Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Naphtha Is A Flammable Liquid Made
Caricato da
ed modo0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
16 visualizzazioni2 paginePolymers are long chains of repeating molecular units that are used to make many everyday plastic products. Plastics are typically made from petroleum-based materials like naphtha, which is cracked and decomposed into raw materials like ethylene and propylene. There are several common manufacturing processes for turning these raw materials into plastic products, including blow molding, extrusion, injection molding, and structural foam molding. Blow molding uses air pressure to push melted plastic into molds, while extrusion squeezes plastic through a die to form continuous shapes.
Descrizione originale:
Industrial Chemistry Script
Titolo originale
SCRIPT Indkem
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoPolymers are long chains of repeating molecular units that are used to make many everyday plastic products. Plastics are typically made from petroleum-based materials like naphtha, which is cracked and decomposed into raw materials like ethylene and propylene. There are several common manufacturing processes for turning these raw materials into plastic products, including blow molding, extrusion, injection molding, and structural foam molding. Blow molding uses air pressure to push melted plastic into molds, while extrusion squeezes plastic through a die to form continuous shapes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
16 visualizzazioni2 pagineNaphtha Is A Flammable Liquid Made
Caricato da
ed modoPolymers are long chains of repeating molecular units that are used to make many everyday plastic products. Plastics are typically made from petroleum-based materials like naphtha, which is cracked and decomposed into raw materials like ethylene and propylene. There are several common manufacturing processes for turning these raw materials into plastic products, including blow molding, extrusion, injection molding, and structural foam molding. Blow molding uses air pressure to push melted plastic into molds, while extrusion squeezes plastic through a die to form continuous shapes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
SCRIPT
from liquid to gas occurs) to form
The use of plastics has been an ethylene and propylene, which are the
important part in the history of raw materials for plastics.
engineering and product design in the
twentieth century. They have given us Slide 3:
the ability to develop a range of products Blow molding (BrE moulding) is a
in a very wide number of areas, from specific manufacturing process by which
lightweight unbreakable containers, safe hollow plastic parts are formed and can
hygienic toys and inexpensive be joined together. It is also used for
household objects to artificial limbs and forming glass bottles or other hollow
life saving medical equipment. shapes.
Slide 1: In general, there are three main types of
Polymers are long chain of molecules blow molding:
made up of repeating units of smaller extrusion blow molding, injection blow
molecules called monomers. (Monomers molding, and injection stretch blow
– small molecular fragments) It’s like molding.
making a necklace from many small The blow molding process begins with
beads. Almost all of the things we use in melting down the plastic and forming it
our everyday lives are all synthesized into a parison or, in the case of injection
polymers. and injection stretch blow molding (ISB),
Synthetic polymers are polymers which a preform. The parison is a tube-like
are man-made using chemical piece of plastic with a hole in one end
processes. They were made by copying through which compressed air can pass.
the structures of natural polymers to The parison is then clamped into
produce synthetic polymers. Almost all a mold and air is blown into it. The air
of the raw materials for synthetic pressure then pushes the plastic out to
polymers are obtained from petroleum match the mold. Once the plastic has
by refining and cracking processes. cooled and hardened the mold opens up
One type and the most common and the part is ejected. The cost of blow
synthetic polymer of all is polyethylene. molded parts is higher than that of
injection-molded parts but lower than
Slide 2: rotational molded parts.
Naphtha is a flammable liquid made
from distilling petroleum. It looks like Slide 4:
gasoline.Naphtha is used to dilute Extrusion is a process that can be
heavy oil to help move it through compared to squeezing toothpaste out
pipelines, to make high-octane gas, to of a tube.
make lighter fluid, and even to clean Extrusion is a continuous process of
metal. converting a solid plastic mass, pellet or
Plastics are made from oil. ... powder into a melted form where it is
Most plastics use naphtha as main raw pushed through a die into a shape. This
material.Naphtha is further decomposed shape is then moved through various
thermally and separated utilizing the secondary operations where it is cooled
difference in the boiling point then cut, coiled or experiences a variety
(temperature at which the phase change of other possible operations.
