Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Classification of English Sound Speech Styles
Caricato da
Jøhn Anrol ParochaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Classification of English Sound Speech Styles
Caricato da
Jøhn Anrol ParochaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CLASSIFICATION OF ENGLISH SOUND SPEECH STYLES
1. VOWEL – tongue does not touch the INTIMATE – private styles, not shared in
lips, (a,e,i,o,u) teeth and the roof top. public
2. CONSONANT – voiced/voiceless (no CASUAL – common among friends,
vibration) peers. (language) – like beki words
3. DIPTHONGS – means two sounds (ai, CONSULTATIVE – Prof. are mutually
ae, ao, au) accepted.
FORMAL – one way seen writing than
ORAL AND WRITTEN
speaking
Putting down words (writing) FROZEN – time and remain unchanged
Delivering of words mostly ceremonies.
FORMAL AND INFORMAL INTERCULTURAL COMMUNICATION
Opposite of formal with no
formalities INTER – comes from the latin word
With observation of between communication. Exchanging
appropriateness info.
COMMUNICATIVE COMPETENCE CULTURE – way of life of a group of
people
*coined by Dell Hymes
SPEECH – spoken expression, of ideas, opinion, 3P’s
etc. PRODUCT:
-product
TYPES OF SPEECH
-clothes
INTRAPERSONAL -accessories
Thinking out loud or “soliloquy” P – festivals – superstition beliefs –
Takes place within a single person practices
INTERPERSONAL P – perception – perspective
SUB-TYPES: DYADIC – means 2
DMIS
GROUP – 3 or more Developmental model of intercultural
person (small group) sensitivity
PUBLIC – large group , one way STAGES
monologue 1. DENIAL – does not recognize
Ex. Teacher in class or lecture in cultural diff.
university. 2. DEFENSE – start to recognize
cultural diff.
MASS COM – Expanded 3. MINIMIZATION – bank more on
form of public com. universality of ideas rather cultural
- Large and diverse diff.
audience through 4. ACCEPTANCE – appreciate cultural
technology like diff.
media 5. ADAPTATION – accepting
6. INTEGRATION – starts to go beyond VISUAL – acts of using photographers, drawings
their own culture etc.
COMMUNICATION
SPEECH ACTS by JL. AUSTIN
Latin words:
ILLOCUTIONARY – what is said
PERLOCUTIONARY – The result Communis – sharing
LOCUTIONARY – saying something Communicare – common
PERFORMATIVES – the speaker to
perform something just by stating
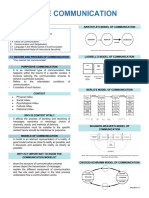
ILLOCUTIONARY ACTS 5 CATEGORIES by Austin MODELS OF COMMUNICATION
John Searle Linear Communication
Assertive – the fact of the Aristotle – occasion like Public
speaker express belief about speaking
the truth Shannon and weaver – noise
EX. No one makes better affects the flow
pancakes than I do.
David Berlo(SMBC) – step-by-
Directive – asking, ordering, step sequence of events
requesting etc. complete charge of
Ex. Please close the door communication
Commisive – Planning and
promising INTERACTIVE
EX. From now on, I will review
*Schramms – Receiver or listener react also to
for incoming test this week
the sender or the speaker
Expressive – thanking,
apologizing *Frank dance – Helix 0 3 dimensional shapes
EX. Thank you that you come to
TANSACTIONAL – Interdependent: no receiver
my life
Declaration – blessing, firing etc No feedback
. EX. You are fired.
Dean Barlund 0 engaging in the sending and
ORAL COMMUNICATION receiving of message
Did you know?
7% We communicate based on FUNCTIONS OF COMMUNICATION
vocabulary
*CONTROL – BEHAVIOR
38% voice inflection (tone or pitch)
*SOCIAL –INTERACTION – INTERACT WITH
55% non-verbal behavior OTHERS
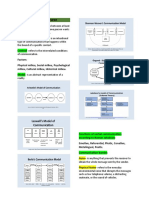
FOUR MAIN TYPES OF COMMUNICATION *MOTIVATION – ENCOURAGE PEOPLE TO LIVE
BETTER
VERBAL – use language to transfer info
NON-VERBAL – writing, typing printing
* EMOTIONAL EXPRESSION – APPRECIATE DIFFERENT NON-VERBAL
FEELINGS
KINESICS – MOVEMENT
*INFORMATION DISSEMINATION – DATA OF PARALINGUISTIC – VOCAL
INFO OCULESICS – EYE
PROXEMICS – SPACES
HAPTICS – TOUCH
FEATURES (7c’S By: prof. Broom Cutlip) CHROMENICS – TIME
1. Completeness – properly evaluate OLFATICS – SMELL
2. Conciseness – direct to the point CHROMATICS – COLOR
3. Consideration 0 background, status, GUSTORICS – TASTE
race, etc. VERBAL
4. Concreteness – supported by facts
5. Courtesy – respect cultures, values, APPPROPRIATENESS – SUITABLE TO
beliefs ENVIRONMENT AND OCCASION
6. Clearness use simple and specific BREVITY – SIMPLE YET PRECISE AND POWERFUL
words
7. Correctness – correction or grammar ETHICS – CONSIDER GENDER TOLES
eliminates neg. Impact.
