Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Acyl Halide Rxns
Caricato da
api-465421809Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Acyl Halide Rxns
Caricato da
api-465421809Copyright:
Formati disponibili
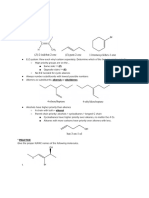
CA DERIVATIVES ACYL HALIDE RXNS Chemistry Specialist: Alicia Hart
UC Davis - SASC
a) Hydrolysis
O O
H2O
R Cl R OH
- pyridine is often used to prevent the formation of HCl when reacting with acyl chlorides
b) Alcoholysis
O O
R'OH, pyridine
or NaOR', R'OH
R Cl R OR'
c) Ammonolysis/Aminolysis
O O
NH3
R Cl R NH2
- can use 1 and 2 amine, but NR with 3 amine
d) Alkylation
i) Organometallic Reagents
OH
O
1. R'Li or R'MgX, Ether
R R'
R Cl 2. H3O+ R'
- given 2 eq. of the organometallic reagent, does alkylation twice by kicking off the Cl and reforming the carbonyl.
ii) Organocuprate
O
O
1. R'2CuLi
R R'
R Cl 2. H3O+
- unlike the grignard above, organocuprate adds only one R' stopping at the ketone
- Mcmurry 7 edition states, "diorganocuprate only reacts with acyl halides; does not with carbox. acid, anhydrides, ester and amides."
e) Reduction OH
O
NaBH4, EtOH
or 1. LiAlH 4, ether R H
R Cl 2. H3O+ H
O
To stop at aldehyde, 1. LiAlOC(CH 3)3H, THF
use less reactive red. agent...
2. H3O+ R H
- Note: DIBAL is still too reactive to stop at aldehyde with acy halide.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Nitrile RxnsDocumento1 paginaNitrile Rxnsapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anhydride RxnsDocumento1 paginaAnhydride Rxnsapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- Amide RxnsDocumento1 paginaAmide Rxnsapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ester RxnsDocumento1 paginaEster Rxnsapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- Benzene RxnsDocumento1 paginaBenzene Rxnsapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alcohol, Phenols and Ethers Ch-10Documento19 pagineAlcohol, Phenols and Ethers Ch-10Literal ShTNessuna valutazione finora
- Ca Rxns IDocumento1 paginaCa Rxns Iapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- Amine SynthDocumento1 paginaAmine Synthapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ca SynthDocumento1 paginaCa Synthapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ca RXN CheckDocumento1 paginaCa RXN Checkapi-4654218090% (1)
- Phenol Rxns IDocumento1 paginaPhenol Rxns Iapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- Phenol SynthDocumento1 paginaPhenol Synthapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- ch15-16 SummaryDocumento1 paginach15-16 Summaryapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- OQR (Oragnic Quick Revision) (ALIPHATIC) : Mcpba Conc. H SO DDocumento2 pagineOQR (Oragnic Quick Revision) (ALIPHATIC) : Mcpba Conc. H SO Dmanya9b32100% (1)
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes1Documento15 pagineHaloalkanes and Haloarenes1Poorni RenuNessuna valutazione finora
- Aliphatic and Aromatic FlowchartDocumento4 pagineAliphatic and Aromatic FlowchartapaperclipNessuna valutazione finora
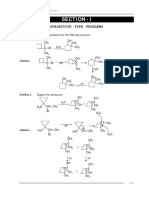
- Roadmap Problem - 9Documento1 paginaRoadmap Problem - 9abhyudaipathwayNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrocarbon: Ashwani Tyagi Sir (Code: ATJEE)Documento22 pagineHydrocarbon: Ashwani Tyagi Sir (Code: ATJEE)Prince DigvijayNessuna valutazione finora
- AIEEE Chemistry Quick ReviewDocumento1 paginaAIEEE Chemistry Quick ReviewYashwanth KalyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Reagents: 1. Alcoholic KOH 2. Aluminium EthoxideDocumento9 pagineOrganic Reagents: 1. Alcoholic KOH 2. Aluminium EthoxideAarya Nandal100% (1)
- Haloalkanes MADDocumento31 pagineHaloalkanes MADggdfjkkvvNessuna valutazione finora