The extrusion is cooled by water or air combined with either an inert physical
as it leaves the die and is finally cut to gas, such as nitrogen, or a chemical
the required length. The shape of the die blowing agent during the molding
can be varied from a simple hole with a process. The result is not a solid
centrally supported core to produce material but a low-density, microcellular
tubes such as pipes, to very complex “core” combined with a high density
sections for curtain tracks or hollow outer “skin”. The core decreases the
window frames. overall weight of the material while the
solid skin allows it to remain strong and
Slide 5: impact resistant.
This process is one of the most common The texture of the core has been
of all plastics manufacturing processes. frequently described as resembling a
The polymer, in granule form, is heated “sponge” or a “honeycomb”. Because of
until fused and forced into a closed its unique core texture, structural foam is
mould. Because of the viscous (thick, typically anywhere from 20% to 40%
syrupy) nature of the fused polymer, lighter than solid polymers, aluminum,
very high pressures are needed to make steel, sheet molding compound or other
it flow, which means that the machine commonly used materials.
and mould have to be very strong to Commonly used thermoplastics include
withstand the forces involved. but are not limited to: polyurethane,
Because of the ability of the plastic to polycarbonate, polyphenylene oxide
show even the smallest of marks very (Noryl), polybutylene terephthalate
fine detail can be cut into the surface of (Valox), and acrylonitrile butadiene
the mould, for example in the form of styrene.
trade marks, lettering or textures. Process:
It is a fast process and is used to The process of molding parts from
produce large numbers of identical items structural foam is very similar to the
from high precision engineering traditional method of reaction injection
components to disposable consumer molding. Two components, for example
goods. polyol and isocyanate (which are
Pressures from 70-200 MPa (10-30 combined in order to create
Kpsi) polyurethane) are stored in liquid form in
separate containers. They are mixed
Slide 6: together to form a resin which is injected
Structural foam is a composite material into a pre-prepared mold and cures via
produced when a polymer, usually the means of a chemical reaction.
thermoset (but can be thermoplastic), is
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Processing of PolymersDocumento36 pagineProcessing of Polymerssaadahmedkalidaas100% (1)
- LDPE BagsDocumento38 pagineLDPE BagsRajesh Galgalikar100% (1)
- Plastics: Mohammed Bilal 1 N S 1 9 AT 0 2 7 MMBC VDocumento21 paginePlastics: Mohammed Bilal 1 N S 1 9 AT 0 2 7 MMBC Vlalu mikeyNessuna valutazione finora
- The World of Plastics Engr. Lina D. Dela Cruz Chemical Engineering DepartmntDocumento27 pagineThe World of Plastics Engr. Lina D. Dela Cruz Chemical Engineering DepartmntMarnel Roy MayorNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.2 Plastics: Called Thermo Sets: 5.2.1 Thermoplastics. Thermoplastics Become Soften When Heated and Hard When CooledDocumento4 pagine5.2 Plastics: Called Thermo Sets: 5.2.1 Thermoplastics. Thermoplastics Become Soften When Heated and Hard When CooledBereket BlessingNessuna valutazione finora
- The World of Plastics Engr. Lina D. Dela Cruz Chemical Engineering DepartmntDocumento29 pagineThe World of Plastics Engr. Lina D. Dela Cruz Chemical Engineering DepartmntKristine Ann VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 16: Plastics: Plastic ManufacturingDocumento3 pagineChapter 16: Plastics: Plastic ManufacturingSkeletonBaakohaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment # 01: Manufacturing ProcessDocumento6 pagineAssignment # 01: Manufacturing Processwaqas qadirNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1Documento26 pagineUnit 1vaishnavi ChamartiNessuna valutazione finora
