Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Lesson 4-9 Reviewer MATH146
Caricato da
Platonus Doesn'texistCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Lesson 4-9 Reviewer MATH146
Caricato da
Platonus Doesn'texistCopyright:
Formati disponibili
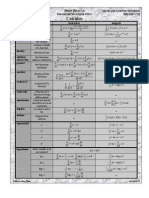
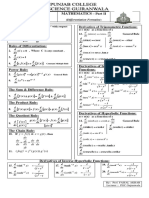
Lesson 4: DIFFERENTIATION OF ALGEBRAIC FUNCTIONS
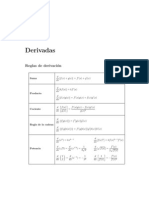
DIFFERENTIATION FORMULAS
• Constant
• Chain Rule
d
[c ] = 0
dx
• Power Rule
d n
[ x ] = nx n −1
dx • Radical with index equal to 2
• Constant Times a Function (Constant Multiple Rule)
du
d
cf ( x) = c f ( x)
d d
( ) u = dx
dx dx dx 2 u
• Sums or Differences
• Radical with index other than 2
d
( f g ) = d ( f ) d (g )
d n 1 n −1 du
1 1
dx dx dx
d u = u
f ( x ) g ( x ) =
d
f ( x )
d
g ( x ) dx n dx
dx dx dx
• Product Rule
HIGHER DERIVATIVES
d
( f g ) = f dg + g df
dx dx dx f ' , f ' ' = ( f ' )' , f ' ' ' = ( f ' ' )' ,
d
f ( x) g ( x) = f ( x) d [ g ( x)] + g ( x) d f ( x)
f ' , f ' ' = ( f ' )' , f ' ' ' = ( f ' ' )' , f 4 = ( f ' ' ' )' , f 5 = ( f 4 )' ,.....
dx dx dx
•
• Quotient Rule
df dg
g −f Steps in Implicit Differentiation:
d f dx dx
= 1. Differentiate both sides of the equation with respect to x.
dx g g2 2. Collect all the terms with
dy
on one side of the equation.
dx
f ( x) − f ( x) d g ( x)
d 3. Factor out
dy
g ( x)
d f ( x) dx dx dydx
=
dx g ( x)
4. Solve for .
g ( x)2
dx
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Tables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesDa EverandTables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesNessuna valutazione finora
- Tables of Weber Functions: Mathematical Tables, Vol. 1Da EverandTables of Weber Functions: Mathematical Tables, Vol. 1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Techniques of Differentiation-1Documento3 pagineTechniques of Differentiation-1lqmandyNessuna valutazione finora
- CalculusDocumento2 pagineCalculusdissipog1932Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2Documento13 pagineLecture 2James KarenNessuna valutazione finora
- Tabla de Derivadas e IntegralesDocumento2 pagineTabla de Derivadas e IntegralesLuz Evelyn HerreraNessuna valutazione finora
- BananesDocumento16 pagineBananesxalove3892Nessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus NotesDocumento10 pagineCalculus NotesGirija ParpallyNessuna valutazione finora
- Derivatives Cheat SheetDocumento3 pagineDerivatives Cheat SheetalexNessuna valutazione finora
- Derivatives: 1. Definition & NotationDocumento6 pagineDerivatives: 1. Definition & NotationVivek GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Differentiation: Additional Mathematics Cheat SheetDocumento2 pagineDifferentiation: Additional Mathematics Cheat SheetKiro HeadsifterNessuna valutazione finora
- Derivatives: Definition and NotationDocumento4 pagineDerivatives: Definition and NotationHarsh VyasNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Derivatives PDFDocumento4 pagineCalculus Cheat Sheet Derivatives PDFShivamNessuna valutazione finora
- 1551 FinalExam ProblemBankDocumento12 pagine1551 FinalExam ProblemBankPedro TNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus Cheat Sheet DerivativesDocumento4 pagineCalculus Cheat Sheet Derivativeshyd arnes100% (4)
- 01 - Differentiation - ADocumento38 pagine01 - Differentiation - ASpandan BhutkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Differentiation - Mind Maps - Lakshya JEE 2024Documento2 pagineDifferentiation - Mind Maps - Lakshya JEE 2024SAMRIDH SAHANessuna valutazione finora
- Tabla de DerivadasDocumento2 pagineTabla de DerivadasJorge Luis Osorio MurilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Differentiation (Day-5)Documento4 pagineDifferentiation (Day-5)Faizan AnsariNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 - Basic Differentiation: X F DX D y DX DDocumento9 pagineLesson 1 - Basic Differentiation: X F DX D y DX DJoshuaNessuna valutazione finora
- ENG 1005 Notes (Mathematics)Documento363 pagineENG 1005 Notes (Mathematics)SiddhantNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Further Differentiation and Integration: Mathematics - MATH 1111Documento62 pagineUnit 1 Further Differentiation and Integration: Mathematics - MATH 1111Akshay BundhooNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics DerivativesDocumento4 pagineMathematics DerivativesmontuNessuna valutazione finora
- Derivadas e IntegralesDocumento2 pagineDerivadas e IntegralesARIZACA SILVESTRE JUAN GABRIELNessuna valutazione finora
- Derivadas Por Tabla. - : Sik CtteDocumento2 pagineDerivadas Por Tabla. - : Sik CtteGary PomaNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential CalculusDocumento25 pagineDifferential CalculusSamNessuna valutazione finora
