Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Transistor Junction: Llanes, Shyrell Katrin D. Malayan Colleges Laguna
Caricato da
Shyrell Katrin Llanes0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
33 visualizzazioni2 pagineelab
Titolo originale
Experiment 4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoelab
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
33 visualizzazioni2 pagineTransistor Junction: Llanes, Shyrell Katrin D. Malayan Colleges Laguna
Caricato da
Shyrell Katrin Llaneselab
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
Transistor Junction
Llanes, Shyrell Katrin D.
Malayan Colleges Laguna
shykatrin07@gmail.com
ABSTRACT
This experiment demonstrates a basic
understanding of transistor fundamentals. It test
transistor junctions using transistor and the
results are verified with a multimeter. It also
determines the proper biasing and circuit voltages
using a PNP current control unit. The result are
also verified with a multimeter.
KEYWORDS
Transistors
Junctions
Diode
Collector
Emitter
INTRODUCTION
RESULTS
Table 1. Result in Exercise 5-1.
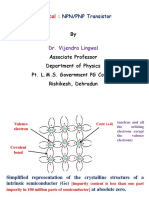
when base current was provided to the
transistor. When the base current was
removed, the transistor was switch off, and
the LED was off too. We also observed that
the transistor acts as an amplifier because the
small base current can control a larger
collector current.
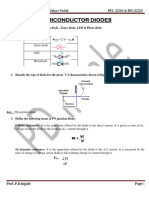
We have noticed that diodes, which are Zener
and a light emitting diode, has a different
symbol from one another. We also noticed
that the emitter arrow symbol points toward
the PNP and away from the NPN.
We learned that semiconductor diode
consists of PN junction made up of positively
and negatively doped areas of semiconductor
materials. Leaning that the positive are is the
anode and the negative area is the cathode.
We have observed that when CR1 has a
current flowing in it, it is in forward biased,
and when we have observed no current
flowing in it, it is in reversed biased. Therefor
we can conclude that a diode is in forward
biased if it has a current flowing from it and
it is in reversed biased if there is no current
flowing in it.
REFERENCES
EE lab manual (electronics and electrical
engineering laboratory manual )
Semiconductors: Experiment (2007). Retrieved
from https://www.uni-
muenster.de/Physik.AP/Purwins/Research-
Summary/07Semiconductors,_Experiment.pdf
CONCLUSIONS
It was concluded that transistor operating as
a switch by noting that current flowed
through the transistor’s collector and LED
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Troubleshooting Electronic Components With The PET BloodhoundDa EverandTroubleshooting Electronic Components With The PET BloodhoundNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 5 CarinoDocumento5 pagineExperiment 5 Carinocent carinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of SemiconductorDocumento4 pagineTypes of SemiconductorKylejun MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamental of Diodes e BookDocumento12 pagineFundamental of Diodes e BookJean-Charles LEBEAUNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electronics PDFDocumento15 pagineBasic Electronics PDFMaham ZaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Physics 100 Viva Questions With AnswersDocumento25 pagineEngineering Physics 100 Viva Questions With AnswersGood MorningNessuna valutazione finora
- Activities: Collection of Such IlemsDocumento3 pagineActivities: Collection of Such IlemsRakeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Activities: Collection of Such IlemsDocumento3 pagineActivities: Collection of Such IlemsRakeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Viva Questions With Answers: Prepared by Gajendra & Parag (Civil Branch)Documento16 paginePhysics Viva Questions With Answers: Prepared by Gajendra & Parag (Civil Branch)Good MorningNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Map Phy 12Documento1 paginaRevision Map Phy 12Grey KoalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Passing Package - 2024Documento16 paginePhysics Passing Package - 2024pnm057459Nessuna valutazione finora
