation
Iron efficiently absorbed!only
Diarrhea
preparations ferrous salts should be
Iron deficiency anemia!hypochromic microcytic anemia used
Iron dextran
Sodium ferric gluconate complex Parenteral iron therapy
Reserved for pts who can’t tolerate oral iron or in pts w/ chronic anemia who
Iron sucrose
can’t be maintained on oral iron alone
Acute Iron Toxicity: seen in young children who ingest iron pills!necrotizing
Deferoxamine gastroenteritis with vomiting, abdominal pain, and bloody diarrhea followed
by shock, metabolic acidosis coma and death
Binds to iron which has
Chronic Iron Toxicity/Hemochromatosis: XS iron is deposited in the heart,
already been absorbed!
Iron chelator Given parentally liver, pancreas, etc.!organ failure and death; seen in pts with inherited
promotes excretion in
hemochromatosis or pts receiving many red cell transfusions (thalassemia
Deferasirox urine and feces
major pts) & sickle cell
disease
Acute Iron Toxicity
Therapy must be continued for life in
Vitamin B12 deficiency! megaloblastic, macrocytic anemia Two reactions: pts with pernicious anemia
Cyanocobalamin homocysteine →
Parenteral Vitamin B12
Hydroxocobalamin Hydroxocobalamin preferred b/c it is more highly protein-bound and this methionine Deficiency of cobalamin can cause
Vitamins
(inactive) activated to:
remains longer in circulation methylmalonyl → succinyl neurologic abnormalities due to
(macrocytic) • dihydroacetylcobalamin? (Methylmalonyl CoA path)
• methylcobalamin (methionine pathway) increased homocysteine
Folic acid deficiency and B12 deficiency Required for purine
Deficiency is a lot more common than Masking of neurologic deficits in B12
Folic Acid Prevents neural tube defects (spina bifida) in the fetus when given to a synthesis Need B12 to form
B12, but can be easily corrected deficiency
pregnant woman THF → folate trap
Stimulates erythroid proliferation and
• Chronic Renal Disease (intrinsic low EPO)
differentiation via JAK/STAT Produced in the kidney in
Erythropoietin • cannot be used if extra-renal anemia (EPO normal)
cytokine receptor
Anemia with renal disease [can’t produce endogenous EPO → best response to hypoxia
Hyperviscosity → HTN & thrombosis
Induces release of reticulocytes from BM responders] • MI
3x Longer acting than EPO ↓clearance in comparison • stroke
Darbepoetin
Hematopoietic Two CHO chains to erythropoietin
Growth Filgrastim (G-CSF)! production/fxn of neutrophils
Myeloid growth factors with JAK/STAT C-CSF!bone pain
Factors Sargramostin (GM-CSF)! production/fxn of neutrophils +production of other
Filgrastim G-CSF receptors GM-CSF! fever, arthralgia, and
myeloid megakaryocyte progenitors
Sargramostin GM-CSF capillary damage with edema
patients with
(cytokine receptor) Allergic rxns=rare
BM supression Primary and secondary neutropenia; after cancer chemotherapy
along with Txt of pts with prior episode of thrombocytopenia after chemo
IL-11 Megakaryocyte growth factor : platelets
thrombopoeitin Reduced need for platelet transfusions
Sickle cell Anemia + folate supplements
Sickle cell Increases fetal Hb!dilute HbS!relieve Bone marrow suppression aplastic
Hydroxyurea Chronic myelogenous leukemia
Agents painful crisis (less hypoxia) Cutaneous vasculitis crisis
Polycythemia Vera
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Asthma - Respiratory PDFDocumento1 paginaAsthma - Respiratory PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee0% (1)
- ANS DrugsDocumento2 pagineANS Drugsmed testNessuna valutazione finora
- Opioids PDFDocumento2 pagineOpioids PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Opioids PDFDocumento2 pagineOpioids PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Aluminum OH Magnesium OH Calcium Carbonate: Pud & GerdDocumento4 pagineAluminum OH Magnesium OH Calcium Carbonate: Pud & Gerdmed testNessuna valutazione finora
- Local Anesthetics - Blockers K+ Channel Blockers Ca2+ Channel BlockersDocumento4 pagineLocal Anesthetics - Blockers K+ Channel Blockers Ca2+ Channel Blockersmed testNessuna valutazione finora
- Ninja - Anti-HTN PDFDocumento6 pagineNinja - Anti-HTN PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (2)
- Ninja - Anti-HTN PDFDocumento6 pagineNinja - Anti-HTN PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (2)