- Grignard Reagent Q.B.Documento12 pagineGrignard Reagent Q.B.Aariya KumariNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch 19 - Claisen Condensation and Diekmann CyclizationDocumento68 pagineCh 19 - Claisen Condensation and Diekmann CyclizationBritany DyerNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Coordination CompoundsDocumento329 pagine7 Coordination CompoundsArka100% (1)
- 6carboxylic AcidsDocumento1 pagina6carboxylic AcidssharmimiameerasanadyNessuna valutazione finora
- Alkyl Halides and Aryl Halides SkillsDocumento23 pagineAlkyl Halides and Aryl Halides SkillsNETHAKANI SUJATHA100% (1)
- Chem 212 Alkyl Halide Problems 2Documento1 paginaChem 212 Alkyl Halide Problems 2kevinamy100% (1)
- Chapter 12 Lecture PDFDocumento156 pagineChapter 12 Lecture PDFjoseph changNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER25 HeterocyclesDocumento44 pagineCHAPTER25 HeterocyclesRiyanto WidodoNessuna valutazione finora
- 118c Practice Synthesis KeyDocumento18 pagine118c Practice Synthesis Keyapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chem-GA 1311 Spring 2021 F, ReductionDocumento38 pagineChem-GA 1311 Spring 2021 F, ReductionHY-11 Đỗ Quốc TiệpNessuna valutazione finora
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocumento26 pagineHaloalkanes and Haloarenesrajputrishi1982Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 212 Alkyl Halide Problems 4Documento1 paginaChem 212 Alkyl Halide Problems 4kevinamyNessuna valutazione finora
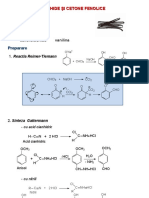
- Aldehide Şi Cetone FenoliceDocumento9 pagineAldehide Şi Cetone FenoliceMarinelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry ChartsDocumento84 pagineOrganic Chemistry ChartsPRIYANSHU KUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter36 - BiomoleculesDocumento19 pagineChapter36 - BiomoleculesAkash GoelNessuna valutazione finora
- Alkyl Halides & Aryl Halides-02 - Solved ProblemsDocumento13 pagineAlkyl Halides & Aryl Halides-02 - Solved ProblemsRaju SinghNessuna valutazione finora
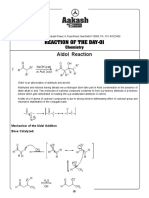
- Aldol Reaction - ChemistryDocumento7 pagineAldol Reaction - ChemistryGamer HelperNessuna valutazione finora
- Road Map (3) Problem: Aq. KOHDocumento1 paginaRoad Map (3) Problem: Aq. KOHShubham RajNessuna valutazione finora
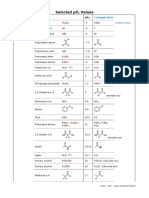
- Selected PK Values: Strongest AcidDocumento2 pagineSelected PK Values: Strongest AcidFernandaIbarraVázquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Ape Assignment 3Documento7 pagineApe Assignment 3Atharva KulkarniNessuna valutazione finora
- Reactions and Interconversions of Organic Functional GroupsDocumento3 pagineReactions and Interconversions of Organic Functional Groupsmichelsonyip100% (1)
- Enol Dan EnolatDocumento40 pagineEnol Dan EnolatRiyan KateeNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbocation RearrangementDocumento4 pagineCarbocation RearrangementManas J. AggarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 Reactions of AlcoholsDocumento12 pagineChapter 8 Reactions of AlcoholsRoberto SIlvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Reactions and Functional Group SynthesisDocumento48 pagineOrganic Reactions and Functional Group SynthesisRonak MantriNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEM 360 NOTES: CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND ESTERSDocumento36 pagineCHEM 360 NOTES: CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND ESTERSThục NghiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 20: Introduction To Carbonyl Chemistry Organometallic Reagents Oxidation and ReductionDocumento41 pagineChapter 20: Introduction To Carbonyl Chemistry Organometallic Reagents Oxidation and ReductionRavi JaiswalNessuna valutazione finora
- Alkyl Halide and Aryl HalideDocumento46 pagineAlkyl Halide and Aryl Halidekartikbarot884Nessuna valutazione finora
- Microsoft PowerPoint - Aldehydes and KetonesDocumento24 pagineMicrosoft PowerPoint - Aldehydes and KetonesAR LazagaNessuna valutazione finora