- EI2203 EDC 2marksDocumento14 pagineEI2203 EDC 2marksBhanu KodaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Ii YearDocumento27 pagineElectronic Devices and Circuits - Ii YearT ThirumuruganNessuna valutazione finora
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - NotesDocumento170 pagineEee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - NoteschaitanyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Formation of A Diode: Positive Terminal of A Diode Cathode, Which Is The Negative Terminal IsDocumento47 pagineFormation of A Diode: Positive Terminal of A Diode Cathode, Which Is The Negative Terminal Ispatrick kamiruNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Diode CircuitsDocumento29 pagineUnit 1 Diode Circuitseee3 semNessuna valutazione finora
- Bel Bec Ch01 Print OutDocumento38 pagineBel Bec Ch01 Print Outkenemep346Nessuna valutazione finora
- CI-04 Feb2010Documento2 pagineCI-04 Feb2010Javeed AhamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3 QB BeeceDocumento5 pagineUnit 3 QB BeeceMANSOOR REEMANessuna valutazione finora
- Semiconductors 1Documento16 pagineSemiconductors 1Rohit SwamiNessuna valutazione finora
- AEC Module1 Clipping and ClampingDocumento43 pagineAEC Module1 Clipping and ClampingVinay kumar havinalNessuna valutazione finora
- NPN/PNP Transistor Characteristics - Common Base ConfigurationDocumento25 pagineNPN/PNP Transistor Characteristics - Common Base ConfigurationDastaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Euro International School: Class Xi-ADocumento22 pagineEuro International School: Class Xi-AI am NanyNessuna valutazione finora
- Transistor ParametersDocumento10 pagineTransistor ParametersKhabab NazirNessuna valutazione finora
- Intrinsic Vs Extrinsic: Forward BiasingDocumento9 pagineIntrinsic Vs Extrinsic: Forward BiasingnuruthinNessuna valutazione finora
- Aim of Experiment: To Plot Forward & Reverse Biased Characteristics ofDocumento4 pagineAim of Experiment: To Plot Forward & Reverse Biased Characteristics ofTapobroto ChatterjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- STP211 ELECTRONICS NOTE PART 3 & 4Documento8 pagineSTP211 ELECTRONICS NOTE PART 3 & 4SOFTY SOFTYNessuna valutazione finora
- What is a PNP Transistor? Its Construction, Working Principles and ApplicationsDocumento34 pagineWhat is a PNP Transistor? Its Construction, Working Principles and ApplicationsgezahegnNessuna valutazione finora
- PhysicsDocumento19 paginePhysicsArjav PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Activity 1 To 6Documento12 paginePhysics Activity 1 To 6Aadit “ThePROkiller”0% (1)
- Electronics PhyDocumento32 pagineElectronics Phydavididosa40Nessuna valutazione finora
- EDC Question Bank 18Documento33 pagineEDC Question Bank 18kalaiselvanNessuna valutazione finora
- Conduction Through LiquidDocumento1 paginaConduction Through LiquidMuskan RangrejNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento25 pagineChapter 2Bizuayehu Ze GeorgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electronics GuideDocumento101 pagineBasic Electronics GuideShia Yee KeongNessuna valutazione finora
- Diode DC Characteristics and Rectifiction: Transistor, Diode, LED, Forward Bias, Reverse Bias, Characteristic CurveDocumento3 pagineDiode DC Characteristics and Rectifiction: Transistor, Diode, LED, Forward Bias, Reverse Bias, Characteristic CurveJoule BellosilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Investigatory Project On LDRDocumento21 paginePhysics Investigatory Project On LDRDiwakerNessuna valutazione finora
- Seca1306 1Documento125 pagineSeca1306 1OLAVIDES, TEOPY MARIE D.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sjeee 6Documento6 pagineSjeee 6maxmanishNessuna valutazione finora
- Tuquero, Melinyo L Industrialelecslab#2Documento7 pagineTuquero, Melinyo L Industrialelecslab#2melenyo tuqueroNessuna valutazione finora
