Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Chapter 1 - Introduction To Project: 1.1 Abstract
Caricato da
Trupti WaghDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chapter 1 - Introduction To Project: 1.1 Abstract
Caricato da
Trupti WaghCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Series and parallel circuit
Chapter 1 –INTRODUCTION TO PROJECT
1.1 ABSTRACT
Electrical wiring is an electrical installation of cabling and associated devices such as switches, distribution
boards, sockets, and light fittings in a structure.
Wiring is subject to safety standards for design and installation. Allowable wire and cable types and sizes are
specified according to the circuit operating voltage and electric current capability, with further restrictions on
the environmental conditions, such as ambient temperature range, moisture levels, and exposure to sunlight
and chemicals.
Associated circuit protection, control and distribution devices within a building's wiring system are subject to
voltage, current and functional specification. Wiring safety codes vary by locality, country or region.
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) is attempting to harmonies’ wiring standards amongst
member countries, but significant variations in design and installation requirements still exist.
1.2 INTRODUCTION TO PROJECT
Homes typically have several kinds of home wiring, including Electrical wiring for lighting and power
distribution, permanently installed and portable appliances, telephone, heating or ventilation system control, and
increasingly for home theatre and computer networks. [1]
Safety regulations for wiring installation vary widely around the world, with national, regional, and municipal
rules sometimes in effect. Some places allow the homeowner to install some or all of the wiring in a home; other
jurisdictions require electrical wiring to be installed by licensed electricians only.
Typical featuresEdit
Single-phase ~230 V/40 A/9 kW fuse box for apartment rewiring. Each appliance and each room are highlighted into
autonomous circuits - this apartment has 14 individual circuits. A relay is used to control the light fixtures in a large
room.
Electrical Engineering -1- R. C. Patel Polytechnic
Series and parallel circuit
In new home construction, wiring for all electrical services can be easily installed before the walls are finished. In
existing buildings, installation of a new system, such as a security system or home theatre, may require additional
effort to install concealed wiring. Multiple unit dwellings such as condominiums and apartment houses may have
additional installation complexity in distributing services within a house.
Services commonly found include:
1] Power points (wall outlets)
2] Light fixtures and switches
3] Telephone
4] Internet
5] Television, either broadcast, cable, or satellite
High-end features might include:
1] Home theater
2] Distributed audio
3] Security monitoring
4] Security CCTV
5] Automation
6] Energy management
Power and telecommunication services generally require entry points into the home and a location for connection
equipment. For electric power supply, a cable is run either overhead or underground into a distribution board in
the home. A distribution board, or circuit breaker panel, is typically a metal box mounted on a wall of the home. In
many new homes the location of the electrical switchboard is on the outside of the external wall of the garage.
How services are connected will vary depending on the service provider and location of the home.
The following home services are supported by discrete wiring systems [2]
1 Information and Communications
2 Entertainment
3 Energy Management
4 Security and Safety
5 Digital Home Health
6 Aged and Assisted Living
7 Intelligent Lighting and Power.
Electrical Engineering -2- R. C. Patel Polytechnic
Series and parallel circuit
PROJECT OBJECTIVES
an element in a camera or microscope
The Objective, a 2008 science fiction horror film
Objective pronoun, a personal pronoun that is used as a grammatical object
Objective Productions, a British television production company
Goal, a result or possible outcome that a person or a system desires
Electrical Engineering -3- R. C. Patel Polytechnic
Series and parallel circuit
Chapter 3–PROJECT
Chapter 4
ADVANTAGES, DISADVANTAGES & APPLICATIONS
4.1 ADVANTAGES
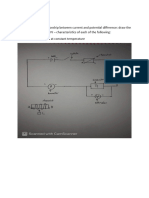
Parallel Circuit:
Every unit that is connected in a parallel circuit gets equal amount of voltage.
It becomes easy to connect or disconnect a new element without affecting the
working of other elements.
If any fault happened to the circuit, then also the current is able to pass through
the circuit through different paths.
Series Circuit:
Series circuits do not overheat easily. This makes them very useful in the case
of something that might be around a potentially flammable source, like dry
plants or cloth.
Series circuits are easy to learn and to make. Their simple design is easy to
understand, and this means that it’s simple to conduct repairs .
we can add more power devices, they have a higher output in terms of voltage .