- L6 Reactions of Carboxylic Acid DerivativesDocumento21 pagineL6 Reactions of Carboxylic Acid DerivativesCheng FuNessuna valutazione finora
- II Reduction Reactions: ObjectivesDocumento34 pagineII Reduction Reactions: ObjectivesHemendra PrasannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry: AlcoholsDocumento11 pagineChemistry: AlcoholsGaelle TomkoNessuna valutazione finora
- ReductionDocumento7 pagineReductionPranayNessuna valutazione finora
- Aldehyde and KetonesDocumento95 pagineAldehyde and KetoneskeerthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Carboxylic AcidsDocumento26 pagineCarboxylic Acidsapi-3734333100% (1)
- Alcohol, Aldehyde and KetonesDocumento12 pagineAlcohol, Aldehyde and KetonesFranky TeeNessuna valutazione finora
- 26_halogen_derivatives_formula_sheets_quizrrDocumento8 pagine26_halogen_derivatives_formula_sheets_quizrradarsh.rajesh69Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alcohol (Theory) Module-4Documento18 pagineAlcohol (Theory) Module-4Raju SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocumento19 pagineAldehydes and KetonesVaibhav TarkasbandNessuna valutazione finora
- Ca RXN CheckDocumento1 paginaCa RXN Checkapi-4654218090% (1)
- 118c Practice Synthesis KeyDocumento18 pagine118c Practice Synthesis Keyapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- 118c Practice Synthesis KeyDocumento18 pagine118c Practice Synthesis Keyapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- Amine SynthDocumento1 paginaAmine Synthapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ca SynthDocumento1 paginaCa Synthapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- Phenol Rxns IDocumento1 paginaPhenol Rxns Iapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- Phenol SynthDocumento1 paginaPhenol Synthapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- CH 17: Aldehydes and Ketones: Nasiri CHE118B Final Study Guide Spring 2019 - S. Ly Sdly@ucdavis - EduDocumento17 pagineCH 17: Aldehydes and Ketones: Nasiri CHE118B Final Study Guide Spring 2019 - S. Ly Sdly@ucdavis - Eduapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ca Rxns IDocumento1 paginaCa Rxns Iapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ca RXN CheckDocumento1 paginaCa RXN Checkapi-4654218090% (1)
- ch17 SummaryDocumento1 paginach17 Summaryapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ca Rxns IIDocumento1 paginaCa Rxns IIapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ca SynthDocumento1 paginaCa Synthapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- MOC Alcohol RXN Map PDFDocumento2 pagineMOC Alcohol RXN Map PDFNickOoPandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 5 Practice Final Part 1 - New Material 1Documento3 pagineWeek 5 Practice Final Part 1 - New Material 1api-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- 118b mt1 Study Guide 2Documento21 pagine118b mt1 Study Guide 2api-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- Week 6 Practice Final Part 2 Chapter 18Documento4 pagineWeek 6 Practice Final Part 2 Chapter 18api-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- 118b mt2 Study Guide 2Documento20 pagine118b mt2 Study Guide 2api-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- ch18 SummaryDocumento1 paginach18 Summaryapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm 1 Practice QuestionsDocumento8 pagineMidterm 1 Practice Questionsapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- ch15-16 SummaryDocumento1 paginach15-16 Summaryapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- 118 BprsynthDocumento19 pagine118 Bprsynthapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- ch14 SummaryDocumento1 paginach14 Summaryapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- Resonance Practice ProblemsDocumento12 pagineResonance Practice Problemsapi-465421809Nessuna valutazione finora
