Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Blood Transfusion Incompabilities
Caricato da
Roxanne FloresCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Blood Transfusion Incompabilities
Caricato da
Roxanne FloresCopyright:
Formati disponibili
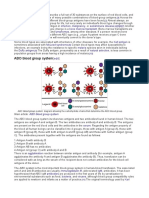
VanPutte, Regan, & Russo (2014) stated that there are categories of antigens on the surface
of red blood cells. The human blood is categorized by ABO blood group system. In this blood
group system, the antigens found in the surface of the red blood cells are genetically determined.
Type A antigens are present in type A blood while type B antigens are present in type B blood.
Type AB has both of type A and type B antigens. Neither A nor B is present in type O blood. If a
person receives blood that does not match his/her blood type, transfusion reactions can occur. Type
A blood contains anti-B antibodies, which will act against type B antigens; plasma from type B
blood contains anti-A antibodies, which act against type A antigens. The AB blood plasma has
neither type of antibody, and type O blood plasma has both anti-A and anti-B antibodies.
Historically, type O blood are known as universal donors because they can usually donate blood
to the other ABO blood types without causing ABO transfusion reactions. Their red blood cells
have no surface ABO antigens and therefore do not react with the recipient’s anti-A or anti-B
antibodies. However, people with type O blood can only receive from type O blood.
The antibodies present in the recipient’s blood will attack the blood of the donor if they are
incompatible. Hemolytic reaction occurs when the immune system of the recipient attacks the
donor’s red blood cells which will cause them to burst. The body will produce antibodies that will
destroy the donor’s blood cells. It is during this process when transfusion reaction occurs. In an
article reviewed by Klatt, he stated that transfusion reactions include febrile reaction, allergic
reaction, transfusion related acute lung injury (TRALI), and Transfusion-associated graft versus
host disease (TAGVHD).
Patient’s antibodies is directed against
Febrile Reaction antigens that are present on transfused
lymphocytes or granulocytes.
Allergic Reactions Complaints of hives and itching to anaphylaxis
Transfusion related acute lung injury Introduction of the donor antibodies into the
recipient causes granulocyte enzymes to be
released, increasing capillary permeability and
resulting in sudden respiratory distress from
pulmonary edema, typically within 6 hours of
transfusion.
Transfusion-associated graft occurs when the blood products contain T-
lymphocytes and attack many host tissues
Klatt, E. C. (n.d.). Adverse Reactions to Blood Products. Retrieved from
https://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/TUTORIAL/BLDBANK/BBTXRXN.html
VanPutte, C., Regan, J., & Russo, A. (2014). Seeley's Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology(10th
ed.). New York: Mc Graw Hill Education
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Understanding Transfusion Reactions in Oncology by NurseDocumento6 pagineUnderstanding Transfusion Reactions in Oncology by NursefitriNessuna valutazione finora
- The Hazards of Blood TransfusionDocumento4 pagineThe Hazards of Blood TransfusionyascheNessuna valutazione finora
- Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI) - Blood Transfusion ComplicationDocumento4 pagineTransfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI) - Blood Transfusion ComplicationFitri Nur DiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Hemagglutination AssayDocumento4 pagineHemagglutination Assayऋषभ गर्गNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanisms of Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI) : Anti-Leukocyte AntibodiesDocumento6 pagineMechanisms of Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI) : Anti-Leukocyte AntibodiesBladimir CentenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Transplantation 1Documento48 pagineTransplantation 1Shahansha Sharan DhammatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Transfusion-Related Immunomodulation (TRIM) : An Update: Eleftherios C. Vamvakas, Morris A. BlajchmanDocumento22 pagineTransfusion-Related Immunomodulation (TRIM) : An Update: Eleftherios C. Vamvakas, Morris A. BlajchmanLaura Francisca Urrutia IbacetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Group IncompatibilityDocumento7 pagineBlood Group IncompatibilityHendrikus Surya Adhi PutraNessuna valutazione finora