The current that flows in a series circuit has to flow through every component
in the circuit. Therefore, all of the components in a series connection carry the
same current.
4.2DISADVANTAGES
Parallel Circuit:
It requires the use of lot of wires.
Electrical Engineering -4- R. C. Patel Polytechnic
Series and parallel circuit
We cannot increase or multiply the voltage in a parallel circuit.
Parallel connection fails at the time when it is required to pass exactly same amount of
current through the units.
Series Circuit:
If one point breaks in the series circuit,the total circuit will break.
As the number of components in a circuit increases ,greater will be the circuit
resistance.
4.3APPLICATIONS
A common application of series circuit in consumer electronics is in batteries, where
several cells connected in series are used to obtain a convenient operating voltage.
Two disposable zinc cells in series might power a flashlight or remote control at 3
volts; the battery pack for a hand-held power tool might contain a dozen lithium-ion
cells wired in series to provide 48 volts.
Series circuits were formerly used for lighting in electric multiple units trains. For
example, if the supply voltage was 600 volts there might be eight 70-volt bulbs in
series (total 560 volts) plus a resistor to drop the remaining 40 volts. Series circuits for
train lighting were superseded, first by motor-generators, then by solid state devices.
Series resistance can also be applied to the arrangement of blood vessels within a
given organ. Each organ is supplied by a large artery, smaller arteries, arterioles,
capillaries, and veins arranged in series. The total resistance is the sum of the
individual resistances, as expressed by the following equation: Rtotal = Rartery +
Rarterioles + Rcapillaries. The largest proportion of resistance in this series is contributed by
the arterioles.
Parallel resistance is illustrated by the circulatory system. Each organ is supplied by
an artery that branches off the aorta. The total resistance of this parallel arrangement is
expressed by the following equation: 1/Rtotal = 1/Ra + 1/Rb + ... 1/Rn. Ra, Rb, and Rn are
the resistances of the renal, hepatic, and other arteries respectively. The total
resistance is less than the resistance of any of the individual arteries.
Electrical Engineering -5- R. C. Patel Polytechnic
Series and parallel circuit
Chapter 5
CONCLUSIONS, FUTURE SCOPE& REFERENCES
5.1CONCLUSION
In this experiment, we were able to determine the total current flowing through
a series circuit and parallel circuit, the voltage across each resistors and the current
flowing through aseries circuit and parallel circuit; to investigate the relationship
between the voltages across each resistor and the parallel circuit
5.2FUTURE SCOPE
1. Trying to run circuits without clocks. Clocking is the major source of power loss in
a circuit and there is research currently trying to figure out to build circuits and
operate gates without clocks.
2. Understanding the human brain and trying to model circuits in an analogous way.
3. Carbon Nanotubes and Organic FET's.
4. 3D fabrication. Designing chips in stacks one over another.
As I said I am still in the course of learning, so this answer is certainly not a complete
one. But as I keep learning I will try to make sure that this answer is periodically
updated.
Electrical Engineering -6- R. C. Patel Polytechnic
Series and parallel circuit
5.3REFERENCES
[1]www.wikipedia.com
[2]www.youtube.com
WEEKLY WORK / PROGRESS REPORT
Details of 16 Engagement Hours of the Student
Regarding Completion of the Project
Timing Sign
Week
Date Duration Work/Activity Performed of
No. From To
in Hours Guide
Discussion and Finalization of the
1. 01
Project Title
Preparation and Submission of
2. 02
Abstracts
3. 02 Literature Review
4. 02 Collection of Data
5. 02 Collection of Data
6. 01 Discussion and Outline of Content
7. 02 Rough Writing of the Projects Contents
Editing and Proof Reading of the
8. 01
Contents
Electrical Engineering -7- R. C. Patel Polytechnic
Series and parallel circuit
9. 02 Final Completion of the Project
Seminar Presentation, Viva-Vice,
10. 01
Assessment and Submission of Report
NOTE: Weekly Report content can vary based on Project type, Subject, Department of student.
DO NOT KEEP THIS LINE IN REPORT.
