Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Pharmacology Trans ANS Drugs II
Caricato da
Princess Mara DuranCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Pharmacology Trans ANS Drugs II
Caricato da
Princess Mara DuranCopyright:
Formati disponibili
*Guanfacine, and Guanabenz: are also classified
AUTONOMIC DRUGS
as Alpha 2 agonist that act primarily also in the
Dr. Paguirigan (August 23, 2019) central nervous system
- The pharmacologic properties of
DOPAMINE AGONIST DRUGS Guanfacine, and Guanabenz are similar to
those of clonidine
LEVODOPA - the most common drug used
- The possible site of action of Clonidine is
- is it is converted to dopamine in the
in the nucleus tactus solitarius in the lower
body as simple drug
brain stem. This region is very rich in nerve
DOPAMINE AGONIST WITH CENTRAL ACTIONS bodies and nerve terminals that contain
epinephrine or norepinephrine
These are used for Parkinsonism,
Parkinson’s disease and in cases of - Side effects of Clonidine:
prolactinemia.
Sedation
SUMMARY OF SYMPATHOMIMETIC DRUGS dry mouth
rebound hypertension - if it is
ALPHA 1 AGONIST DRUGS: abruptly discontinued it will result
in -- most dreaded side effect if it is
1. Midocrine - activates Phospholipase C abruptly discontinued
which results in increased intracellular - Taper use prior to discontinuation to
calcium and vasoconstriction avoid rebound hypertension
2. Phenylephrine - can be used intravenously - To treat rebound hypertension
for short term maintenance of blood administer Phentolamine to counteract
pressure in acute hypotension and the effect
intranasally to produce local
vasoconstriction as a decongestant 2. Methyldopa- popularly known as Aldomet
in the market.
ALPHA 2 AGONIST DRUGS: - This is also used as a central
sympatholytic drug-- it exerts its effect by
1. Clonidine - inhibits adenylyl cyclase and central mechanism
interacts with other intracellular pathways
Vasoconstriction is masked by central -Methyldopa enters the central nervous
sympatholytic effect which lowers blood system readily then it is beta oxidated to
pressure
alpha methlyldopamine and beta
-it is an anti-hypertensive drug that
hydroxylated to alpha
paradoxically possess primarily alpha 2
methylnorepinephrine
adrenergic agonist properties
-Clonidine exerts its anti-hypertensive -In the central adrenergic neurons, the
effect with a predominant action in the alpha methyl norepinephrine is released
central nervous where it decreases the from such neurons is a very potent agonist
sympathetic output of the brain of the Alpha 2 receptors of central nervous
Labayog, Malazzab, Onate, Tupaz 1
system and so in the same manner like -Is a direct acting drug with selectivity
clonidine, it inhibits central sympathetic for the beta 1 adrenergic receptors
outflow relatively more effective in enhancing
the contractile force of the heart than
-The alpha methylnorepinephrine like in increasing the heart rate
clonidine is a more potent stimulator at - It does not affect conduction velocity
but it augments the conduction
the alpha 2 receptors than in alpha 1
velocity through the AV node
receptors
-There is little or no effect on the
ventricular impulse conduction
- The most popular clinical use of
-It does not produce renal vasodilation
methyldopa is for pre eclampsia
-Plasma half- life is about 2 minutes it’s
-Side effects of methyldopa: not effective in gestated ovary??
-The usual dose is 2.5-10 ng/kcal/min
Sedation -It is rapidly metabolized in the liver to
hemolytic anemia (positive coombs inactive conjugate glucuronic
acid 3,2 methyl docutamine
test)
-Could not be used in px with atrial
fibrillation
3. Apraclonidine and Brimonidine: these are -Side effects:
also sympatholytic Alpha 2 selective drugs Nausea
and they decrease the secretion of Headeache
aqueous humor that’s why it’s used in Palpitations
shortness of breath anginal
glaucoma
pain
-Activates alpha 2 adrenergic
-Therapeutic uses:
receptor congestive heart failure
-Side effects: cardiogenic shock
blurring vision -Contraindicated in patients with
dry mouth marked obstruction to cardiac ejection
conjunctivitis like in idiopathic hyperthropic sub-
aortic stenosis
4. Dexmedetomidine: prominent sedative
BETA 2 AGONISTS
effects and used in anesthesia
1. Albuterol – most commonly used
5. Tizanidine: used as a muscle relaxant -activates adenylyl cyclase
-it is a bronchial smooth muscle
dilator. It used in asthma.