VIVIDNESS – CHARM YOUR AUDIENCES
BARRIERS
CATEGORY: internal, external VERBAL COMMUNICATION
Psychological barriers – stress or anger VOICE – IMPORTANT ELEMENT OF
COMMUNICATION
Physiological – reduce hearing
VOICE PRODUCTION
Physical - Geographic distance between the
s&k. RESPIRATION – breathing
VIBRATION – production of
Systematic – lack of understanding and
voice sounds
responsibility
RESONATION – amplifying
Attitudinal – personality conflict or lack or sounds
motivation PRONUNCIATION – last phase
DIMENSION OF COMMUCICATION
PAIRS
Verbal and non-verbal
Oral and written
Formal and informal
Intentional and unintentional
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Reviewer in Oral CommunicationDocumento3 pagineReviewer in Oral CommunicationJøhn Anrol ParochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral CommunicationDocumento4 pagineOral CommunicationKujira FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Ge Elec MTE ReviewerDocumento8 pagineGe Elec MTE ReviewerChet Buenfeliz TacliadNessuna valutazione finora
- PEOPLE." Keep As A Reminder.Documento4 paginePEOPLE." Keep As A Reminder.Angelica Ross de LunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Oralcom TranseDocumento4 pagineOralcom TranseShiela Clarisse Galano Sera IINessuna valutazione finora
- Oc ReviewerDocumento4 pagineOc Reviewerx5b5qr6qy2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Oral Communication Q1 Reviewer For G11Documento6 pagineOral Communication Q1 Reviewer For G11Katleya Balitaan75% (8)
- LESSON 1 - Nature, Elements..Documento20 pagineLESSON 1 - Nature, Elements..Joanne Ronquillo1-BSED-ENGNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral Communicaton HandoutsDocumento2 pagineOral Communicaton Handoutskenkerby64Nessuna valutazione finora
- Oral Comms Reviewer (3RD Quarter - Second Semester)Documento2 pagineOral Comms Reviewer (3RD Quarter - Second Semester)Kaye LumodNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral Comm Pre-LimsDocumento3 pagineOral Comm Pre-LimsANDREA NICOLE DE LEONNessuna valutazione finora
- Purc Transes PrelimDocumento4 paginePurc Transes PrelimGelo AlonzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral Communication COMMUNICATION-comes From The Latin Word "Communis"Documento2 pagineOral Communication COMMUNICATION-comes From The Latin Word "Communis"Alyssa Naima GuilingNessuna valutazione finora
- OralCom-Prelim Exam Reviewer-For SendDocumento3 pagineOralCom-Prelim Exam Reviewer-For SendAngie EsponillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ge-Pc Midterm NotesDocumento7 pagineGe-Pc Midterm NotesJamaica JaneNessuna valutazione finora
- OralCom REVDocumento3 pagineOralCom REVNics CodmNessuna valutazione finora
- Speaker Speech Audience: Which Channel To, Whom and With WhatDocumento2 pagineSpeaker Speech Audience: Which Channel To, Whom and With WhatLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNessuna valutazione finora
- PURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION - Prelim ReviewerDocumento3 paginePURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION - Prelim ReviewerkyladimaanoNessuna valutazione finora
- PCM Midterm ReviewerDocumento4 paginePCM Midterm ReviewerEM PatindolNessuna valutazione finora
- COMMUNICATIONDocumento4 pagineCOMMUNICATIONAngel Grace SumagayNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral CommunicationDocumento4 pagineOral CommunicationJuliene Ermie Parel BerameNessuna valutazione finora
- PurCom ReviewerDocumento3 paginePurCom Reviewerlucerocatapanggwen.03Nessuna valutazione finora
- PC 100 PrelimsDocumento12 paginePC 100 Prelimscali kNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral Communication ReviewerDocumento2 pagineOral Communication Reviewerralpharchie01Nessuna valutazione finora
- PCM ReviewerDocumento19 paginePCM ReviewerAlexa Mae Villasis MajeranoNessuna valutazione finora
- EFCOMDocumento5 pagineEFCOMPia SolNessuna valutazione finora
- Lasswell's Model Aristotle's Model Shannon Weaver Model Berlo's S-M-C-R ModelDocumento4 pagineLasswell's Model Aristotle's Model Shannon Weaver Model Berlo's S-M-C-R ModelMary Shine Magno MartinNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral Com Reviewer 1ST QuarterDocumento10 pagineOral Com Reviewer 1ST QuarterRaian PaderesuNessuna valutazione finora