- 15 Multistep Synthesis Synthons DisconDocumento38 pagine15 Multistep Synthesis Synthons DisconGowtham LecturesNessuna valutazione finora
- Aromatic Notes 2 PDFDocumento6 pagineAromatic Notes 2 PDFChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Chemical Kinetics Simulator: An Interactive Graphical ApproachDocumento8 pagineChemical Kinetics Simulator: An Interactive Graphical Approachnurul ismiNessuna valutazione finora
- Acid CatalysisDocumento16 pagineAcid CatalysisTayyaba SadaqNessuna valutazione finora
- B.SC 1st Year SyllDocumento1 paginaB.SC 1st Year SyllJayAroraNessuna valutazione finora
- "Metal-Catalysis in Industrial Organic Processes": Reviewed by Robin B. BedfordDocumento2 pagine"Metal-Catalysis in Industrial Organic Processes": Reviewed by Robin B. Bedfordreset00Nessuna valutazione finora
- Organic ReactionsDocumento50 pagineOrganic ReactionsRyea Chayankka TwentysevendNessuna valutazione finora
- Catalyst: Ostwald (1895) Redefined A Catalyst As, "A Substance Which ChangesDocumento14 pagineCatalyst: Ostwald (1895) Redefined A Catalyst As, "A Substance Which ChangesRahul ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Catalyst Size, Shape, and EfficiencyDocumento21 pagineCatalyst Size, Shape, and Efficiencyjann youngNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry 11Th Edition Solomons Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento67 pagineOrganic Chemistry 11Th Edition Solomons Test Bank Full Chapter PDFdannyblackerzawcfyni100% (7)
- Palladium Precatalyst Design and Its Applications in Cross-CouplingDocumento27 paginePalladium Precatalyst Design and Its Applications in Cross-CouplingiammouliNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Kinetics Short NotesDocumento4 pagineChemical Kinetics Short NotesSanket Patil100% (1)
- Alkyl and Aryl Halide TestDocumento6 pagineAlkyl and Aryl Halide TestSoren Sharma50% (6)
- Alkenes by Dehydration of AlcoholsDocumento7 pagineAlkenes by Dehydration of Alcoholssbgowda100100% (1)
- CHM 111 Chemical Kinetics Course OutlineDocumento34 pagineCHM 111 Chemical Kinetics Course OutlineOluwaferanmi OgunleyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Rates of Reaction Order and Constants from Experimental DataDocumento4 pagineRates of Reaction Order and Constants from Experimental DataGopi KupuchittyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 - Elimination ReactionsDocumento68 pagineChapter 8 - Elimination ReactionsBianca-Rebeca PetreNessuna valutazione finora
- Greener Reaction Under Solvent Free Reaction and SolidDocumento23 pagineGreener Reaction Under Solvent Free Reaction and Solidmytrya debNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinetic and non-kinetic methods to study reaction pathwaysDocumento57 pagineKinetic and non-kinetic methods to study reaction pathwaysRAJA AYYA100% (8)
- Chem101103 Summerfinalexam SolutionDocumento5 pagineChem101103 Summerfinalexam SolutionbrianNessuna valutazione finora
- Examples and exercises – Reactor designDocumento19 pagineExamples and exercises – Reactor designtehbear0% (1)
- Organic Chemistry From Retrosynthesis To Asymmetric Synthesis (PDFDrive)Documento221 pagineOrganic Chemistry From Retrosynthesis To Asymmetric Synthesis (PDFDrive)I CbergNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinetika MEGDocumento5 pagineKinetika MEGIndri Boo-drumsky FebrianNessuna valutazione finora
- Conjugate Addition Reactions ExplainedDocumento4 pagineConjugate Addition Reactions ExplainedAsma AlnuaimiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Important QuestionsDocumento5 pagineChemistry Important QuestionsKARTHIK MNessuna valutazione finora
- l4 Alkyl HalidesDocumento50 paginel4 Alkyl HalidesSiti Fatimah0% (1)
- S9 Unit 8 WorksheetsDocumento11 pagineS9 Unit 8 WorksheetsShahana AhthNessuna valutazione finora
- Preparatory Problems PDFDocumento4 paginePreparatory Problems PDFGerel BayrmagnaiNessuna valutazione finora