Name & Signature of Project Guide
Prof. XYZ
Electrical Engineering -8- R. C. Patel Polytechnic
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingDa EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Barredo, Bsa 3a1 PDFDocumento5 pagineBarredo, Bsa 3a1 PDFCrisostomo Andiong BaltazarNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical WiringDocumento11 pagineElectrical WiringRasydan AliNessuna valutazione finora
- The Electricity Supply System - Newcastle University UKDocumento10 pagineThe Electricity Supply System - Newcastle University UKkija lemaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bee 2021Documento87 pagineBee 2021Nirav ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bài 2,3 Thí Nghiệm Trang Bị ĐiệnDocumento37 pagineBài 2,3 Thí Nghiệm Trang Bị ĐiệnNguyen TrongNessuna valutazione finora
- Philippine Electrical CodeDocumento26 paginePhilippine Electrical CodeDwight ponce100% (1)
- BSD - M Odule 5Documento38 pagineBSD - M Odule 5M MNessuna valutazione finora
- Schedule of LoadsDocumento44 pagineSchedule of LoadsIsha MancenidoNessuna valutazione finora
- BLDG Ser Elect BSCDocumento12 pagineBLDG Ser Elect BSCDon MustyNessuna valutazione finora
- Building Electrical System FM ALL CHAPTERSDocumento267 pagineBuilding Electrical System FM ALL CHAPTERSabrarulh522Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3.2 Uee2521 RRPDocumento54 pagine3.2 Uee2521 RRPmohammad2110959Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 8&9-Electric and LightningDocumento62 pagineLecture 8&9-Electric and LightningMuhammad FakhriNessuna valutazione finora
- DB Fault 1 - 5 (2nd Edition)Documento48 pagineDB Fault 1 - 5 (2nd Edition)Oseloka OnyeaboNessuna valutazione finora
- Y3 - Module 3 - Drafting Electrical and Electronic Layout and DetailsDocumento71 pagineY3 - Module 3 - Drafting Electrical and Electronic Layout and DetailsRod Aquino78% (9)
- Electrical Power Distribution & Utilization: Lab ManualDocumento40 pagineElectrical Power Distribution & Utilization: Lab ManualUzair HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- About PCBDocumento13 pagineAbout PCBRussel Matthew EspirituNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical and Elctronic Design GuidelineDocumento36 pagineElectrical and Elctronic Design GuidelineBramNessuna valutazione finora
- Ei Nvq2 Ch06Documento32 pagineEi Nvq2 Ch06Nihar RoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Education PUBLIC TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL High SchoolsDocumento32 pagineDepartment of Education PUBLIC TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL High SchoolsReinier Paclibar FederizoNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 6 Electrical Services To BuildingsDocumento14 pagineTopic 6 Electrical Services To Buildingsullhan84100% (1)
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Notes 121129165717 Phpapp01Documento42 pagineRefrigeration and Air Conditioning Notes 121129165717 Phpapp01zohaib now engineering easyNessuna valutazione finora
- Catilcong, Rebert BSCE-2BDocumento6 pagineCatilcong, Rebert BSCE-2BGonzales AlexNessuna valutazione finora
- Doan 2014Documento7 pagineDoan 2014Matheus dos Reis BravimNessuna valutazione finora
- EE114 1 Homework 2Documento3 pagineEE114 1 Homework 2Denver John TejadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Manual PDFDocumento40 pagineLab Manual PDFAngelline MalikNessuna valutazione finora
- Terminating, Connecting and Testing Electrical Wirings and Electronic CircuitsDocumento4 pagineTerminating, Connecting and Testing Electrical Wirings and Electronic CircuitsCyril Joy N. Fernando50% (2)
- Unit 53 Electrical Installation PDFDocumento12 pagineUnit 53 Electrical Installation PDFnadeem UddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Idosr JST 41 81 105 2019. PuDocumento25 pagineIdosr JST 41 81 105 2019. Pujamiu1175Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2-Electrical Wiring CircuitsDocumento43 pagineChapter 2-Electrical Wiring CircuitsyeabmotherNessuna valutazione finora