- University of The East College of Engineering: Plate No. 5 PolymersDocumento22 pagineUniversity of The East College of Engineering: Plate No. 5 PolymersJOHNEDERSON PABLONessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Plastic Processing ReducedDocumento16 pagine6 Plastic Processing Reducedhb8btk4s8cNessuna valutazione finora
- Task Sheet Names USI Task Carried Out in Report: All Members Assisted in Conducting The PresentationDocumento11 pagineTask Sheet Names USI Task Carried Out in Report: All Members Assisted in Conducting The PresentationhannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastic ProcessesDocumento27 paginePlastic Processesnitouch3564Nessuna valutazione finora
- Plastic Injection Moulding: Guide Name: DR - PRASAD KDocumento19 paginePlastic Injection Moulding: Guide Name: DR - PRASAD Ktejas p nNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation1 6.10.15Documento31 paginePresentation1 6.10.15Paramasivam VeerappanNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastics 140928093734 Phpapp02Documento27 paginePlastics 140928093734 Phpapp02Siyyadula Chandra SekharNessuna valutazione finora
- VisteonDocumento34 pagineVisteonAmbareesh NarayanpetNessuna valutazione finora
- University of The East - Manila Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocumento12 pagineUniversity of The East - Manila Mechanical Engineering DepartmentAngelica AndresNessuna valutazione finora
- PlasticsDocumento23 paginePlasticsIsaac JebNessuna valutazione finora
- PlasticsDocumento7 paginePlasticsAminaah AlhassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Write A Report On Composite Materials, The Reason Why They Are Used. Their Major Applications in Few Fields, and Some of The Latest Composite Materials.Documento17 pagineWrite A Report On Composite Materials, The Reason Why They Are Used. Their Major Applications in Few Fields, and Some of The Latest Composite Materials.Raushan Jha100% (1)
- Thermo Setting PlasticDocumento33 pagineThermo Setting PlasticAnkit AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Sintex Part 2Documento29 pagineSintex Part 2payalmalayNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastics AssignDocumento6 paginePlastics AssignMaria Mikaela PelagioNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastic Moulding ProcessDocumento28 paginePlastic Moulding ProcessQUAZI ADYAN AHMAD 160419736049Nessuna valutazione finora
- POLYMER PROCESSING HandoutDocumento4 paginePOLYMER PROCESSING HandoutAmabelle SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymers PPT PDFDocumento47 paginePolymers PPT PDFShivani RajeevNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 (BCHE-602)Documento14 pagineUnit 4 (BCHE-602)Garima TamtaNessuna valutazione finora
- Composite MaterialDocumento11 pagineComposite Materialalexrobertp1989Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 MoldingDocumento46 pagineChapter 4 MoldingTamirat NemomsaNessuna valutazione finora
- DJF5053-Jigs & Fixtures and Tooling DesignDocumento21 pagineDJF5053-Jigs & Fixtures and Tooling DesignMd Aziq Md RaziNessuna valutazione finora
- 202004032240236827nksingh Polymer ProcessingDocumento9 pagine202004032240236827nksingh Polymer ProcessingMuhammad Umair Akbar GujjarNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing Processes: ME 335 432 Lecture #16Documento36 pagineManufacturing Processes: ME 335 432 Lecture #16abdullah sulimanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bai Giang Ve Cong Nghe Chat DeoDocumento16 pagineBai Giang Ve Cong Nghe Chat DeotoanfbkNessuna valutazione finora
- ManufacturingDocumento29 pagineManufacturingAbel BatuNessuna valutazione finora
- INJECTION AND BLOW 12 Dani 1Documento12 pagineINJECTION AND BLOW 12 Dani 1abdulber kedirNessuna valutazione finora
- Mec131 Topic Report Last.Documento17 pagineMec131 Topic Report Last.mansang.mc62Nessuna valutazione finora
- 11.plastics LabDocumento21 pagine11.plastics Labalinader20022Nessuna valutazione finora