BETA1 AGONIST DRUGS
1. Dobutamine - most popular member 2. Methaproterenol - is quite similar
- activates adenylyl cyclase, chemically to isoproterenol but it is
-Increases myocardial contractility it resistant to methylation by COMT it is
has a positive inotropic effect effective when given orally it has longer
duration of action than isoproterenol
Labayog, Malazzab, Onate, Tupaz 2
-Primarily a beta 2 adrenergic agonists - After oral dose of 5mg, it produces
-Administered by inhalation it has bronchodilation after an hour and will last
relatively little effect on the beta 1 for 7 hours
receptors of the heart - Given by subcutaneous route and the
-After either oral or inhalation, effects will start within 5 minutes and it
methaproterenol will produce and increase will last for 4 hours.
in the force expiratory volume and - Side effects:
maximal rate of force expiratory flow but it Muscle tremors
decreases the airway resistance Nervousness
-After an oral dose you will see an Headache
improvement of airway function an Tachycardia
improvement in airway function will be Palpitations
demonstrable for up to 4 hours. Drowsiness
-After inhalation of the drug the improved Nausea
respiratory function will be apparent for 3- Vomiting
4 hours approximately 40% of sweating.
metaproterenol is absorbed after oral
administration and the drug is excreted in 4. Albuterol - is selective Beta-2 adrenergic
the urine primarily as a conjugate with agonist also.
glucoronic acid - has the same pharmacologic property
and therapeutic implications similar to
-The adverse effect of methaproterenol :
those of with terbutaline.
Tachycardia - When albuterol is given by inhalation
Hypertension the effect will start within 15 minutes
Nervousness and will last for 3-4 hours.
Tremors
Palpitation
nausea 5. Trithotrine - which is a selective B-2
vomiting adrenergic agonist also.
-Since it is a beta 2 adrenergic agonist it is - The clinical use of trithotrine is to
used as a bronchodilator prevent or delay the premature
parturition or premature labor.
3. Terbutaline - synthetic sympathomimetic - Trithotrine is rapidly but incompletely
agonist administered orally, absorbed, only 30% of the drug is
subcutaneously or by inhalation absorbed following administration
- Used as a treatment of reversible orally, 90% of the drug is excreted in
obstruction of the airways the urine as inactive conjugate and
- it is relatively selective beta-2 agonist about 50% of the drug is excreted
- not methylated by COMP unchanged after IV administration.
Labayog, Malazzab, Onate, Tupaz 3
(24:26) The other two mentioned is the Urapidil
Isoetharine which is Used for thrombo-spastic labetalol C
disease and prealterol? which is selective beta-1 chlorpromazine
adrenergic agonist use for chronic congestive haloperidol
heart failure. Trazodone
Trimazosin
DOPAMINE D1 AGONIST
Ergotamine
1. Fenoldopam - The most popular name Dihydroergotamine
-activates the adenyl-cyclase, so it is a Yohimbine.
vascular smooth muscle relaxant. 1. Phenoxybenxamine binds covalently to
- It relaxes the smooth muscle so the alpha receptor, so it causes irreversible
arteries, it is used for the treatment of blockade which is of long duration of 14-48
hypertension. hours or longer, it is somewhat selective
for a-1 receptor but it is less so than the
selectivity of prazosin.
DOPAMINE D2 AGONIST - the same as dimedamine? (30:05) They
block the alpha adrenergic receptors
1. bromocriptine - most popular
but they do not have alpha adrenergic
- an inhibitior, it inhibits adeny-cyclase, it
agonistic activity.
interrupts other intracellular pathways.
- It mimics or imitates the dopamine action
2. Pentolamine and tolazoline both produce a
in the Central Nervous System.
moderately effective competitive a-
- one of the drugs used for Parkinson’s
adrenergic blockade that is relatively
disease and Prolactenemia.
transient.
- It is used as a cardiac stimulant and as
a stimulant of gastrointestinal tract
ADRENOCEPTOR AGONIST DRUGS
that is blocked by atropine.
- Divided into alpha receptor agonist drugs and - It also stimulates gastric secretion and
beta receptor agonist drugs peripheral vasodilation.
- Pentolamine is more potent than
ALPHA RECEPTOR AGONIST DRUGS: tolazoline. However, both drugs can
phenoxybenzamine cause alarming tachycardia, cardiac
pentolamine arrhythmia and anginal pain.
prazosin - Pentolamine is a potent competitive
terasozine antagonist both the alpha-1 and alpha-
Doxasozin 2 receptors.