- NSS M2V2 09 FS EngDocumento41 pagineNSS M2V2 09 FS EngWong TonyNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 3 Differentiation - RulesDocumento19 pagineCH 3 Differentiation - Rulesserhataydin451Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1551 FinalExam ProblemBank SolDocumento54 pagine1551 FinalExam ProblemBank SolPedro TNessuna valutazione finora
- Hand Out Continuity and DifferentiabilityDocumento3 pagineHand Out Continuity and DifferentiabilityKriti SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 - DifferentiationDocumento6 pagine6 - DifferentiationabanerjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Mat CeroDocumento17 pagineMat CeroYuber CcoaNessuna valutazione finora
- Formula 2Documento2 pagineFormula 2randhawa03023Nessuna valutazione finora
- Derivatives of Basic Elementary FunctionsDocumento7 pagineDerivatives of Basic Elementary Functionsi Don't knowNessuna valutazione finora
- The Rules of DifferentiationDocumento6 pagineThe Rules of DifferentiationWhateverNessuna valutazione finora
- Differentiation Bridge ClassDocumento4 pagineDifferentiation Bridge ClassManoj GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- T2 - IntegrationDocumento100 pagineT2 - IntegrationMahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- Derivative FormulasDocumento2 pagineDerivative FormulasZhi Wei ChowNessuna valutazione finora
- 14 2+lecDocumento3 pagine14 2+lec고혜인Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ch.10 Derivatives and Differentiation RulesDocumento2 pagineCh.10 Derivatives and Differentiation RulesshunnieeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Derivadas Folha de Apoio - SymbolabDocumento2 pagineDerivadas Folha de Apoio - SymbolabLeonardo AlmadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFDocumento2 pagineCommon Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFBob DoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Derivatives Integrals ReducedDocumento2 pagineCommon Derivatives Integrals ReducedmohamedehabNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFDocumento2 pagineCommon Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFHiếu SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFDocumento2 pagineCommon Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFA 47Nessuna valutazione finora
- Formulario CálculoDocumento2 pagineFormulario CálculoMARJORIE PEÑANessuna valutazione finora
- Common Derivatives Integrals ReducedDocumento2 pagineCommon Derivatives Integrals ReducedMary Jane Sebial ManceraNessuna valutazione finora
- Integrals PDFDocumento2 pagineIntegrals PDFRachit JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFDocumento2 pagineCommon Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFKristen Brooks SandlerNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFDocumento2 pagineCommon Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFA 47Nessuna valutazione finora
- Common Derivatives Integrals Reduced23 PDFDocumento2 pagineCommon Derivatives Integrals Reduced23 PDFBob DoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFDocumento2 pagineCommon Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFNatte SuzukiNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFDocumento2 pagineCommon Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFFree AcxNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFDocumento2 pagineCommon Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFJussi VuoriNessuna valutazione finora
- Transmutation and Operator Differential EquationsDa EverandTransmutation and Operator Differential EquationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometric functions in computer aided geometric designDa EverandGeometric functions in computer aided geometric designNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)Da EverandFunctional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)Da EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970Da EverandNonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970Louis B. RallNessuna valutazione finora
- My AnswersDocumento8 pagineMy AnswersPlatonus Doesn'texistNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Hero Lab AnswersDocumento2 pagineCourse Hero Lab AnswersPlatonus Doesn'texistNessuna valutazione finora
- Questions For Report 6Documento4 pagineQuestions For Report 6Platonus Doesn'texist0% (1)
- A PLATE 3 Model PDFDocumento1 paginaA PLATE 3 Model PDFPlatonus Doesn'texistNessuna valutazione finora
- LAB REPORT 3 ChemDocumento4 pagineLAB REPORT 3 ChemPlatonus Doesn'texistNessuna valutazione finora