- Plastics: (Chapter 12)Documento88 paginePlastics: (Chapter 12)Shawn Ann SilanNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastic Injection Molding and Other Manufacturing Outsourcing Processes.20121231.150839Documento2 paginePlastic Injection Molding and Other Manufacturing Outsourcing Processes.20121231.150839anon_98449167Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Vi. Polymeric Materials: Topic OutlineDocumento7 pagineUnit Vi. Polymeric Materials: Topic OutlineIvyy Joyce BuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 3. Plastics and TextilesDocumento7 pagineTopic 3. Plastics and TextilesSergio GonzalezNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastics ProcessingDocumento19 paginePlastics ProcessingAnonymous mRBbdopMKfNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-6 Plastic MouldingDocumento12 pagineUnit-6 Plastic MouldingManav Patel100% (1)
- Untitled 1Documento2 pagineUntitled 1John Paul Godinez SuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Life Cycle AnalysisDocumento5 pagineLife Cycle AnalysisSonia YuNessuna valutazione finora
- FilmsDocumento2 pagineFilmsElisya DiantyNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastics Injection Moulding ProcessDocumento16 paginePlastics Injection Moulding Processरोहित मदानNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing of Plastic ComponentsDocumento50 pagineManufacturing of Plastic ComponentsrameshwarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastics and Related ProductsDocumento74 paginePlastics and Related ProductsRoland CepedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 1Documento24 pagineLec 1Osama Aadil SaadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Foam Molding - 11Documento27 pagineFoam Molding - 11José Luis TolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Processing of PolymersDocumento15 pagineProcessing of PolymersK Sruti RaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastic FormingDocumento11 paginePlastic FormingAngeloLorenzoSalvadorTamayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastic Bottle ManufacturingDocumento12 paginePlastic Bottle ManufacturingMartinBalanagNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Foam Molding Is A LowDocumento2 pagineStructural Foam Molding Is A LowRaqib RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymer FoamsDocumento17 paginePolymer FoamsSachin PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- The Study of Heredity.: Engr. Yvonne Ligaya F. MusicoDocumento34 pagineThe Study of Heredity.: Engr. Yvonne Ligaya F. Musicoed modoNessuna valutazione finora
- RAMIREZ 01BasicConceptsOfProcessDynamicsAndControlDocumento19 pagineRAMIREZ 01BasicConceptsOfProcessDynamicsAndControled modoNessuna valutazione finora
- Healthcare: Francesca Reane M. RamirezDocumento13 pagineHealthcare: Francesca Reane M. Ramirezed modoNessuna valutazione finora
- Iso 14000Documento8 pagineIso 14000ed modoNessuna valutazione finora
- Technological Institute of The Philippines: Psychosocial HazardsDocumento8 pagineTechnological Institute of The Philippines: Psychosocial Hazardsed modoNessuna valutazione finora
- Best of MilkteaDocumento5 pagineBest of Milkteaed modoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sweden's Revolutionary Waste ManagementDocumento3 pagineSweden's Revolutionary Waste Managemented modoNessuna valutazione finora
- Integ and DiffcalDocumento8 pagineInteg and Diffcaled modoNessuna valutazione finora
- Case StudyDocumento13 pagineCase Studyed modoNessuna valutazione finora
- Linkages Form The Sugar-Phosphate Backbone of Both DNA and RNADocumento3 pagineLinkages Form The Sugar-Phosphate Backbone of Both DNA and RNAed modoNessuna valutazione finora
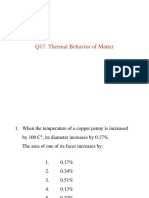
- Q17. Thermal Behavior of MatterDocumento9 pagineQ17. Thermal Behavior of Mattered modoNessuna valutazione finora
- Refining of Sugar: Dela Vega, Ela Jane P. Bs CheDocumento9 pagineRefining of Sugar: Dela Vega, Ela Jane P. Bs Cheed modoNessuna valutazione finora