- TransfusiónDocumento5 pagineTransfusiónMayra Alejandra Prada SerranoNessuna valutazione finora
- Dobkin Et Al 2023 The Ultimate Tradeoff How Red Cell Adaptations To Malaria Alter The Host Response During CriticalDocumento10 pagineDobkin Et Al 2023 The Ultimate Tradeoff How Red Cell Adaptations To Malaria Alter The Host Response During CriticalLeonel CamposNessuna valutazione finora
- ASH Guidlines On Platelet RefractorinessDocumento6 pagineASH Guidlines On Platelet RefractorinessM Asif NaveedNessuna valutazione finora
- How Blood Type Is Determined and Why You Need To Know: A+, A-B+, B - O+, O - AB+, ABDocumento6 pagineHow Blood Type Is Determined and Why You Need To Know: A+, A-B+, B - O+, O - AB+, ABShanne Katherine MarasiganNessuna valutazione finora
- BT ReactionDocumento8 pagineBT ReactionMary Elijah Jane PopesNessuna valutazione finora
- Hsci Lesson 8 (Print 2)Documento11 pagineHsci Lesson 8 (Print 2)Eyvette GoNessuna valutazione finora
- Originalresearch: ABO-incompatible Platelets Are Associated With Increased Transfusion Reaction RatesDocumento9 pagineOriginalresearch: ABO-incompatible Platelets Are Associated With Increased Transfusion Reaction Ratesmy accountNessuna valutazione finora
- Transfusion ReactionDocumento66 pagineTransfusion ReactionAbhineet SalveNessuna valutazione finora
- A Brief Overview of Clinical Significance of Blood Group AntibodiesDocumento3 pagineA Brief Overview of Clinical Significance of Blood Group AntibodiesSantiago López JosueNessuna valutazione finora
- Alter, Klein - 2008 - The Hazards of Blood Transfusion in Historical PerspectiveDocumento11 pagineAlter, Klein - 2008 - The Hazards of Blood Transfusion in Historical Perspectivesushmakumari009Nessuna valutazione finora
- ABO Blood Group SystemDocumento7 pagineABO Blood Group SystemBogdan OdobescuNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Group Incompatibility PDFDocumento7 pagineBlood Group Incompatibility PDFSekar MarzukiNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Transfusion Reactions: Dr. Madhuvan GuptaDocumento42 pagineBlood Transfusion Reactions: Dr. Madhuvan GuptaDr. Madhuvan GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Type - Wikipedia 08-26-2021Documento14 pagineBlood Type - Wikipedia 08-26-2021michael_sr_44Nessuna valutazione finora
- Immunology 7Documento25 pagineImmunology 7ukashazam19Nessuna valutazione finora
- Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury: Pearl Toy,, and Ognjen GajicDocumento2 pagineTransfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury: Pearl Toy,, and Ognjen GajicMaulana Akbar LubisNessuna valutazione finora
- The Serological Investigation of Red Cell Incompatible Transfusion ReactionsDocumento5 pagineThe Serological Investigation of Red Cell Incompatible Transfusion ReactionsKAILA SOPHIA CRUZNessuna valutazione finora
- Platelet Transfusion Refractoriness How Do IDocumento6 paginePlatelet Transfusion Refractoriness How Do IJuan Manuel Cano CalderónNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Transfusion ReactionsDocumento8 pagineBlood Transfusion ReactionsStephanie AngelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hubungan Jenis Packed Red Cell (PRC) Yang Ditransfusikan Dengan Reaksi Transfusi Febrile NonDocumento5 pagineHubungan Jenis Packed Red Cell (PRC) Yang Ditransfusikan Dengan Reaksi Transfusi Febrile NonazizahNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Transfusion Notes..Documento9 pagineBlood Transfusion Notes..queenethNessuna valutazione finora
- Probleme La TransfuziiDocumento6 pagineProbleme La TransfuziiAdina TîrnoveanuNessuna valutazione finora
- FebrileDocumento4 pagineFebrileEDIWOWNessuna valutazione finora