- Ritchie Mar C. Ugsod: First Semester, A.Y. 2020-2021Documento5 pagineRitchie Mar C. Ugsod: First Semester, A.Y. 2020-2021Gaming DeathNessuna valutazione finora
- On Going (Chapter 1)Documento49 pagineOn Going (Chapter 1)Video Music0% (1)
- TVE 1st Quarter ReviewerDocumento12 pagineTVE 1st Quarter ReviewerGaming DeathNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Activity No 1 - Electrical SymbolsDocumento8 pagineLearning Activity No 1 - Electrical SymbolsShiela SalvillaNessuna valutazione finora
- ICT 9: Computer Hardware Servicing: Basic Concepts of ElectricityDocumento44 pagineICT 9: Computer Hardware Servicing: Basic Concepts of ElectricityJian Patrick SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Installation and MaintenanceDocumento25 pagineElectrical Installation and MaintenanceMarc HillNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Wireless Power Transfer SystemDocumento29 pagineAdvanced Wireless Power Transfer SystemOssai IsraelNessuna valutazione finora
- IE Project Report Group 3Documento9 pagineIE Project Report Group 3john jkillerzsNessuna valutazione finora
- Iagnostics Field Testing of Medium-Voltage Cables: Special FeatureDocumento4 pagineIagnostics Field Testing of Medium-Voltage Cables: Special FeatureShredder WardatNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.ecm346 - Level 1 - Electrical SupplyDocumento6 pagine4.ecm346 - Level 1 - Electrical SupplyhhazimabNessuna valutazione finora
- Inspeccion Sistema SolarDocumento8 pagineInspeccion Sistema SolarManuel TorijaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of The Electric Field Distribution Within MV Cable Joint in The Presence of Defects in Cable InsulationDocumento11 pagineAnalysis of The Electric Field Distribution Within MV Cable Joint in The Presence of Defects in Cable InsulationEdgardo Ariel RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Tieu Chuan IECDocumento410 pagineTieu Chuan IECAlexander GuzmánNessuna valutazione finora
- Free Tutorial: Circuit Breaker The Muscle of Electrical Power SystemDocumento14 pagineFree Tutorial: Circuit Breaker The Muscle of Electrical Power SystemlohakareshivajiNessuna valutazione finora
- Deshaunie SullivanDocumento17 pagineDeshaunie SullivanK KgfdfNessuna valutazione finora
- Tejada - Homework 2Documento3 pagineTejada - Homework 2Denver John TejadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Wireless Ac Power Detector 1Documento27 pagineWireless Ac Power Detector 1belacheweshetu222Nessuna valutazione finora
- EE114-1 Homework 2Documento2 pagineEE114-1 Homework 2GuiaSanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture-6 Types of Electrical Wiring SystemDocumento32 pagineLecture-6 Types of Electrical Wiring Systemaditya100% (1)
- Lecture-6 Types of Electrical Wiring SystemDocumento32 pagineLecture-6 Types of Electrical Wiring Systemaditya0% (1)
- GE19122 - EPL Manual With BonafideDocumento26 pagineGE19122 - EPL Manual With BonafidejitheeswaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Railway ProjectDocumento38 pagineRailway Projectalankar123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation Slides Understanding NECDocumento48 paginePresentation Slides Understanding NECMarcosGodoyPereyraNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Shop in A Ship Repair Yard PDFDocumento21 pagineElectrical Shop in A Ship Repair Yard PDFBachhanChaubey100% (1)
- HVE - Unit1 - Full PPT Notes PDFDocumento130 pagineHVE - Unit1 - Full PPT Notes PDFJ VEERENDRA KUMAR100% (1)
- Theor Na Moyu Model1 PDFDocumento4 pagineTheor Na Moyu Model1 PDFАлексей ЯмаNessuna valutazione finora
- Back To Basics - Conductors, Currents and Circuit Protection - IAEI MagazineDocumento13 pagineBack To Basics - Conductors, Currents and Circuit Protection - IAEI MagazineMORALES2197Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Installation in BuildingsDocumento14 pagineElectrical Installation in BuildingsMasar Abdul Rakman100% (1)