Tamsulosin
Alfuzosin
Silodosin
Indoramin
Labayog, Malazzab, Onate, Tupaz 4
3. Prazosin is highly selective drug for a-1 9. Indoramin is another a-1 selective
receptors. antagonist that also has weak a-2
- It is anti-hypertensive drug that antagonist but it is used for hypertension
appears to exert its vasodilator action
thru blockade of the post-synaptic
alpha-1 receptors. 10. Urapidil is an a-1 antagonist also for
- It can cause reversal of the pressor hypertension and BPH (pacheck sis 35:37)
responses to epinephrine and it blocks
the pressor response to 11. Labetalol is a popular a-1 selective b
norepinephrine. antagonist drug.
- Prazosin reduces the vascular tone in
both resistance and capacitance
vessels. Therefore, its effect is 12. Chlorpromazine and haloperidol are both
associated with a reduction in the potent dopamine receptor antagonist but
venous return and reduction in the they also antagonist in the alpha receptor
cardiac output.
13. Trazodone which is an anti-depressant has
4. Terasozine is another reversible selective a capacity to block the a-1 receptor
a-1 receptor antagonist and it is also use as
anti-hypertensive drug. 14. Trimazosin this is clinically related to
prazosin and exhibits similar
5. Doxasozin has a long half-life of 22 hours pharmacologic properties like prazosin, but
and it is use for hypertension and benign it has less potent inhibition of a-1
prostatic hypertrophy. adrenergic receptor.
-It has half life 42 hours and it’s
extensively metabolized in the
6. Tamsulosin is a competitive a-1 antagonist, liver.
it has a very high bioavailability and the
15. Ergotamine and Dihydroergotamine these
half-life is 9-15 hours
are ergot alkaloids, they are ergot derivatives
but they can cause a-receptor blockade via a
7. Alfuzosin is another a-1 selective
partial agonist action.
quinazoline derivative and it is used for
benign prostatic hypertrophy - They act to the barrowing degree as
partial agonist or antagonist at the alpha
adrenergic, at the tryptominergic and
8. Silodosin is also used for benign prostatic dopaminergic receptors.
hypertrophy
- Ergotamine ___________ (38:06)
alkaloids produce coronary vaso-
constriction and associated ischemic
changes that are evident in ECG and it can
Labayog, Malazzab, Onate, Tupaz 5
even cause anginal pains to patients with Pindolol
coronary artery disease. Sotalol
uses:
- Another side effects of the ergot alkaloids
lowers BP
(that is not very much welcome) is that it
slows heart rate
induces bradychardia.
reduce renin secretion
- The primary therapeutic use of these
ergot alkaloids is for the stimulation of 1. PROPRANOLOL
uterine contraction post-partum, it is also blocks both beta-1 and beta-2 receptors
used to relief the pain of migraine. competitively
widely used for the treatment of
16. chlorpromazine which is an anti-emetic drug hypertension
which can prolong and enhance also the pressor for the prophylaxis of angina pectoris
response to norepinephrine. control certain types of cardiac
17. Haloperidol inhibits dopamine induced renal arrhythmias
vasodilatation. does not exhibit any intrinsic agonistic
properties
- It is an alpha-2 selective antagonist. It decreases heart rate and cardiac output
produces an alpha-adrenergic blockade of prolongs mechanical systole
limited duration, and has little direct effect slightly decreases BP in resting subjects
on the smooth muscles but it readily effects on the heart is more marked;
penetrates the CNS increased demand and sympathetic tone
the total myocardial consumption in
18. Yohimbine is sometimes used in the
coronary blood flow are also increased as a
treatment of orthostatic hypotension.