- Chart - WBC DisordersDocumento1 paginaChart - WBC DisordersSamuel RothschildNessuna valutazione finora
- ECG Interpretations GoodDocumento104 pagineECG Interpretations GoodaymenNessuna valutazione finora
- GI Drugs PDFDocumento6 pagineGI Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Cardiovascular History: Chest PainDocumento5 pagineCardiovascular History: Chest PainTom MallinsonNessuna valutazione finora
- UWorld - Psych Review Charts (From Questions)Documento47 pagineUWorld - Psych Review Charts (From Questions)uowhywxuuiragjadchNessuna valutazione finora
- Ninja - Cholinergic Drugs PDFDocumento4 pagineNinja - Cholinergic Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (2)
- Ninja - Cholinergic Drugs PDFDocumento4 pagineNinja - Cholinergic Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (2)
- Ninja - Drugs Heart Failure PDFDocumento4 pagineNinja - Drugs Heart Failure PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal Guide and Charts: AlbuminDocumento16 pagineRenal Guide and Charts: AlbuminYaima JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- Critical Care Drug Reference SheetDocumento12 pagineCritical Care Drug Reference SheetYanina CoxNessuna valutazione finora
- Understand Acid-Base DisordersDocumento89 pagineUnderstand Acid-Base DisordersEdouinaNessuna valutazione finora
- NSAIDS and SteroidsDocumento2 pagineNSAIDS and Steroidsmed testNessuna valutazione finora
- Antibiotics Chart 2Documento10 pagineAntibiotics Chart 2Vee MendNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical School Lecture Notes: Cardiovascular, Pulmonary, GI, Renal, Neuro, and MoreDocumento1 paginaMedical School Lecture Notes: Cardiovascular, Pulmonary, GI, Renal, Neuro, and MoreGabriella RosinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ninja - Diuretics PDFDocumento3 pagineNinja - Diuretics PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Nsaids: Celecoxib, Meloxicam Aspirin, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Indomethacin Ketorolac, Naproxen, PiroxicamDocumento2 pagineNsaids: Celecoxib, Meloxicam Aspirin, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Indomethacin Ketorolac, Naproxen, PiroxicamErica Hyeyeon LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ninja - Anti-Coagulants PDFDocumento3 pagineNinja - Anti-Coagulants PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Ninja - Anti-Coagulants PDFDocumento3 pagineNinja - Anti-Coagulants PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Ninja - Adrenergic Drugs PDFDocumento6 pagineNinja - Adrenergic Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Glomerulonephritis Cheat Sheet PDFDocumento1 paginaGlomerulonephritis Cheat Sheet PDFAnonymous aA9Ol6239Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacogenomics PDFDocumento1 paginaPharmacogenomics PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Path CNS Robbins Outline: Owl Club Review Sheets 1Documento37 paginePath CNS Robbins Outline: Owl Club Review Sheets 1Coy NuñezNessuna valutazione finora
- Spinal Cord CompressionDocumento4 pagineSpinal Cord Compressionian3yeung-2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Panasonic 2012 PDP Troubleshooting Guide ST50 ST Series (TM)Documento39 paginePanasonic 2012 PDP Troubleshooting Guide ST50 ST Series (TM)Gordon Elder100% (5)
- Sphere: These DiarrheaDocumento3 pagineSphere: These Diarrheamed testNessuna valutazione finora
- Autonomic drugs to antineoplastics overviewDocumento5 pagineAutonomic drugs to antineoplastics overviewBerkay ArslanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharm Fall Cardiovascular Pharmacology Study Guide-106Documento47 paginePharm Fall Cardiovascular Pharmacology Study Guide-106sean liyanageNessuna valutazione finora
- Ninja - Antihyperlipidemics PDFDocumento3 pagineNinja - Antihyperlipidemics PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Respiratory and Cardiovascular DrugsDocumento21 pagineRespiratory and Cardiovascular DrugsCandace Flowers100% (3)
- Hypertensive Work Up Age Work Up Ugib Work Up Stroke Work UpDocumento5 pagineHypertensive Work Up Age Work Up Ugib Work Up Stroke Work UpGeraldine Marie SalvoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharm C Exam 10 Drug ListDocumento2 paginePharm C Exam 10 Drug ListVokdadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric Hematooncology Alarm SymptomsDocumento22 paginePediatric Hematooncology Alarm SymptomsMuhammad ArifNessuna valutazione finora