- FEED or RPT 08 004 - Applicable Codes and Standard - Rev.ADocumento36 pagineFEED or RPT 08 004 - Applicable Codes and Standard - Rev.AMinh DoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sony str-k5Documento56 pagineSony str-k5jimmy osorioNessuna valutazione finora
- Rittal VX25 Ri4Power - The Switchgear and Power Distribution System For The VX25Documento118 pagineRittal VX25 Ri4Power - The Switchgear and Power Distribution System For The VX25Guh CamposNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 96 - Electrical System: BHT-206L3-MM-10Documento52 pagineChapter 96 - Electrical System: BHT-206L3-MM-10chiri003Nessuna valutazione finora
- EEC 129 PracticalDocumento48 pagineEEC 129 PracticalVietHungCao100% (6)
- Site Boss 530 ManualDocumento101 pagineSite Boss 530 Manualmfkhan123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Draft SPEC NO 0013-2011-19.06.14 PDFDocumento37 pagineDraft SPEC NO 0013-2011-19.06.14 PDFKatikareddy Sreenu100% (1)
- MEP Site Inspection ReportDocumento5 pagineMEP Site Inspection Reportpsn_kylm50% (4)
- Growatt 30000-40000 TL3-SE PDFDocumento31 pagineGrowatt 30000-40000 TL3-SE PDFDibyendu MaityNessuna valutazione finora
- ACCOR Engineering Solutions: QuotationDocumento38 pagineACCOR Engineering Solutions: QuotationgopalraojiNessuna valutazione finora
- Shellmax Training: WelcomeDocumento114 pagineShellmax Training: WelcomeDuggineni Ramakrishna100% (1)
- B. Walk Ways To BeDocumento4 pagineB. Walk Ways To BeikeagharanyaNessuna valutazione finora
- SM PC350LC (HD) - 8 A10001-Up Cebm007501Documento1.097 pagineSM PC350LC (HD) - 8 A10001-Up Cebm007501Aaron Campos SalazarrNessuna valutazione finora
- TOE-606-3.1 vs-606 PC3 Instructions (Spec U)Documento157 pagineTOE-606-3.1 vs-606 PC3 Instructions (Spec U)JonNessuna valutazione finora
- Siemens Rva53.280Documento184 pagineSiemens Rva53.280ttiinneell8932Nessuna valutazione finora
- TDPDocumento3 pagineTDPHarshad JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Haynes Motorcycle Workshop PracticeDocumento226 pagineHaynes Motorcycle Workshop Practiceholloway.richard123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Operation and Maintenance Manual: 2206F-E13TA and 2206J-E13TA Industrial EngineDocumento128 pagineOperation and Maintenance Manual: 2206F-E13TA and 2206J-E13TA Industrial EngineAbdelbagiNessuna valutazione finora
- Annexure P TPD 004 Earthingspec - 0Documento20 pagineAnnexure P TPD 004 Earthingspec - 0patitay036817Nessuna valutazione finora
- ASBEILA S30G 1-12hp Compressor R134a Refrigeration LBP Technical Datasheet Specs SpecificationDocumento8 pagineASBEILA S30G 1-12hp Compressor R134a Refrigeration LBP Technical Datasheet Specs SpecificationRicardoHagelNessuna valutazione finora
- Installation Manual: Automatic & Non-Automatic Transfer & Bypass-Isolation SwitchesDocumento20 pagineInstallation Manual: Automatic & Non-Automatic Transfer & Bypass-Isolation SwitchesCarlos MirkoNessuna valutazione finora
- Boq PDFDocumento12 pagineBoq PDFChandeshwor Shah0% (1)
- Bitzer Selection SoftwareDocumento14 pagineBitzer Selection SoftwareNam ĐặngNessuna valutazione finora
- Reefer Unit Inspection Form ChecklistDocumento1 paginaReefer Unit Inspection Form ChecklistImtiaz Nazir-KhaleelNessuna valutazione finora
- Eim Module 7Documento13 pagineEim Module 7Aldrin SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- FR ABR H2 2k PDFDocumento13 pagineFR ABR H2 2k PDFMárcio FernandesNessuna valutazione finora
- Features & Specifications: Click Here For Acrylic-Polycarbonate Compatibility Table For Suitable UsesDocumento16 pagineFeatures & Specifications: Click Here For Acrylic-Polycarbonate Compatibility Table For Suitable UsesAARON ROMERO RODRIGUEZNessuna valutazione finora
- Tender 10 KW Rooftop SolarDocumento14 pagineTender 10 KW Rooftop Solarsrirajt4uNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 130205 V7.13 EVRC2A-N6, NT Manual ControlDocumento306 pagine02 130205 V7.13 EVRC2A-N6, NT Manual ControlGiancarlo Barahona Aguilar67% (3)
- Millermatic251s PDFDocumento72 pagineMillermatic251s PDFwilliam ortizNessuna valutazione finora