result of the reduction of heart rate and
the ventricular systolic system and
contractility
BETA-RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST DRUGS the release of renin from juxtaglomerular
First group. blocks B1- and B-2 - These are your apparatus is stimulated by beta adrenergic
nadolol, propranolol, timolol agonists but its effect is locked by
Propranol
A. NONSELECTIVE BETA-ADRENERGIC BLOCKERS also inhibits the Vasopressin and
block beta-1 and beta-2 vasodilator effect of Isoproterenol
includes: augments the pressor effects of
Propranolol Epinephrine
Nadolol reduces the sinus rate
Timolol decreases the spontaneous rate of
Alprenolol depolarization of topic pacemakers
Oxprenolol slows conduction of atrial endothelium
Penbutolol
Labayog, Malazzab, Onate, Tupaz 6
blocks actions of sympathomimetic amines 2. NADOLOL
(beta adrenergic receptors - stops salivary) long-acting nonselective beta-adrenergic
almost completely absorbed following oral receptor blocking drug
administration not catalyzed extensively
much of the drug is metabolized by the excreted largely unchanged in the urine
liver during its first passage through the half-life: 6 to 20 hrs
circulation given once a day (OD)
1/3 of the dose reaches the systemic does not possess membrane-stabilizing
circulation pigment and lacks partial agonist activity
half-life: does not readily pass the blood-brain
o initial: 3hrs barrier
o after chronic: 4hrs adverse effects are same with Propranolol
ingestion of food will reduce the first pass available as: 40-160mg tablet
effect on Propranolol and increases its
bioavailability
90-95% of the drug is found in the plasma 3. TIMOLOL
protein nonselective beta-adrenergic antagonist
It is completely metabolized before excretion without local anesthetic properties
through the urine has minimal intrinsic sympathomimetic
metabolites are: activity
o 4-hydroxyl propranolol 5-10x more potent than Propranolol as a
o Naphthyloxylactic acid beta adrenergic blocking drug
o N-desisopropylpropranolol well-absorbed if given orally but
o Propranolol glucoronide undergoes considerable first pass hepatic
Marketed as Inderal; available as 10-90 mg metabolism
tablet; also available as ampule for IV and as Timolol and its metabolites are excreted in
sustained-release capsule the urine rapidly
half-life in the plasma: about 4 hrs
SE: used in hypertension and angina pectoris
heart failure also effective in reducing the incidence and
rebound hypertension death after myocardial infarction
increase airway resistance (CI for available as:
asthma) o 5, 10, 20 tablet
hypoglycemia o also available as ophthalmic
nausea preparation for chronic wide angle
vomiting glaucoma (other type: secondary
mild diarrhea glaucoma)
constipation o also available as eyedrops in 0.25-0.5%
solution
Labayog, Malazzab, Onate, Tupaz 7
initial dose: 1 drop to the affected eye twice a 3. PINDOLOL - is preferred to patient with less
day cardiac reserve and those liable for severe
duration of action: more than 7 hours bradycardia.
must be used with caution in patients with -It will block the decrease heart rate and
asthma, heart block or heart failure cardiac output with exercise.
-efficiently absorbed under those with the
little first pass metabolism and have 50 %
B. SELECTIVE BETA-1 ADRENERGIC BLOCKERS of the drug is metabolized.
- The principal metabolites are contributed
blocks beta-1 more than beta-2
with either glucoranide or intake and is
uses:
excreted in the urine.
lowers BP
- Half-life is short, approximately 3-4 hours
slows heart rate
-Is available as 5 mg and 10 mg tablet
reduce renin
safer for asthmatic patients
4. LABETALOL AND CARVEDILOL
includes:
- the other drug that are in this group
Metoprolol
that are not listed
Atenolol - have the same pharmacologic
Alprenolol characteristics as what have discussed.
Betaxolol
Nebivolol
Celiprolol GROUP THAT BLOCK BETA 1 THAN BETA 2
Bisoprolol
Esmolol SELECTIVE BETA 1 BLOCKER
Acebutolol - They lower the heart rate and they lower
the blood pressure and reduced the renin
secretion.
1. TIMOLOL: when used as an ophthalmic
drug, its effect is for 7 hours but as a beta Members are:
blockers for causes of asthma, heart block Metoprolol
and heart failure Acebutolol
Atenolol
2. INDOLOL - is a non-selective and beta Betaxolol
adrenergic antagonist drug also but it has a Nevibolol
considerable partial agonist activity Bisoprolol
- it does not have a membrane stabilizing
activity with the usual dose. 1. METOPROLOL - most popular
- There is a smaller reduction in testing - Is a relatively selective beta 1 adrenergic
with the one with decreased cardiac antagonist and it does not have many
output and heart rate than the one seen in agonist activity.
drugs which are partial agonist. -It effectively inhibits the inotropic and
chronotropic response to isoproterenol
Labayog, Malazzab, Onate, Tupaz 8
-it reduces plasma renin activity in
hypertensive patients and in normal 2. ATENOLOL - selective beta 1 adrenergic
subjects. drug
-it inhibits the rise in plasma renin activity - with insignificant partial antagonist
that is normally induced by cardiovascular activity
stress. - with membrane stabilizing
- Efficiently and rapidly absorbed in gastro property.
intestinal tract - It is completely absorbed if given
- it is subject to first pass metabolism in orally
the liver - excreted largely in the urine
- 40 % of the drug will reach the general or - Plasma half-life is 6-8 hours but its
systemic circulation. anti-hypertensive effect appears to
- Peak plasma concentration: is about the last for a longer period of time
switch of 90 minutes - Given once a day, but dosage
- Plasma Half Life: 3 hours. interval should be increase if renal
- It is effectively metabolized in the body. impairment is present in significant.