- The Temple of ChaosDocumento43 pagineThe Temple of ChaosGauthier GohorryNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmayield: Must Know Pharmacology NotesDocumento2 paginePharmayield: Must Know Pharmacology NotesBianca Desiree VergaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ninja - Antiarrhythmic Drugs PDFDocumento7 pagineNinja - Antiarrhythmic Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Cell Wall Inhibitors and Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Antibiotics Mechanisms of ActionDocumento3 pagineCell Wall Inhibitors and Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Antibiotics Mechanisms of Actionyanks1120Nessuna valutazione finora
- Drug ClassDocumento13 pagineDrug ClassEdfren Salazar Colon100% (1)
- Genetic Conditions For USMLEDocumento2 pagineGenetic Conditions For USMLEkcxieNessuna valutazione finora
- Elevator Traction Machine CatalogDocumento24 pagineElevator Traction Machine CatalogRafif100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Drug IntroductionDocumento3 pagineCardiovascular Drug IntroductionSamah Khan100% (1)
- Concise SEO-Optimized Title for Clotting DocumentDocumento3 pagineConcise SEO-Optimized Title for Clotting DocumentRyan TurnerNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes Mellitus Drug ChartDocumento3 pagineDiabetes Mellitus Drug Chartlui.stephanie1751100% (1)
- Sibuyan Island ResiliencyDocumento12 pagineSibuyan Island ResiliencyEndangeredSpeciesNessuna valutazione finora
- Ricoh 4055 PDFDocumento1.280 pagineRicoh 4055 PDFPham Nguyen Hoang Minh100% (1)
- Nikola Tesla Was Murdered by Otto Skorzeny.Documento12 pagineNikola Tesla Was Murdered by Otto Skorzeny.Jason Lamb50% (2)
- Ninja - Antianginal Drugs PDFDocumento2 pagineNinja - Antianginal Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- 0.5. ANS Quicksheet PDFDocumento1 pagina0.5. ANS Quicksheet PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunopharmacology PDFDocumento2 pagineImmunopharmacology PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Approximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMDocumento8 pagineApproximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMakane ryuNessuna valutazione finora
- SketchyPath ChecklistDocumento1 paginaSketchyPath ChecklistFajar Raza100% (1)
- Diseases - BiochemDocumento4 pagineDiseases - BiochemJay FeldmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ninja - Autacoids PDFDocumento3 pagineNinja - Autacoids PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti FungalsDocumento5 pagineAnti FungalskakuNessuna valutazione finora
- Arteriolar Dilator Decreases After Load Ejection FractionDocumento1 paginaArteriolar Dilator Decreases After Load Ejection FractionJack GuccioneNessuna valutazione finora
- Interpreting the Biochemisty PanelDocumento4 pagineInterpreting the Biochemisty PanelNatalie KingNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology Main DrugsDocumento14 paginePharmacology Main DrugsSabir KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Gout DrugsDocumento1 paginaGout DrugsMichael BrownNessuna valutazione finora
- IV Fluid ChartDocumento2 pagineIV Fluid Chartbenny christantoNessuna valutazione finora
- MC Tumors and Cancers of Various OrgansDocumento12 pagineMC Tumors and Cancers of Various OrgansRyan TurnerNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathology Block 2 CandyDocumento44 paginePathology Block 2 CandyAndleeb ImranNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Medications UsedDocumento3 pagineCommon Medications UsedRay Michael CasupananNessuna valutazione finora
- Cancer Drugs Drugs Indication Adverse Effects Interaction and ContraindicationDocumento5 pagineCancer Drugs Drugs Indication Adverse Effects Interaction and ContraindicationOndari gisemba OSINDENessuna valutazione finora
- Digestive Domain Guide 1Documento31 pagineDigestive Domain Guide 1surviving nursing school100% (1)
- (CV2) Pharmacology of AnticoagulantsDocumento6 pagine(CV2) Pharmacology of AnticoagulantsHanifa Shereen B. AliNessuna valutazione finora