- Graft Rejection Immunological Suppression PDFDocumento7 pagineGraft Rejection Immunological Suppression PDFmanoj_rkl_07Nessuna valutazione finora
- Transplantation: Saba Shahzadi 1721138054Documento6 pagineTransplantation: Saba Shahzadi 1721138054sandy candyNessuna valutazione finora
- Nej MR A 0902927Documento12 pagineNej MR A 0902927Pepita GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Esplenectomia Autoimune-2017Documento14 pagineEsplenectomia Autoimune-2017depositoperpetuoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Hazards: OF Blood TransfusionDocumento7 pagineThe Hazards: OF Blood TransfusionPranjal Kr SahariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aloinmunizacion en IndiaDocumento4 pagineAloinmunizacion en Indiabioqclin20Nessuna valutazione finora
- Aiha 3Documento5 pagineAiha 3Andi WahyudiNessuna valutazione finora
- TRALI - A Review.: TRALI Is Transfusion Related Acute Lung Injury Due To Immune MediatedDocumento6 pagineTRALI - A Review.: TRALI Is Transfusion Related Acute Lung Injury Due To Immune MediatedArun KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Adverse Reactions To TransfusionDocumento8 pagine7 Adverse Reactions To Transfusioncryztelle2720027476Nessuna valutazione finora
- Transplantation PDFDocumento18 pagineTransplantation PDFChandan Kumar100% (1)
- Irradiated Blood Products - Deranged PhysiologyDocumento4 pagineIrradiated Blood Products - Deranged Physiologyhnzzn2bymdNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Groups and Blood Transfusion BioDocumento23 pagineBlood Groups and Blood Transfusion BiowhyyoucareNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Typing, Rhesus Factor, and BloodDocumento40 pagineBlood Typing, Rhesus Factor, and BloodHalima IliyasuNessuna valutazione finora
- De Novo Aih After LT GuidoDocumento11 pagineDe Novo Aih After LT GuidoEmma SaelensNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood 3Documento62 pagineBlood 3Ajee ANessuna valutazione finora
- Transfusion Related ImmunemodulationDocumento12 pagineTransfusion Related ImmunemodulationOwais QarniNessuna valutazione finora
- Transfusion Related Acute Lung Injury (Trali) : Presented by Intern DR Khagendra AcharyaDocumento24 pagineTransfusion Related Acute Lung Injury (Trali) : Presented by Intern DR Khagendra AcharyaBungas ArisudanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluate The Presence of Auto-Antibodies in Subjects With B - Thalassemia Major For Early Intervention To Decrease Morbidity and MortalityDocumento9 pagineEvaluate The Presence of Auto-Antibodies in Subjects With B - Thalassemia Major For Early Intervention To Decrease Morbidity and MortalityCentral Asian StudiesNessuna valutazione finora
- Ricci 2014Documento7 pagineRicci 2014rinduNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Group of AnimalsDocumento26 pagineBlood Group of Animals김소정Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Effect of HLADocumento9 pagineThe Effect of HLAMihai PerescuNessuna valutazione finora
- Questions ExplanationDocumento24 pagineQuestions ExplanationnomintmNessuna valutazione finora
- Att 5KJBXUZs14QHOXaS8FJcB5Fkf0M-SsmsUCS5rCUA7t8Documento9 pagineAtt 5KJBXUZs14QHOXaS8FJcB5Fkf0M-SsmsUCS5rCUA7t8mackienmao1999Nessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Adverse Reactions ToDocumento7 pagine7 Adverse Reactions ToambadepravinNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Surgery and Cold-Reactive Proteins - Agarwal Et Al. 60 (4) - 1143 - The Annals of Thoracic SurgeryDocumento14 pagineCardiac Surgery and Cold-Reactive Proteins - Agarwal Et Al. 60 (4) - 1143 - The Annals of Thoracic SurgeryIza SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Plasma Convalesen HLADocumento19 paginePlasma Convalesen HLAVincentius Michael WilliantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Groups Practical NewDocumento19 pagineBlood Groups Practical NewSreedeep TejaNessuna valutazione finora
- TransfusionDocumento48 pagineTransfusionSandy LavedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA) Associated VasculitisDa EverandAnti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA) Associated VasculitisRenato Alberto SinicoNessuna valutazione finora