- The 10 % of the drug is excreted in the - does not enter the CNS to a
significant degree but fatigue and
urine depression are not uncommon side
- the metabolites lack significant effects.
pharmacological activity - Other side effects- same as
- Side Effect Of Toxic Reaction: metoprolol
Some reduction in post expiratory - However, they found out that
volume in asthmatic patients atenolol does not appear to
There is a reduced glucose potentiate the insulin induced
tolerance in diabetes mellitus hypoglycemia.
patients and even in normal - It is taken orally with 50-100 mg per
individuals. tablet,
fatigue, HA, dizziness and insommia - usual initial dose is 50 mg OD
- the most common side effects
- usually given by injection
- it is used in early case of suspected or 3. BUTOXAMINE - the one that blocks beta 2
definite acute MI more than beta 1
- contraindicated to patients with: - decreases the total peripheral
bradycardia resistance and there is no current
heart block clinical indication to this drugs
systolic blood pressure of
less than 100 mmmhg
those with moderate to
severe cardiac failure
with hypertension, angina
and MI
Labayog, Malazzab, Onate, Tupaz 9
BETA 1 AND BETA 2 BLOCKER DRUGS thyrotoxicosis
myocardial cardiac ischemia
-have intrinsic sympathomimetic activity - only given parentally. Not orally.
that means they have partial agonist effect
- lower blood pressure and moderately DRUGS THAT BLOCK BETA RECEPTORS MORE
lower heart rate THAN THE ALCOHOL RECEPTORS
o They are used for remedy for heart failure.
Drugs Under this Group
o They are given orally and they have a long
Indolol half-life.
Acetebutolol o The most common toxic reaction is fatigue.
clopidolol o Drugs under this:
1. Balberilol
penbutolol
2. Medroxanol
acebedelol
3. Mucipulol
carteolol
4. Lametrolol
oxypenolol
penirolol
DRUGS THAT BLOCK BETA 1 MORE THAN BETA 2
o There is only one step that appeared. It is
BETA RECEPTORS BLOCKERS MORE THAN THE
escolol.
ALPHA 1 RECEPTORS
o Escolol – is the benedrift alpha1 beta
- they are used commonly for heart failure blocker.
- given orally It is used for:
- has a long half-life 1. Rapid control of the blood
- fatigue - Most common toxic reaction pressure
2. Arrhythmias
Drug under this: 3. Thyrotoxicosis
Carvedilol 4. Myocardial stigma
Medroxalol 5. It is used for the omefterol,
mupicolol so give it orally
methoxelol – half life: 10 minutes
Carbedilol – Toxic effects: Bradycardia and
Laehtelol hypotension
o Labetalol – a beta adrenergic blocking
drug.
ESMOLOL
- It is used for the protection. It is a
- only one listed drug that blocks pyrimethoxine drug with unique
beta 1 more that beta 2 receptor and complex autonomic properties.
- is a very brief cardiac beta blocker - With such goal that selective alpha
rapid control of : 1 and nonselective beta adrenergic
hypertension blocking activity. It is also able to
arrhythmias inhibit the reuptake of
Labayog, Malazzab, Onate, Tupaz 10
norepinephrine into the nerve - In the CNS, it may elicit
terminals. extrapyramidal effects due to low
- 1/3 as potent as phentolamine in dopamine.
blocking alpha receptors. - It is used in pleochromocytoma.
- 1/3 as potent as propranolol in - Toxic effect: extrapyramidal
blocking beta receptors. symptoms and it can also produce
- After the ganglionic blocking, orthostatic hypotension
labetalol has little effect on the
OTHER ANS DRUGS
heart rate that it produces
vasodilation that is blocked by o Reserpine – a very old drug but it is still
propranolol. used in some clinical conditions.
- Appears to have an intrinsic - One of the adrenergic neuron
sympathomimetic activity that is blocking drugs.
largely defined to beta 2 adrenergic - It takes this course of
receptors. catecholamine in many organs,
- It is well absorbed when it is taken including the brain.
orally and very large portion of the - After parenteral administration of
drug is metabolized during the first relatively large doses, it causes this
circulation in the liver. An extensive cholinomimetic fall in blood
hepatic first pass metabolism. pressure. It is frequently associated
- Plasma half-life: 5 hours with bradycardia.
- 5% of the drug is excreted in the - It requires up to three weeks for
urine full tactile, hypertensive. So,
- It is used for sexual hypertension, reserpine cannot be used in
pleochromocytoma, and abrupt emergency purposes.
withdrawal of _____? - It is rarely used. It used only but
- Labetolol is a great also rarely in psychiatric patients
vasculoconstrictor because they have a good effect on
- Initial dose: 100 mg 2X a day the behavior of psychiatric patients.