- Incorrect.: Click If You Would Like To Show Work For This QuestionDocumento2 pagineIncorrect.: Click If You Would Like To Show Work For This QuestionPlatonus Doesn'texistNessuna valutazione finora
- Marine Enginnering SyllabusDocumento3 pagineMarine Enginnering SyllabusRam Prasad YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Diff Cal Book (For Review Only)Documento131 pagineDiff Cal Book (For Review Only)Arn Stefhan JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- B Tech Syllabus Avionics - R2022 - V1 - 26.08.2022 PDFDocumento97 pagineB Tech Syllabus Avionics - R2022 - V1 - 26.08.2022 PDFLoves MusicNessuna valutazione finora
- ECON 4035 - Excel GuideDocumento13 pagineECON 4035 - Excel GuideRosario Rivera NegrónNessuna valutazione finora
- CAP Book 11 - 12Documento41 pagineCAP Book 11 - 12cookjb1Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2021 Geometry Study Guide 2 PDFDocumento23 pagine2021 Geometry Study Guide 2 PDFTaffohouo Nwaffeu Yves ValdezNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Solutions Manual and Study Guide To Advanced Engineering MathematicsDocumento222 pagineStudent Solutions Manual and Study Guide To Advanced Engineering MathematicsMuhammad AsifNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Syllabus: General: Units and Dimensions, Dimensional Analysis Least Count, SignificantDocumento14 paginePhysics Syllabus: General: Units and Dimensions, Dimensional Analysis Least Count, SignificantBharat RaghunathanNessuna valutazione finora
- PPT10-Multivariate CalculusDocumento13 paginePPT10-Multivariate CalculusRano AcunNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus Strauss PDFDocumento1.114 pagineCalculus Strauss PDFR.V. Raghavan78% (37)
- Survey of Finite Element Shape FunctionsDocumento9 pagineSurvey of Finite Element Shape FunctionsvtalatsNessuna valutazione finora
- 2009 RI Prelims Math H2 P1Documento5 pagine2009 RI Prelims Math H2 P1Vivath LyNessuna valutazione finora
- Diff. Calc. Module 8 Exponential & Logarithmic FunctionsDocumento8 pagineDiff. Calc. Module 8 Exponential & Logarithmic FunctionsWild RiftNessuna valutazione finora
- Luis Moreno A.Documento13 pagineLuis Moreno A.Andrea Del Pilar Gallego RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Continuation Power Flow A Tool For Steady State Voltage Stability AnalysisDocumento8 pagineThe Continuation Power Flow A Tool For Steady State Voltage Stability AnalysisProsen DeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Bank For Calculus & Linear Algebra: Course OutcomesDocumento15 pagineQuestion Bank For Calculus & Linear Algebra: Course Outcomesmoaaz ahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Diploma C-09 Mechanical SyllabusDocumento175 pagineDiploma C-09 Mechanical SyllabusghambiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Tut 101 DSC1520 2013 PDFDocumento122 pagineTut 101 DSC1520 2013 PDFKhathutshelo KharivheNessuna valutazione finora
- 2008 Multiple Choice WITH ANSWERSDocumento29 pagine2008 Multiple Choice WITH ANSWERSAradheea GawadeNessuna valutazione finora
- 8CCSDocumento8 pagine8CCSvuongkien.workNessuna valutazione finora
- Weekly Exam 7: Analytic Geometry 2/ Differential Calculus 1 and 2Documento2 pagineWeekly Exam 7: Analytic Geometry 2/ Differential Calculus 1 and 2Jonas ParreñoNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Formulas For IntergrationDocumento11 pagineBasic Formulas For Intergrationbhanuka2009Nessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 3. DifferentiationDocumento36 pagineCHAPTER 3. DifferentiationAmira AzkiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Test 1 ReviewDocumento9 pagineTest 1 ReviewmplukieNessuna valutazione finora
- DifferentiationDocumento13 pagineDifferentiationMayank TiwaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Vector Calculus - Understanding The Gradient - BetterExplainedDocumento30 pagineVector Calculus - Understanding The Gradient - BetterExplainedOzawa MagooNessuna valutazione finora
- Microsoft Word - 21af04 - PDEDocumento35 pagineMicrosoft Word - 21af04 - PDEJuvil GotelNessuna valutazione finora
- Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics University of Kalyani West Bengal, IndiaDocumento7 pagineAssistant Professor Department of Mathematics University of Kalyani West Bengal, IndiaRatnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mba Regulations Student Copy 2010-2011Documento94 pagineMba Regulations Student Copy 2010-2011vamsibrilliantNessuna valutazione finora
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Fundamental Concepts in Modern Analysisan Introduction To Nonlinear Analysis 2nd Edition PDF ScribdDocumento41 pagineInstant Download Ebook PDF Fundamental Concepts in Modern Analysisan Introduction To Nonlinear Analysis 2nd Edition PDF Scribdjudi.hawkins744100% (43)