- Etiopathogenesis of Diabetes MellitusDocumento35 pagineEtiopathogenesis of Diabetes MellitusironNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Toxicity of Percutaneously Absorbed MalathionDocumento5 pagineAcute Toxicity of Percutaneously Absorbed Malathionjoemark_narsico5796Nessuna valutazione finora
- Stress BustingDocumento24 pagineStress BustingMarianne ChristieNessuna valutazione finora
- Which Is Better in Smoking Using Vape oDocumento17 pagineWhich Is Better in Smoking Using Vape oTata Duero LachicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Background: Abruptio PlacentaeDocumento6 pagineBackground: Abruptio PlacentaeEj ZGNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Assessment CosmeticsDocumento29 pagineSafety Assessment CosmeticsHananAhmed100% (2)
- Liver Fibrosis: Causes and Methods of Assessment, A ReviewDocumento11 pagineLiver Fibrosis: Causes and Methods of Assessment, A ReviewVICKI ANDREANNessuna valutazione finora
- ch01 PDFDocumento5 paginech01 PDFHugsNessuna valutazione finora
- Pisula Et AlDocumento42 paginePisula Et AlAnonymous 75M6uB3OwNessuna valutazione finora
- Turn Up The Heat - Unlock The Fat-Burning Power of Your MetabolismDocumento378 pagineTurn Up The Heat - Unlock The Fat-Burning Power of Your MetabolismElvis Florentino96% (23)
- Menstrual CycleDocumento22 pagineMenstrual CycleDaniel AtiehNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 Forensic Serology DNA and DrugsDocumento24 pagineModule 3 Forensic Serology DNA and DrugskyanjamesmontuyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hepatic CellsDocumento2 pagineHepatic CellsSteven RiosNessuna valutazione finora
- Gene Technology ...Documento28 pagineGene Technology ...Jelita AlviolinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gram Negative Positive NotesDocumento8 pagineGram Negative Positive NotesKusum Roy100% (1)
- Advs202104006 Sup 0001 SuppmatDocumento20 pagineAdvs202104006 Sup 0001 SuppmatLe Victor DungNessuna valutazione finora
- Output 8 and 9Documento11 pagineOutput 8 and 9Angelo ParaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Luminescent ATP Detection Assay Kit Ab113849 Luminescent ATP Detection Assay Kit Ab113849Documento4 pagineLuminescent ATP Detection Assay Kit Ab113849 Luminescent ATP Detection Assay Kit Ab113849carlosNessuna valutazione finora
- Mual MuntahDocumento8 pagineMual MuntahRosalindaRezkyNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Dot ElisaDocumento3 paginePractical Dot Elisavyastrupti1100% (1)
- Endosymbiotic TheoryDocumento4 pagineEndosymbiotic TheoryJoshi MaitreyeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Paul Toonders snc2p Biology Unit PlanDocumento25 paginePaul Toonders snc2p Biology Unit Planapi-351067903Nessuna valutazione finora
- Curriculum Vitae: G.SethuramanDocumento4 pagineCurriculum Vitae: G.SethuramanSethuNessuna valutazione finora
- Bacteriophage MCQsDocumento3 pagineBacteriophage MCQsMahi ShafiqueNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.panoramic Radiograph in PathologyDocumento53 pagine1.panoramic Radiograph in PathologyMIREYANessuna valutazione finora
- New Orbital Single Use BioreactorDocumento1 paginaNew Orbital Single Use BioreactorCharles LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Parapneumonic Pleural Effusions and Empyema Thoracis - Background, Pathophysiology, EpidemiologyDocumento4 pagineParapneumonic Pleural Effusions and Empyema Thoracis - Background, Pathophysiology, EpidemiologyLorentina Den PanjaitanNessuna valutazione finora
- Eye Cancer - Stages and Grades - 2015-09-01Documento7 pagineEye Cancer - Stages and Grades - 2015-09-01Ruslan KamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Criteria For Diagnosing Personality DisordersDocumento43 pagineCriteria For Diagnosing Personality DisordersKhrycys Olairez RNNessuna valutazione finora
- Harpers Illustrated Biochemistry 32Th Ed 32Nd Edition Peter J Kennelly Full ChapterDocumento67 pagineHarpers Illustrated Biochemistry 32Th Ed 32Nd Edition Peter J Kennelly Full Chaptersally.kimberlin556Nessuna valutazione finora