- One dreaded effect of reserpine is
o Acebutanol – 1/3 as potent as propranolol that it causes severe depression
- It has local anesthetic activity and it even cause some suicidal
- It has an decreasing tendencies.
sympathomimetic activity
- Plasma half-life: 3 hours
DRUGS THAT ARE USED FOR THE TREATMENT OF
TYROSINE HYDROXYLASE INHIBITORS LIPOMA are also autonomic drugs like:
o Beta blockers (Most commonly used:
o Metyrosine – blocks tyrosine hydroxylase.
Picolol)
- It reduces the synthesis of
o Osmotic agents (Most commonly used:
dopamine, norepinephrine, and
Sanitol)
epinephrine; therefore, it lowers
o Alpha 2 agonists (except apraclonidin)
the blood pressure.
Labayog, Malazzab, Onate, Tupaz 11
o Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
(Acetylamide and dosolamide)
*All of these decrease the secretion of
aqueous tumor from the single epithelium.
They decrease the secretion of aldosterone
o While the hepatic drugs – the
cholinomimetics, like pilocarpine and
physostigmine – act on the ciliary muscle
production so they open the trachidial
escort by increasing outflow … [‘Di
maintindihan –1:42:19]
o Prostaglandin, like labanofros – it
increases the outflow to the canal of
Schlemm
o Non-selective alpha agonist (Most
commonly used: epinephrine) – it
increases the outflow of aqueous tumor by
the manubrioscleral veins.
Baka lalabas sa exam according to doc
1. Esmolol is a pluropractic
betablocker, used only parenteral
2. Anulol is the longest acting beta
blocker
3. Acebutanol and adenolol are less
lipid soluble than the other beta
blockers, so they probably enter
the CNS through the …
4. high lipid solubility - Propranolol
5. Moderate lipid solubility -
Labetamol, mecoprolol, picolol, and
pimolol
6. Very low lipid solubility –
Acebutanol, adenolol, desmolol,
and anulol
Labayog, Malazzab, Onate, Tupaz 12
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Adrenergic AgentsDocumento45 pagineAdrenergic AgentsAmit ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Autonomic Nervous System PharmacologyDocumento7 pagineAutonomic Nervous System Pharmacologydonordarah93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology Trans ANS Drugs IDocumento20 paginePharmacology Trans ANS Drugs IPrincess Mara DuranNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology Important Things To RememberDocumento5 paginePharmacology Important Things To RememberHydie100% (1)
- 6 Beta Adrenergic BlockersDocumento19 pagine6 Beta Adrenergic Blockersmatchees-gone rogue100% (1)
- (Pharm) 1s-2 Ans DrugsDocumento16 pagine(Pharm) 1s-2 Ans DrugsKim Ramos67% (3)
- Cholinergics and Cholinergic BlockersDocumento5 pagineCholinergics and Cholinergic Blockersapi-3739910100% (3)
- Mechanism of Action For Each Class of AntiDocumento146 pagineMechanism of Action For Each Class of AntiReynaldo RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Comprehensive Pharmacology Study NotesDocumento123 pagineComprehensive Pharmacology Study NotesEdil M Jama100% (1)
- Cholinergic Drug MnemonicsDocumento1 paginaCholinergic Drug Mnemonicssunshine151100% (1)
- Pharmacokinetics ReviewerDocumento3 paginePharmacokinetics ReviewerJennifer HerediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharma MnemonicsDocumento10 paginePharma MnemonicsMuhammad Ali Aziz100% (4)
- Pharmacology HandoutDocumento5 paginePharmacology HandoutMark Elben Teodoro100% (1)
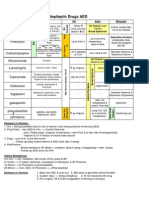
- Antiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE AdvDocumento1 paginaAntiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE Advrayooona88Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology CNS DrugsDocumento15 paginePharmacology CNS DrugsM Youssif Elkady100% (1)
- 7 - Cholinomimetic DrugsDocumento50 pagine7 - Cholinomimetic DrugslalitrajindoliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology FirecrackerDocumento37 paginePharmacology FirecrackerRehan Usman100% (1)
- Adrenergics & Adrenergic BlockersDocumento5 pagineAdrenergics & Adrenergic Blockersapi-3739910100% (4)
- Drug Interactions of Antianginal Drugs..Documento40 pagineDrug Interactions of Antianginal Drugs..Kamal SikandarNessuna valutazione finora
- ACE InhibitorDocumento19 pagineACE InhibitorApurba Sarker ApuNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenergic and NonadrenergicDocumento49 pagineAdrenergic and Nonadrenergicsweta sumanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharma ChartsDocumento33 paginePharma ChartsNooreen Hussain100% (1)