- Discussion For The Most Part, in Performing This Experiment, We Only Used Diodes of Different Kinds, Multimeters, and A Power SupplyDocumento2 pagineDiscussion For The Most Part, in Performing This Experiment, We Only Used Diodes of Different Kinds, Multimeters, and A Power SupplyEj HidalgoNessuna valutazione finora
- Quebral, Darlene Joy Bsit 1-D (Transistor Assignment)Documento1 paginaQuebral, Darlene Joy Bsit 1-D (Transistor Assignment)DARLENE JOY QUEBRALNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab01 FinalDocumento5 pagineLab01 Finalnts91Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics 121: Electricity & Magnetism - Lecture 12 Induction II & E-M OscillationsDocumento24 paginePhysics 121: Electricity & Magnetism - Lecture 12 Induction II & E-M OscillationsbellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Semiconductor Material and DevicesDocumento46 pagineSemiconductor Material and DevicesSolomon ThomasNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Detectors: Wei-Chih Wang Department of Power Mechanical Engineering National Tsing Hua UniversityDocumento71 pagineOptical Detectors: Wei-Chih Wang Department of Power Mechanical Engineering National Tsing Hua UniversityDivya BajpaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 4Documento3 pagineActivity 4kanishkgang1231Nessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Idea by Nurul Amin SirDocumento12 pagineBasic Idea by Nurul Amin SirFardeen KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 & 4 Special - Purpose - Diodes and BJTsDocumento50 pagineChapter 3 & 4 Special - Purpose - Diodes and BJTsAbdul RehmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Semiconductor 4M QuestionsDocumento29 pagineSemiconductor 4M Questionsbhanu010420Nessuna valutazione finora
- PN Diodes: Atif Imam Avijit Jain Avinash Reddy Aviral Aggarwal Ayush Asthana Joshitha ReddyDocumento15 paginePN Diodes: Atif Imam Avijit Jain Avinash Reddy Aviral Aggarwal Ayush Asthana Joshitha ReddyAtif ImamNessuna valutazione finora
- ST Unit 4 NotesDocumento25 pagineST Unit 4 Notesabc fun facts100% (1)
- Name: Anthony A. Reyes Jr. Date: August 22, 2014 Professor: Eng. Jeffrey Odtohan Experiment No. 2 Title: Clipper and Clamper MaterialsDocumento1 paginaName: Anthony A. Reyes Jr. Date: August 22, 2014 Professor: Eng. Jeffrey Odtohan Experiment No. 2 Title: Clipper and Clamper MaterialsAnthony ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Different Experiment in DiodesDocumento16 pagineDifferent Experiment in DiodesDivine Grace GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- 18Ees101J - Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Unit - Iii Electronic DevicesDocumento46 pagine18Ees101J - Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Unit - Iii Electronic DevicesPERIYASAMY BALAMOORTHYNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Project FileDocumento22 paginePhysics Project Filerohilsingh01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Notes On Semiconductor ElectronicsDocumento11 pagineNotes On Semiconductor Electronicsmarudev nathawatNessuna valutazione finora
- ActivitiesDocumento4 pagineActivitieslalitadithyas77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To DiodesDocumento46 pagineChapter 1 - Introduction To DiodesYazik DurdiyevNessuna valutazione finora
- BUTANE FEED Revised FinalDocumento6 pagineBUTANE FEED Revised FinalShyrell Katrin LlanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Reaction Paper in PREAMBLE OF THE 1987 PHILIPPINE CONSTITUTIONDocumento1 paginaReaction Paper in PREAMBLE OF THE 1987 PHILIPPINE CONSTITUTIONKervin Lance Pascua85% (20)
- EXPERIMENT1 EElabDocumento3 pagineEXPERIMENT1 EElabShyrell Katrin LlanesNessuna valutazione finora
- SS015 AssignmentDocumento2 pagineSS015 AssignmentShyrell Katrin LlanesNessuna valutazione finora