- 2ND Day ReviewerDocumento4 pagine2ND Day ReviewerJasmine de LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- Purposive CommunicationDocumento6 paginePurposive CommunicationRea EbotNessuna valutazione finora
- Functions of CommunicationDocumento4 pagineFunctions of CommunicationVhea LeynesNessuna valutazione finora
- Purposive Communication PrelimsDocumento21 paginePurposive Communication PrelimsMichiiee Batalla0% (1)
- Communication The Value of CommunicationDocumento4 pagineCommunication The Value of CommunicationJared PaulateNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral Comm ReviewerDocumento10 pagineOral Comm ReviewerLucille Marie SabioNessuna valutazione finora
- J. Paul LeaganDocumento15 pagineJ. Paul LeaganAries C. GavinoNessuna valutazione finora
- PurCom Sem 1 1Documento18 paginePurCom Sem 1 1Mhavs CasimiroNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral CommunicationDocumento4 pagineOral CommunicationPrincess Cherry C. EstradaNessuna valutazione finora
- PRELIMDocumento3 paginePRELIMTemptations MnlNessuna valutazione finora
- Anthro 1 - FinalsDocumento4 pagineAnthro 1 - FinalsAlexie Anne MariñoNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication ExcellenseDocumento57 pagineCommunication ExcellensechjsbabuNessuna valutazione finora
- Oc ReviewerDocumento3 pagineOc ReviewerRia RegaspiNessuna valutazione finora
- Settings Participants Codes, and Message Content and FormDocumento3 pagineSettings Participants Codes, and Message Content and FormJhessa May CanuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Purposive Communication Prelim ReviewerDocumento6 paginePurposive Communication Prelim ReviewerJade PaulosNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson3&4 Types of Speech Context and StyleDocumento31 pagineLesson3&4 Types of Speech Context and StyleRuschelle LaoNessuna valutazione finora
- A. Emblems:: These Are Body Movements, Which Have Direct Translations Into WordsDocumento5 pagineA. Emblems:: These Are Body Movements, Which Have Direct Translations Into WordsAlliana VicencioNessuna valutazione finora
- Purposive CommunicationsDocumento2 paginePurposive Communicationsviannametharam30Nessuna valutazione finora
- Communication Processes, Principles and Ethics. (FIRST SEMESTER EXAMDocumento4 pagineCommunication Processes, Principles and Ethics. (FIRST SEMESTER EXAMyaoi yuriNessuna valutazione finora
- Social Relation, Concept of Time, Concept of Space, GesturesDocumento1 paginaSocial Relation, Concept of Time, Concept of Space, GesturesVincent EmilioNessuna valutazione finora
- S2 OralCom ReviewerDocumento11 pagineS2 OralCom ReviewerArabella MejoradaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer For Purposive CommunicationDocumento2 pagineReviewer For Purposive Communicationjohn ivan GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Purcom ReviewerDocumento15 paginePurcom ReviewerJhae Zharie Delasan PanosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral Communication in Context ReviewDocumento37 pagineOral Communication in Context ReviewArnez Jewell Dotillos100% (8)
- Oral Comm RevDocumento5 pagineOral Comm RevCharlie jade MagbanuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral Communication ReviewerDocumento2 pagineOral Communication ReviewereukiNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral Communication ReviewerDocumento5 pagineOral Communication ReviewerMaureen AkimoriNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral Communication Reviewer Unit 1&2Documento4 pagineOral Communication Reviewer Unit 1&2Leigh Anne CaminceNessuna valutazione finora
- Purposive Communication Midterm ReviewerDocumento9 paginePurposive Communication Midterm ReviewerIrish MaeNessuna valutazione finora
- PurComm ReviewerDocumento9 paginePurComm Reviewererichalthea29Nessuna valutazione finora
- PURCOM-POINTERSDocumento7 paginePURCOM-POINTERSNoel CastrodesNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Helpers 2Documento9 pagineCommunity Helpers 2Damara Sad All'overNessuna valutazione finora