- Linkages Form The Sugar-Phosphate Backbone of Both DNA and RNADocumento3 pagineLinkages Form The Sugar-Phosphate Backbone of Both DNA and RNAed modoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrogen PeroxideDocumento42 pagineHydrogen Peroxideed modoNessuna valutazione finora
- Genset Load TestDocumento10 pagineGenset Load Testjavad100% (1)
- Appendix BDocumento11 pagineAppendix BypkaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Volvo FMX Product Guide Euro6 en GBDocumento24 pagineVolvo FMX Product Guide Euro6 en GBMaxNessuna valutazione finora
- W3330NDocumento2 pagineW3330Nmaris_sasec0% (1)
- Cortem Group - Ex PosterDocumento1 paginaCortem Group - Ex PosterMuhammad HannanNessuna valutazione finora
- Himsen Cat h2533Documento12 pagineHimsen Cat h2533Mohsen50% (2)
- 2013 Fuel Consumption GuideDocumento40 pagine2013 Fuel Consumption Guideslysoft.20009951Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4Th .SubsurfaceDocumento67 pagine4Th .SubsurfaceDana AbkhNessuna valutazione finora
- Corolla Engine ControlDocumento12 pagineCorolla Engine ControlPatricio ValenciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Leutert Catalog SlicklineToolsDocumento57 pagineLeutert Catalog SlicklineToolsCarlos Apolo Ramirez100% (1)
- GPCDOC Local TDS United Kingdom Shell Helix Ultra Professional AG 5W-30 (Dexos 2) (en-GB) TDSDocumento2 pagineGPCDOC Local TDS United Kingdom Shell Helix Ultra Professional AG 5W-30 (Dexos 2) (en-GB) TDSJohn SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Api 2030Documento1 paginaApi 2030Adil MominNessuna valutazione finora
- Liquefied Petroleum Gas Cylinder Level Indicator and Transporting DeviceDocumento14 pagineLiquefied Petroleum Gas Cylinder Level Indicator and Transporting DeviceAyorinde Oladele TiwaladeNessuna valutazione finora
- Taboo Opinions #87: by Richard E. GeisDocumento5 pagineTaboo Opinions #87: by Richard E. Geistelematico69Nessuna valutazione finora
- WPS Sa 335 P91 PipeDocumento3 pagineWPS Sa 335 P91 Pipecsankarananth50% (2)
- Baleno Manual PDFDocumento334 pagineBaleno Manual PDFgheorghe gardu100% (1)
- US Navy Course NAVEDTRA 14331 - Engineman 3Documento413 pagineUS Navy Course NAVEDTRA 14331 - Engineman 3Georges100% (7)
- Report On CGD Business in IndiaDocumento24 pagineReport On CGD Business in IndiaKunal SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Handout (Basic)Documento6 pagineChemistry Handout (Basic)Tin SumangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Submersible Sewage Ejector Pump: Pump Installation and Service ManualDocumento8 pagineSubmersible Sewage Ejector Pump: Pump Installation and Service Manualallen_worstNessuna valutazione finora
- A 247Documento1 paginaA 247AnuranjanNessuna valutazione finora
- NPSHDocumento4 pagineNPSHrex tanongNessuna valutazione finora
- EuropeLPGReport Sample02082013Documento5 pagineEuropeLPGReport Sample02082013Melody CottonNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultramid, Ultradur, Ultraform PDFDocumento52 pagineUltramid, Ultradur, Ultraform PDFkfaravNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimization, Calibration, and Validation of Atomic Absorption Spectrometry For Metal Analysis of Petroleum Products and LubricantsDocumento9 pagineOptimization, Calibration, and Validation of Atomic Absorption Spectrometry For Metal Analysis of Petroleum Products and LubricantscamiloNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Drilling RigsDocumento18 pagineMobile Drilling RigsGonzalo Rial Muíños100% (2)
- Natural Gas Engine E 2876 E 312 Technical DataDocumento9 pagineNatural Gas Engine E 2876 E 312 Technical DataPetar MiletićNessuna valutazione finora
- Marine Diesel Engine - Preparations For Standby, Starting, Reversing and Running at Full Speed PDFDocumento15 pagineMarine Diesel Engine - Preparations For Standby, Starting, Reversing and Running at Full Speed PDFHein Htet AungNessuna valutazione finora