- OME StudyGuide 3monthDocumento6 pagineOME StudyGuide 3monthanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Internal Medicine #1Documento167 pagineInternal Medicine #1Nikhil RayarakulaNessuna valutazione finora
- For 2 Year Medical Students: 2022 EditionDocumento13 pagineFor 2 Year Medical Students: 2022 Editionsherif mamdoohNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunopharmacology PDFDocumento2 pagineImmunopharmacology PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ninja - Autacoids PDFDocumento3 pagineNinja - Autacoids PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacokinetics - Introduction To ANS PDFDocumento2 paginePharmacokinetics - Introduction To ANS PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- 24.postpartum Period-Physiological Changes in The MotherDocumento16 pagine24.postpartum Period-Physiological Changes in The MotherHem KumariNessuna valutazione finora
- QP (2016) 2Documento1 paginaQP (2016) 2pedro carrapicoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial On The ITU GDocumento7 pagineTutorial On The ITU GCh RambabuNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Projectiles Without Air ResistanceDocumento4 pagineLesson Plan: Lesson: Projectiles Without Air ResistanceeltytanNessuna valutazione finora
- LSUBL6432ADocumento4 pagineLSUBL6432ATotoxaHCNessuna valutazione finora
- B. Pharmacy 2nd Year Subjects Syllabus PDF B Pharm Second Year 3 4 Semester PDF DOWNLOADDocumento25 pagineB. Pharmacy 2nd Year Subjects Syllabus PDF B Pharm Second Year 3 4 Semester PDF DOWNLOADarshad alamNessuna valutazione finora
- Motor Wiring Diagram: D.C. Motor ConnectionsDocumento1 paginaMotor Wiring Diagram: D.C. Motor Connectionsczds6594Nessuna valutazione finora
- Math 202: Di Fferential Equations: Course DescriptionDocumento2 pagineMath 202: Di Fferential Equations: Course DescriptionNyannue FlomoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Specifications For Fiberbond ProductDocumento8 pagineMechanical Specifications For Fiberbond ProducthasnizaNessuna valutazione finora
- TutorialDocumento324 pagineTutorialLuisAguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Antennas Since Hertz and MarconiDocumento7 pagineAntennas Since Hertz and MarconiTaiwo Ayodeji100% (1)
- Discuss The Challenges For Firms To Operate in The Hard-Boiled Confectionery Market in India?Documento4 pagineDiscuss The Challenges For Firms To Operate in The Hard-Boiled Confectionery Market in India?harryNessuna valutazione finora
- Pioneer XC-L11Documento52 paginePioneer XC-L11adriangtamas1983Nessuna valutazione finora
- ADIET Digital Image Processing Question BankDocumento7 pagineADIET Digital Image Processing Question BankAdarshNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar Spesifikasi Teknis Pembangunan Gedung Kantor BPN BojonegoroDocumento6 pagineDaftar Spesifikasi Teknis Pembangunan Gedung Kantor BPN BojonegoroIrwin DarmansyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Cs8791 Cloud Computing Unit2 NotesDocumento37 pagineCs8791 Cloud Computing Unit2 NotesTeju MelapattuNessuna valutazione finora
- ML AiDocumento2 pagineML AiSUYASH SHARTHINessuna valutazione finora
- Naukri LalitaSharma (3y 4m)Documento2 pagineNaukri LalitaSharma (3y 4m)rashika asraniNessuna valutazione finora
- VT6050 VT6010 QuickGuide ENDocumento19 pagineVT6050 VT6010 QuickGuide ENPriyank KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Draft Initial Study - San Joaquin Apartments and Precinct Improvements ProjectDocumento190 pagineDraft Initial Study - San Joaquin Apartments and Precinct Improvements Projectapi-249457935Nessuna valutazione finora
- Swatchh Bharat AbhiyanDocumento13 pagineSwatchh Bharat AbhiyanHRISHI SHARMANessuna valutazione finora
- Features Integration of Differential Binomial: DX BX A X P N MDocumento4 pagineFeatures Integration of Differential Binomial: DX BX A X P N Mابو سامرNessuna valutazione finora
- Young Women's Sexuality in Perrault and CarterDocumento4 pagineYoung Women's Sexuality in Perrault and CarterOuki MilestoneNessuna valutazione finora
- Sattvik Brochure - Web VersionDocumento4 pagineSattvik Brochure - Web Versionudiptya_papai2007Nessuna valutazione finora