- PharmacologyDocumento3 paginePharmacologyMohd Afiq AizuddinNessuna valutazione finora
- LECTURE 22: Antipsychotic Agents & Lithium: OutlineDocumento5 pagineLECTURE 22: Antipsychotic Agents & Lithium: OutlineRosa PalconitNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology Test 1Documento39 paginePharmacology Test 1Niki BolinNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To ANS PharmacologyDocumento34 pagineIntroduction To ANS PharmacologySebontu HasenNessuna valutazione finora
- Northern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016Documento48 pagineNorthern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016dreneavalentinstefanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cholinergic Pharmacology - Drug TableDocumento2 pagineCholinergic Pharmacology - Drug TableFNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)Documento40 pagineDrugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)HiwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cholinergic Drugs - TablesDocumento7 pagineCholinergic Drugs - TablesThuan Tăng NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- ChemotherapyDocumento11 pagineChemotherapyNedaAbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharm Drug Outline AdrDocumento1 paginaPharm Drug Outline AdrCess Lagera YbanezNessuna valutazione finora
- Psycho PharmaDocumento8 paginePsycho PharmaMark JosephNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology Reviewer 001Documento7 paginePharmacology Reviewer 001Kath MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Interactions: What Is An Interaction?Documento4 pagineDrug Interactions: What Is An Interaction?Leyla MajundaNessuna valutazione finora
- Katzung Tables Chapter 11-15 (CV and Renal)Documento26 pagineKatzung Tables Chapter 11-15 (CV and Renal)Karl CNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology Final Study GuideDocumento28 paginePharmacology Final Study GuideAnthony Palladeno100% (1)
- NORADRENALINE (Norepinephrine) : Presentation DescriptionDocumento3 pagineNORADRENALINE (Norepinephrine) : Presentation DescriptionMutiaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug CardsDocumento3 pagineDrug CardsDave HillNessuna valutazione finora
- Family Names of DrugsDocumento1 paginaFamily Names of DrugsangelNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology Notes (Chapter 20 and 21)Documento2 paginePharmacology Notes (Chapter 20 and 21)graycorypNessuna valutazione finora
- Anticholinergic SDocumento22 pagineAnticholinergic SALNAKINessuna valutazione finora
- Prefix Suffix MnemonicsDocumento5 paginePrefix Suffix MnemonicsPj MontecilloNessuna valutazione finora
- PharmacologyDocumento19 paginePharmacologyBhanu K Prakash100% (1)
- AlbuterolDocumento1 paginaAlbuterolCassieNessuna valutazione finora
- DiureticsDocumento4 pagineDiureticsNazmul Islam AbirNessuna valutazione finora
- Semester Iv Pharmacology I (BP404 TP) Multiple Choice Questions Chapter 1 & 2Documento34 pagineSemester Iv Pharmacology I (BP404 TP) Multiple Choice Questions Chapter 1 & 2Aman Gurjar100% (1)
- General Pharmacology (1-7)Documento7 pagineGeneral Pharmacology (1-7)LotfyAdel100% (1)
- PCOL Maps PDFDocumento11 paginePCOL Maps PDFZinc YuloNessuna valutazione finora
- A New Way of Mnemonics - Hypertension-cough-asthma-NSAID - WMDocumento26 pagineA New Way of Mnemonics - Hypertension-cough-asthma-NSAID - WMKartik Mendiratta100% (1)
- Pharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsDocumento18 paginePharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsPadmavathy Naidu Chokkapu100% (2)
- Pharma 2Documento6 paginePharma 2Mohammad ShafiqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Case 8-13Documento24 pagineCase 8-13Trizian ManaliliNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology of Drugs Acting On Sympathetic Nervous SystemDocumento65 paginePharmacology of Drugs Acting On Sympathetic Nervous SystemCharles DapitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Generic Name Brand Name Mechanism of ActionDocumento10 pagineGeneric Name Brand Name Mechanism of ActionRosario VicencioNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology Module For FinalsDocumento11 paginePharmacology Module For FinalsCarlo GaradoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 (Adrenergic Agonists)Documento44 pagineChapter 6 (Adrenergic Agonists)Aneeza AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenergic Antagonist: PharmacologyDocumento3 pagineAdrenergic Antagonist: PharmacologyJB RSNJNNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenergic AgonistsDocumento52 pagineAdrenergic AgonistsTsegaye HailuNessuna valutazione finora