- 2011 - Farazmand Et - Al - Is Religious Culture A Factor in Negotiation - A Cross-Cultural Comparison of Iran, Taiwan and The United StatesDocumento19 pagine2011 - Farazmand Et - Al - Is Religious Culture A Factor in Negotiation - A Cross-Cultural Comparison of Iran, Taiwan and The United StatesPrima VandayaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Kto12 OverviewDocumento13 pagineKto12 OverviewLawrence RolluquiNessuna valutazione finora
- MetaethicsDocumento20 pagineMetaethicsanthonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Application - Discharge NoteDocumento2 pagineApplication - Discharge NoteAlissa AtismeNessuna valutazione finora
- Mapeh 7 3RD QuarterDocumento3 pagineMapeh 7 3RD QuarterKatty Cedro Dela Cruz100% (2)
- Dirjen Dikti - Kebijakan Dikti TTG KKNI Dan KurikulumDocumento6 pagineDirjen Dikti - Kebijakan Dikti TTG KKNI Dan KurikulumReza Ramadhan rezaramadhan.2018Nessuna valutazione finora
- All 3 Answers in OneDocumento4 pagineAll 3 Answers in OneUnushka ShresthaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Philosophy Behind Froebel's Kindergarten ApproachDocumento2 pagineThe Philosophy Behind Froebel's Kindergarten Approachmohanraj2purushothamNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Carmela DivinDocumento5 pagine3 Carmela DivinKaren Khiane Flores ArsenioNessuna valutazione finora
- 2014-15 TBEM Criteria PDFDocumento110 pagine2014-15 TBEM Criteria PDFekonextg100% (1)
- BLOG POST BYOB' A Beginner's Guide To Meditating Written For A Spoonful of Sukha,' Personal Mindfulness Blog in 2016Documento3 pagineBLOG POST BYOB' A Beginner's Guide To Meditating Written For A Spoonful of Sukha,' Personal Mindfulness Blog in 2016api-280615080Nessuna valutazione finora
- Why Does Social Media Affect Kids?Documento6 pagineWhy Does Social Media Affect Kids?Safwara SindhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Education Lesson Week 5 Lesson PlanDocumento4 paginePhysical Education Lesson Week 5 Lesson Planapi-451266317Nessuna valutazione finora
- Critique Paper: Bullying: Students Themselves May Be The Key To Solving ProblemsDocumento3 pagineCritique Paper: Bullying: Students Themselves May Be The Key To Solving ProblemsBlessed ValdezNessuna valutazione finora
- English 7 Summative Test 1 3RD QuarterDocumento2 pagineEnglish 7 Summative Test 1 3RD QuarterCLARK TERRADONessuna valutazione finora
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5Documento3 pagineDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5Geoffrey Tolentino-Unida50% (2)
- Syllabus: Ilocos Sur Polytechnic State CollegeDocumento10 pagineSyllabus: Ilocos Sur Polytechnic State CollegeKaj PagatpatanNessuna valutazione finora
- Business English Job SatisfactionDocumento9 pagineBusiness English Job SatisfactionEnglish Plus PodcastNessuna valutazione finora
- 2017 Capstone Outline FormDocumento2 pagine2017 Capstone Outline Formapi-403212419Nessuna valutazione finora
- Novitasari R G2A009063 Bab8KTIDocumento30 pagineNovitasari R G2A009063 Bab8KTIMas sobah SobahNessuna valutazione finora
- Prince of Peace College, Inc.: Unit 1: Child Development - Foundations of Child and Adolescent PsychologyDocumento8 paginePrince of Peace College, Inc.: Unit 1: Child Development - Foundations of Child and Adolescent Psychologysweetzel paigmaneNessuna valutazione finora
- 107 - Activity 1 YzmDocumento1 pagina107 - Activity 1 YzmYvonne De Venecia MalicdemNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2 Lesson 3 Speaking PersuasivelyDocumento9 pagineModule 2 Lesson 3 Speaking Persuasivelyjayolores16Nessuna valutazione finora
- Disciplines And: Schools Division of Olongapo CityDocumento79 pagineDisciplines And: Schools Division of Olongapo CityJoseph Mondo�edo100% (2)
- Unit 4Documento15 pagineUnit 4s@nNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Read PalmsDocumento40 pagineHow To Read Palmsgur14100% (1)
- Scoring Rubric For Skit Level of PerformanceDocumento1 paginaScoring Rubric For Skit Level of PerformanceRichelle TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Education Shiny MamDocumento42 pagineEducation Shiny Mamkalla sharonNessuna valutazione finora
- Case 6 A Difficult Task Force Case Study AnswersDocumento3 pagineCase 6 A Difficult Task Force Case Study AnswerssakshidamanNessuna valutazione finora