- SS015 AssignmentDocumento2 pagineSS015 AssignmentShyrell Katrin LlanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp 2Documento4 pagineExp 2Shyrell Katrin LlanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Gantt Chart ExampleDocumento3 pagineGantt Chart ExampleShyrell Katrin LlanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 5 LDocumento4 pagineExperiment 5 LShyrell Katrin LlanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Extractores GrasasDocumento6 pagineExtractores GrasasJosé Manuel Gómez VázquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Singlemultiplelimitswitches TecknicDocumento18 pagineSinglemultiplelimitswitches Tecknicchidambaram kasiNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminarski Rad - Merenje TemperatureDocumento93 pagineSeminarski Rad - Merenje TemperatureĐura ĐukanovićNessuna valutazione finora
- VersaLight: An Eco-Friendly Emergency LightDocumento28 pagineVersaLight: An Eco-Friendly Emergency LightCHELSIE KAITLYN DE GUZMANNessuna valutazione finora
- 42pt250b Manual ServicioDocumento63 pagine42pt250b Manual ServicioLuis Carlos Bonilla AldanaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 53Documento3 pagine2 53Eric KialNessuna valutazione finora
- VSSC6 MOV 24VAC DC enDocumento4 pagineVSSC6 MOV 24VAC DC enparas99Nessuna valutazione finora
- Microwaves and Behavior - 1975 PDFDocumento11 pagineMicrowaves and Behavior - 1975 PDFnailsss100% (1)
- RTD Section's Wring DiagramDocumento1 paginaRTD Section's Wring DiagramARTHURS316Nessuna valutazione finora
- Installation Manual APS596C - IMDocumento16 pagineInstallation Manual APS596C - IMMauro SteffenNessuna valutazione finora
- Vbhw1149jte 100 TRDocumento26 pagineVbhw1149jte 100 TRdenysenkovovan84Nessuna valutazione finora
- Soldering and Desoldering Electronics ComponentsDocumento4 pagineSoldering and Desoldering Electronics ComponentsDulce DeNessuna valutazione finora
- 3038 - Seiko 1320ADocumento4 pagine3038 - Seiko 1320Aaaronsmokes1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Designing TurbogeneratorDocumento6 pagineDesigning TurbogeneratorMadhan GopalNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab3 - MOSFET IV CharacteristicDocumento11 pagineLab3 - MOSFET IV Characteristickzankz100% (1)
- MicrosemiZLE38AVSHardwareUserGuide 1836047195 PDFDocumento21 pagineMicrosemiZLE38AVSHardwareUserGuide 1836047195 PDFshootingstarmh4Nessuna valutazione finora
- WWW Slideshare Net Rahulkushwaha06 Physics Investigatory Project Class 12Documento4 pagineWWW Slideshare Net Rahulkushwaha06 Physics Investigatory Project Class 12Shreyash DadaNessuna valutazione finora
- l149 Linear DriverDocumento6 paginel149 Linear DriverandrasorNessuna valutazione finora
- Inventions/Discoveries Name of The Scientist/PersonDocumento17 pagineInventions/Discoveries Name of The Scientist/PersonEngr Suleman MemonNessuna valutazione finora
- ABB - Power-One Monitoring & CommunicationDocumento80 pagineABB - Power-One Monitoring & Communicationedimidias sociaisNessuna valutazione finora
- Divar 5000 Series Operation ManualDocumento162 pagineDivar 5000 Series Operation ManualyubaileNessuna valutazione finora
- EPIC-1: User GuideDocumento56 pagineEPIC-1: User Guidepp1jlbrNessuna valutazione finora
- D5G6 DatasheetDocumento3 pagineD5G6 DatasheetchichedemorenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Bts 7960Documento28 pagineBts 7960Nairo FilhoNessuna valutazione finora
- EHV CableDocumento19 pagineEHV Cablevikrant jainNessuna valutazione finora
- Modicon Quantum - 140ACI04000Documento2 pagineModicon Quantum - 140ACI04000Miguel CasillasNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Logic FamiliesDocumento19 pagineDigital Logic FamiliesThairu Muiruri100% (1)
- Permittivity in Free Space (Shift Constant 1 4) Permeability in Free Space (Shift Constant 1 5)Documento10 paginePermittivity in Free Space (Shift Constant 1 4) Permeability in Free Space (Shift Constant 1 5)Jizelle JumaquioNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice Questions of Electric Traction For 4-4 JntuDocumento26 pagineMultiple Choice Questions of Electric Traction For 4-4 JntuChandra Sekhar67% (3)
- Designand Fabricationof Drug Delivery Infusion PumpDocumento12 pagineDesignand Fabricationof Drug Delivery Infusion Pumporthodox mezmur lyricsNessuna valutazione finora