- Antihypertensive & Antianginal DrugsDocumento5 pagineAntihypertensive & Antianginal Drugsdomememe1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Slow MovingDocumento88 pagineSlow MovingshahidashraftNessuna valutazione finora
- FARMAKOGNOSI - Obat AntihipertensiDocumento7 pagineFARMAKOGNOSI - Obat AntihipertensiTrianisa FebyNessuna valutazione finora
- Medicamentos SimiDocumento28 pagineMedicamentos SimiAnabel RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Arrhythmias Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocumento29 pagineCardiac Arrhythmias Cardiac ArrhythmiasgowthamNessuna valutazione finora
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs-Test-1-QuestionsDocumento7 pagineAntiarrhythmic Drugs-Test-1-QuestionsDrishya Bioplannet100% (2)
- 7,8-Antihypertensive Drugs PDFDocumento10 pagine7,8-Antihypertensive Drugs PDFSaktai DiyamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Pencegahan Dan Pengobatan Hipertensi Pada Penderita Usia DewasaDocumento7 paginePencegahan Dan Pengobatan Hipertensi Pada Penderita Usia DewasaGladys SariowanNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenergics & Adrenergic BlockersDocumento5 pagineAdrenergics & Adrenergic Blockersapi-3739910100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan On HypertensionDocumento5 pagineNursing Care Plan On Hypertensionbhavana100% (1)
- Hypertension: PharmacotherapyDocumento23 pagineHypertension: Pharmacotherapytorr123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Padmanabha T S Dept of Pharmacology Aims, B.G.NagarDocumento19 pagineDr. Padmanabha T S Dept of Pharmacology Aims, B.G.NagarPadmanabha GowdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiovascular Drugs - WsDocumento45 pagineCardiovascular Drugs - WsCowox Post PartumNessuna valutazione finora
- MBBS Antiarrhythmics 2014 Class II (Antiarrhythmic Drugs)Documento23 pagineMBBS Antiarrhythmics 2014 Class II (Antiarrhythmic Drugs)Dr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHM100% (1)
- Cardiovasculardrugs 1Documento2 pagineCardiovasculardrugs 1Marj Ladica MangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Arrhythmia Pharmacology MindmapDocumento1 paginaArrhythmia Pharmacology MindmapTesnikolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar Obat Emergency Dan ResusitasiDocumento5 pagineDaftar Obat Emergency Dan ResusitasiDita IsnarillahNessuna valutazione finora
- Calcium Channel Blockers (CCBS)Documento3 pagineCalcium Channel Blockers (CCBS)Yohanes SutrisnoNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar Tabel Dosis Maksimal DMDocumento7 pagineDaftar Tabel Dosis Maksimal DMNUNE IDHAMNessuna valutazione finora
- Liste MedicamenteDocumento128 pagineListe MedicamenteTomuta GabrielNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar Obat Lasa 2017Documento5 pagineDaftar Obat Lasa 2017watiapotikNessuna valutazione finora
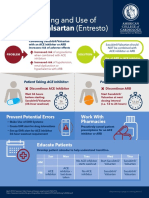
- Sacubitril/Valsartan (Entresto) : Safe Prescribing and Use ofDocumento1 paginaSacubitril/Valsartan (Entresto) : Safe Prescribing and Use ofpatricia wageyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac MedicationsDocumento8 pagineCardiac Medicationsangeline totaram100% (2)
- Daftar Nama Obat Di Farmasi Klinik Ibnu SinaDocumento5 pagineDaftar Nama Obat Di Farmasi Klinik Ibnu SinaAfifa RahmahNessuna valutazione finora
- 1129-Vademecum Osdop General 01-08-2018Documento237 pagine1129-Vademecum Osdop General 01-08-2018Eli PintagroNessuna valutazione finora
- "Emergency Drugs": Pictures/ Generic Name Brand Name/ Classification/ Stock Dose/ Indication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento7 pagine"Emergency Drugs": Pictures/ Generic Name Brand Name/ Classification/ Stock Dose/ Indication Nursing ResponsibilitiesJohn Balgoa100% (2)
- Obat Anti HipertensiDocumento9 pagineObat Anti Hipertensisilvanus giovannyNessuna valutazione finora
- Questions PharmcologyDocumento17 pagineQuestions Pharmcologylalitrajindolia100% (2)
- 3-23-22 Sa Gamot Na Abot Kaya, Sakit Makakaya 3Documento21 pagine3-23-22 Sa Gamot Na Abot Kaya, Sakit Makakaya 3Rachelle Joy G. Bugatan100% (1)
- NefrologiDocumento25 pagineNefrologifitriNessuna valutazione finora